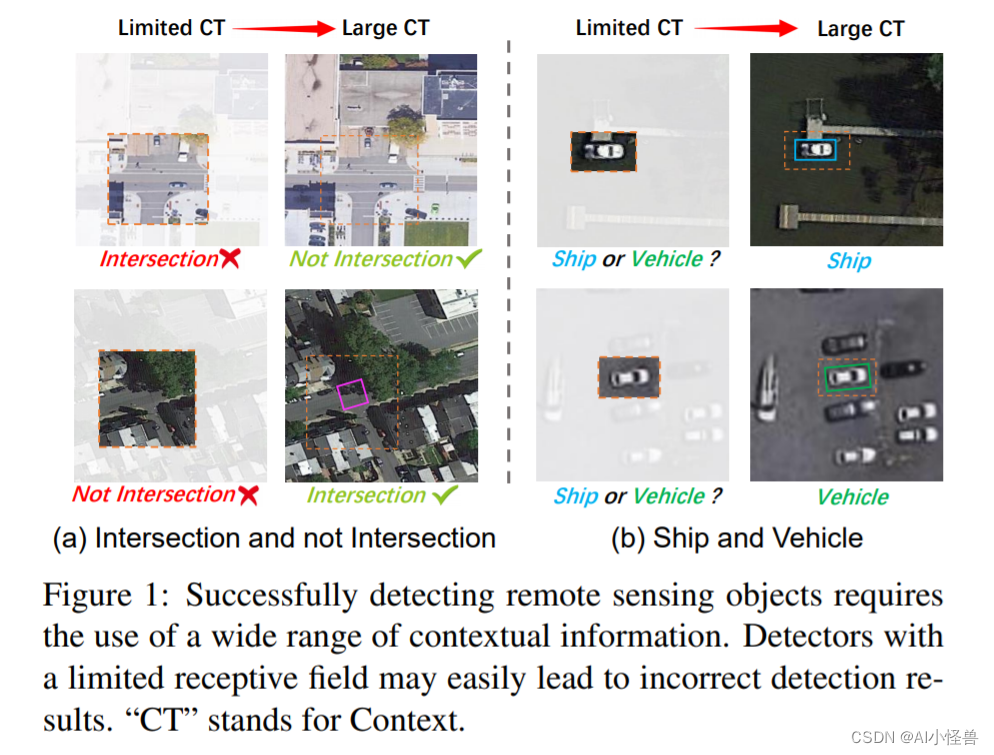
- Python GUI设计
- GUI 设计可以大大简化你的工作
- 编代码最头疼的内容就是
- 你不能以超快的速度获得你想要的结果
- 这是最头疼的
- 尤其是你要调试的时候
tkinter module 中的属性与方法
创建窗口
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("GUI example") # 设置窗口标题.pack
- pack方法是tkinter模块中常用的布局管理器之一,它会根据组件的添加顺序自动调整组件的位置和大小
- 如果希望更精确地控制组件的位置和大小,可以考虑使用其他布局管理器 如 .grid
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Pack example")
label1 = tk.Label(root, text="label 1")
label1.pack()
label2 = tk.Label(root, text="long long label 2")
label2.pack()
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="button 1")
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="button 2")
button2.pack()
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.pack()
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()

Entry
- 提供一个输入框
.get()
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Entry example")
label = tk.Label(root, text="entry your name:")
label.pack()
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.pack()
# 定义按钮点击事件的函数
def submit():
name = entry.get()
try:
result_label.config(text=f"Hello, {name}!")
except:
result_label.config(text="entry your name:")
button = tk.Button(root, text="submit", command=submit)
button.pack()
result_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
result_label.pack()
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()

.insert()、.delete()和.config()
- 使用.insert()方法,可以设置输入框的默认值
- 使用.delete()方法,可以删除输入框中的内容
- 使用.get()方法,可以获取输入框中的内容
- 使用.config()方法和state参数,可以禁用或启用输入框
- 禁用按钮的点击事件函数disable_entry()
- 使用entry.config(state="disabled")来禁用输入框
- 启用按钮的点击事件函数enable_entry()
- 使用entry.config(state="normal")来启用输入框。
- 禁用按钮的点击事件函数disable_entry()
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Entry example")
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.pack()
entry.insert(0, "default text")
def clear_entry():
entry.delete(0, tk.END)
def get_text():
text = entry.get()
print("entry:", text)
def disable_entry():
entry.config(state="disabled")
def enable_entry():
entry.config(state="normal")
button_clear = tk.Button(root, text="clear", command=clear_entry)
button_clear.pack()
button_get = tk.Button(root, text="get", command=get_text)
button_get.pack()
button_disable = tk.Button(root, text="disable", command=disable_entry)
button_disable.pack()
button_enable = tk.Button(root, text="enable", command=enable_entry)
button_enable.pack()
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()
添加标签
label = tkinter.Label(root, text="GUI example")
label.pack()import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Label example")
label = tk.Label(root)
label.pack()
label.config(font=("Arial", 20))
label.config(fg="white", bg="blue")
label.config(justify="center")
label.config(relief="solid", bd=2)
label.config(width=20, height=3)
label.config(text="Hello, Li Xu")
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()

- .config(text="Hello, CSDN!"):设置标签的文本内容
- .config(font=("Arial", 20)):设置标签的字体为Arial,大小为20
- .config(fg="white", bg="blue"):设置标签的前景色为白色,背景色为蓝色
- .config(justify="center"):设置标签的对齐方式为居中对齐
- .config(relief="solid", bd=2):设置标签的边框样式为实线边框,边框宽度为2
- .config(width=20, height=3):设置标签的宽度为20个字符,高度为3行
添加按钮
- 定义按钮点击事件处理函数
def button_click():
messagebox.showinfo("tips", "button click")
button = tkinter.Button(root, text="click", command=button_click)
button.pack()import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Button example")
button = tk.Button(root, text="click ")
button.pack()
button.config(text="click")
button.config(fg="white", bg="blue")
button.config(font=("Arial", 16))
button.config(width=10, height=2)
button.config(relief="solid", bd=2)
# 设置按钮的命令函数
def button_click():
print("has clicked!")
button.config(command=button_click)
button.config(state="normal")
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()
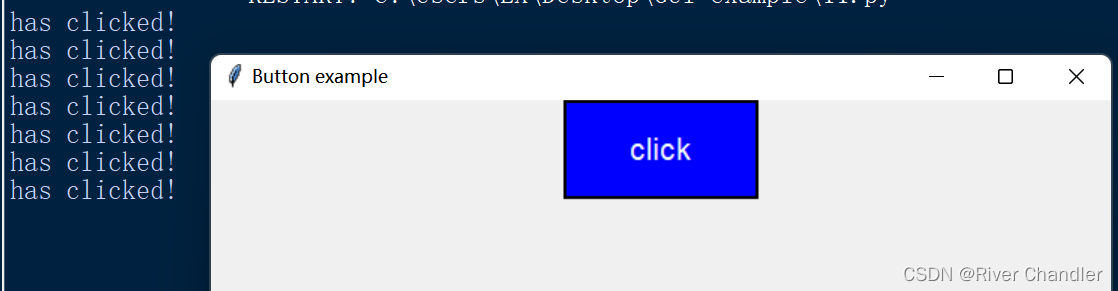
- .config(text):设置按钮的文本
- .config(fg="white", bg="blue"):设置按钮的前景色为白色,背景色为蓝色
- .config(font=("Arial", 16)):设置按钮的字体为Arial,大小为16
- .config(width=10, height=2):设置按钮的宽度为10个字符,高度为2行
- .config(relief="solid", bd=2):设置按钮的边框样式为实线边框,边框宽度为2
- .config(command=button_click):设置按钮的命令函数为button_click,即当按钮被点击时执行button_click函数
- .config(state="disabled"/"normal"):设置按钮的状态
.grid 方法
- row
- column
- columnspan
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Grid example")
label1 = tk.Label(root, text="label 1")
label1.grid(row=0, column=0)
label2 = tk.Label(root, text="long long label 2")
label2.grid(row=0, column=2)
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="button 1")
button1.grid(row=1, column=0)
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="button 2")
button2.grid(row=1, column=2)
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="button 3")
button3.grid(row=2, column=0)
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="button 4")
button4.grid(row=2, column=2)
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=4)
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()

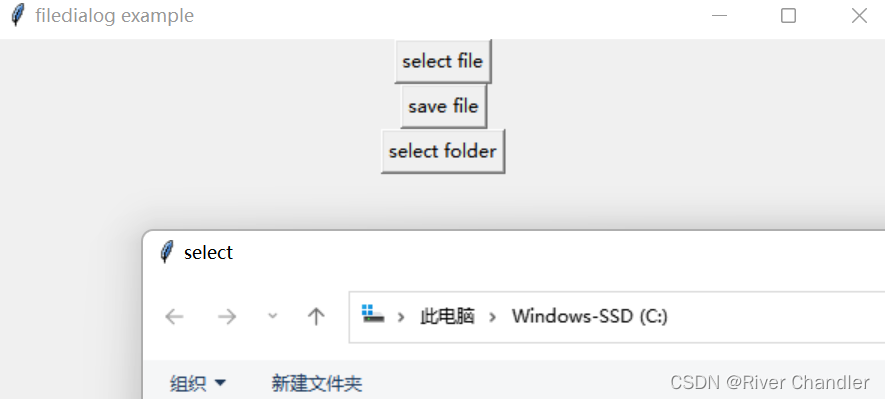
filedialog module
- filedialog.askopenfilename()方法
- 可以打开文件对话框来选择一个文件
- 点击事件函数open_file_dialog()
- filedialog.askopenfilename():显示文件选择对话框
- initialdir:设置初始目录
- title:设置对话框标题
- filetypes:设置文件类型过滤器
- 返回值:被选中的文件的路径
- filedialog.asksaveasfilename()方法
- 可以打开保存文件对话框来选择保存位置和文件名
- 点击事件函数save_file_dialog()
- filedialog.asksaveasfilename():显示保存文件对话框
- defaultextension:设置默认文件扩展名
- 返回值:选择的保存路径和文件名。
- filedialog.askdirectory()方法
- 可以打开选择文件夹对话框来选择一个文件夹
- 点击事件函数select_directory_dialog()
- filedialog.askdirectory():显示选择文件夹对话框
- 返回值:被选中的文件夹的路径
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
root = tk.Tk()
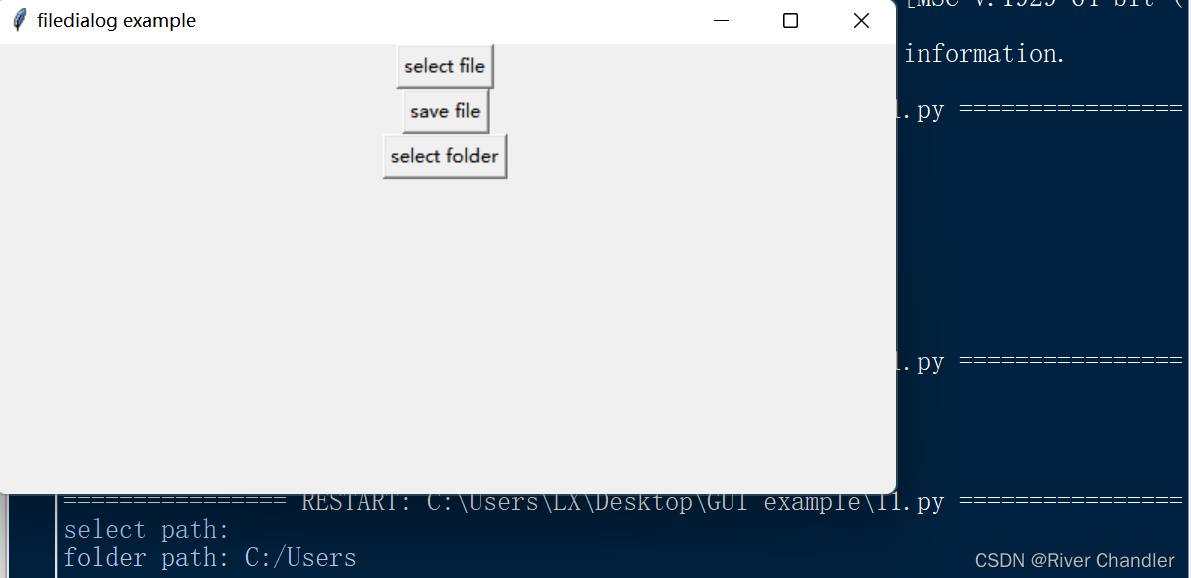
root.title("filedialog example")
def open_file_dialog():
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
initialdir="/",
title="select",
filetypes=(("Text Files", "*.txt"), ("All Files", "*.*"))
)
print("select path:", file_path)
def save_file_dialog():
file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(
initialdir="/",
title="save",
defaultextension=".txt",
filetypes=(("Text Files", "*.txt"), ("All Files", "*.*"))
)
print("save paht:", file_path)
def select_directory_dialog():
directory_path = filedialog.askdirectory(
initialdir="/",
title="select file folder"
)
print("folder path:", directory_path)
button_open = tk.Button(root, text="select file", command=open_file_dialog)
button_open.pack()
button_save = tk.Button(root, text="save file", command=save_file_dialog)
button_save.pack()
button_select_directory = tk.Button(root, text="select folder", command=select_directory_dialog)
button_select_directory.pack()
root.geometry("600x300")
root.mainloop()