大家好,我是带我去滑雪!
局部放大图可以展示图像中的细节信息,使图像更加直观和精美,此次使用magnify工具实现对绘制的figure选择区域绘制,图像效果如下:
1、基本图像绘制
这里选择绘制一个散点图,数据来源是使用决策树预测的真实值和预测值:
clear;
clc;%导入数据
data = load('E:\工作\硕士\博客\预测值.csv');%给没列数据赋变量名
TrueValue= data(:,1);
rfp= data(:,2);
svm= data(:,3);
sjwl= data(:,4);
LGBMR= data(:,5);
XGBOOST= data(:,6);
DTR= data(:,7);
KNR= data(:,8);
y=linspace(1,304,304)
%绘图
figure(1);
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,rfp,'k','LineWidth',1.2);
figure(2)
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,svm,'b','LineWidth',1.2);
figure(3)
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,sjwl,'c','LineWidth',1.2);
figure(4)
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,LGBMR,'y','LineWidth',1.2);
figure(5)
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,XGBOOST,'g','LineWidth',1.2);
figure(6)
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,DTR,'k','LineWidth',1.2);
figure(7)
plot(y,TrueValue,'r','LineWidth',1.2);
hold on;
plot(y,KNR,'b','LineWidth',1.2);
部分输出结果(图6):
2、局部放大图绘制
初始数据图绘制完成后,调用放大函数,代码如下:
% start of program
function magnify(f1)
% magnify(f1)
% Figure creates a magnification box when under the mouse position when a button is pressed. Press '+'/'-' while
% button pressed to increase/decrease magnification. Press '>'/'<' while button pressed to increase/decrease box size.
% Hold 'Ctrl' while clicking to leave magnification on figure.
%
% Example:
% plot(1:100,randn(1,100),(1:300)/3,rand(1,300)), grid on,
% magnify;if (nargin == 0), f1 = gcf; end;
figure(f1);
set(f1, ...
'WindowButtonDownFcn', @ButtonDownCallback, ...
'WindowButtonUpFcn', @ButtonUpCallback, ...
'WindowButtonMotionFcn', @ButtonMotionCallback, ...
'KeyPressFcn', @KeyPressCallback);
return;function ButtonDownCallback(src,eventdata)
f1 = src;
a1 = get(f1,'CurrentAxes');
a2 = copyobj(a1,f1);set(f1, ...
'UserData',[f1,a1,a2], ...
'Pointer','fullcrosshair', ...
'CurrentAxes',a2);
set(a2, ...
'UserData',[2,0.2], ... %magnification, frame size
'Color',get(a1,'Color'), ...
'Box','on');
xlabel(''); ylabel(''); zlabel(''); title('');
set(get(a2,'Children'), ...
'LineWidth', 2);
set(a1, ...
'Color',get(a1,'Color')*0.95);
set(f1, ...
'CurrentAxes',a1);
ButtonMotionCallback(src);
return;function ButtonUpCallback(src,eventdata)
H = get(src,'UserData');
f1 = H(1); a1 = H(2); a2 = H(3);
set(a1, ...
'Color',get(a2,'Color'));
set(f1, ...
'UserData',[], ...
'Pointer','arrow', ...
'CurrentAxes',a1);
if ~strcmp(get(f1,'SelectionType'),'alt'),
delete(a2);
end;
return;function ButtonMotionCallback(src,eventdata)
H = get(src,'UserData');
if ~isempty(H)
f1 = H(1); a1 = H(2); a2 = H(3);
a2_param = get(a2,'UserData');
f_pos = get(f1,'Position');
a1_pos = get(a1,'Position');[f_cp, a1_cp] = pointer2d(f1,a1);
set(a2,'Position',[(f_cp./f_pos(3:4)) 0 0]+a2_param(2)*a1_pos(3)*[-1 -1 2 2]);
a2_pos = get(a2,'Position');set(a2,'XLim',a1_cp(1)+(1/a2_param(1))*(a2_pos(3)/a1_pos(3))*diff(get(a1,'XLim'))*[-0.5 0.5]);
set(a2,'YLim',a1_cp(2)+(1/a2_param(1))*(a2_pos(4)/a1_pos(4))*diff(get(a1,'YLim'))*[-0.5 0.5]);
end;
return;function KeyPressCallback(src,eventdata)
H = get(gcf,'UserData');
if ~isempty(H)
f1 = H(1); a1 = H(2); a2 = H(3);
a2_param = get(a2,'UserData');
if (strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'+') | strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'='))
a2_param(1) = a2_param(1)*1.2;
elseif (strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'-') | strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'_'))
a2_param(1) = a2_param(1)/1.2;
elseif (strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'<') | strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),','))
a2_param(2) = a2_param(2)/1.2;
elseif (strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'>') | strcmp(get(f1,'CurrentCharacter'),'.'))
a2_param(2) = a2_param(2)*1.2;
end;
set(a2,'UserData',a2_param);
ButtonMotionCallback(src);
end;
return;% Included for completeness (usually in own file)
function [fig_pointer_pos, axes_pointer_val] = pointer2d(fig_hndl,axes_hndl)
%
%pointer2d(fig_hndl,axes_hndl)
%
%Returns the coordinates of the pointer (in pixels)
%in the desired figure (fig_hndl) and the coordinates
% in the desired axis (axes coordinates)
%
% Example:
% figure(1),
% hold on,
% for i = 1:1000,
% [figp,axp]=pointer2d;
% plot(axp(1),axp(2),'.','EraseMode','none');
% drawnow;
% end;
% hold off% Rick Hindman - 4/18/01
if (nargin == 0), fig_hndl = gcf; axes_hndl = gca; end;
if (nargin == 1), axes_hndl = get(fig_hndl,'CurrentAxes'); end;set(fig_hndl,'Units','pixels');
pointer_pos = get(0,'PointerLocation');%pixels {0,0} lower left
fig_pos = get(fig_hndl,'Position');%pixels {l,b,w,h}fig_pointer_pos = pointer_pos - fig_pos([1,2]);
set(fig_hndl,'CurrentPoint',fig_pointer_pos);if (isempty(axes_hndl)),
axes_pointer_val = [];
elseif (nargout == 2),
axes_pointer_line = get(axes_hndl,'CurrentPoint');
axes_pointer_val = sum(axes_pointer_line)/2;
end;% end of program
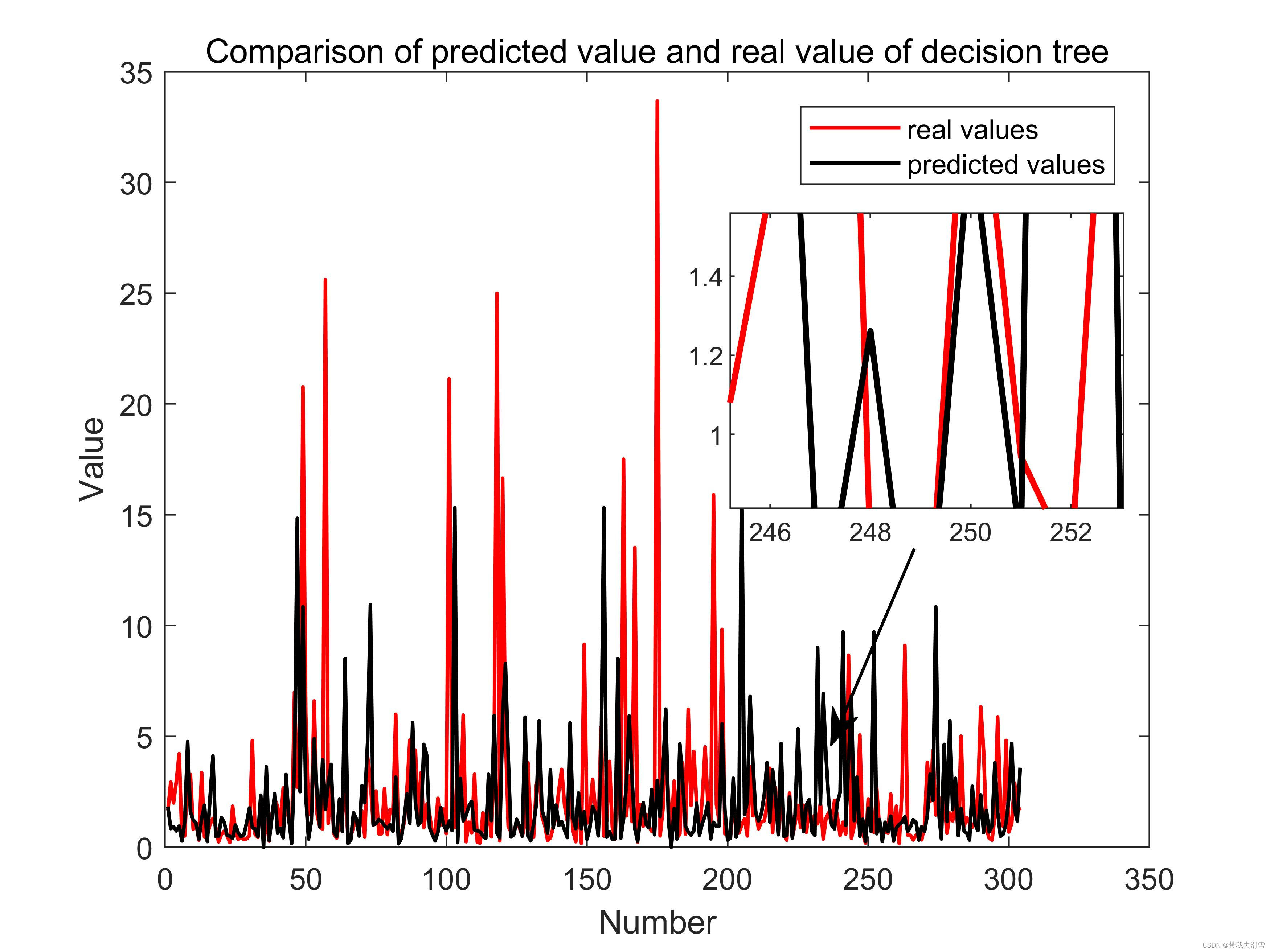
接下来使用鼠标右键选中想要放大的区域,同时可以使用‘<’和‘>’缩放方法范围,‘+’和‘-’缩放放大比例,松开右键确认,还可以通过工具中的编辑图形调整子图位置等,绘制的图像效果如下:

3、优化图像
为放大后的图像添加横纵坐标标签、图例、标题,代码如下:
function createfigure(X1, YMatrix1)
figure1 = figure;
axes1 = axes('Parent',figure1);
hold(axes1,'on');
plot1 = plot(X1,YMatrix1,'Parent',axes1,'LineWidth',1.2);
set(plot1(1),'DisplayName','real values','Color',[1 0 0]);
set(plot1(2),'DisplayName','predicted values','Color',[0 0 0]);
ylabel({'Value'});
xlabel({'Number'});
title({'Comparison of predicted value and real value of decision tree'});box(axes1,'on');
legend1 = legend(axes1,'show');
set(legend1,...
'Position',[0.629880949860529 0.803888887072368 0.248214289460863 0.0869047637212844]);
axes2 = axes('Parent',figure1,...
'Position',[0.574999999999999 0.465952380952387 0.31 0.310000000000004]);
hold(axes2,'on');
plot2 = plot(X1,YMatrix1,'Parent',axes2,'LineWidth',2);
set(plot2(1),'Color',[1 0 0]);
set(plot2(2),'Color',[0 0 0]);
box(axes2,'on');
annotation(figure1,'arrow',[0.72 0.654285714285714],...
[0.423761904761905 0.217142857142857],'LineWidth',1);最终输出结果:
需要数据集的家人们可以去百度网盘(永久有效)获取:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1E59qYZuGhwlrx6gn4JJZTg?pwd=2138
提取码:2138
更多优质内容持续发布中,请移步主页查看。
点赞+关注,下次不迷路!