1, 输入"fastboot flashing unlock" in adb ,waiting for the device
2, 输入"fastboot flashing unlock_critical"in adb ,waiting for the device
3, 输入"fastboot reboot" reboot the stb, press any key entering the boot mode
4, after the stb reboot then 输入"adb root"
5, 输入"adb disable-verity"
6, 输入"adb reboot"
7 输入"adb root"
8 输入"adb remount"1、adb remount 重新挂载system分区,实现对system分区重新挂载,重新挂载的时候将修改分区的属性,常见的修改参数为分区的读写。
使用该命令主要是因为android系统的system分区在启动之后是只读分区,但在开发过程中需要对system分区进行修改,则需重新挂载成读写模式。
2、在将文件 push 到 '/system' 文件夹之前,必须先输入命令 'adb remount'。
'adb remount' 的作用相当于 'adb shell mount -o rw,remount,rw /system'。
ADB工作原理
ADB(安卓调试桥Android debug Bridge),包含ADB client、ADB server 和adbd 三部分。
ADB client:运行在PC 上,通过在命令行执行ADB,就启动了ADB Client 程序。比如 Eclipse DDMS,Windows 终端命令行,豌豆荚等。Client本质上就是 Shell, 用来发送命令给Server。
ADB server:运行在PC 上,作为ADB client 的server 端,也作为adbd 服务进程的客户端。
adbd 服务进程:作为daemon进程运行在Android 系统上,以服务进程运行,当Android 系统启动时,由init 程序启动adbd。
在 PC 端,ADB 会fork 出一个守护进程,即ADB Server,而父进程(ADB Client)继续处理Client 请求,所有的Client 通过TCP 端口号5037 进行与Server 通信,而Server 创建local socket 与 remote socket,前者用于和Client 通信,后者用与远端进行通信,emulator 通过TCP,real device 则通过usb。ADB工作原理图:
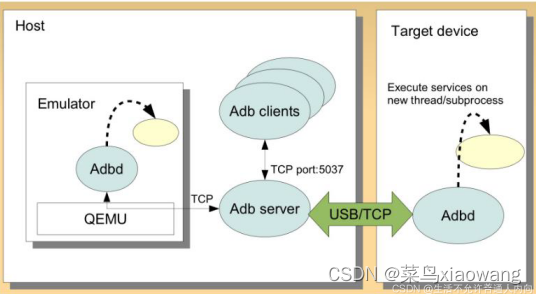
当启动某个ADB客户端时,客户端会先检查是否有ADB服务器进程正在运行。如果没有,它将启动服务器进程。服务器在启动后会与本地TCP 端口5037 绑定,并监听ADB客户端发出的命令-所有ADB客户端均通过端口5037 与ADB服务器通信。然后,服务器会与所有正在运行的设备建立连接。它通过扫描5555 到5585 之间(该范围供前16 个模拟器使用)的奇数号端口查找模拟器。服务器一旦发现ADB守护进程(adbd),便会与相应的端口建立连接。
ADB client 与ADB server 之间是通过tcp 进行通信,adb server 和adbd 通过usb 或者tcp 进行通信。ADB Server 对本地的TCP 5037 端口进行监听,等待ADB Client 的命令