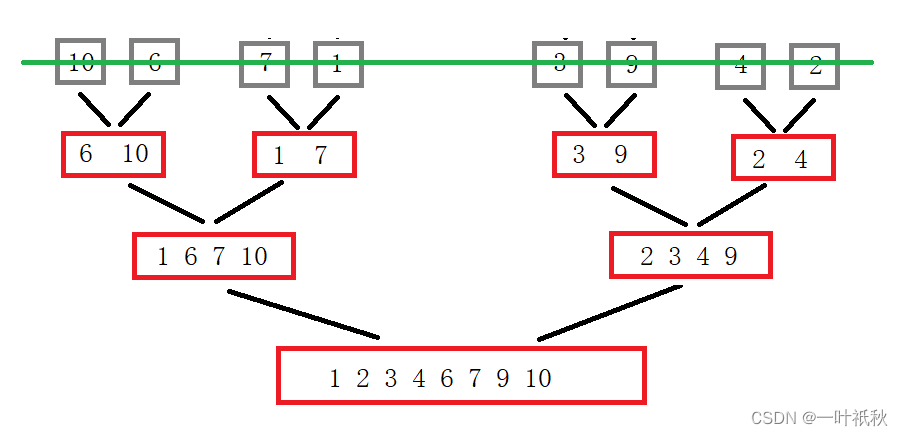
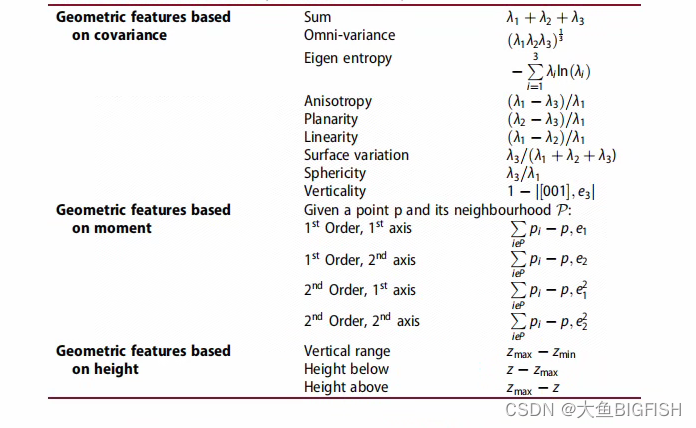
代码:
package dl;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.*;
import weka.core.Instances;
/**
* Active learning through density clustering.
*/
public class Alec {
/**
* The whole dataset.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* The maximal number of queries that can be provided.
*/
int maxNumQuery;
/**
* The actual number of queries.
*/
int numQuery;
/**
* The radius, also dc in the paper. It is employed for density computation.
*/
double radius;
/**
* The densities of instances, also rho in the paper.
*/
double[] densities;
/**
* distanceToMaster
*/
double[] distanceToMaster;
/**
* Sorted indices, where the first element indicates the instance with the
* biggest density.
*/
int[] descendantDensities;
/**
* Priority
*/
double[] priority;
/**
* The maximal distance between any pair of points.
*/
double maximalDistance;
/**
* Who is my master?
*/
int[] masters;
/**
* Predicted labels.
*/
int[] predictedLabels;
/**
* Instance status. 0 for unprocessed, 1 for queried, 2 for classified.
*/
int[] instanceStatusArray;
/**
* The descendant indices to show the representativeness of instances in a
* descendant order.
*/
int[] descendantRepresentatives;
/**
* Indicate the cluster of each instance. It is only used in
* clusterInTwo(int[]);
*/
int[] clusterIndices;
/**
* Blocks with size no more than this threshold should not be split further.
*/
int smallBlockThreshold = 3;
/**
**********************************
* The constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The data filename.
**********************************
*/
public Alec(String paraFilename) {
try {
FileReader tempReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(tempReader);
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
tempReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of fry
computeMaximalDistance();
clusterIndices = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
}// Of the constructor
/**
**********************************
* Merge sort in descendant order to obtain an index array. The original
* array is unchanged. The method should be tested further. <br>
* Examples: input [1.2, 2.3, 0.4, 0.5], output [1, 0, 3, 2]. <br>
* input [3.1, 5.2, 6.3, 2.1, 4.4], output [2, 1, 4, 0, 3].
*
* @param paraArray
* the original array
* @return The sorted indices.
**********************************
*/
public static int[] mergeSortToIndices(double[] paraArray) {
int tempLength = paraArray.length;
int[][] resultMatrix = new int[2][tempLength];// For merge sort.
// Initialize
int tempIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempLength; i++) {
resultMatrix[tempIndex][i] = i;
} // Of for i
// Merge
int tempCurrentLength = 1;
// The indices for current merged groups.
int tempFirstStart, tempSecondStart, tempSecondEnd;
while (tempCurrentLength < tempLength) {
// Divide into a number of groups.
// Here the boundary is adaptive to array length not equal to 2^k.
for (int i = 0; i < Math.ceil((tempLength + 0.0) / tempCurrentLength / 2); i++) {
// Boundaries of the group
tempFirstStart = i * tempCurrentLength * 2;
tempSecondStart = tempFirstStart + tempCurrentLength;
tempSecondEnd = tempSecondStart + tempCurrentLength - 1;
if (tempSecondEnd >= tempLength) {
tempSecondEnd = tempLength - 1;
} // Of if
// Merge this group
int tempFirstIndex = tempFirstStart;
int tempSecondIndex = tempSecondStart;
int tempCurrentIndex = tempFirstStart;
if (tempSecondStart >= tempLength) {
for (int j = tempFirstIndex; j < tempLength; j++) {
resultMatrix[(tempIndex + 1) % 2][tempCurrentIndex] = resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][j];
tempFirstIndex++;
tempCurrentIndex++;
} // Of for j
break;
} // Of if
while ((tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1)
&& (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd)) {
if (paraArray[resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][tempFirstIndex]] >= paraArray[resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][tempSecondIndex]]) {
resultMatrix[(tempIndex + 1) % 2][tempCurrentIndex] = resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
} else {
resultMatrix[(tempIndex + 1) % 2][tempCurrentIndex] = resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][tempSecondIndex];
tempSecondIndex++;
} // Of if
tempCurrentIndex++;
} // Of while
// Remaining part
for (int j = tempFirstIndex; j < tempSecondStart; j++) {
resultMatrix[(tempIndex + 1) % 2][tempCurrentIndex] = resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][j];
tempCurrentIndex++;
} // Of for j
for (int j = tempSecondIndex; j <= tempSecondEnd; j++) {
resultMatrix[(tempIndex + 1) % 2][tempCurrentIndex] = resultMatrix[tempIndex
% 2][j];
tempCurrentIndex++;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
tempCurrentLength *= 2;
tempIndex++;
} // Of while
return resultMatrix[tempIndex % 2];
}// Of mergeSortToIndices
/**
*********************
* The Euclidean distance between two instances. Other distance measures
* unsupported for simplicity.
*
*
* @param paraI
* The index of the first instance.
* @param paraJ
* The index of the second instance.
* @return The distance.
*********************
*/
public double distance(int paraI, int paraJ) {
double resultDistance = 0;
double tempDifference;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
resultDistance += tempDifference * tempDifference;
} // Of for i
resultDistance = Math.sqrt(resultDistance);
return resultDistance;
}// Of distance
/**
**********************************
* Compute the maximal distance. The result is stored in a member variable.
**********************************
*/
public void computeMaximalDistance() {
maximalDistance = 0;
double tempDistance;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dataset.numInstances(); j++) {
tempDistance = distance(i, j);
if (maximalDistance < tempDistance) {
maximalDistance = tempDistance;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("maximalDistance = " + maximalDistance);
}// Of computeMaximalDistance
/**
******************
* Compute the densities using Gaussian kernel.
******************
*/
public void computeDensitiesGaussian() {
System.out.println("radius = " + radius);
densities = new double[dataset.numInstances()];
double tempDistance;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dataset.numInstances(); j++) {
tempDistance = distance(i, j);
densities[i] += Math.exp(-tempDistance * tempDistance / radius / radius);
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("The densities are " + Arrays.toString(densities) + "\r\n");
}// Of computeDensitiesGaussian
/**
**********************************
* Compute distanceToMaster, the distance to its master.
**********************************
*/
public void computeDistanceToMaster() {
distanceToMaster = new double[dataset.numInstances()];
masters = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
descendantDensities = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
instanceStatusArray = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
descendantDensities = mergeSortToIndices(densities);
distanceToMaster[descendantDensities[0]] = maximalDistance;
double tempDistance;
for (int i = 1; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Initialize.
distanceToMaster[descendantDensities[i]] = maximalDistance;
for (int j = 0; j <= i - 1; j++) {
tempDistance = distance(descendantDensities[i], descendantDensities[j]);
if (distanceToMaster[descendantDensities[i]] > tempDistance) {
distanceToMaster[descendantDensities[i]] = tempDistance;
masters[descendantDensities[i]] = descendantDensities[j];
} // Of if
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("First compute, masters = " + Arrays.toString(masters));
System.out.println("descendantDensities = " + Arrays.toString(descendantDensities));
}// Of computeDistanceToMaster
/**
**********************************
* Compute priority. Element with higher priority is more likely to be
* selected as a cluster center. Now it is rho * distanceToMaster. It can
* also be rho^alpha * distanceToMaster.
**********************************
*/
public void computePriority() {
priority = new double[dataset.numInstances()];
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
priority[i] = densities[i] * distanceToMaster[i];
} // Of for i
}// Of computePriority
/**
*************************
* The block of a node should be same as its master. This recursive method
* is efficient.
*
* @param paraIndex
* The index of the given node.
* @return The cluster index of the current node.
*************************
*/
public int coincideWithMaster(int paraIndex) {
if (clusterIndices[paraIndex] == -1) {
int tempMaster = masters[paraIndex];
clusterIndices[paraIndex] = coincideWithMaster(tempMaster);
} // Of if
return clusterIndices[paraIndex];
}// Of coincideWithMaster
/**
*************************
* Cluster a block in two. According to the master tree.
*
* @param paraBlock
* The given block.
* @return The new blocks where the two most represent instances serve as
* the root.
*************************
*/
public int[][] clusterInTwo(int[] paraBlock) {
// Reinitialize. In fact, only instances in the given block is
// considered.
Arrays.fill(clusterIndices, -1);
// Initialize the cluster number of the two roots.
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
clusterIndices[paraBlock[i]] = i;
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (clusterIndices[paraBlock[i]] != -1) {
// Already have a cluster number.
continue;
} // Of if
clusterIndices[paraBlock[i]] = coincideWithMaster(masters[paraBlock[i]]);
} // Of for i
// The sub blocks.
int[][] resultBlocks = new int[2][];
int tempFistBlockCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < clusterIndices.length; i++) {
if (clusterIndices[i] == 0) {
tempFistBlockCount++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
resultBlocks[0] = new int[tempFistBlockCount];
resultBlocks[1] = new int[paraBlock.length - tempFistBlockCount];
// Copy. You can design shorter code when the number of clusters is
// greater than 2.
int tempFirstIndex = 0;
int tempSecondIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (clusterIndices[paraBlock[i]] == 0) {
resultBlocks[0][tempFirstIndex] = paraBlock[i];
tempFirstIndex++;
} else {
resultBlocks[1][tempSecondIndex] = paraBlock[i];
tempSecondIndex++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Split (" + paraBlock.length + ") instances "
+ Arrays.toString(paraBlock) + "\r\nto (" + resultBlocks[0].length + ") instances "
+ Arrays.toString(resultBlocks[0]) + "\r\nand (" + resultBlocks[1].length
+ ") instances " + Arrays.toString(resultBlocks[1]));
return resultBlocks;
}// Of clusterInTwo
/**
**********************************
* Classify instances in the block by simple voting.
*
* @param paraBlock
* The given block.
**********************************
*/
public void vote(int[] paraBlock) {
int[] tempClassCounts = new int[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] == 1) {
tempClassCounts[(int) dataset.instance(paraBlock[i]).classValue()]++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
int tempMaxClass = -1;
int tempMaxCount = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < tempClassCounts.length; i++) {
if (tempMaxCount < tempClassCounts[i]) {
tempMaxClass = i;
tempMaxCount = tempClassCounts[i];
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Classify unprocessed instances.
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] == 0) {
predictedLabels[paraBlock[i]] = tempMaxClass;
instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] = 2;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of vote
/**
**********************************
* Cluster based active learning. Prepare for
*
* @param paraRatio
* The ratio of the maximal distance as the dc.
* @param paraMaxNumQuery
* The maximal number of queries for the whole dataset.
* @parm paraSmallBlockThreshold The small block threshold.
**********************************
*/
public void clusterBasedActiveLearning(double paraRatio, int paraMaxNumQuery,
int paraSmallBlockThreshold) {
radius = maximalDistance * paraRatio;
smallBlockThreshold = paraSmallBlockThreshold;
maxNumQuery = paraMaxNumQuery;
predictedLabels = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
predictedLabels[i] = -1;
} // Of for i
computeDensitiesGaussian();
computeDistanceToMaster();
computePriority();
descendantRepresentatives = mergeSortToIndices(priority);
System.out.println(
"descendantRepresentatives = " + Arrays.toString(descendantRepresentatives));
numQuery = 0;
clusterBasedActiveLearning(descendantRepresentatives);
}// Of clusterBasedActiveLearning
/**
**********************************
* Cluster based active learning.
*
* @param paraBlock
* The given block. This block must be sorted according to the
* priority in descendant order.
**********************************
*/
public void clusterBasedActiveLearning(int[] paraBlock) {
System.out.println("clusterBasedActiveLearning for block " + Arrays.toString(paraBlock));
// Step 1. How many labels are queried for this block.
int tempExpectedQueries = (int) Math.sqrt(paraBlock.length);
int tempNumQuery = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] == 1) {
tempNumQuery++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Vote for small blocks.
if ((tempNumQuery >= tempExpectedQueries) && (paraBlock.length <= smallBlockThreshold)) {
System.out.println("" + tempNumQuery + " instances are queried, vote for block: \r\n"
+ Arrays.toString(paraBlock));
vote(paraBlock);
return;
} // Of if
// Step 3. Query enough labels.
for (int i = 0; i < tempExpectedQueries; i++) {
if (numQuery >= maxNumQuery) {
System.out.println("No more queries are provided, numQuery = " + numQuery + ".");
vote(paraBlock);
return;
} // Of if
if (instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] == 0) {
instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] = 1;
predictedLabels[paraBlock[i]] = (int) dataset.instance(paraBlock[i]).classValue();
// System.out.println("Query #" + paraBlock[i] + ", numQuery = "
// + numQuery);
numQuery++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Step 4. Pure?
int tempFirstLabel = predictedLabels[paraBlock[0]];
boolean tempPure = true;
for (int i = 1; i < tempExpectedQueries; i++) {
if (predictedLabels[paraBlock[i]] != tempFirstLabel) {
tempPure = false;
break;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
if (tempPure) {
System.out.println("Classify for pure block: " + Arrays.toString(paraBlock));
for (int i = tempExpectedQueries; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] == 0) {
predictedLabels[paraBlock[i]] = tempFirstLabel;
instanceStatusArray[paraBlock[i]] = 2;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return;
} // Of if
// Step 5. Split in two and process them independently.
int[][] tempBlocks = clusterInTwo(paraBlock);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
// Attention: recursive invoking here.
clusterBasedActiveLearning(tempBlocks[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of clusterBasedActiveLearning
/**
*******************
* Show the statistics information.
*******************
*/
public String toString() {
int[] tempStatusCounts = new int[3];
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
tempStatusCounts[instanceStatusArray[i]]++;
if (predictedLabels[i] == (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
String resultString = "(unhandled, queried, classified) = "
+ Arrays.toString(tempStatusCounts);
resultString += "\r\nCorrect = " + tempCorrect + ", accuracy = "
+ (tempCorrect / dataset.numInstances());
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
**********************************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args:
* Not used now.
**********************************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
long tempStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Starting ALEC.");
String arffFilename = "C:\\Users\\86183\\IdeaProjects\\deepLearning\\src\\main\\java\\resources\\iris.arff";
//String arffFilename = "C:\\Users\\86183\\IdeaProjects\\deepLearning\\src\\main\\java\\resources\\mushroom.arff";
Alec tempAlec = new Alec(arffFilename);
// The settings for iris
tempAlec.clusterBasedActiveLearning(0.15, 30, 3);
// The settings for mushroom
// tempAlec.clusterBasedActiveLearning(0.1, 800, 3);
System.out.println(tempAlec);
long tempEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Runtime: " + (tempEnd - tempStart) + "ms.");
}// Of main
}// Of class Alec
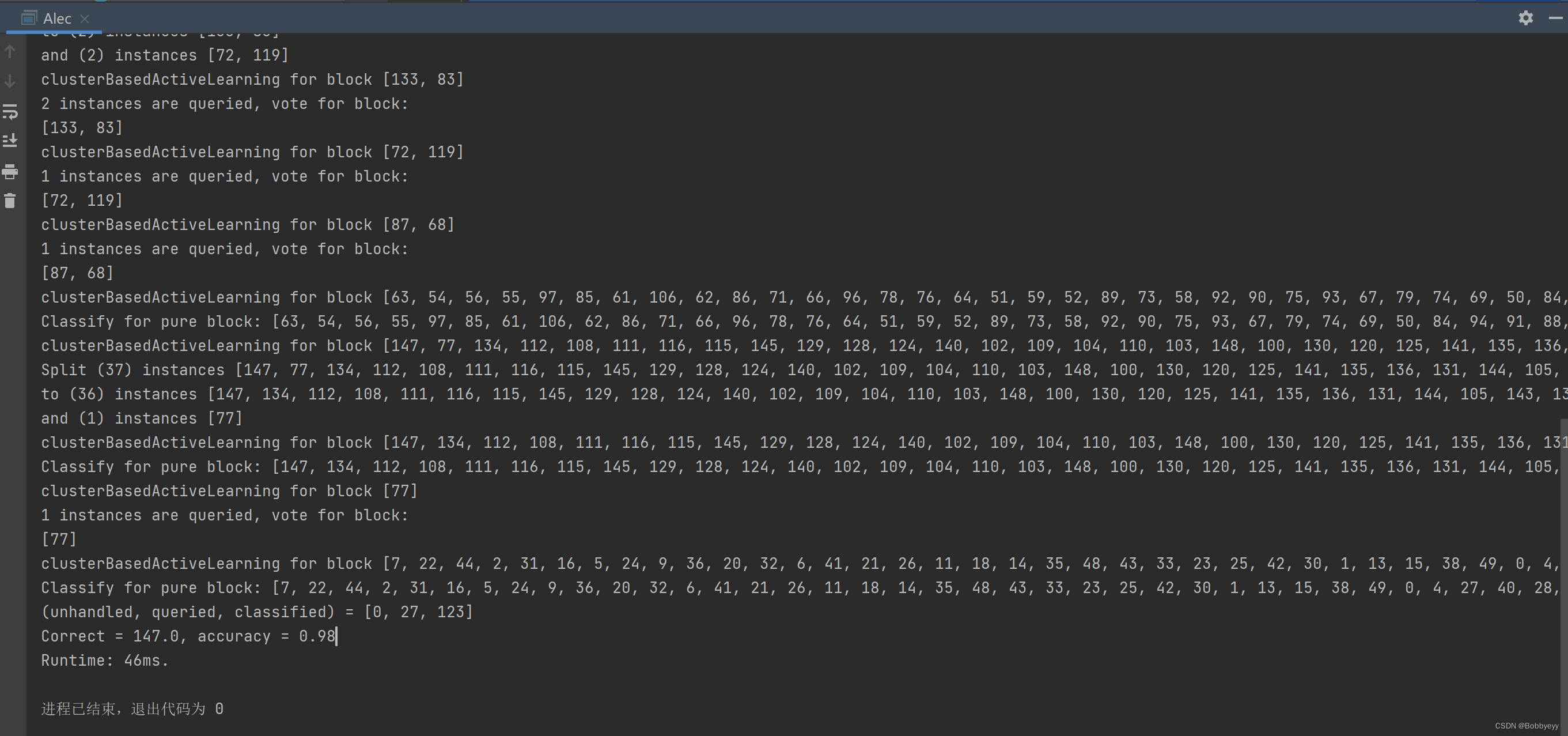
结果: