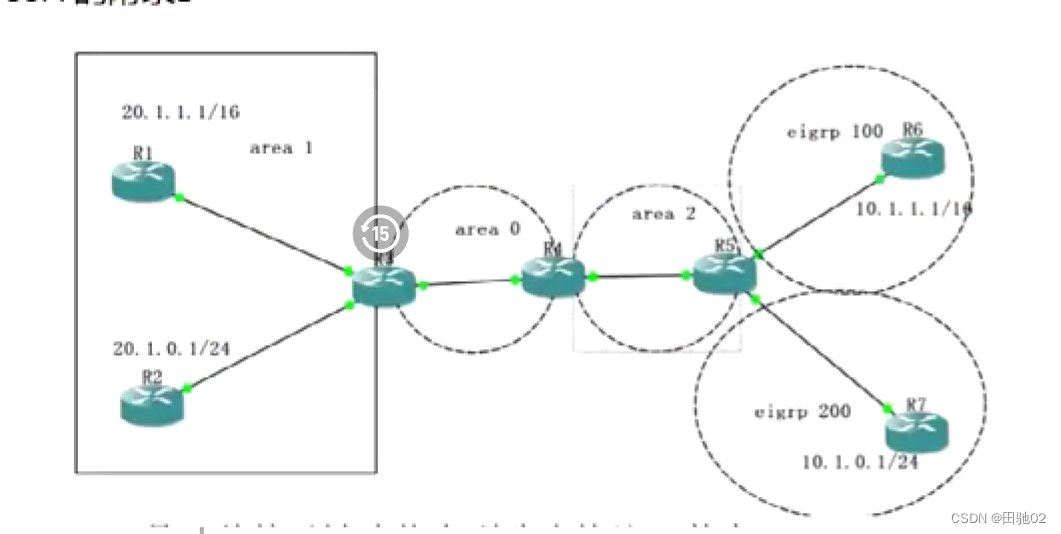
37款传感器与执行器的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止这37种的。鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器和执行器模块,依照实践出真知(一定要动手做)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里准备逐一动手尝试系列实验,不管成功(程序走通)与否,都会记录下来—小小的进步或是搞不掂的问题,希望能够抛砖引玉。
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验九十三:0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块

知识点:OLED(OrganicLight-Emitting Diode)
又称为有机电激光显示、有机发光半导体(OrganicElectroluminesence Display,OLED)。OLED属于一种电流型的有机发光器件,是通过载流子的注入和复合而致发光的现象,发光强度与注入的电流成正比。OLED在电场的作用下,阳极产生的空穴和阴极产生的电子就会发生移动,分别向空穴传输层和电子传输层注入,迁移到发光层。当二者在发光层相遇时,产生能量激子,从而激发发光分子最终产生可见光。一般而言,OLED可按发光材料分为两种:小分子OLED和高分子OLED(也可称为PLED)。OLED是一种利用多层有机薄膜结构产生电致发光的器件,它很容易制作,而且只需要低的驱动电压,这些主要的特征使得OLED在满足平面显示器的应用上显得非常突出。OLED显示屏比LCD更轻薄、亮度高、功耗低、响应快、清晰度高、柔性好、发光效率高,能满足消费者对显示技术的新需求。全球越来越多的显示器厂家纷纷投入研发,大大的推动了OLED的产业化进程。

OLED特点
(1)功耗低——与LCD相比,OLED不需要背光源,而背光源在LCD中是比较耗能的一部分,所以OLED是比较节能的。例如,24in的AMOLED模块功耗仅仅为440mw,而24in的多晶硅LCD模块达到了605mw。
(2)响应速度快——OLED技术与其他技术相比,其响应速度快,响应时间可以达到微秒级别。较高的响应速度更好的实现了运动的图像。根据有关的数据分析,其响应速度达到了液晶显示器响应速度的1000倍左右。
(3)较宽的视角——与其他显示相比,由于OLED是主动发光的,所以在很大视角范围内画面是不会显示失真的。其上下,左右的视角宽度超过170度。
(4)能实现高分辨率显示——大多高分辨率的OLED显示采用的是有源矩阵也就是AMOLED,它的发光层可以是吸纳26万真彩色的高分辨率,并且随着科学技术的发展,其分辨率在以后会得到更高的提升。
(5)宽温度特性——与LCD相比,OLED可以在很大的温度范围内进行工作,根据有关的技术分析,温度在-40摄氏度到80摄氏度都是可以正常运行的。这样就可以降低地域限制,在极寒地带也可以正常使用。
(6)OLED能够实现软屏——OLED可以在塑料、树脂等不同的柔性衬底材料上进行生产,将有机层蒸镀或涂布在塑料基衬上,就可以实现软屏。
(7)OLED成品的质量比较轻——与其他产品相比,OLED的质量比较小,厚度与LCD相比是比较小的,其抗震系数较高,能够适应较大的加速度,振动等比较恶劣的环境。

Arduino实验接线示意图


【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十三: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目四十七:简单的文本反转
实验场景图
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十七: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目四十七:简单的文本反转
实验接线:
oled模块 Ardunio Uno
GND---------GND接地线
VCC---------5V 接电源
SDA---------A4
SCL ------- A5
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SSD1306Ascii.h"
#include "SSD1306AsciiWire.h"
// 0X3C+SA0 - 0x3C or 0x3D
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x3C
// Define proper RST_PIN if required.
#define RST_PIN -1
SSD1306AsciiWire oled;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000L);
#if RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x64, I2C_ADDRESS, RST_PIN);
#else // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x64, I2C_ADDRESS);
#endif // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.setFont(System5x7);
oled.clear();
oled.println("normal");
oled.println();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
// Toggle invert mode for next line of text.
oled.setInvertMode(i%2);
oled.print("\rinvert");
delay(500);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
// Invert all text on screen.
oled.invertDisplay(!(i%2));
delay(1000);
}
}
Arduino实验场景图


【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十三: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目四十八:64 像素高显示的示例滚动显示
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十七: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目四十八:64 像素高显示的示例滚动显示
实验接线:
oled模块 Ardunio Uno
GND---------GND接地线
VCC---------5V 接电源
SDA---------A4
SCL ------- A5
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SSD1306Ascii.h"
#include "SSD1306AsciiWire.h"
// 0X3C+SA0 - 0x3C or 0x3D
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x3C
// Define proper RST_PIN if required.
#define RST_PIN -1
SSD1306AsciiWire oled;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000L);
#if RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x64, I2C_ADDRESS, RST_PIN);
#else // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x64, I2C_ADDRESS);
#endif // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.setFont(System5x7);
#if INCLUDE_SCROLLING == 0
#error INCLUDE_SCROLLING must be non-zero. Edit SSD1306Ascii.h
#endif // INCLUDE_SCROLLING
// Set auto scrolling at end of window.
oled.setScrollMode(SCROLL_MODE_AUTO);
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) {
if (i == 10) {
oled.clear();
}
oled.print("Line ");
oled.println(i);
delay(500);
}
// don't scroll last line.
oled.print("Done");
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {}
Arduino实验场景图

【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十三: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目四十九:动态读取、显示六个 ADC 的值
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十七: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目四十九:动态读取、显示六个 ADC 的值
实验接线:
oled模块 Ardunio Uno
GND---------GND接地线
VCC---------5V 接电源
SDA---------A4
SCL ------- A5
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SSD1306Ascii.h"
#include "SSD1306AsciiWire.h"
// 0X3C+SA0 - 0x3C or 0x3D
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x3C
// Define proper RST_PIN if required.
#define RST_PIN -1
SSD1306AsciiWire oled;
uint8_t col[2]; // Columns for ADC values.
uint8_t rows; // Rows per line.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000L);
#if RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x64, I2C_ADDRESS, RST_PIN);
#else // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x64, I2C_ADDRESS);
#endif // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.setFont(System5x7);
oled.clear();
// Setup form. Could use F() macro to save RAM on AVR.
oled.println("ADC0: 9999 ADC1: 9999");
oled.println("ADC2: 9999 ADC3: 9999");
oled.println("ADC4: 9999 ADC5: 9999");
// Calculate columns for ADC values. No RAM is used by strings.
// Compiler replaces strlen() calc with 6 and 17.
col[0] = oled.fieldWidth(strlen("ADC0: "));
col[1] = oled.fieldWidth(strlen("ADC0: 9999 ADC1: "));
rows = oled.fontRows();
delay(3000);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
oled.clearField(col[i%2], rows*(i/2), 4);
oled.print(analogRead(i));
}
delay(1000);
}
Arduino实验场景图

【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十三: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目五十:上下高级滚动功能显示文本
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验九十七: 0.96寸I2C IIC通信128*64显示器 OLED液晶屏模块
项目五十:上下高级滚动功能显示文本
实验接线:
oled模块 Ardunio Uno
GND---------GND接地线
VCC---------5V 接电源
SDA---------A4
SCL ------- A5
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SSD1306Ascii.h"
#include "SSD1306AsciiWire.h"
// 0X3C+SA0 - 0x3C or 0x3D
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x3C
// Define proper RST_PIN if required.
#define RST_PIN 8
SSD1306AsciiWire oled;
int blank = 0; // Count of blank lines.
int count = 0; // Count of displayed lines.
int dir = 1; // Scroll direction.
uint32_t scrollTime = 0;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup () {
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000L);
// MicroOLED64x48 or Adafruit128x32 work well.
#if RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x32, I2C_ADDRESS, RST_PIN);
#else // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.begin(&Adafruit128x32, I2C_ADDRESS);
#endif // RST_PIN >= 0
oled.setFont(System5x7);
oled.clear();
// Not really needed since newline will not scroll the display in this example.
oled.setScrollMode(SCROLL_MODE_APP);
oled.print("Smooth\nScrolling\ndemo");
delay(3000);
// Set cursor to last row of window.
oled.setRow(oled.displayRows() - oled.fontRows());
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop () {
if (!oled.scrollIsSynced()) {
uint32_t now = millis();
if ((now - scrollTime) >= 15) {
// Scroll display window.
oled.scrollDisplay(dir);
scrollTime = now;
}
// Reduce flicker by allowing display to scroll before writing.
} else if ((millis() - scrollTime) > 15) {
// Done if screen is blank.
if (blank*oled.fontRows() > oled.displayRows()) {
// Set new direction and magnification.
blank = 0;
count = 0;
// Reverse scroll direction.
dir = -dir;
// Set font magnification.
if (dir > 0) {
if (oled.magFactor() == 1) {
oled.set2X();
} else {
oled.set1X();
}
}
// Set cursor to first or last line of memory window.
oled.setCursor(0, dir < 0 ? 0 : oled.displayRows() - oled.fontRows());
}
// Scroll memory window.
oled.scrollMemory(dir*oled.fontRows());
oled.setCol(0);
if (count*oled.fontRows() <= oled.displayRows()) {
oled.print(dir < 0 ? "DN " : "UP ");
oled.print(++count);
} else {
blank++;
}
oled.clearToEOL();
}
}
实验场景图(字体移动速度有一点快,拍虚了)