目录
104. 二叉树的最大深度
559. N 叉树的最大深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
104. 二叉树的最大深度
学了回溯之后再来做一下

思路:
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
dfs,bfs,迭代三个方法都可以做这道题;
代码:
// dfs
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftMax = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightMax = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax) + 1;
}
}
// bfs
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int len = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 不影响
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
int l = maxDepth(root.left);
int r = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
}
}
559. N 叉树的最大深度

代码:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root.children.size(); i++) {
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(root.children.get(i)));
}
return depth + 1;
}
}111. 二叉树的最小深度
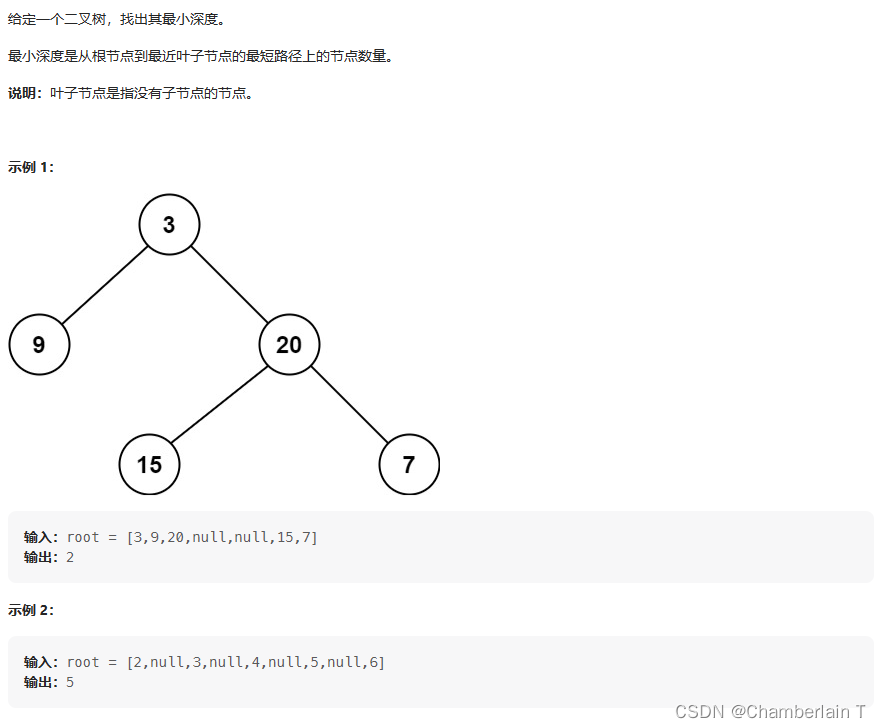
思路:
叶子节点是指左右节点都为空的情况,不能直接比较左右子树的最小深度,需要加以限制。例如[1, null, 2],的最小深度为2,但如果直接取左右最小深度则容易算成1。
· 所以需要分情况:如果左子树为空,则最小深度为右子树最小深度+1;如果右子树为空,最小深度为左子树最小深度+1。左右子树都不为空,再去二者较小的深度+1;
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// dfs
// 叶子节点是指左右孩子都为空的节点
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
// 左右孩子都为空
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
// 只有左孩子为空
if (root.left == null) {
return right + 1;
}
// 只有右孩子为空
if (root.right == null) {
return left + 1;
}
// 左右孩子都不为空
return Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
}
// bfs
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int minD = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int len = queue.size();
minD++;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 层序遍历,左右节点为空说明是叶子节点,第一个叶子节点对应最小深度
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return minD;
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return minD;
}
}222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
思路:
愉快的简单题。
代码:
// dfs
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return root == null? 0: countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
// 迭代前序
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
int count = 0;
if (root == null) {
return count;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
count++;
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return count;
}
}