这篇文章主要介绍怎么实现角色权限的快捷分配功能,不需要像大多数项目的授权一样,使用类似穿梭框的组件来授权。
具体实现:通过菜单树的勾选和取消勾选来给角色分配权限,在这之前,需要得到角色的菜单树,角色已有的权限对应树节点的选中状态为true,否则为false。
一、树的格式
首先简单了解一下easyui的tree组件的数据格式
官网截图
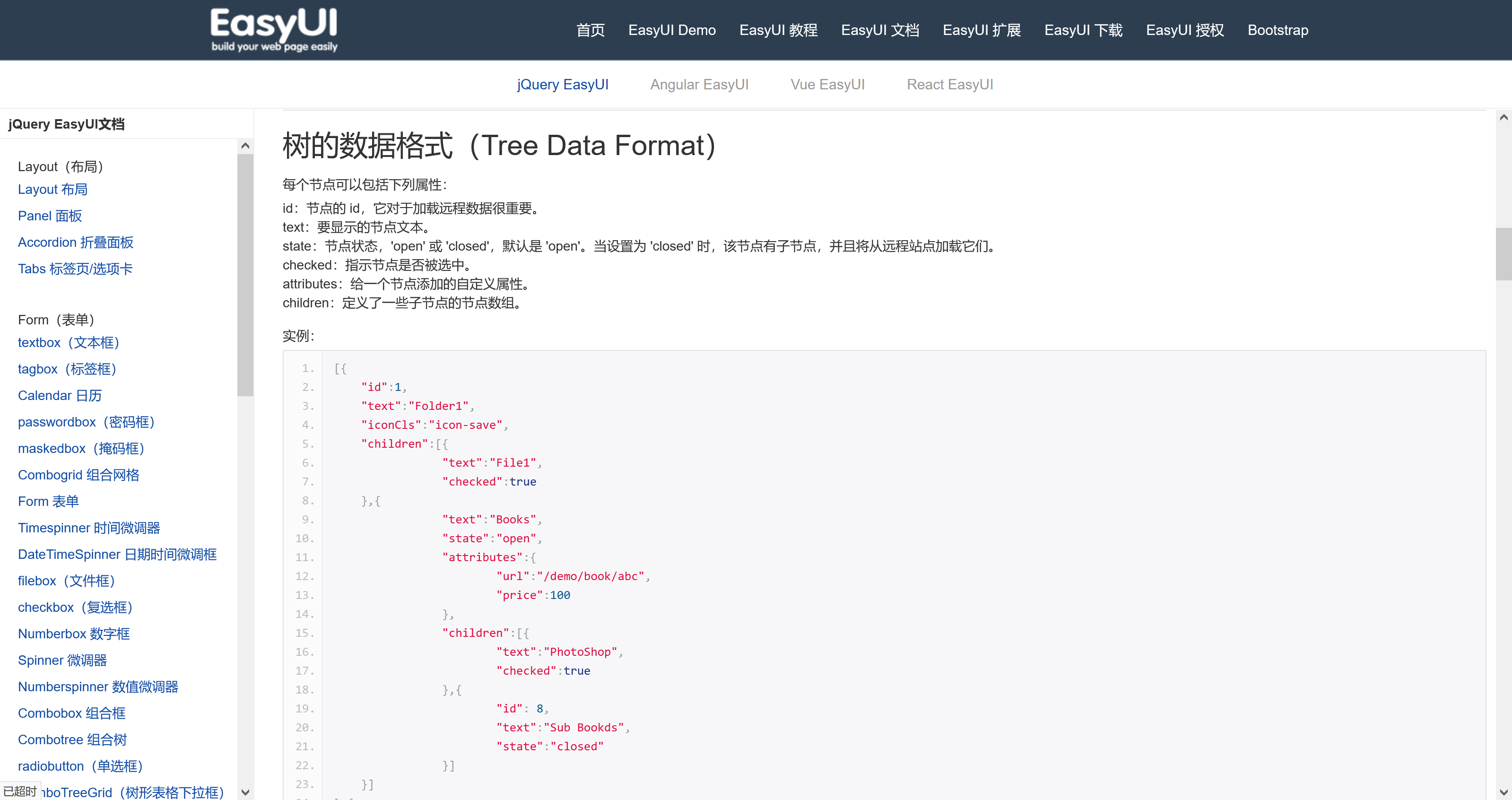
树的json数据格式
[{
"id":1,
"text":"Folder1",
"iconCls":"icon-save",
"children":[{
"text":"File1",
"checked":true
},{
"text":"Books",
"state":"open",
"attributes":{
"url":"/demo/book/abc",
"price":100
},
"children":[{
"text":"PhotoShop",
"checked":true
},{
"id": 8,
"text":"Sub Bookds",
"state":"closed"
}]
}]
},{
"text":"Languages",
"state":"closed",
"children":[{
"text":"Java"
},{
"text":"C#"
}]
}]二、创建实体类
根据这个格式,创建一个满足tree组件数据格式要求的实体类,其中attributes属性一般是用不到的,扩展了一个pxh字段,用于实现排序(本篇文章用不到)。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.component;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
/**
* easyui树对象
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
/*
树的数据格式
每个节点可以包括下列属性:
id:节点的 id,它对于加载远程数据很重要。
text:要显示的节点文本。
state:节点状态,'open' 或 'closed',默认是 'open'。当设置为 'closed' 时,该节点有子节点,并且将从远程站点加载它们。
checked:指示节点是否被选中。
attributes:给一个节点添加的自定义属性。
children:定义了一些子节点的节点数组。
*/
@Data
public class Tree<T> {
private String id;
/**
* 节点名称
*/
private String text;
/**
* 树节点的展开状态open/closed
*/
private String state;
/**
* 是否被选中
*/
private boolean checked;
/**
* 子树
*/
private List<Tree<T>> children;
/**
* 自定义属性
*/
T attributes;
/**
* 排序号
*/
private Integer pxh;
}三、获取角色的菜单树
完成分配角色权限的功能之前,需要根据角色的权限生成一个权限树
第一步:查询所有系统权限;
第二步:根据角色ID查询角色拥有的权限;
第三步:遍历所有系统权限生成菜单树,角色拥有的权限,对应树节点选中状态checked属性设置为true;
因为实际保存的是系统中的子权限,即controller接口的所有方法对应的url地址,如:/user/login。
所以在生成树的时候,需要查询父级权限,把父权限的信息设置到树的根结点上。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.service.impl;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.base.Pager;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.component.Tree;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.dto.PermissionTreeDTO;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.entity.Permission;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.entity.RolePermission;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.enums.PermissionType;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.exception.GlobalException;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.mapper.PermissionMapper;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.mapper.RolePermissionMapper;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.pager.RolePermissionPager;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.restful.ResponseCode;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.service.RolePermissionService;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.authority.util.StringUtils;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.update.UpdateWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.pagination.Page;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Service
public class RolePermissionServiceImpl implements RolePermissionService {
private final PermissionMapper permissionMapper;
private final RolePermissionMapper rolePermissionMapper;
public RolePermissionServiceImpl(PermissionMapper permissionMapper, RolePermissionMapper rolePermissionMapper) {
this.permissionMapper = permissionMapper;
this.rolePermissionMapper = rolePermissionMapper;
}
@Override
public List<Tree<Void>> listTree(Integer roleId) {
// 查询所有父级权限(权限类型为0),并生成权限ID和权限信息的map
Map<String, Permission> parentMap = new HashMap<>();
List<Permission> parentPermissions = permissionMapper.selectByType(PermissionType.FQX.getValue());
for (Permission permission : parentPermissions) {
parentMap.put(permission.getId(), permission);
}
// 查询角色的权限
List<Permission> permissions = rolePermissionMapper.selectByRoleId(roleId);
// 查询全部二级权限(权限类型为1)
List<Permission> subPermissions = permissionMapper.selectByType(PermissionType.ZQX.getValue());
// 并根据父级权限ID分组存放到map中
Map<String, List<Tree<Void>>> listHashMap = new HashMap<>();
// 遍历,把查询出来的权限按照parentId存到map中
for (Permission permission : subPermissions) {
Tree<Void> children = new Tree<>();
children.setId(permission.getId());
children.setText(permission.getName());
children.setChecked(permissions.contains(permission));
String parentId = permission.getParentId();
if (listHashMap.containsKey(parentId)) {
listHashMap.get(parentId).add(children);
} else {
listHashMap.put(parentId, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
// 构建返回结果对象
List<Tree<Void>> trees = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历map,生成菜单树
listHashMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
Permission parent = parentMap.get(key);
Tree<Void> tree = new Tree<>();
tree.setState("open");
tree.setChildren(value);
tree.setId(parent.getId());
tree.setText(parent.getName());
trees.add(tree);
});
return trees;
}
}四、分配权限功能实现
页面效果图
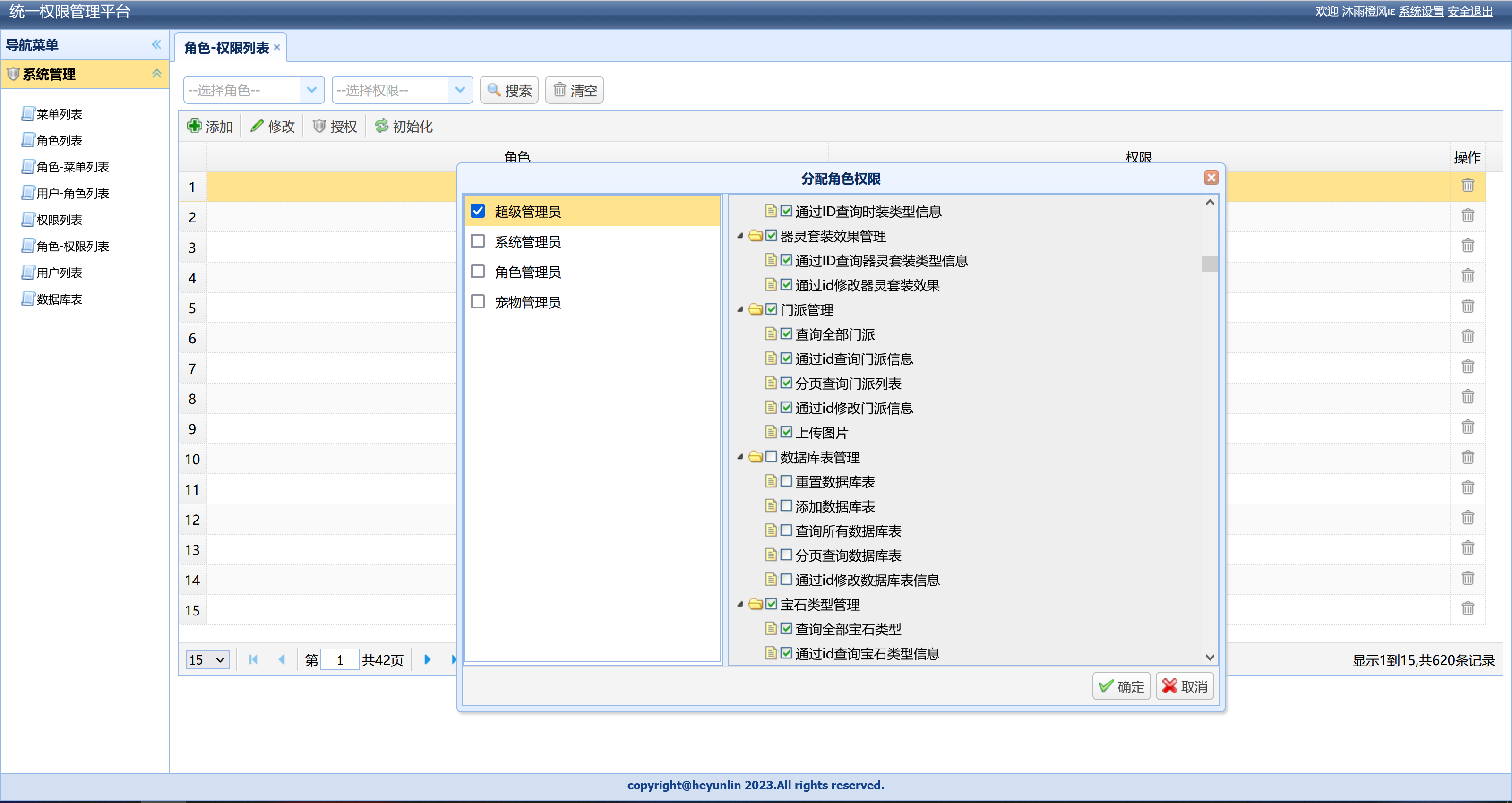
当我们勾选树的节点左边的对话框时,会把当前节点的ID添加到数组里,创建两个数组分别存放勾选和取消勾选的树的ID,不要求数组元素唯一,因为在后端去重了(List => Set)。
前端页面的js代码如下:当勾选和取消勾选的是非叶子节点,实际添加到数组中的是该节点下所有的叶子结点。点击对话框的【√确定】按钮时,会把数组的数据提交到后台,当没有选中或者取消选中树节点的时候不提交。
let insertIds = [];
let deleteIds = [];
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#tree").tree({
dnd: true,
animate: true,
checkbox: true,
onCheck: function (node, checked) {
let children = node.children;
// 父节点点击复选框
if (children) {
if (checked) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
insertIds.push(children[i].id);
}
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
deleteIds.push(children[i].id);
}
}
} else {
if (checked) {
insertIds.push(node.id);
} else {
deleteIds.push(node.id);
}
}
},
onContextMenu: function(e, node){
e.preventDefault();
$("#tree").tree("select", node.target);
$("#mm").menu("show", {
left: e.pageX,
top: e.pageY
});
}
});
$("#authorize_dialog").dialog({
title: "分配角色权限",
closed: true,
closable: true,
draggable: false,
buttons: [{
iconCls: "icon-ok",
text: "确定",
handler: function() {
let row = $("#role_list").datalist("getSelected");
if (row) {
if (insertIds.length > 0 || deleteIds.length > 0) {
let data = new FormData();
data.append("roleId", row.id);
if (insertIds.length > 0) {
data.append("insertIds", insertIds);
}
if (deleteIds.length > 0) {
data.append("deleteIds", deleteIds);
}
ajaxPost("/role_permission/distribute", data, function (res) {
insertIds = [];
deleteIds = [];
showMsg(res.message);
$("#tree").tree("reload");
}, error);
}
}
$("#authorize_dialog").dialog("close");
}
}, {
iconCls: "icon-cancel",
text: "取消",
handler: function() {
$("#authorize_dialog").dialog("close");
}
}]
});
});好了,这篇文章就分享到这里了,完整代码可通过下方git地址获取,看完之后如果对你有所帮助,不要忘了点赞+收藏哦~
统一权限平台![]() https://gitee.com/he-yunlin/authority.git
https://gitee.com/he-yunlin/authority.git