目录:导读
- 前言
- 一、Python编程入门到精通
- 二、接口自动化项目实战
- 三、Web自动化项目实战
- 四、App自动化项目实战
- 五、一线大厂简历
- 六、测试开发DevOps体系
- 七、常用自动化测试工具
- 八、JMeter性能测试
- 九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
前言
1、pytest前置条件+后置条件的两种写法
使用yield关键字来是实现:
推荐使用这种,因为yield关键字能返回函数的值
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def befor_func():
print('xxxxxxxxxxxxx测试用例的初始化xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx')
yield 10 #yield后面跟的是测试用例的后置条件,支持用例执行后就执行yield里的内容
print('zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz测试用例的清除zzzzzzzzzzzzzz')
def test_001(befor_func):
print("测试用例001")
res=befor_func
print(res)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["test1.py",'-s'])
使用finc()函数来实现:
这种就不能返回返回值了
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def befor_func(request):
print('xxxxxxxxxxxxx测试用例的初始化xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx')
def fin(): #尾部这是后置条件,测试用例执行后就会调用这个函数
print('zzzzzzzzzzzz测试用例的清除zzzzzzzzzzz')
request.addfinalizer(fin) #回调,当我整个包运行完了后回调fin这个方法
def test_001(befor_func):
print("测试用例001")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["test1.py",'-s'])
2、pytest数据驱动(参数化)
pytest数据驱动的意义:
参数化(登录用例4条,每一个账号密码都不同,使用框架把4个用例全部执行完,不需要for循环遍历执行,采用数据驱动方案来做)
pytest内置装饰器@pytest.mark.parametrize可以让测试数据参数化,把测试数据单独管理,类似ddt数据驱动的作用,方便代码和测试数据分离
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a",[1,2,3]): # 参数化传一组参数
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b", [(1,2),(3,4),(5,6)]) # 参数化传多组参数
登录账户密码(name和psw不同的用例组合,一个接口几十个用例怎么做----几十组数据----传的参数不同(什么请求方式和各种都一样)
可以把name和psw分别采取多组数据进行参数化,数据分离,一个接口跑4次,每次用不同的参数)
import pytest
#[(1,2),(3,4),(5,6)] [1,2,3]
class Test_login():
def setup_class(self):
print("执行测试类之前,我需要执行操作")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a",[1,2,3]) #("变量名",[1,2,3]),数据需要封装成一个列表,多个数据需要封装成列表嵌套元组 ----数据驱动
def test_login01(self,a): #数据驱动,一定要把变量名a引入引来,不然无法参数化
print("---test_login01----")
assert 1 + 1 == a
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b", [(1,2),(3,4),(5,6)]) #数据驱动传多组参数
def test_login02(self,a,b):
print("---test_login02----")
assert a + 1 == b
def teardown_class(self):
print("------该测试类的环境清除-----")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["test_func01.py","-s"])
3、pytest结合allure报告操作
pytest自带的报告框架 pytest-html;
allure环境搭建(allure是报告库不是python专属的,很全面的框架)-allure报告漂亮;
下载allure.zip(压缩包);
解压allure.zip到一个文件目录;
将allure-2.13.3\bin路径添加到环境变量path;
pip install allure-pytest -------allure报告本身不是很漂亮,通过allure-pytest这个库可以定制化报告,让报告变得很漂亮;
验证(cmd输入allure);
allure和pytest联合执行生成报告:运行两条语句
执行pytest单元测试,生成的allure报告需要的数据存在/tmp目录
pytest -sq --alluredir=../report/tmp #pytest把allure报告的生成的中间文件放到一个临时文件里面(pytets生成报告,需要数据,所以先把数据存起来)
所有的报告需要数据支持的,数据来源pytest框架本身,结果数据存到一个文件,存在…/report/tmp文件夹;
tmp临时文件,一般json格式;
执行命令,生成测试报告
allure generate ../report/tmp -o ../report/report -clean #allure指令生成对应报告
allure模拟代码
import pytest
import os
class Test_login():
def setup_class(self):
print("执行测试类之前,我需要执行操作")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a",[1,2,3])
def test_login01(self,a):
print("---test_login01----")
assert 1 + 1 == a
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b", [(1,2),(3,4),(5,6)])
def test_login02(self,a,b):
print("---test_login02----")
assert a + 1 == b
def teardown_class(self):
print("------该测试类的环境清除-----")
if __name__ == '__main__':
#需要打印对应的信息,需要在列表里面加-s
#1:--alluredir ---生成临时文件,测试用例的结果数据放到目录 --alluredir 存放目录
pytest.main(["test_func01.py","-s","--alluredir","../report/tmp"]) #框架自己调用函数
#通过--alluredir把allure需要的数据存到../report/tmp这个路径下面
#../--所在路径的父级别目录是test_case的目录隔壁邻居report文件下tmp,专门放alluer报告生成的需要的数据源
# 2:临时数据没有报告的,allure generate allure才会生成报告 -----allure生成器生成allure报告--generate allure生成器,cmd指令
#需要os模块os.system()调用指令可以在local的cmd里面敲
os.system("allure generate ../report/tmp -o ../report/report --clean")
#os.system("allure generate 报告需要的数据 -o 报告存放目录 --clean")
#-o生成
#allure generate生成报告指令,把../report/tmp 的文件-o生成报告out out一下,生成的报告放在../report/report
#--clean把上次报告清除一下用--clean #allure报告生成的是一个服务,(本地服务)和jinkins结合,放在整个里面去集成,放到公共服务器里面
allure报告的优化
import pytest
import os
import allure
@allure.feature("登录模块") #一级标题,大模块标题(类标签)
class Test_login():
def setup_class(self):
print("执行测试类之前,我需要执行操作")
@allure.story("登录login01") # 二级标签(每个接口的标签)
@allure.title("login01") # 标题,每个用例带个标题(报告体现在每个测试用例)(一个接口有几个用例,title用例的标签)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a",[1,2,3])
def test_login01(self,a):
print("---test_login01----")
assert 1 + 1 == a
@allure.story("登录login02") # 二级标签,定制allure报告层级
@allure.title("login02") #标题,每个用例带个标题(报告体现在每个测试用例)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b", [(1,2),(3,4),(5,6)])
def test_login02(self,a,b):
print("---test_login02----")
assert a + 1 == b
def teardown_class(self):
print("------该测试类的环境清除-----")
@allure.feature("购物模块")
class Test_Shopping():
@allure.story("shopping")
@allure.title("shopping01")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b", [(1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6)])
def test_shopping(self, a, b):
print("---test_login02----")
assert a + 1 == b
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["test_func01.py","-s","--alluredir","../report/tmp"])
os.system("allure generate ../report/tmp -o ../report/report --clean")
#allure报告生成的是一个服务,(本地服务)和jinkins结合,放在整个里面去集成,放到公共服务器里面
其他知识点:
测试用例一般写在excel表格文件里面,数据分离(维护好excel就行);
pytest–从头到尾到报告执行发邮件;
字典是一种存储类型,json是一种格式(完全不同);
4、pytest参数解析
pytest.main([‘test_boss.py’,‘-s’,‘-k test_modify_psw’,‘–alluredir=tmp/my_allure_results’])
说明:
test_boss.py:指定测试用例文件;
-s:显示print语句;
-k test_modify_psw:指定某个测试用例;
-n:表示用两个进程启动测试脚本
生成报告缓存文件:–alluredir=tmp/my_allure_results
os.system(‘allure serve tmp/my_allure_results’):打开测试报告,命令行需要python 的os模块调用
5、pytest的初始化和清除
import pytest
#假设启动被测app的时候需要去填写配置项信息,每个的端口号不同,多终端需要两个appim server
#这时候setup_module和teardown_module不能传参,搞不定,需要换一种方法做测试用例的初始化和清除,
#setup_module以模块为作用域,不写module以测试用例(测试函数)为作用域
# def setup_module(): #测试用例之前执行,原始的setup和teardown有个缺陷,里面不能传参数,
# #默认test级别,每个测试用例执行的时候都会执行一次,希望当前某个模块执行的时候只执行一次(不管里面用例执行多少次)
# #setup初始化和tear_down升个级,升级成module模块级别的
# print("启动被测app")
# print('连接appium服务')
#
# def teardown_module():
# print('关闭被测app')
# print('断开appium服务')
#定义个函数,名字随便取 使用@pytest.fixture装饰器把这个函数装饰成初始化清除函数
@pytest.fixture(scope='module') #作用域默认test,初始化,加装饰器,初始化清除函数,autouse=True(自动执行)这种方法不建议使用 #
def before_test(): #初始化函数升级作用域到module模块级别
print("启动被测app")
print('连接appium服务')
yield #后面写清除动作,
after_test()
#清除函数,清除函数并不会直接被初始化函数使用,我们必须放在初始化函数yiled后面才能回被调用
def after_test():
print('关闭被测app')
print('断开appium服务')
#目前一共有两个port,需要测试两个手机,两个多终端,before_test需要装饰器标记
#测试用例的参数化
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('before_test') #这表示调用某个自定义的初始化函数,括号里面的字符串写被调用函数的名字
@pytest.mark.parametrize('psw',['boss123','boss456'])
def test_app(psw): #测试用例,可能涉及到其他参数,比如需要一些配置信息,测试用例涉及到参数, #多组参数需要使用装饰器pytest.mark.parametrize(数据驱动),psw传参和形参名字对应的
print('测试boss app')
print(f'登录测试账号{psw}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['pytest_ywt.py','-s'])
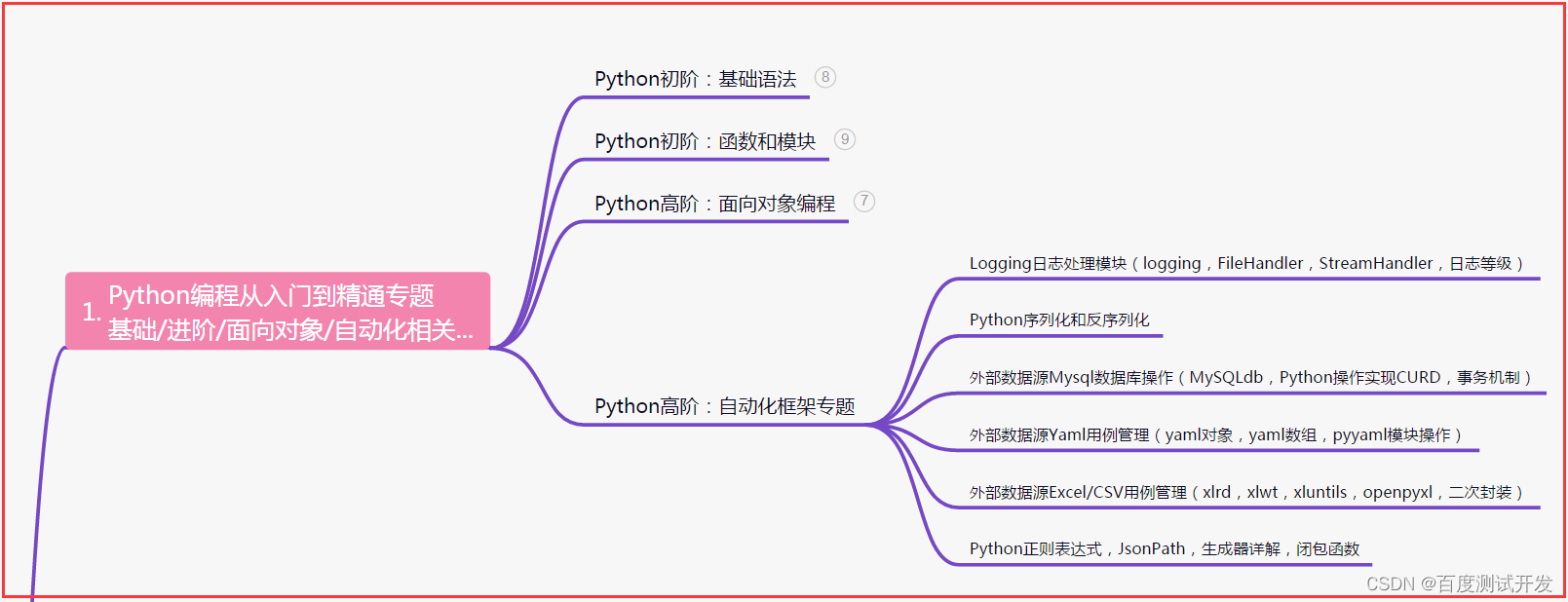
| 下面是我整理的2023年最全的软件测试工程师学习知识架构体系图 |
一、Python编程入门到精通
二、接口自动化项目实战
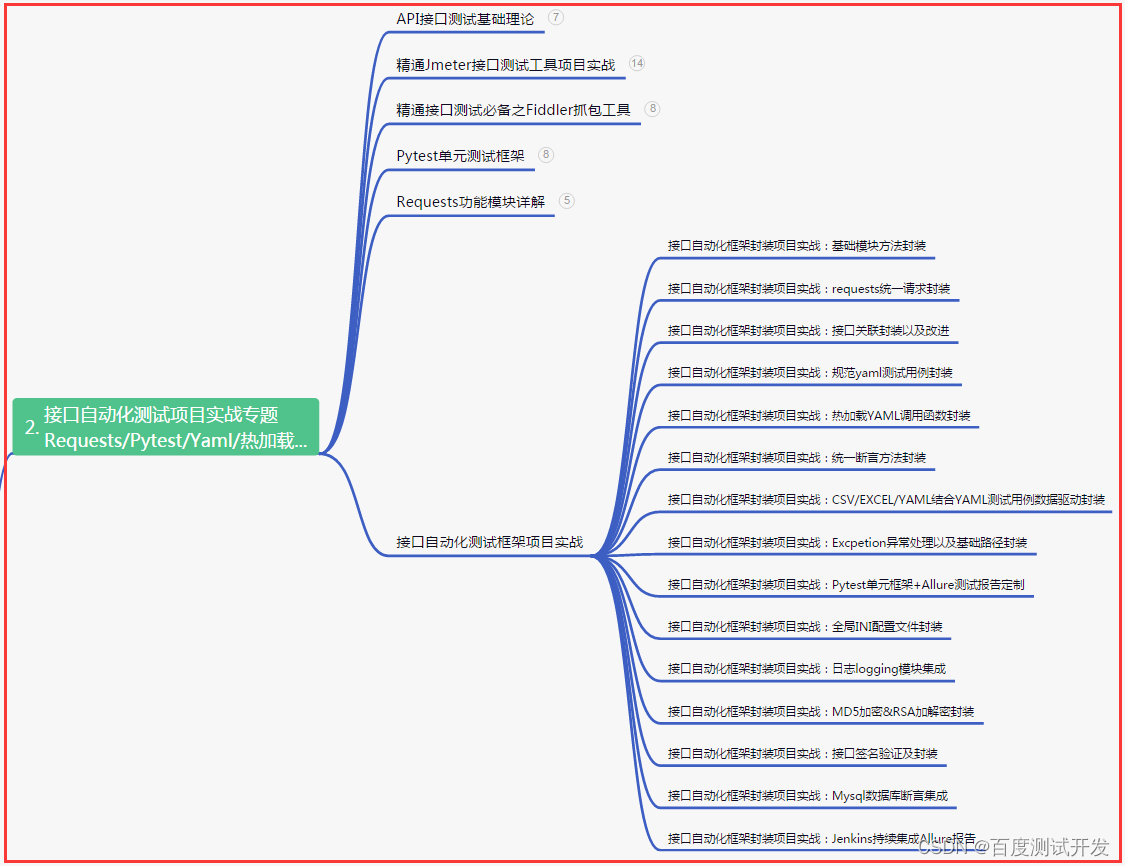
三、Web自动化项目实战
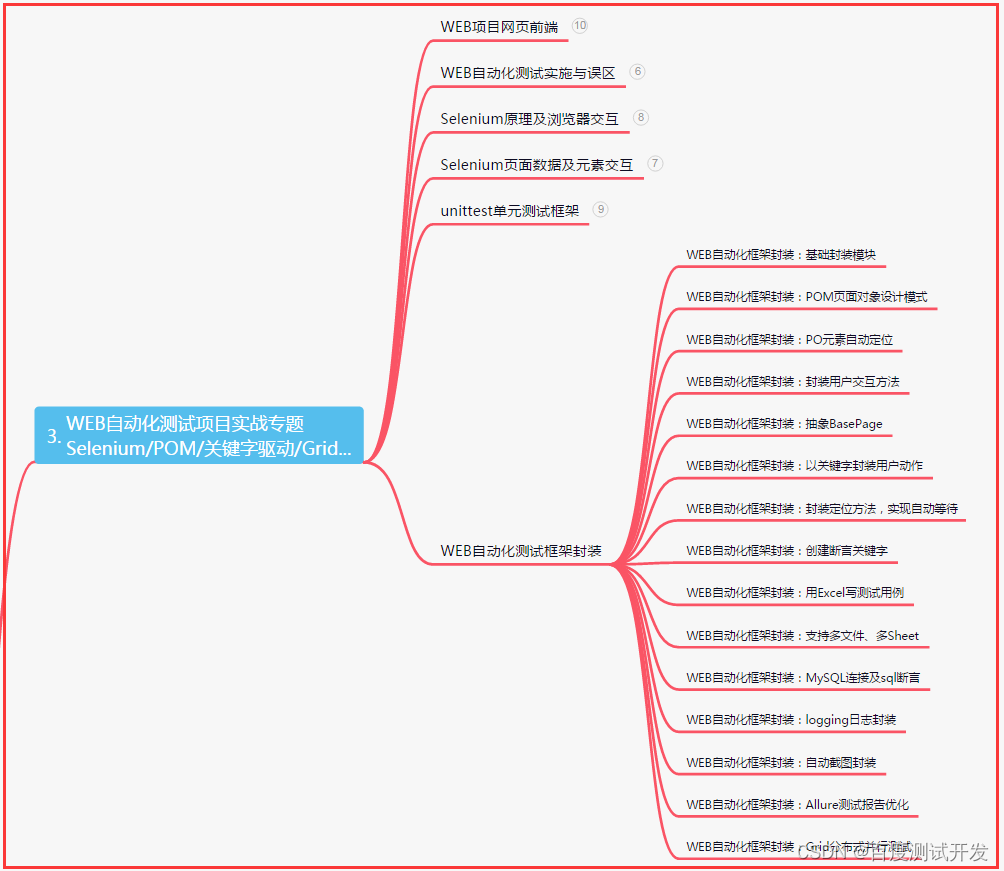
四、App自动化项目实战
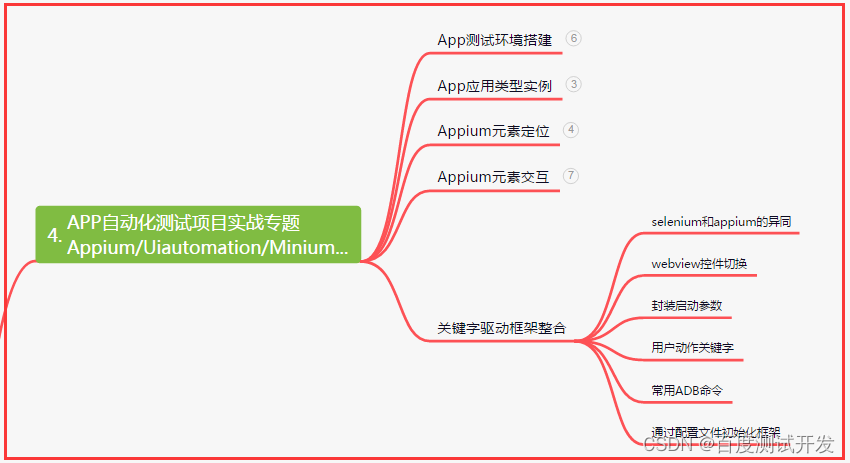
五、一线大厂简历
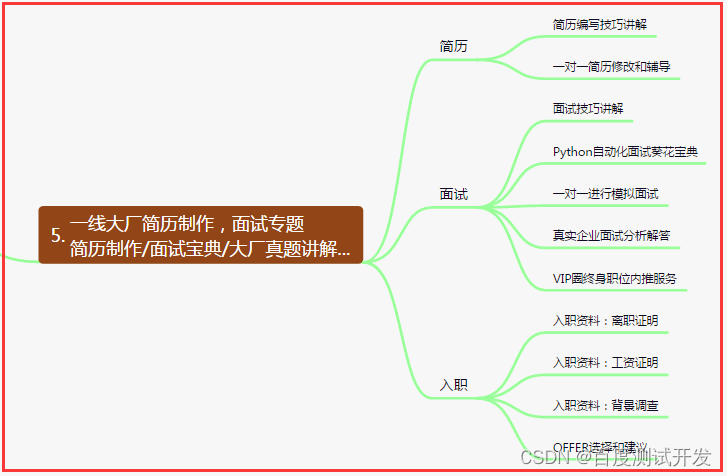
六、测试开发DevOps体系
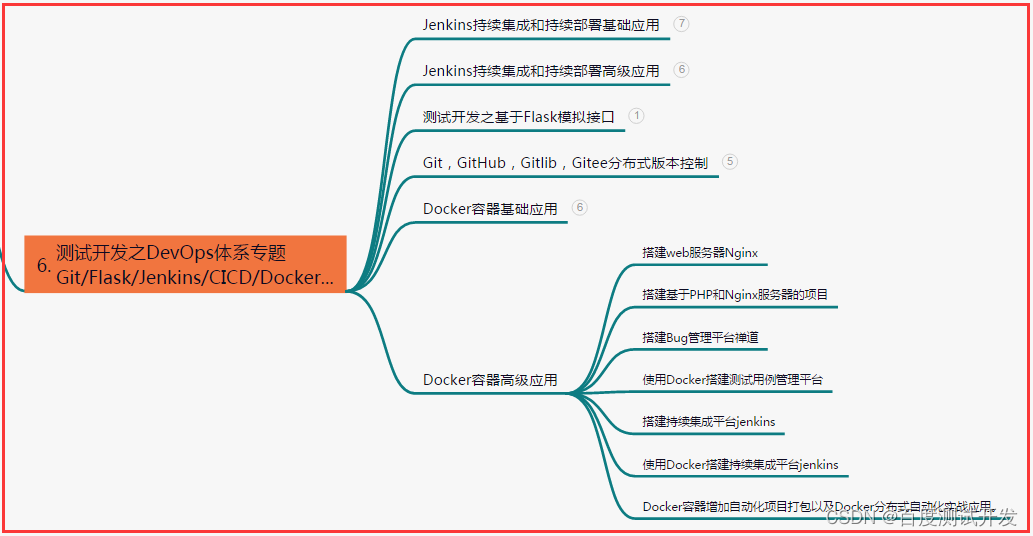
七、常用自动化测试工具
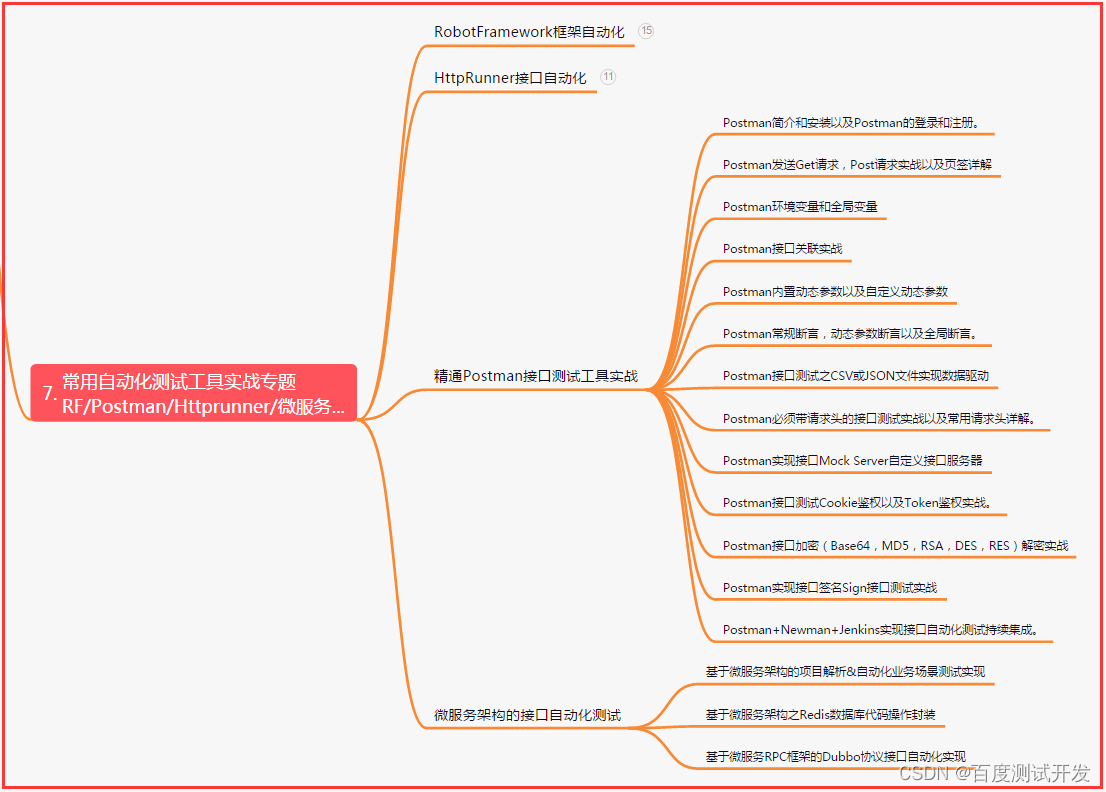
八、JMeter性能测试
九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
千锤百炼方成钢,一腔热血铸辉煌。奋斗是追逐梦想的征程,每一次努力都在为成功铺就坚实的基石。永不放弃,勇往直前,用汗水浇灌希望的花朵,终将开出属于自己的辉煌人生。
生命如一朵盛开的花朵,只有经历风雨的洗礼,才能绽放出光彩夺目的美丽。坚持自己的梦想,勇敢追逐,奋斗不止,你将终获辉煌的成就,因为努力是改变命运的钥匙。
人生如天空之星,只有付出坚持的努力,才能闪耀璀璨的光芒。不畏艰难困境,锲而不舍地追求梦想,奋斗的力量将引领你超越自我,驶向辉煌的彼岸。相信自己,勇往直前,成功必将属于你。






![「网络编程」传输层协议_ TCP协议学习_及原理深入理解(二 - 完结)[万字详解]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8fa0acb456ab4064ada5f08e07a3a012.png)