目录
1.为什么需要文件截断?
2.truncate函数介绍
2.1 truncate函数
2.2 truncate函数内核源码分析
2.3 truncate函数使用示例
3.ftruncate函数介绍
3.1 ftruncate函数
3.2 ftruncate函数内核源码分析
3.3 ftruncate函数使用示例
3.4 ftruncate和文件偏移量的关系?
4.ftruncate和truncate区别
1.为什么需要文件截断?
文件截断是指将文件的长度截断为指定大小或者完全清空文件内容。在操作系统中,文件通常由一系列连续的数据块组成,每个数据块存储文件的一部分内容。通过执行文件截断操作,可以修改文件的大小或清空文件内容。
在执行文件截断操作时,需要注意以下几点:
- 如果截断后的文件大小小于原始大小,那么超出截断长度的部分内容将被删除。
- 如果截断后的文件大小大于原始大小,那么新增部分的内容将会以空字符填充。
- 需要有适当的权限来执行文件截断操作,否则可能会失败。
2.truncate函数介绍
2.1 truncate函数
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);函数简介:truncate函数是一个用于文件截断的系统调用函数,在C语言程序中使用。该函数可以根据指定的大小截断文件,使其变为指定大小或者完全清空文件内容。
函数参数:
path:是要截断的文件路径。
length:要截断的目标大小。
函数返回值:
成功:返回0。
失败:失败返回-1,并设置errno。
2.2 truncate函数内核源码分析
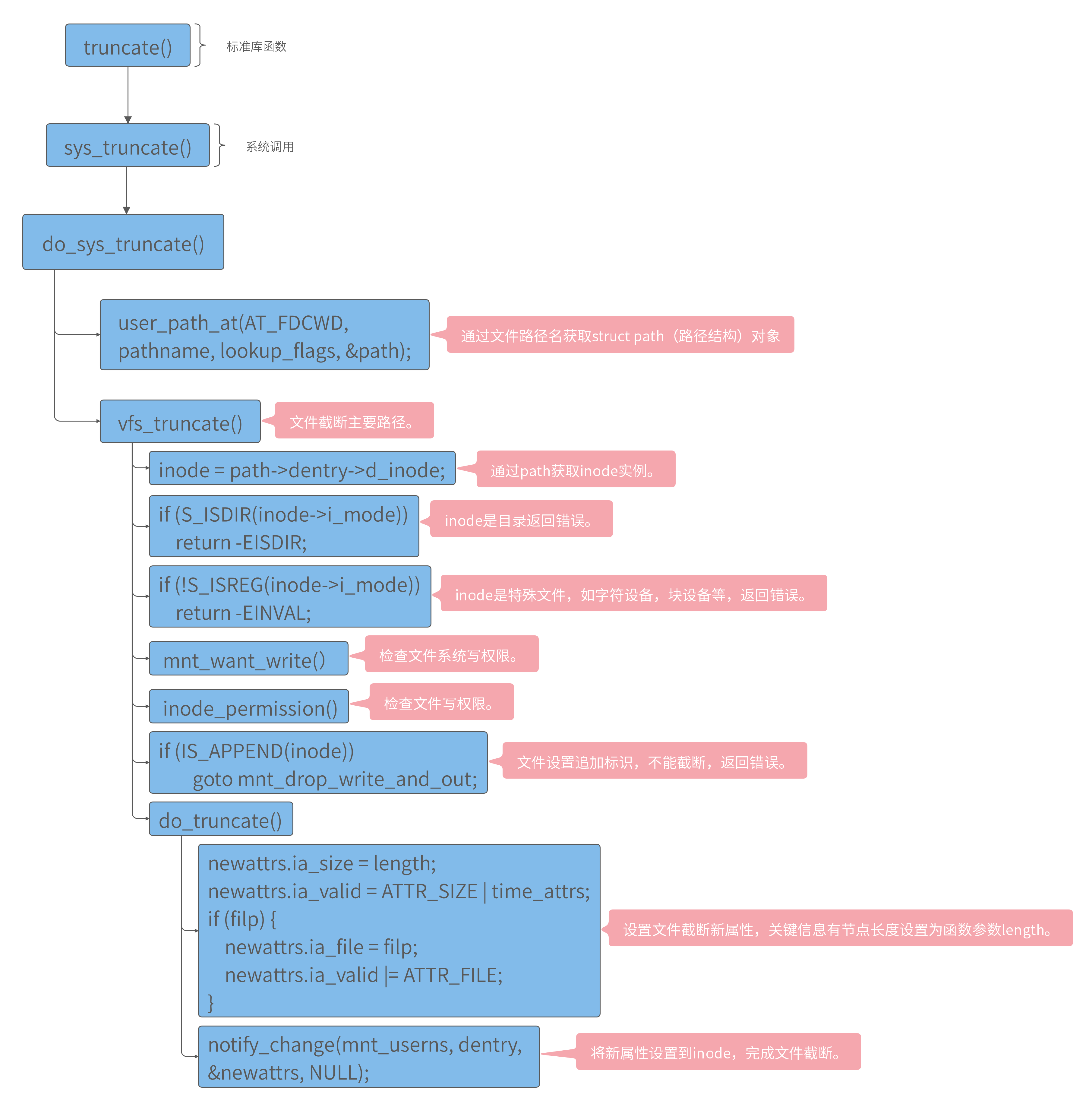
图 2-1 truncate函数内核源码调用流程
truncate函数通过文件路径名(pathname)获取struct path对象,struct path记录了inode信息,进行文件截断之前需要做一些异常判断,比如:inode是否是普通文件,inode是否有写权限,是否是追加模式等等,通过异常检测后,需要设置inode新属性,新属性包括文件大小等信息,再通过notify_change函数通知inode完成新属性同步,从而完成文件截断。
2.3 truncate函数使用示例
int truncate_test() {
int ret = truncate(TEST_FILE, 120);
if (ret == -1) {
perror("truncate error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
3.ftruncate函数介绍
3.1 ftruncate函数
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);
函数简介:ftruncate函数是一个用于文件截断的系统调用函数,它可以在C语言程序中使用。该函数通过文件描述符来操作文件,将文件截断为指定的大小。
函数参数:
fd:文件描述符。
length:要截断的目标大小。
函数返回值:
成功:返回0。
失败:失败返回-1,并设置errno。
3.2 ftruncate函数内核源码分析
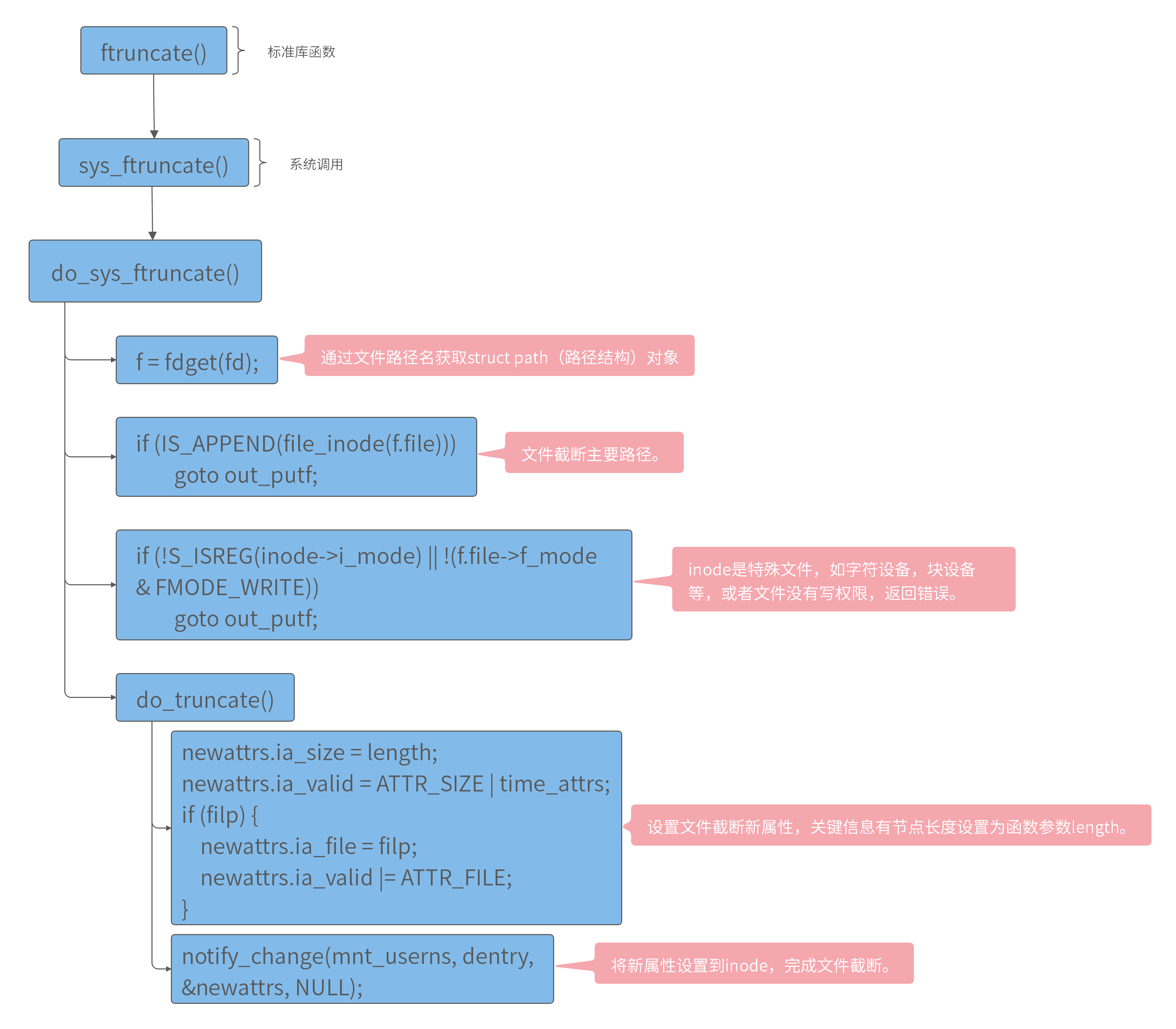
图 3-1 ftruncate函数内核源码调用流程
ftruncate函数内核调用流程和和truncate函数相似,不同点在与ftruncate函数通过fdget函数获取struct file对象,struct file对象有inode记录信息,通过struct file对象完成inode新属性修改,从而完成文件截断。
3.3 ftruncate函数使用示例
#define TEST_FILE "/tmp/test.txt"
void print_buf(unsigned char *buf, int len) {
if (len <= 0) {
printf("error len:%d\n", len);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
printf("%c%02X ", ((i % 16) || (i == 0)) ? : '\n', buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void print_pos(int fd) {
int pos = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
printf("cur pos:%d\n", pos);
}
int read_len_data(int fd, unsigned int len) {
if (len > READ_BUF_SIZE) return -1;
char rbuf[READ_BUF_SIZE] = {0};
int ret = read(fd, rbuf, len);
print_buf((unsigned char *)rbuf, ret);
return ret;
}
int write_len_data(int fd, unsigned char len, char ch) {
unsigned char sbuf[BUF_SIZE] = {0};
for (unsigned char i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sbuf[i] = ch;
}
int ret = write(fd, sbuf, len);
if (ret == -1) {
perror("write error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int ftruncate_test() {
int fd = open(TEST_FILE, O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0644);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
write_len_data(fd, 100, 'a');
int ret = ftruncate(fd, 20);
if (ret == -1) {
perror("ftruncate error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
print_pos(fd);
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
read_len_data(fd, 1000);
close(fd);
return 0;
}3.4 ftruncate和文件偏移量的关系?
ftruncate函数不会改变文件偏移量。可以分为两种情况讨论:
- 情况1:ftruncate截断文件,文件长度变小,文件偏移量还是保留上一次记录,即使文件长度变为0,文件偏移量依然保持不变。
- 情况2:ftruncate填充文件,文件长度变大,文件偏移量还是保留上一次记录。
从ftruncate内核源码分析,ftruncate未修改文件偏移量(f_pos)的值,所以ftruncate不影响文件偏移量。
4.ftruncate和truncate区别
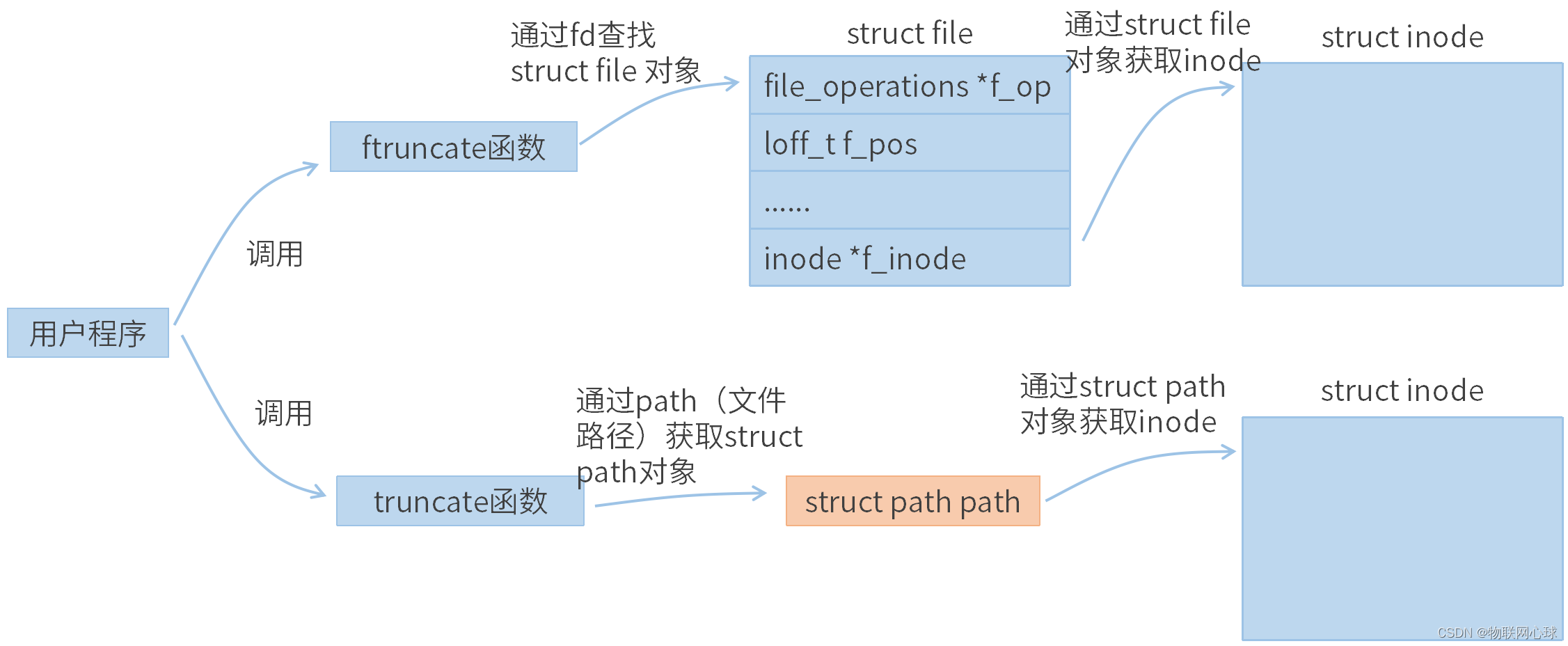
图 4-1 ftruncate和truncate区别
如图4-1,truncate和ftruncate共同点都是修改struct inode属性。不同点是两者采用的路径不一样,
ftruncate函数通过使用fd映射struct file对象,再通过struct file对象查找到inode实例,从而修改inode实例。
truncate函数没有fd参数,采用文件路径名获取struct path(路径结构)对象,再通过struct path对象获取inode实例,从而修改inode实例。