1.fmt相关
CMakeLists.txt中:在后面加上 fmt
target_link_libraries(optical_flow ${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt )
target_link_libraries(direct_method ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES} fmt )
2.不存在用户定义的从 "std::_Bind<void (OpticalFlowTracker::*(OpticalFlowTracker *, std::_Placeholder<1>))(const cv::Range &range)>" 到 "const cv::ParallelLoopBody" 的适当转换:
error: invalid initialization of reference of type ‘const cv::ParallelLoopBody&’ from expression of type ‘std::_Bind_helper<false, void (OpticalFlowTracker::*)(const cv::Range&), OpticalFlowTracker*, const std::_Placeholder<1>&>::type {aka std::_Bind<void (OpticalFlowTracker::*(OpticalFlowTracker*, std::_Placeholder<1>))(const cv::Range&)>}’
std::bind(&OpticalFlowTracker::calculateOpticalFlow, &tracker, placeholders::_1));
原因:这是因为opencv3不支持std::bind函数
解决方式:
1.安装opencv4,然后把CMakeLists.txt中的find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)中的3改成4(不建议)
2.使用修改后的适配opencv3的:
转自此大神修改后的optical_flow.cpp:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <chrono>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
string file_1 = "../LK1.png"; // first image
string file_2 = "../LK2.png"; // second image
/**
* single level optical flow
* @param [in] img1 the first image
* @param [in] img2 the second image
* @param [in] kp1 keypoints in img1
* @param [in|out] kp2 keypoints in img2, if empty, use initial guess in kp1
* @param [out] success true if a keypoint is tracked successfully
* @param [in] inverse use inverse formulation?
*/
void OpticalFlowSingleLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse = false,
bool has_initial_guess = false
);
/**
* multi level optical flow, scale of pyramid is set to 2 by default
* the image pyramid will be create inside the function
* @param [in] img1 the first pyramid
* @param [in] img2 the second pyramid
* @param [in] kp1 keypoints in img1
* @param [out] kp2 keypoints in img2
* @param [out] success true if a keypoint is tracked successfully
* @param [in] inverse set true to enable inverse formulation
*/
void OpticalFlowMultiLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse = false
);
/**
* get a gray scale value from reference image (bi-linear interpolated)
* @param img
* @param x
* @param y
* @return the interpolated value of this pixel
*/
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat &img, float x, float y) {
// boundary check
if (x < 0) x = 0;
if (y < 0) y = 0;
if (x >= img.cols) x = img.cols - 1;
if (y >= img.rows) y = img.rows - 1;
uchar *data = &img.data[int(y) * img.step + int(x)];
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
return float(
(1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * data[0] +
xx * (1 - yy) * data[1] +
(1 - xx) * yy * data[img.step] +
xx * yy * data[img.step + 1]
);
}
/// Optical flow tracker and interface
class OpticalFlowTracker: public cv::ParallelLoopBody {
private:
const Mat &img1;
const Mat &img2;
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1;
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2;
vector<bool> &success;
bool inverse = true;
bool has_initial = false;
public:
OpticalFlowTracker(
const Mat &img1_,
const Mat &img2_,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1_,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2_,
vector<bool> &success_,
bool inverse_ = true, bool has_initial_ = false) :
img1(img1_), img2(img2_), kp1(kp1_), kp2(kp2_), success(success_), inverse(inverse_),
has_initial(has_initial_) {}
// void calculateOpticalFlow(const Range &range);
virtual void operator()(const Range &range) const {
// parameters
int half_patch_size = 4;
int iterations = 10;
for (size_t i = range.start; i < range.end; i++) {
auto kp = kp1[i];
double dx = 0, dy = 0; // dx,dy need to be estimated
if (has_initial) {
dx = kp2[i].pt.x - kp.pt.x;
dy = kp2[i].pt.y - kp.pt.y;
}
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
bool succ = true; // indicate if this point succeeded
// Gauss-Newton iterations
Eigen::Matrix2d H = Eigen::Matrix2d::Zero(); // hessian
Eigen::Vector2d b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero(); // bias
Eigen::Vector2d J; // jacobian
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
if (inverse == false) {
H = Eigen::Matrix2d::Zero();
b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero();
} else {
// only reset b
b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero();
}
cost = 0;
// compute cost and jacobian
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x < half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y < half_patch_size; y++) {
double error = GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + x + dx, kp.pt.y + y + dy);; // Jacobian
if (inverse == false) {
J = -1.0 * Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x + 1, kp.pt.y + dy + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x - 1, kp.pt.y + dy + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x, kp.pt.y + dy + y + 1) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x, kp.pt.y + dy + y - 1))
);
} else if (iter == 0) {
// in inverse mode, J keeps same for all iterations
// NOTE this J does not change when dx, dy is updated, so we can store it and only compute error
J = -1.0 * Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x + 1, kp.pt.y + y) -
GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x - 1, kp.pt.y + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y + 1) -
GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y - 1))
);
}
// compute H, b and set cost;
b += -error * J;
cost += error * error;
if (inverse == false || iter == 0) {
// also update H
H += J * J.transpose();
}
}
// compute update
Eigen::Vector2d update = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (std::isnan(update[0])) {
// sometimes occurred when we have a black or white patch and H is irreversible
cout << "update is nan" << endl;
succ = false;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost > lastCost) {
break;
}
// update dx, dy
dx += update[0];
dy += update[1];
lastCost = cost;
succ = true;
if (update.norm() < 1e-2) {
// converge
break;
}
}
success[i] = succ;
// set kp2
kp2[i].pt = kp.pt + Point2f(dx, dy);
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// images, note they are CV_8UC1, not CV_8UC3
Mat img1 = imread(file_1, 0);
Mat img2 = imread(file_2, 0);
// key points, using GFTT here.
vector<KeyPoint> kp1;
Ptr<GFTTDetector> detector = GFTTDetector::create(500, 0.01, 20); // maximum 500 keypoints
detector->detect(img1, kp1);
// now lets track these key points in the second image
// first use single level LK in the validation picture
vector<KeyPoint> kp2_single;
vector<bool> success_single;
OpticalFlowSingleLevel(img1, img2, kp1, kp2_single, success_single);
// then test multi-level LK
vector<KeyPoint> kp2_multi;
vector<bool> success_multi;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
OpticalFlowMultiLevel(img1, img2, kp1, kp2_multi, success_multi, true);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optical flow by gauss-newton: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// use opencv's flow for validation
vector<Point2f> pt1, pt2;
for (auto &kp: kp1) pt1.push_back(kp.pt);
vector<uchar> status;
vector<float> error;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(img1, img2, pt1, pt2, status, error);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optical flow by opencv: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// plot the differences of those functions
Mat img2_single;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_single, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < kp2_single.size(); i++) {
if (success_single[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_single, kp2_single[i].pt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_single, kp1[i].pt, kp2_single[i].pt, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
Mat img2_multi;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_multi, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < kp2_multi.size(); i++) {
if (success_multi[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_multi, kp2_multi[i].pt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_multi, kp1[i].pt, kp2_multi[i].pt, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
Mat img2_CV;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_CV, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < pt2.size(); i++) {
if (status[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_CV, pt2[i], 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_CV, pt1[i], pt2[i], cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
cv::imshow("tracked single level", img2_single);
cv::imshow("tracked multi level", img2_multi);
cv::imshow("tracked by opencv", img2_CV);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void OpticalFlowSingleLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse, bool has_initial) {
kp2.resize(kp1.size());
success.resize(kp1.size());
OpticalFlowTracker tracker(img1, img2, kp1, kp2, success, inverse, has_initial);
parallel_for_(Range(0, kp1.size()), tracker);
}
void OpticalFlowMultiLevel(
const Mat &img1,
const Mat &img2,
const vector<KeyPoint> &kp1,
vector<KeyPoint> &kp2,
vector<bool> &success,
bool inverse) {
// parameters
int pyramids = 4;
double pyramid_scale = 0.5;
double scales[] = {1.0, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125};
// create pyramids
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
vector<Mat> pyr1, pyr2; // image pyramids
for (int i = 0; i < pyramids; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pyr1.push_back(img1);
pyr2.push_back(img2);
} else {
Mat img1_pyr, img2_pyr;
cv::resize(pyr1[i - 1], img1_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr1[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr1[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
cv::resize(pyr2[i - 1], img2_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr2[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr2[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
pyr1.push_back(img1_pyr);
pyr2.push_back(img2_pyr);
}
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "build pyramid time: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// coarse-to-fine LK tracking in pyramids
vector<KeyPoint> kp1_pyr, kp2_pyr;
for (auto &kp:kp1) {
auto kp_top = kp;
kp_top.pt *= scales[pyramids - 1];
kp1_pyr.push_back(kp_top);
kp2_pyr.push_back(kp_top);
}
for (int level = pyramids - 1; level >= 0; level--) {
// from coarse to fine
success.clear();
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
OpticalFlowSingleLevel(pyr1[level], pyr2[level], kp1_pyr, kp2_pyr, success, inverse, true);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "track pyr " << level << " cost time: " << time_used.count() << endl;
if (level > 0) {
for (auto &kp: kp1_pyr)
kp.pt /= pyramid_scale;
for (auto &kp: kp2_pyr)
kp.pt /= pyramid_scale;
}
}
for (auto &kp: kp2_pyr)
kp2.push_back(kp);
}同样direct_method.cpp:
且还有如下报错: mutex’ in namespace ‘std’ does not name a type
在最上面加入以下:
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <unistd.h>
完整版 direct_method.cpp如下:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<Eigen::Vector2d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector2d>> VecVector2d;
// Camera intrinsics
double fx = 718.856, fy = 718.856, cx = 607.1928, cy = 185.2157;
// baseline
double baseline = 0.573;
// paths
string left_file = "./left.png";
string disparity_file = "./disparity.png";
boost::format fmt_others("./%06d.png"); // other files
// useful typedefs
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> Matrix6d;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> Matrix26d;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
/**
* pose estimation using direct method
* @param img1
* @param img2
* @param px_ref
* @param depth_ref
* @param T21
*/
void DirectPoseEstimationMultiLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21
);
/**
* pose estimation using direct method
* @param img1
* @param img2
* @param px_ref
* @param depth_ref
* @param T21
*/
void DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21
);
// bilinear interpolation
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat &img, float x, float y) {
// boundary check
if (x < 0) x = 0;
if (y < 0) y = 0;
if (x >= img.cols) x = img.cols - 1;
if (y >= img.rows) y = img.rows - 1;
uchar *data = &img.data[int(y) * img.step + int(x)];
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
return float(
(1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * data[0] +
xx * (1 - yy) * data[1] +
(1 - xx) * yy * data[img.step] +
xx * yy * data[img.step + 1]
);
}
/// class for accumulator jacobians in parallel
class JacobianAccumulator: public cv::ParallelLoopBody {
private:
const cv::Mat &img1;
const cv::Mat &img2;
const VecVector2d &px_ref;
const vector<double> depth_ref;
Sophus::SE3d &T21;
mutable VecVector2d projection; // projected points
mutable std::mutex hessian_mutex;
mutable Matrix6d H = Matrix6d::Zero();
mutable Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero();
mutable double cost = 0;
public:
JacobianAccumulator(
const cv::Mat &img1_,
const cv::Mat &img2_,
const VecVector2d &px_ref_,
const vector<double> depth_ref_,
Sophus::SE3d &T21_) :
img1(img1_), img2(img2_), px_ref(px_ref_), depth_ref(depth_ref_), T21(T21_) {
projection = VecVector2d(px_ref.size(), Eigen::Vector2d(0, 0));
}
/// accumulate jacobians in a range
// void accumulate_jacobian(const cv::Range &range);
/// get hessian matrix
Matrix6d hessian() const { return H; }
/// get bias
Vector6d bias() const { return b; }
/// get total cost
double cost_func() const { return cost; }
/// get projected points
VecVector2d projected_points() const { return projection; }
/// reset h, b, cost to zero
void reset() {
H = Matrix6d::Zero();
b = Vector6d::Zero();
cost = 0;
}
virtual void operator()(const cv::Range& range) const {
// parameters
const int half_patch_size = 1;
int cnt_good = 0;
Matrix6d hessian = Matrix6d::Zero();
Vector6d bias = Vector6d::Zero();
double cost_tmp = 0;
for (size_t i = range.start; i < range.end; i++) {
// compute the projection in the second image
Eigen::Vector3d point_ref =
depth_ref[i] * Eigen::Vector3d((px_ref[i][0] - cx) / fx, (px_ref[i][1] - cy) / fy, 1);
Eigen::Vector3d point_cur = T21 * point_ref;
if (point_cur[2] < 0) // depth invalid
continue;
float u = fx * point_cur[0] / point_cur[2] + cx, v = fy * point_cur[1] / point_cur[2] + cy;
if (u < half_patch_size || u > img2.cols - half_patch_size || v < half_patch_size ||
v > img2.rows - half_patch_size)
continue;
projection[i] = Eigen::Vector2d(u, v);
double X = point_cur[0], Y = point_cur[1], Z = point_cur[2],
Z2 = Z * Z, Z_inv = 1.0 / Z, Z2_inv = Z_inv * Z_inv;
cnt_good++;
// and compute error and jacobian
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x <= half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y <= half_patch_size; y++) {
double error = GetPixelValue(img1, px_ref[i][0] + x, px_ref[i][1] + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, u + x, v + y);
Matrix26d J_pixel_xi;
Eigen::Vector2d J_img_pixel;
J_pixel_xi(0, 0) = fx * Z_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 1) = 0;
J_pixel_xi(0, 2) = -fx * X * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 3) = -fx * X * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 4) = fx + fx * X * X * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(0, 5) = -fx * Y * Z_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 0) = 0;
J_pixel_xi(1, 1) = fy * Z_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 2) = -fy * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 3) = -fy - fy * Y * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 4) = fy * X * Y * Z2_inv;
J_pixel_xi(1, 5) = fy * X * Z_inv;
J_img_pixel = Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, u + 1 + x, v + y) - GetPixelValue(img2, u - 1 + x, v + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, u + x, v + 1 + y) - GetPixelValue(img2, u + x, v - 1 + y))
);
// total jacobian
Vector6d J = -1.0 * (J_img_pixel.transpose() * J_pixel_xi).transpose();
hessian += J * J.transpose();
bias += -error * J;
cost_tmp += error * error;
}
}
if (cnt_good) {
// set hessian, bias and cost
unique_lock<mutex> lck(hessian_mutex);
H += hessian;
b += bias;
cost += cost_tmp / cnt_good;
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
cv::Mat left_img = cv::imread(left_file, 0);
cv::Mat disparity_img = cv::imread(disparity_file, 0);
if (left_img.empty() || disparity_img.empty())
{
std::cout << "!!! Failed imread(): image not found" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// let's randomly pick pixels in the first image and generate some 3d points in the first image's frame
cv::RNG rng;
int nPoints = 2000;
int boarder = 20;
VecVector2d pixels_ref;
vector<double> depth_ref;
cout << "left_img.cols" << left_img.cols << endl;
cout << "left_img: " << left_img << endl;
// generate pixels in ref and load depth data
for (int i = 0; i < nPoints; i++) {
int x = rng.uniform(boarder, left_img.cols - boarder); // don't pick pixels close to boarder
int y = rng.uniform(boarder, left_img.rows - boarder); // don't pick pixels close to boarder
int disparity = disparity_img.at<uchar>(y, x);
double depth = fx * baseline / disparity; // you know this is disparity to depth
depth_ref.push_back(depth);
pixels_ref.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(x, y));
}
// estimates 01~05.png's pose using this information
Sophus::SE3d T_cur_ref;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) { // 1~10
cv::Mat img = cv::imread((fmt_others % i).str(), 0);
// try single layer by uncomment this line
// DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(left_img, img, pixels_ref, depth_ref, T_cur_ref);
DirectPoseEstimationMultiLayer(left_img, img, pixels_ref, depth_ref, T_cur_ref);
}
return 0;
}
void DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21) {
const int iterations = 10;
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
auto t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
JacobianAccumulator jaco_accu(img1, img2, px_ref, depth_ref, T21);
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
jaco_accu.reset();
cv::parallel_for_(cv::Range(0, px_ref.size()), jaco_accu);
Matrix6d H = jaco_accu.hessian();
Vector6d b = jaco_accu.bias();
// solve update and put it into estimation
Vector6d update = H.ldlt().solve(b);;
T21 = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update) * T21;
cost = jaco_accu.cost_func();
if (std::isnan(update[0])) {
// sometimes occurred when we have a black or white patch and H is irreversible
cout << "update is nan" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost > lastCost) {
cout << "cost increased: " << cost << ", " << lastCost << endl;
break;
}
if (update.norm() < 1e-3) {
// converge
break;
}
lastCost = cost;
cout << "iteration: " << iter << ", cost: " << cost << endl;
}
cout << "T21 = \n" << T21.matrix() << endl;
auto t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "direct method for single layer: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// plot the projected pixels here
cv::Mat img2_show;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_show, CV_GRAY2BGR);
VecVector2d projection = jaco_accu.projected_points();
for (size_t i = 0; i < px_ref.size(); ++i) {
auto p_ref = px_ref[i];
auto p_cur = projection[i];
if (p_cur[0] > 0 && p_cur[1] > 0) {
cv::circle(img2_show, cv::Point2f(p_cur[0], p_cur[1]), 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_show, cv::Point2f(p_ref[0], p_ref[1]), cv::Point2f(p_cur[0], p_cur[1]),
cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
cv::imshow("current", img2_show);
cv::waitKey();
}
void DirectPoseEstimationMultiLayer(
const cv::Mat &img1,
const cv::Mat &img2,
const VecVector2d &px_ref,
const vector<double> depth_ref,
Sophus::SE3d &T21) {
// parameters
int pyramids = 4;
double pyramid_scale = 0.5;
double scales[] = {1.0, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125};
// create pyramids
vector<cv::Mat> pyr1, pyr2; // image pyramids
for (int i = 0; i < pyramids; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pyr1.push_back(img1);
pyr2.push_back(img2);
} else {
cv::Mat img1_pyr, img2_pyr;
cv::resize(pyr1[i - 1], img1_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr1[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr1[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
cv::resize(pyr2[i - 1], img2_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr2[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr2[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
pyr1.push_back(img1_pyr);
pyr2.push_back(img2_pyr);
}
}
double fxG = fx, fyG = fy, cxG = cx, cyG = cy; // backup the old values
for (int level = pyramids - 1; level >= 0; level--) {
VecVector2d px_ref_pyr; // set the keypoints in this pyramid level
for (auto &px: px_ref) {
px_ref_pyr.push_back(scales[level] * px);
}
// scale fx, fy, cx, cy in different pyramid levels
fx = fxG * scales[level];
fy = fyG * scales[level];
cx = cxG * scales[level];
cy = cyG * scales[level];
DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(pyr1[level], pyr2[level], px_ref_pyr, depth_ref, T21);
}
}图片可以改成绝对路径 : ./optical_flow 运行结果如下:
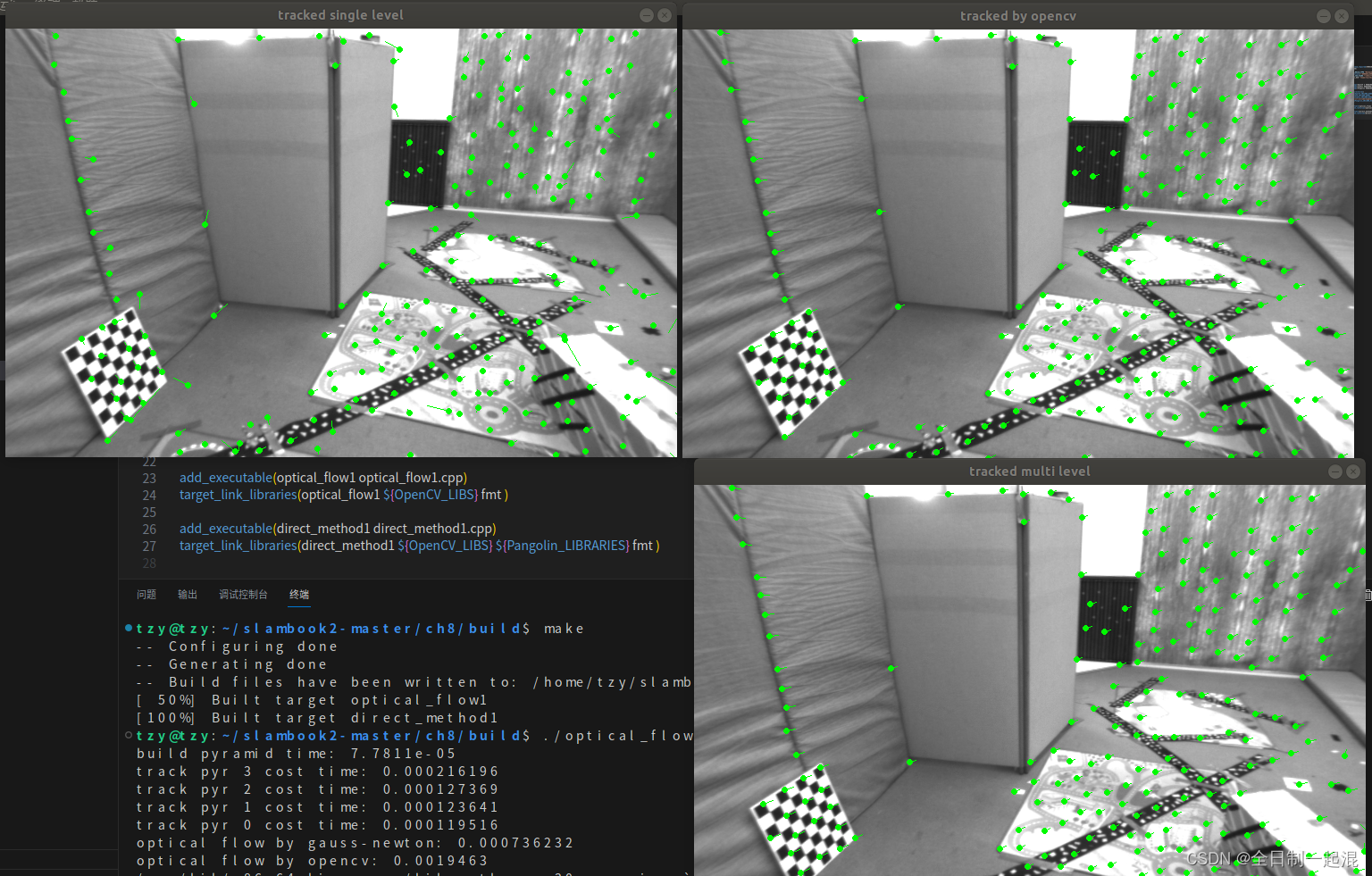
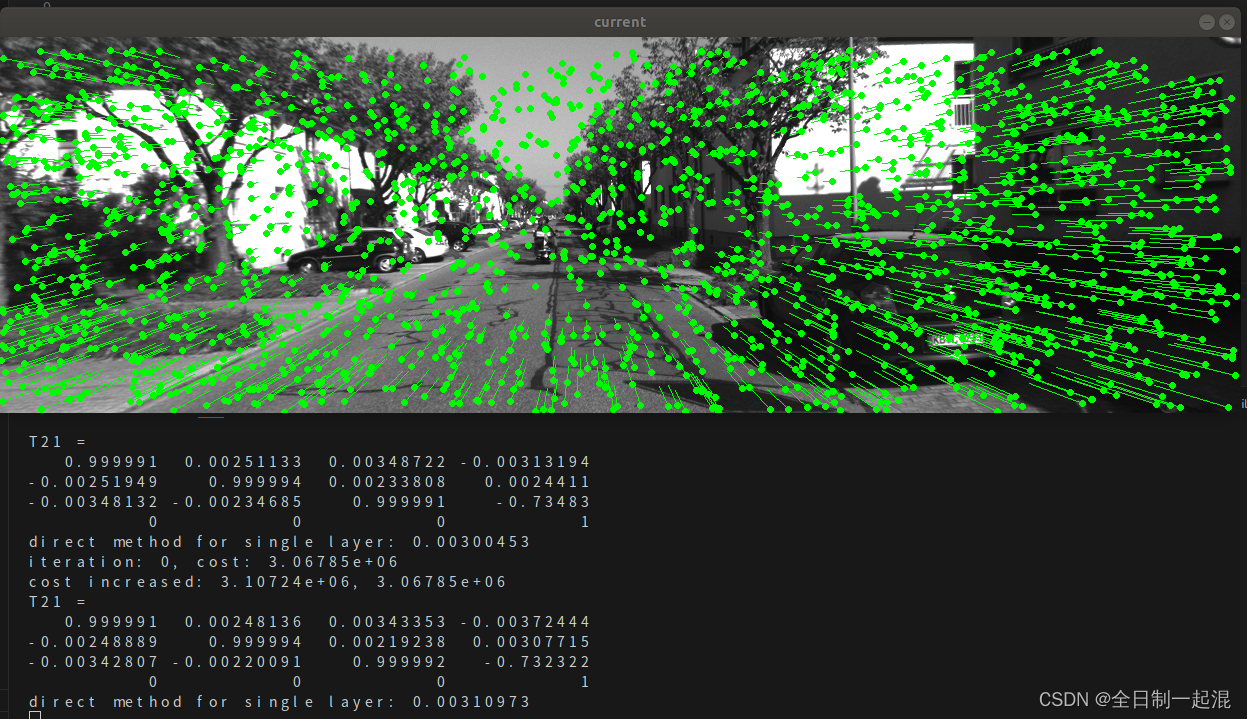
./build/direct_method :