参考资料
- 【转载】关于重定向RedirectAttributes的用法
- RedirectAttributes 的使用
目录
- 前期准备
- 一. RedirecAtrributes重定向传参
- 三. 重定向目标页面接收参数
前期准备
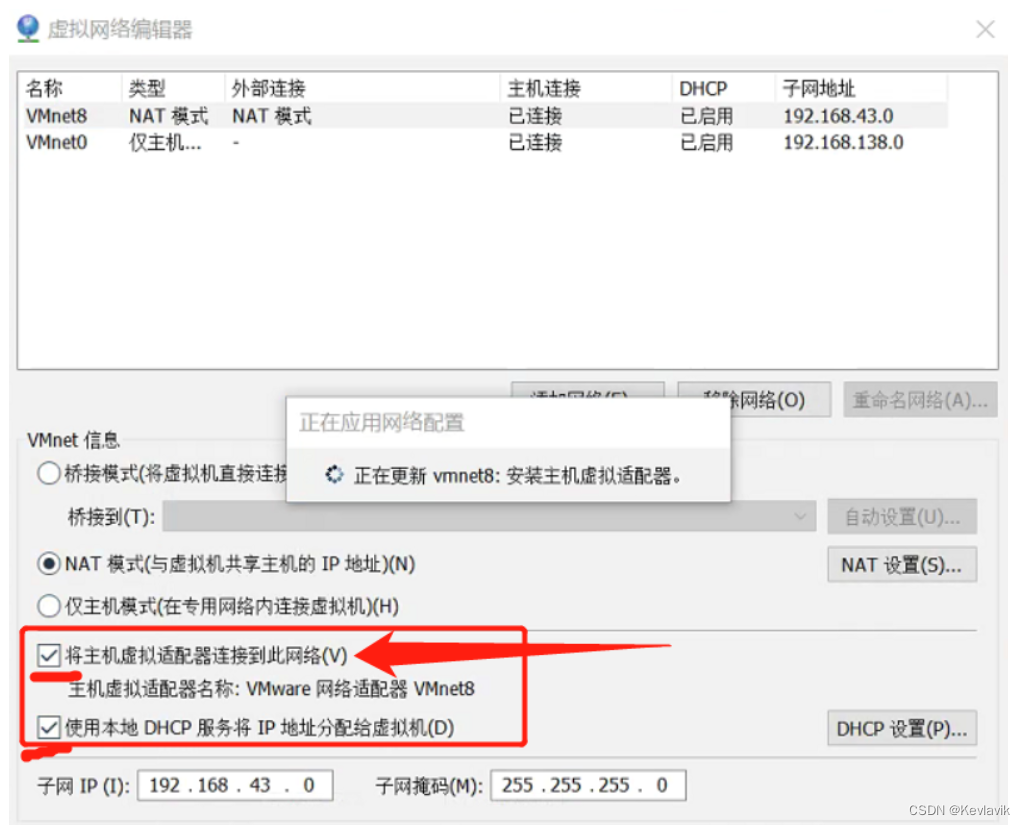
⏹配置文件
server:
servlet:
context-path: /jmw
⏹访问url
http://localhost:8080/jmw/test16/init?name=贾飞天&age=18
⏹test16.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<!--
因为我们配置了 server.servlet.context-path 来指定项目路径,
而使用 @{}的方式可以自动添加项目路径
size=${param.size()},name=${param.name} 会渲染为 ?size=xxx&name=xxx
-->
<a th:href="@{/test16/changeView(size=${param.size()},name=${param.name})}">页面重定向</a>
</div>
</body>
⏹Thymeleaf渲染之后的效果
<a href="/jmw/test16/changeView?size=2&name=%E8%B4%BE%E9%A3%9E%E5%A4%A9">页面重定向</a>
一. RedirecAtrributes重定向传参
-
redirectAttributes.addAttributie("key", value);
这种方法相当于在重定向链接地址追加传递的参数。
以上重定向的方法等同于return "redirect:/重定向目标页面url?key=value",注意这种方法直接将传递的参数暴露在链接地址上,非常的不安全,慎用。 -
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttributie("key", value);
这种方法是隐藏了参数,链接地址上不直接暴露,但是能且只能在重定向的 “页面” 获取 param 参数值。其原理就是将设置的属性放到 session 中,session中的属性在重定向到目标页面后马上销毁。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes;
@GetMapping("/changeView")
public String changeView(@RequestParam String name, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
System.out.println(name); // 贾飞天
// 准备重定向要传递的参数
Map<String, String> mapParam = new HashMap<>();
mapParam.put("key1", "110");
mapParam.put("key2", "120");
// 在重定向时,会将值放入session中,重定向到目标页面之后,会从session中清除
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("mapParam1", mapParam);
// 相当于拼参数放在url后面
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("param2", name);
return "redirect:/test17/init";
}
三. 重定向目标页面接收参数
- 使用
ModelMap来接收 redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute() 中放入的数据 - 也可以使用
ModelAttribute来接收 redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute() 中放入的数据 - 使用
@RequestParam来接收 redirectAttributes.addAttribute() 中放入的数据
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test17")
public class Test17Controller {
@Resource
private HttpServletRequest request;
@GetMapping("/init")
public ModelAndView init(
// 使用ModelMap来接收 redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute() 中放入的数据
ModelMap mapParam1,
// 也可以使用ModelAttribute来接收 redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute() 中放入的数据
@ModelAttribute("mapParam1") Map<String, String> mapParam2,
// 使用@RequestParam来接收 redirectAttributes.addAttribute() 中放入的数据
@RequestParam(value = "param2" ,required = false) String param2
) {
System.out.println(mapParam1); // {mapParam1={key1=110, key2=120}}
System.out.println(param2); // 贾飞天
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
System.out.println(parameterMap);
/*
param2=["贾飞天"]
*/
// 如果不为空,说明是从其他页面重定向过来的
if (!mapParam1.isEmpty()) {
// 两种获取方式相同
Map mapParam_1 = (Map)mapParam1.getAttribute("mapParam1");
System.out.println(mapParam_1.get("key1")); // 110
Map mapParam_2 = (Map)mapParam1.get("mapParam1");
System.out.println(mapParam_2.get("key2")); // 120
// 将map放入request的Attribute中
request.setAttribute("testMap", mapParam2);
}
// 指定跳转的页面
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("test17");
return modelAndView;
}
}
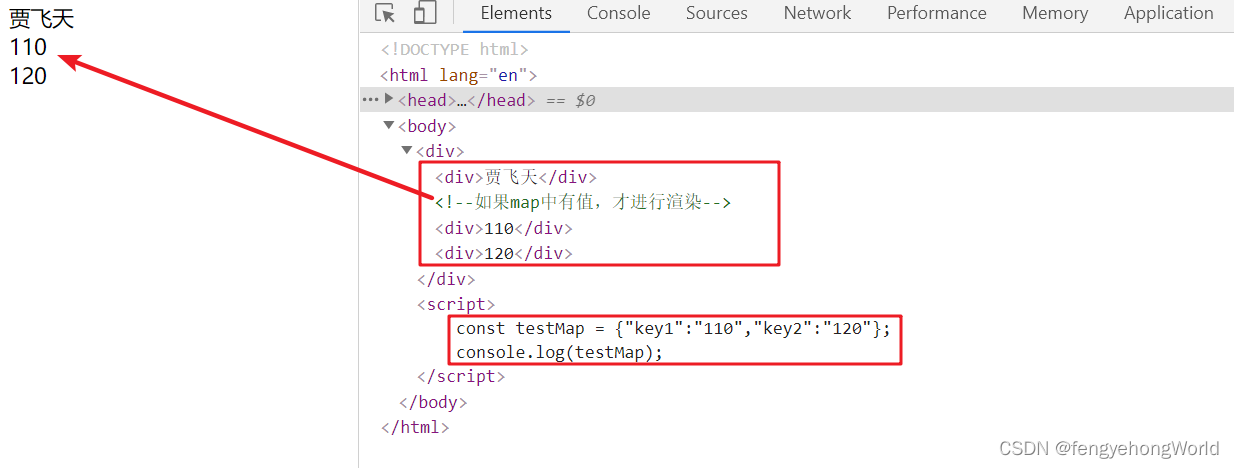
前台页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div>[[${param.param2}]]</div>
<!--如果map中有值,才进行渲染-->
<th:block th:if="${not #maps.isEmpty(testMap)}">
<div>[[${testMap.key1}]]</div>
<div>[[${testMap.key2}]]</div>
</th:block>
</div>
</body>
<script th:inline="javascript">
const testMap = [[${testMap}]];
console.log(testMap);
</script>
</html>




![[附源码]Node.js计算机毕业设计大学生心理咨询系统Express](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d8277d782009496c92227eee024db289.png)