文章目录
- 前言
- Cookie实例
- Cookie缺点
- Cookie案例代码
- Session
- Session的创建与销毁
- Session的创建
- Session的销毁
- Session和Cookie的区别
- 不同
- 联系
前言
提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容:
在Web应用程序中,会话跟踪是一种技术,可以在客户端和服务器之间保持持久连接,以便跟踪用户在不同页面之间的活动。
Servlet的会话跟踪可以通过以下方式实现:
-
Cookies:Servlet可以将一个唯一标识符存储在客户端的Cookie中,以便在每次请求中跟踪用户会话。
-
URL 重写:Servlet 可以将唯一标识符添加到URL中,以便在每个请求中跟踪用户会话。
-
隐藏表单字段:Servlet可以将唯一标识符添加到表单字段中,以便在每个请求中跟踪用户会话。
-
HttpSession 对象:Servlet 可以使用 HttpSession 对象,在服务器端维护用户会话状态。每个 session 对象都有一个唯一的标识符,可以在服务器端跟踪用户会话。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
Cookie实例
准备发送cookie给前端:
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/cookie1")
public class SendCookieToClientServlet extends HttpServlet{
//动态项目 没有去 其他下找 web
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("准备发送cookie给客户端");
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("login", "zhangsan");
cookie.setMaxAge(60*60*24*7); //单位是:秒,这里是7天
resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
}
运行项目:
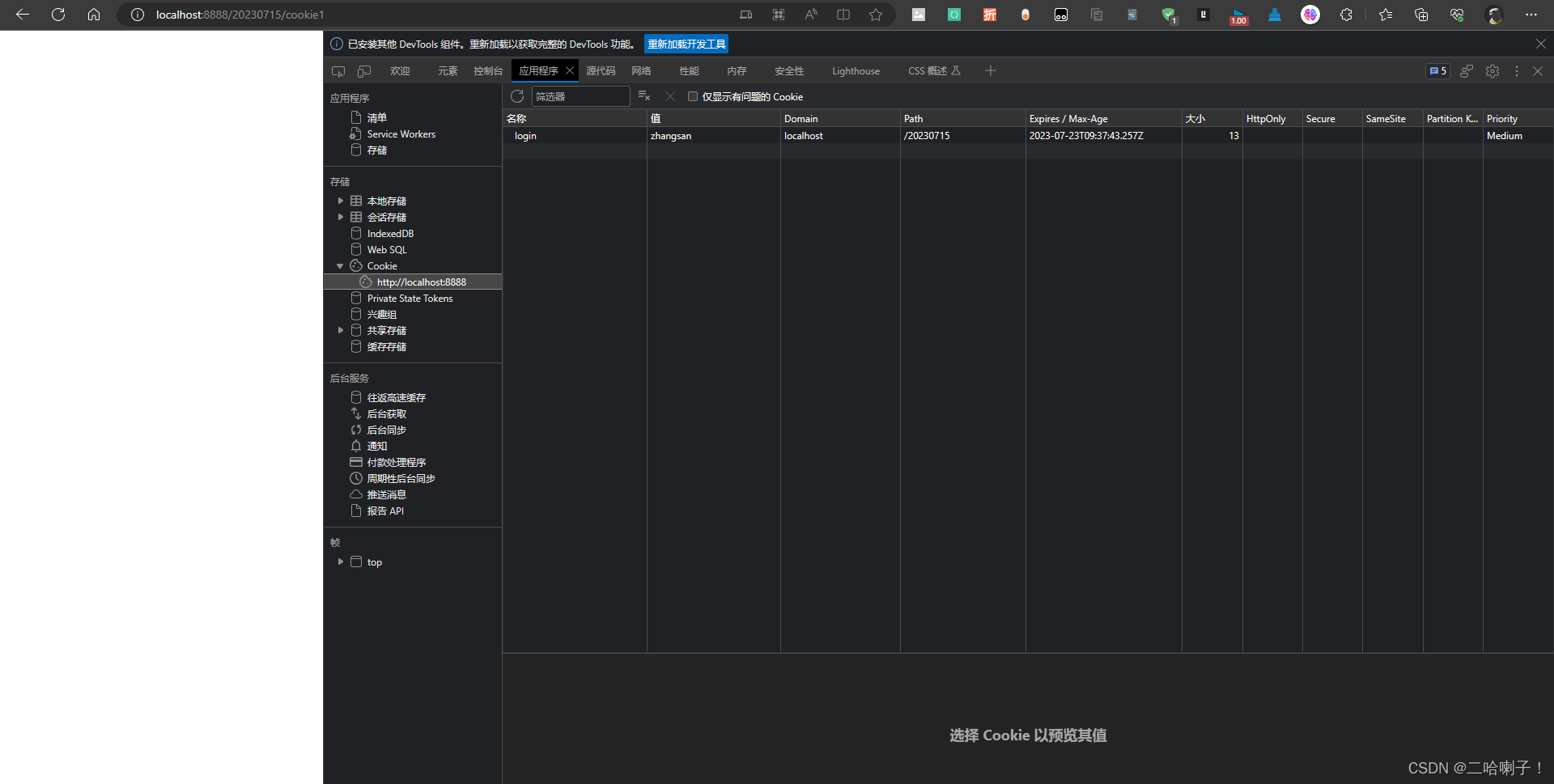
说明代码生效了,cookie发给了客户端
获取客户端的cookie:
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/cookie2")
public class ReciveCookieFromClinetServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("获取客户端的cookie");
Cookie cookiesCookie [] = req.getCookies();
for (int i = 0; i < cookiesCookie.length; i++) {
Cookie cookie = cookiesCookie[i];
System.out.println(cookie.getName()+"-"+cookie.getValue());
}
}
}
重启服务器,清除控制台,网页运行链接
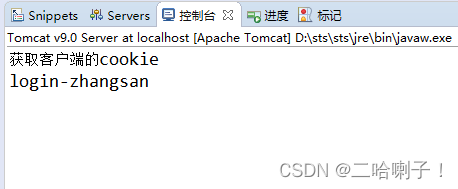
Cookie技术核心:第一次访问时,服务器端发送一些Cookie信息保存到客户端,在有效期内,在同一个客户端里面,向服务器再发请求的时候,默认会把Cookie再发给服务器
Cookie缺点
安全性不高
兼容性问题
时效性问题
存储容量限制
Cookie案例代码
【例1:从Servlet向客户端存入cookie】
//SetCookie Servlet
Cookie c=new Cookie("season","spring");
c.setMaxAge(30);
response.addCookie(c);
Cookie d=new Cookie("nextseason","summer");
d.setMaxAge(10);
response.addCookie(d);
【例2:在客户端读取cookie】
//getCookie.jsp
<%
Cookie[] a=request.getCookies();
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
out.println(a[i].getName()+“:"+a[i].getValue()+"<br>");
}
%>
【例3:利用cookie计数】
//visitCount.jsp计数次数
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%int count = 0;
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); / / 得到所有的Cookie
if(cookies != null) {
for(int i=0; i<cookies.length; i++) {
if(cookies[i].getName().equals("Counter"))
count = Integer.parseInt(cookies[i].getValue()); //获取Counter以前值
} }
count++;
if(count == 1)
out.println("欢迎首次光临");
else
out.println("您已经光临了" + count+"次");
// 将新的count写入客户端
Cookie c = new Cookie("Counter", ""+count);
c.setMaxAge(60*60*24*365); // Cookie 的有效期为 1 年
response.addCookie(c); %>
【例4:删除cookie】
//cookie remove.jsp
<%
int count=0;
// 将新的count写入客户端
Cookie c = new Cookie("Counter", ""+count);
c.setMaxAge(0); // Cookie 的有效期为 0
response.addCookie(c); %>
【例5:购物车登录实验,1、从首页进入购物车页面】
//首页home.html
<a href="cart.jsp">购物车</a>
<a href=”remove.jsp”>删除计数cookie</a>
【例5:购物车登录实验,2、购物车页面,先判断用户是否已经登录,否则跳转登录页面login.html】
//购物车 cart.jsp
<h1>购物车</h1>
<%int count = 0;
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); // 得到所有的Cookie
if(cookies != null) {
for(int i=0; i<cookies.length; i++) {
if(cookies[i].getName().equals("Counter"))
count = Integer.parseInt(cookies[i].getValue()); //获取Counter以前值
} }
if(count==0)response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/login.html");
%>
//login.html
<h1>用户登录</h1>
<form action="visit.jsp" method="post">
用户名<input type="text" name="user"><br><br>
密码
<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
//visit.jsp
<%int count = 0;
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); // 得到所有的Cookie
if(cookies != null) {
for(int i=0; i<cookies.length; i++) {
if(cookies[i].getName().equals("Counter"))
count = Integer.parseInt(cookies[i].getValue()); //获取Counter以前值
} }
count++;
if(count == 1)
response.getWriter().println("欢迎首次光临");
else
response.getWriter().println("您已经光临了" + count+"次");
// 将新的count写入客户端
Cookie c = new Cookie("Counter", ""+count);
c.setMaxAge(60*60*24*365); // Cookie 的有效期为 1 年
response.addCookie(c);
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/cart.jsp");
%>
Session
使用Session维护一个会话的登陆状态:
- 当第一次请求时,在服务器端创建一个Session对象,并且为此对象生成一个sessionId。
- 同时,使用Cookie将此sessionId返回给客户端,并存储在客户端的Cookie中。
- 当客户端发起下一次请求时,必须携带此sessionId发送给服务器端。
- 服务器端根据接收的sessionId,就能找回Session对象,从而获取了上一次请求的信息。
创建StoreDataServlet类:用于在HttpSession中存储一个User对象(代表用户信息)。
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.NEW;
import po.User;
@WebServlet("/store")
public class StoreDataServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.setAttribute("login", new User(1,"二哈喇子","吃饭快"));
}
}
创建User类:表示用户实体,包括用户ID、用户名和角色。
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String role;
public User() {
super();
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}
public User(Integer id, String name, String role) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.role = role;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", role=" + role + "]";
}
}
创建GetDateServlet类:用于从HttpSession中读取存储的User对象,并输出到控制台上。
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@WebServlet("/get")
public class GetDateServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
System.err.println(session.getAttribute("login"));
}
}
这个Web应用程序基于Servlet API实现了会话(Session)管理的功能,即在服务器端存储和管理用户会话信息。当用户登录后,其用户信息会被存储到HttpSession对象中,之后在用户会话期间,这些信息可以被其他Servlet类或JSP页面访问和使用。通过会话管理技术,Web应用程序可以更方便地实现用户状态的管理和控制,提高应用程序的安全性和可靠性。
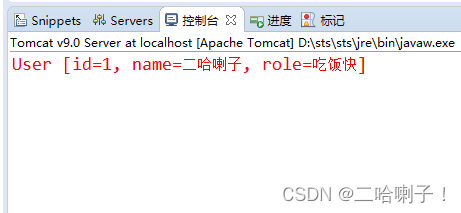
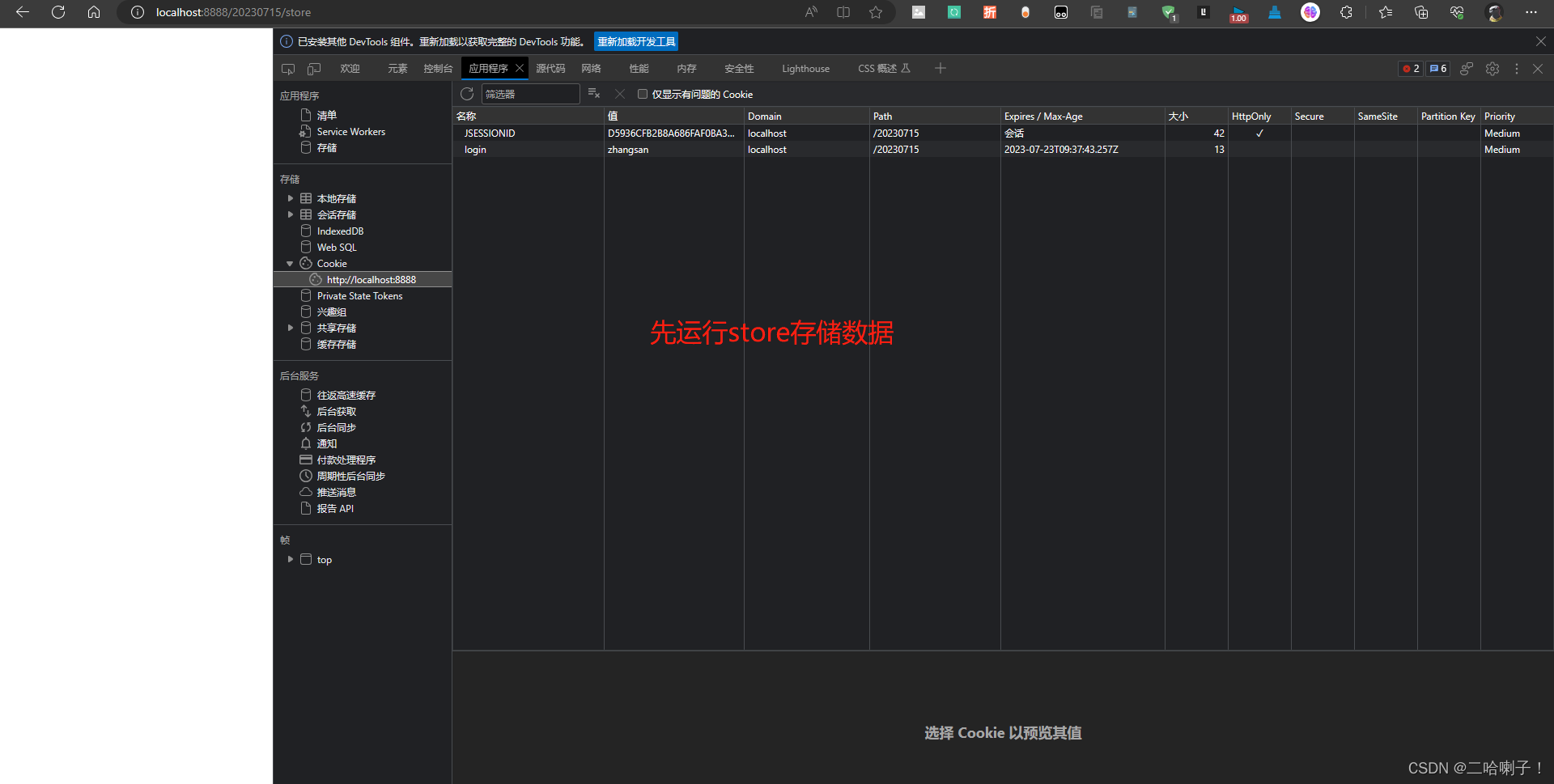
重启服务器,清除控制台,网页运行链接store存储
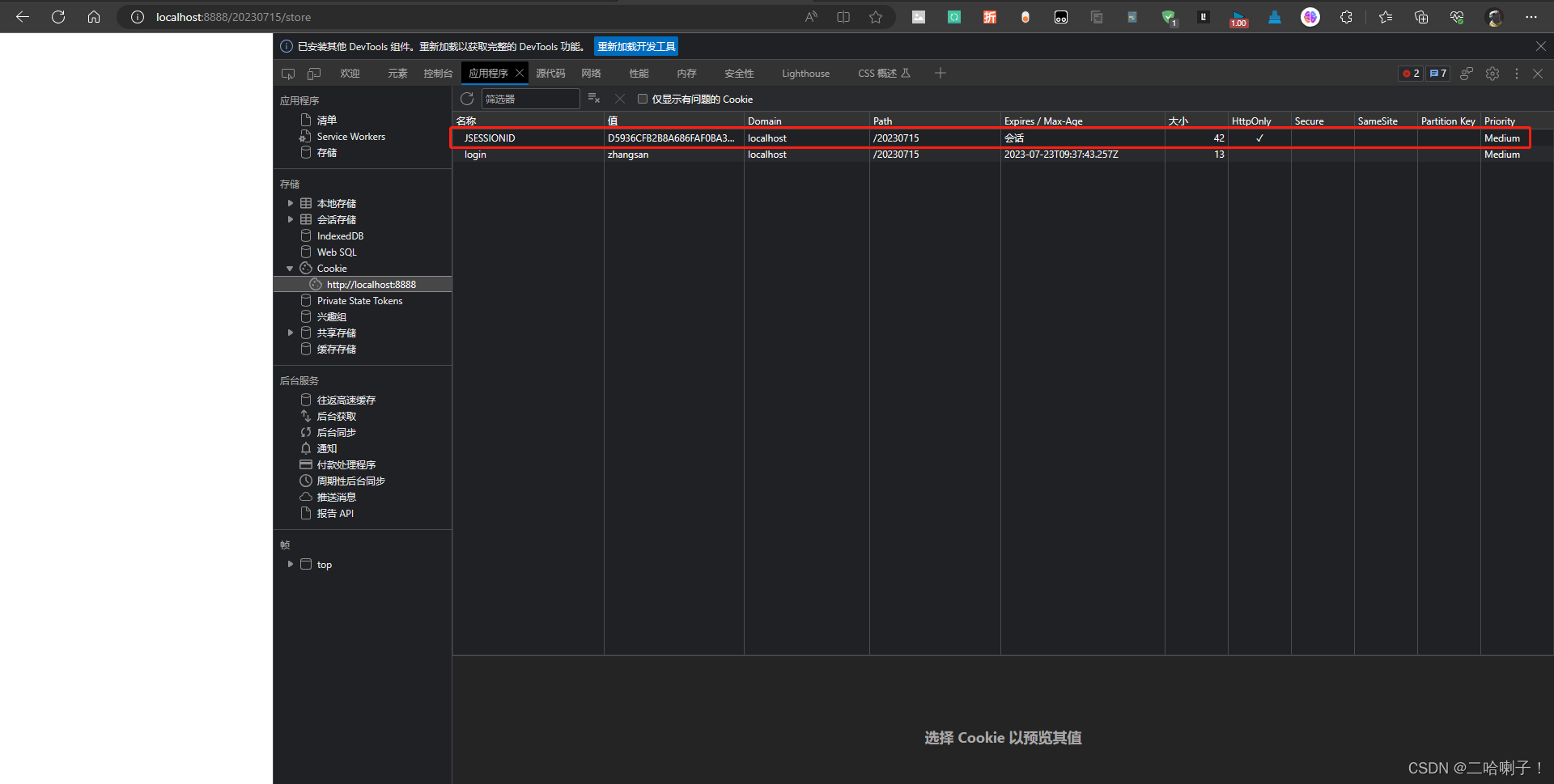
运行get路径取出
Session的创建与销毁
Session的创建
调用request.getSession() 方法获取此Session对象
- 无参:
getSession()如果存在一个Session对象,把有的返回,如果没有就让服务器创建新的Session对象。 - 有参:有参的传一个布尔类型,如果是true就和无参效果一样;如果是false,如果找不到Session对象就不会创建新的了,返回null
没有调用getSession方法则不会创建session。
Session的销毁
Session的销毁只有两种情况:
第一:session调用了 session.invalidate()方法。
第二:前后两次请求超出了session指定的生命周期时间。
默认15分钟销毁,也可以主动销毁
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
//单词多个r
@WebServlet("/destroy")
public class DestroySessionServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.invalidate();
}
}
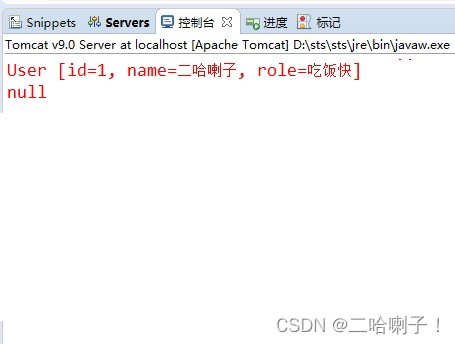
重启服务器,清除控制台,网页依次运行链接

接下来再运行destroy销毁
最后再运行get获取
超时销毁:
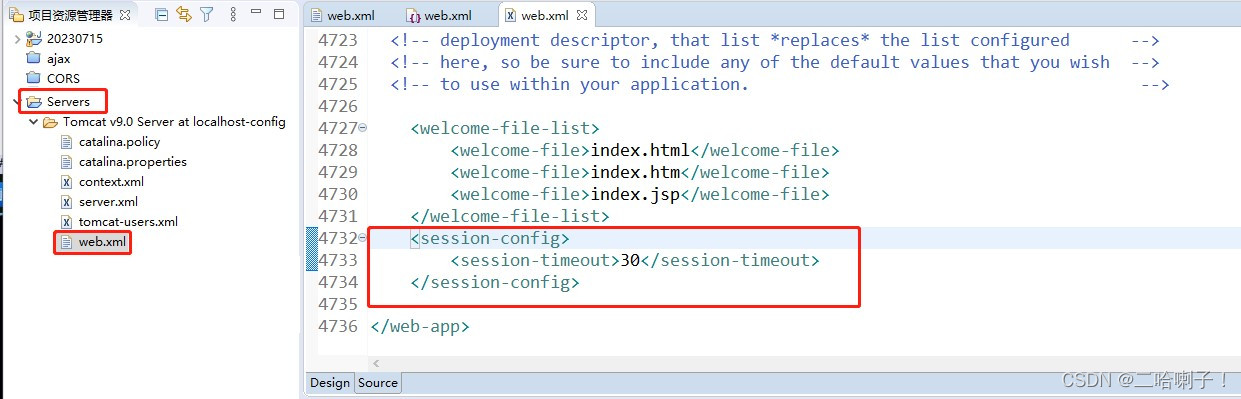
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
超时销毁试完后把代码删除
Session和Cookie的区别
1、Cookie可以存储在浏览器或者本地,Session只能存在服务器
2、session能够存储任意的java对象,cookie 只能存储String 类型的对象
3、Session比Cookie更具有安全性 (Cookie有安全隐患,通过拦截或本地文件找得到你的cookie后可以进行攻击)
4、Session占用服务器性能,Session过多,增加服务器压力
5、单个Cookie保存的数据不能超过4K,很多浏览器都限制一个站点最多保存20个Cookie,Session是没有大小限制和服务器的内存大小有关。
不同
存放地点:cookie存放在客户端的硬盘里,属于离线存放,而session存放在服务器的内存中。
存活时间:cookie可以长期存放在客户端,具体的存活时间由setMaxAge()方法所指定的数值决定,session随用户访问服务器而产生,随客户超时或下线而消失。
安全性:cookie存放在客户端,可能会被别有用心的网站读取,安全性较差,而session存放在服务器的内存中,用户不能修改,且随客户端浏览器的关闭而消失,安全性较好。
联系
不论是cookie还是session隐含对象都需要浏览器支持cookie并且没有禁用cookie。
虽然Session存储在服务器端内存中,但客户端的浏览器需要通过Cookie中的Session ID来标识自己,并通过该ID与服务器上的Session进行绑定,从而实现客户端与服务器端的会话状态管理。
因此Session与Cookie实际上是相互关联的,两者通常一起使用。