文章目录
- 写在前面
- 栈
- 什么是栈
- 栈的实现
- 队列
- 什么是队列
- 队列的实现
- 用队列实现栈
- 用栈模拟队列
写在前面
栈和队列的实现依托的是顺序表和链表,如果对顺序表和链表不清楚是很难真正理解栈和队列的
下面为顺序表和链表的实现和图解讲解
手撕图解顺序表
手撕图解单链表
栈
什么是栈
栈是一种数据结构,遵循的原则是后入先出,简单来说就是先入栈的最后出,最后入栈的先出
栈在实际应用中也是有很多场景,例如在使用网页时,我们点入了多个网页,退出返回的时候遵循的就是栈的后入先出原则
栈的实现
既然知道了栈的原则,那么就进行栈的实现用什么比较好,首先确定是可以用线性表实现,观察栈的使用原则不难发现,它只涉及一端的输入输出,这就意味着使用顺序表是很好的解决方案
栈的功能也不算多,入栈出栈检查栈满查看栈顶元素…整体看,栈就是顺序表的变形,这里对栈的实现不进行过多补充,重点在于后面和队列的相互实现
首先列出栈的定义和栈要实现的部分,声明和定义分离是个好习惯
// stack.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
下面是对栈的实现,几乎都是顺序表的基本操作,实现很简单
// stack.c
#include "stack.h"
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
STDataType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->_capacity * 2;
tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
ps->_a = tmp;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_capacity == ps->_top)
{
STDataType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4:ps->_capacity * 2;
tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a,sizeof(STDataType)* newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
ps->_a = tmp;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
ps->_top++;
}
bool STEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->_top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->_a[ps->_top-1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (0 == ps->_top)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = 0;
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = NULL;
}
整体看,只要掌握了顺序表,栈的实现是很轻松的
队列
什么是队列
从名字来看,队列在日常生活中也经常遇到,不管在哪里都少不了排队的概念,而在有秩序的队列中,进队列都是从后面进队列,出队列都是从头出队列,这就类似于链表中的头删和尾插
那么队列的定义就有了,先进的先出,后进的后出,这就是队列的定义
队列实现还是和线性表有关,具体选顺序表还是链表要进行分析:
如果选用顺序表,顺序表的头删和尾插显然不如链表,你可能有这样的解决方案:我们可以选用数组下标当作头和尾,这样就能模拟头部少一个和尾部加一个,的确,这样可以解决,但是下一个问题是数组的长度并不好管控,如果想要完美的充分利用顺序表,就必须要使用循环数组,循环数组的下标并不好掌控,因此这里使用链表是很合适的选择
这里是关于循环数组的解析和模拟实现队列:
解析循环数组
队列的实现
// queue.h
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
上述函数的声明具体实现如下:
// queue.c
#include "queue.h"
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
// 1、一个节点
// 2、多个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
// 头删
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
栈和队列本身是没有难度的,但是如果使用栈去实现队列,用队列去实现栈呢?
下面分析如何实现队列和栈的相互实现:
用队列实现栈
先看原理图:

代码实现也不算难,实现如下:
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
#include "queue.h"
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
// 1、一个节点
// 2、多个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
// 头删
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
typedef struct Mystack
{
Queue push;
Queue pop;
}Mystack;
void MsInit(Mystack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
QueueInit(&(ps->push));
QueueInit(&(ps->pop));
}
void MsPush(Mystack* ps,QDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
QueuePush(&(ps->push), x);
}
void MsPop(Mystack* ps)
{
while (QueueSize(&(ps->push)) > 1)
{
QueuePush(&(ps->pop), QueueFront(&(ps->push)));
QueuePop(&(ps->push));
}
QueuePop(&(ps->push));
while (!QueueEmpty(&(ps->pop)))
{
QueuePush(&(ps->push), QueueFront(&(ps->pop)));
QueuePop(&(ps->pop));
}
}
QDataType MsTop(Mystack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->push.ptail->data;
}
bool MsEmpty(Mystack* ps)
{
if (ps->push.size == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
Mystack s;
MsInit(&s);
MsPush(&s, 1);
MsPush(&s, 2);
MsPush(&s, 3);
MsPush(&s, 4);
MsPush(&s, 5);
while (!MsEmpty(&s))
{
printf("%d ", MsTop(&s));
MsPop(&s);
}
return 0;
}
用栈模拟队列
和上面的比起来,栈来实现队列就有一些改变:
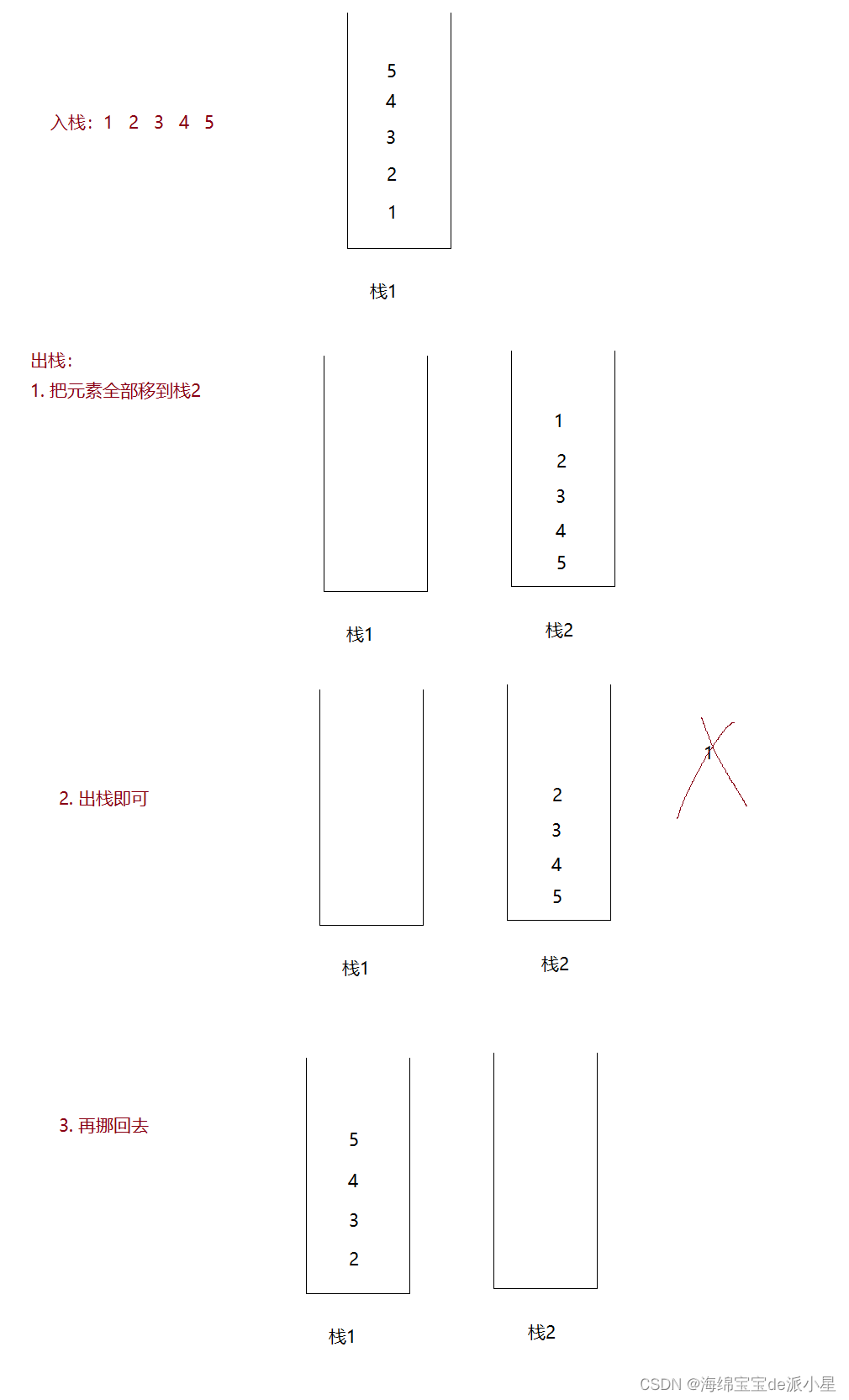
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_capacity == ps->_top)
{
STDataType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4:ps->_capacity * 2;
tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a,sizeof(STDataType)* newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
ps->_a = tmp;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
ps->_top++;
}
bool STEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->_top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->_a[ps->_top-1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (0 == ps->_top)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = 0;
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = NULL;
}
typedef struct Myqueue
{
Stack Push;
Stack Pop;
}Myqueue;
void MqInit(Myqueue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
StackInit(&(pq->Push));
StackInit(&(pq->Pop));
}
void MqPush(Myqueue* pq,STDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
StackPush(&(pq->Push), x);
}
void MqPop(Myqueue* pq)
{
while (!StackEmpty(&(pq->Push)))
{
StackPush(&(pq->Pop), StackTop(&(pq->Push)));
StackPop(&(pq->Push));
}
StackPop(&(pq->Pop));
while (!StackEmpty(&(pq->Pop)))
{
StackPush(&(pq->Push), StackTop(&(pq->Pop)));
StackPop(&(pq->Pop));
}
}
STDataType MqTop(Myqueue* pq)
{
// 把数据从push弄到pop
while (!StackEmpty(&(pq->Push)))
{
StackPush(&(pq->Pop), StackTop(&(pq->Push)));
StackPop(&(pq->Push));
}
STDataType ret = pq->Pop._a[pq->Pop._top-1];
// 再把数据弄回去
while (!StackEmpty(&(pq->Pop)))
{
StackPush(&(pq->Push), StackTop(&(pq->Pop)));
StackPop(&(pq->Pop));
}
return ret;
}
int MqEmpty(Myqueue* pq)
{
if (pq->Push._top == 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Myqueue q;
MqInit(&q);
MqPush(&q, 1);
MqPush(&q, 2);
MqPush(&q, 3);
MqPush(&q, 4);
MqPush(&q, 5);
while (!MqEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", MqTop(&q));
MqPop(&q);
}
return 0;
}
这样就可以直接实现了
整体来说,栈和队列的相互实现的意义不算很大,但是可以很好的更加深入的理解栈和队列的原理