目录
- 零、自己通过 set nx ex 实现的分布式锁存在的问题
- 一、Redisson 介绍
- 二、Redisson 基本使用(改造业务)
- (1) 依赖
- (2) 配置 Redisson 客户端
- (3) 使用 Redisson 的可重入锁
- 三、Redisson 可重入锁原理
- 四、Redisson 可重试原理
- 五、Redisson 超时释放(锁的 ttl)
- 六、主从一致(连锁 MultiLock)
- 七、锁总结
零、自己通过 set nx ex 实现的分布式锁存在的问题
✏️ 不可重入 同一个线程无法多次获取同一把锁
✏️ 不可重试 获取锁只尝试一次就返回 false,没有重试机制
✏️ 超时释放 锁超时释放虽然可以避免死锁,但如果是业务执行耗时较长,也会导致锁释放,存在安全隐患
一、Redisson 介绍
✏️ Redisson 是一个在 Redis 基础上实现的 Java 驻内存数据网格(In-Memory Data Grid)
✏️ 它提供了一系列分布式的 Java 常用对象
✏️ 提供了许多分布式服务,其中包含了各种分布式锁的实现
官网地址 https://redisson.org
GitHub 地址 https://github.com/redisson/redisson
二、Redisson 基本使用(改造业务)
(1) 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.6</version>
</dependency>
(2) 配置 Redisson 客户端
@Configuration
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.88.130:6379")
.setPassword("root");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
✏️ 配置 redis 地址也可以使用
config.useClusterServers()添加集群地址
✏️useSingleServer()是添加单点地址
(3) 使用 Redisson 的可重入锁
@Test
public void tesRedisson() throws InterruptedException {
// 获取可重入锁, 指定锁的名称
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("anLock");
// 尝试获取锁
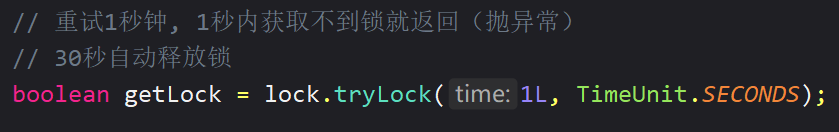
// 参数1:获取锁的最大等待时间(期间会多次重试获取锁)
// 参数2:锁自动释放时间
// 参数3:时间单位
boolean isGetLock = lock.tryLock(1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (isGetLock) {
try {
System.out.println("执行业务");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
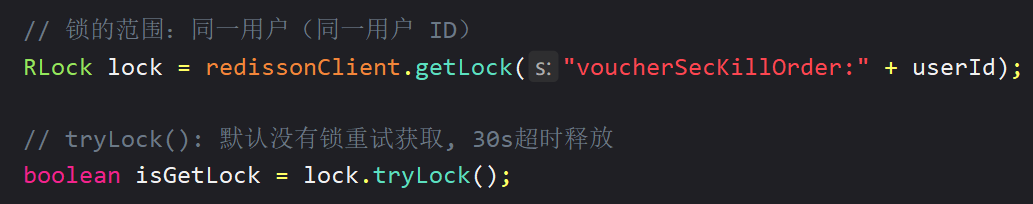
三、Redisson 可重入锁原理

✏️ 通过 Redis 的 Hash 数据结构实现
✏️ 存入线程标识和 counter【记录锁被重入的次数(被使用的次数),被使用(获取)一次就递增1,被释放则 counter 减1】
✏️ 当 counter 为 0 的时候,整个锁会被释放
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
@Test
public void tRedisson() {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("lock");
boolean getLock = lock.tryLock();
if (!getLock) {
System.out.println("tRedisson getLock Failed");
return;
}
try {
System.out.println("tRedisson getLock Success");
m(lock);
} finally {
System.out.println("tRedisson unlock");
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void m(RLock lock) {
boolean getLock = lock.tryLock();
if (!getLock) {
System.out.println("m() getLock Failed");
return;
}
try {
System.out.println("m() getLock Success");
} finally {
System.out.println("m() unlock");
lock.unlock();
}
}
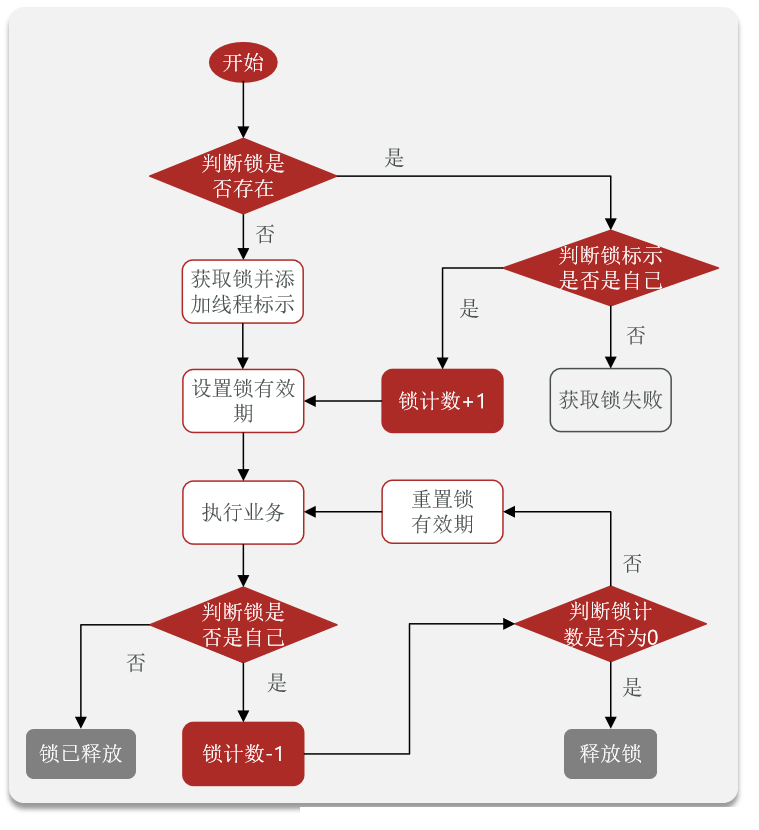
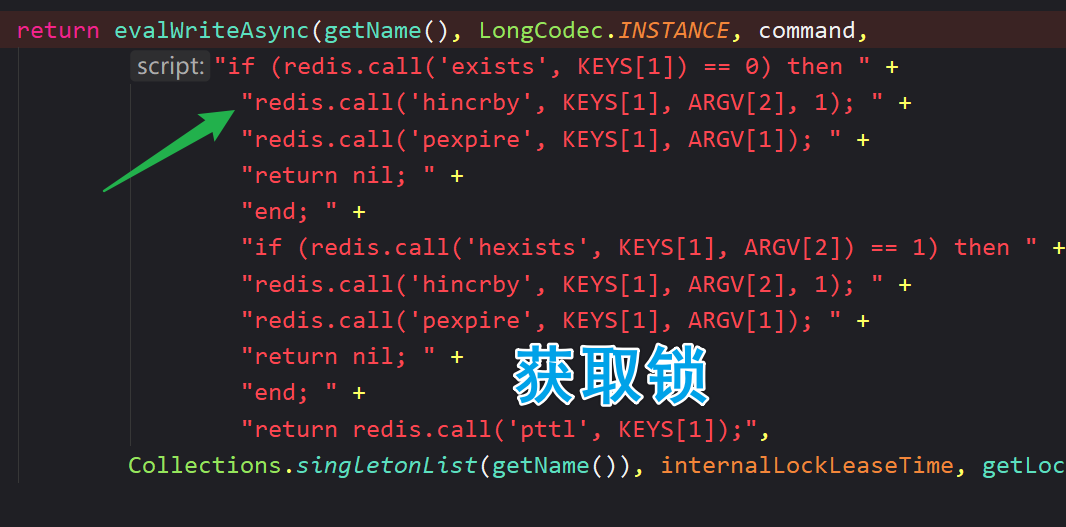
✏️ 没有直接使用 hset
✏️ hincrby 命令:当 key 不存在的时候会自动创建 key
✏️ 获取锁成功:返回 nil;获取锁失败:返回当前锁的存活时间
✏️ pttl 以毫秒为单位返回某个 key 的存活时间
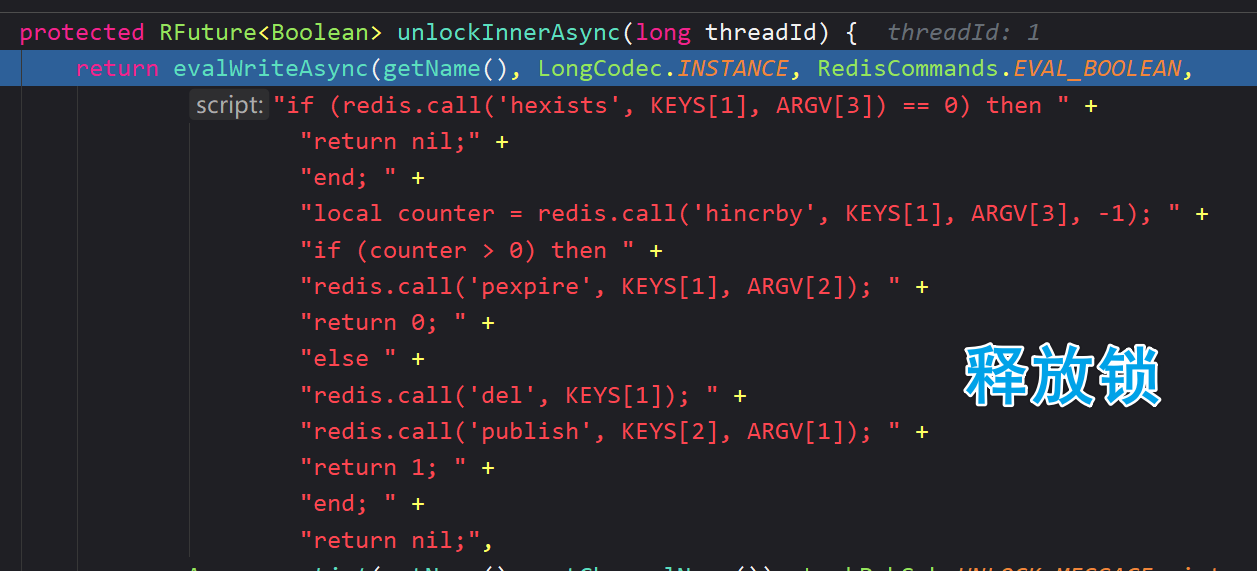
✏️
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]);发布释放锁的消息通知
四、Redisson 可重试原理


下面是 Redisson 的 tryLock() 方法的源码:
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 把超时等待时间转换为毫秒
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
// 获取当前时间(毫秒)
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取线程 ID
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// tryAcquire 尝试获取锁(获取锁成功返回 null, 获取锁失败返回剩余ttl)
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) { // 成功获取锁
return true;
}
// time 是超时释放时间(单位:毫秒)
// time = time - (System.currentTimeMillis() - current)
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; // 刷新超时释放时间
if (time <= 0) { // 超时释放时间到了
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false; // 获取锁失败
}
// 获取 当前时间毫秒值
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 等待释放锁的通知(订阅释放锁的信号)
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
// 等到超时释放时间结束还没有收到释放锁的通知的话, 返回 false
// 获取锁失败
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) { // 取消订阅
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
// 接收到释放锁的信号
try {
// 判断释放到超时时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false; // 获取锁失败
}
while (true) { // 反复尝试
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) { // 获取锁成功
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
// waiting for message
// 代码来到这里:没有获取到锁, 超时时间有剩余
// 等待释放锁的信号
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
// return get(tryLockAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit));
}
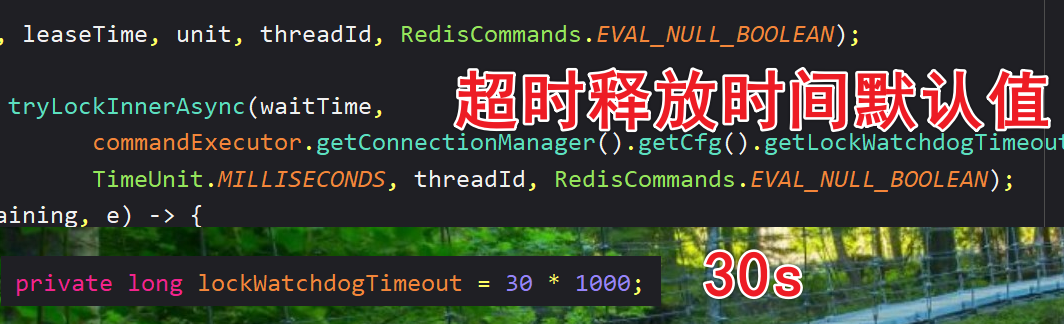
private RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 判断超时释放时间是否是 -1
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
}
// 代码来到这里表示超时释放时间是 -1
// tryLockInnerAsync 异步的方法
RFuture<Boolean> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
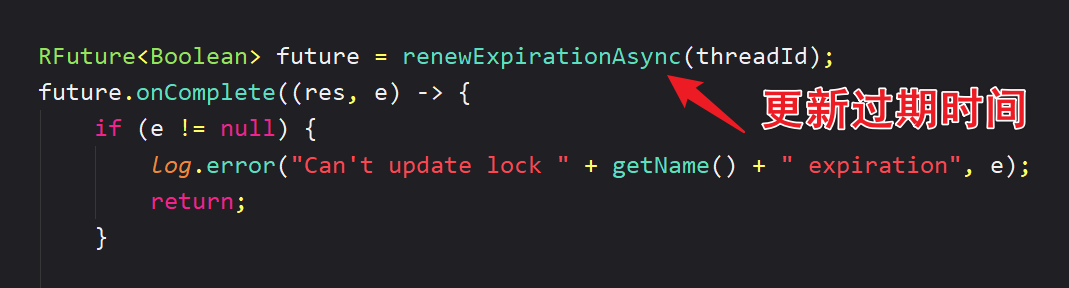
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}

tryLockInnerAsync()、tryAcquire(): ① 尝试获取锁。获取锁成功,返回 nil;获取锁失败,返回超时是否时间(lessTime)
② 该方法是异步的
① 获取锁失败后,不会立刻重新尝试获取锁
② 会等待释放锁的通知
五、Redisson 超时释放(锁的 ttl)


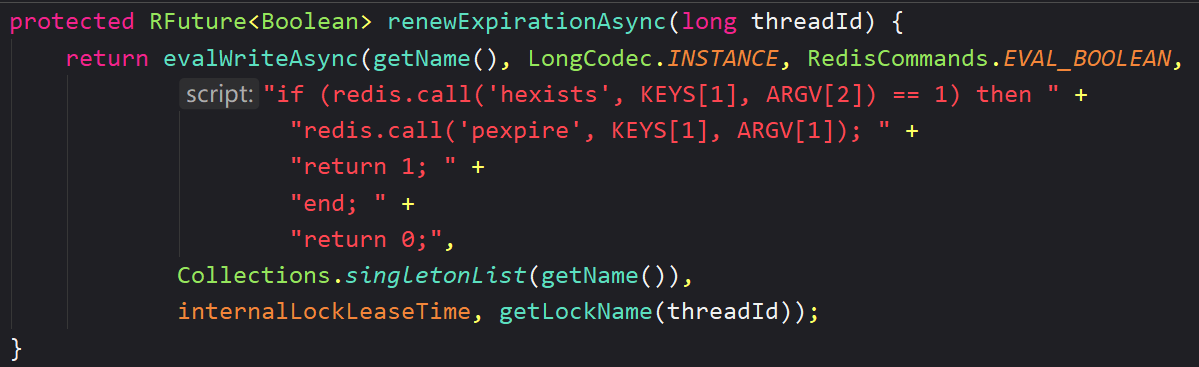
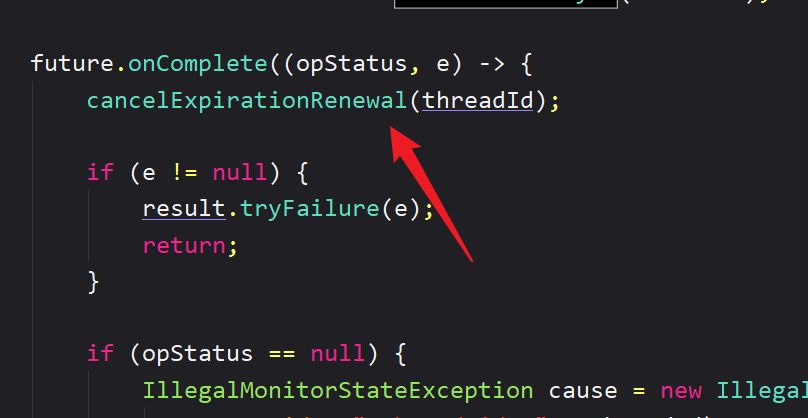
好😵懵逼啊,随便看看得了
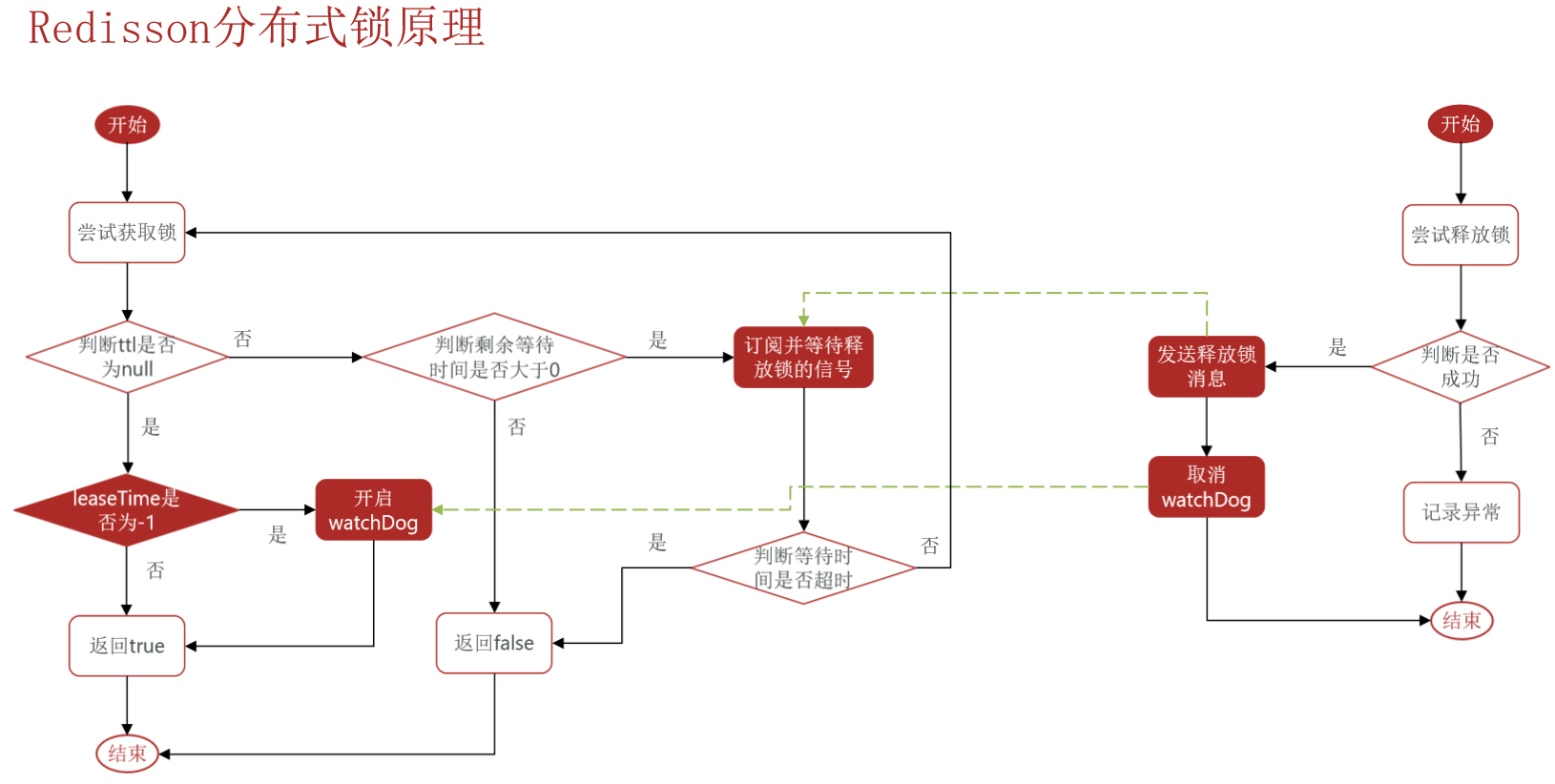
📝 可重入:利用hash结构记录线程id和重入次数
📝 可重试:利用信号量和 PubSub 功能实现等待、唤醒,获取锁失败的重试机制
📝 超时续约:利用 watchDog,每隔一段时间(releaseTime / 3),重置超时时间
六、主从一致(连锁 MultiLock)
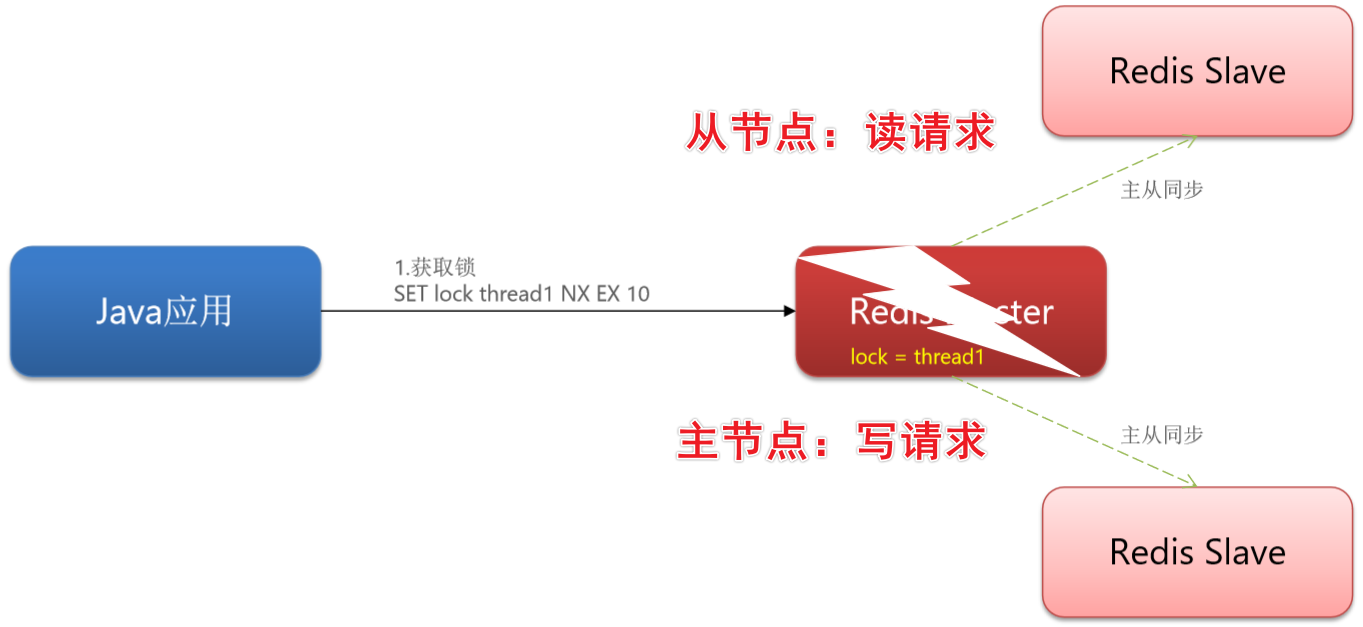
✏️主节点支持写请求
✏️从节点支持读请求
✏️主节点写入的数据要同步到从节点

✏️假如向主节点写入了数据,主节点还没有来得及向从节点同步数据自己就宕机了,此时 Redis 的哨兵机制会从剩下的从节点中选一个从节点作为新的主节点
✏️ 该新的主节点是没有上个主节点中的 lock = thread1 数据的
✏️ 锁失效,可能存在线程安全问题
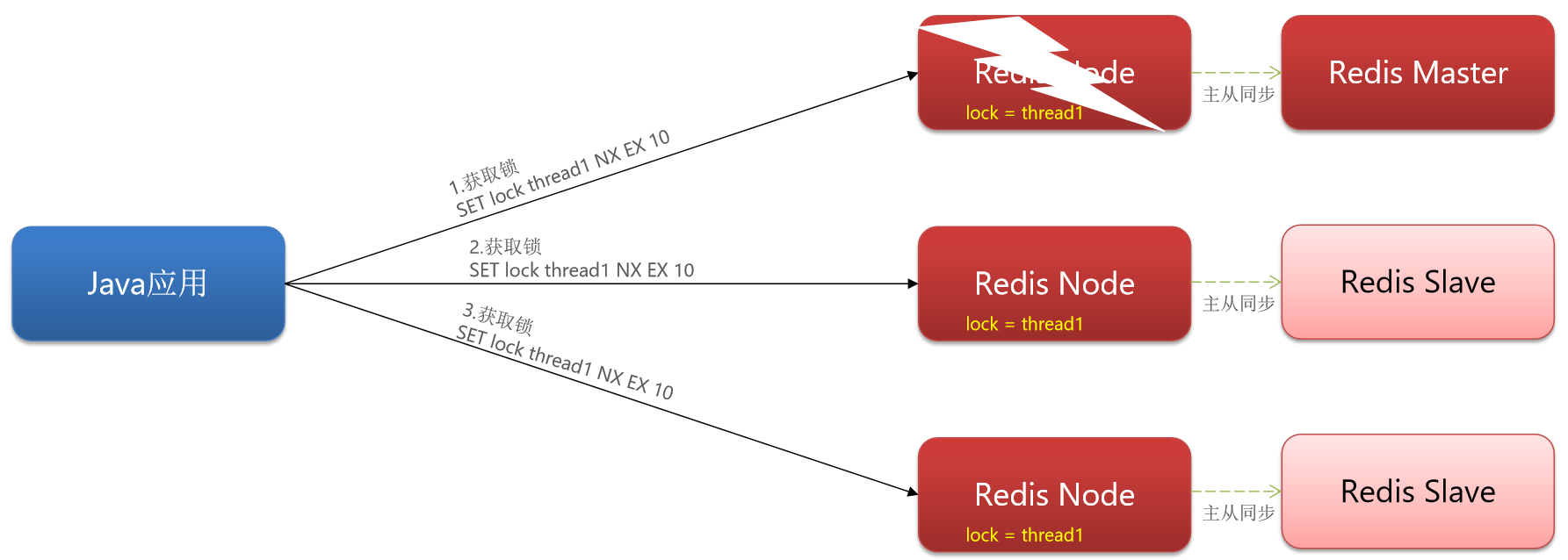
✏️其中有任何一个节点宕机都无法拿到锁
七、锁总结
🎄不可重入 Redis 分布式锁:
原理: 利用 setnx 的互斥性;利用 ex 避免死锁;释放锁时判断线程标
缺陷: 不可重入、无法重试、锁超时失效
🎄可重入的 Redis 分布式锁:
原理: 利用 Hash 结构,记录线程标识和重入次数;利用 watchDog 延续锁过期时间;利用信号量控制锁重试等待
缺陷: redis宕机引起锁失效问题
🎄 Redisson 的 multiLock:
原理: 多个独立的 Redis 节点,必须在所有节点都获取重入锁,才算获取锁成功
缺陷: 运维成本高、实现复杂