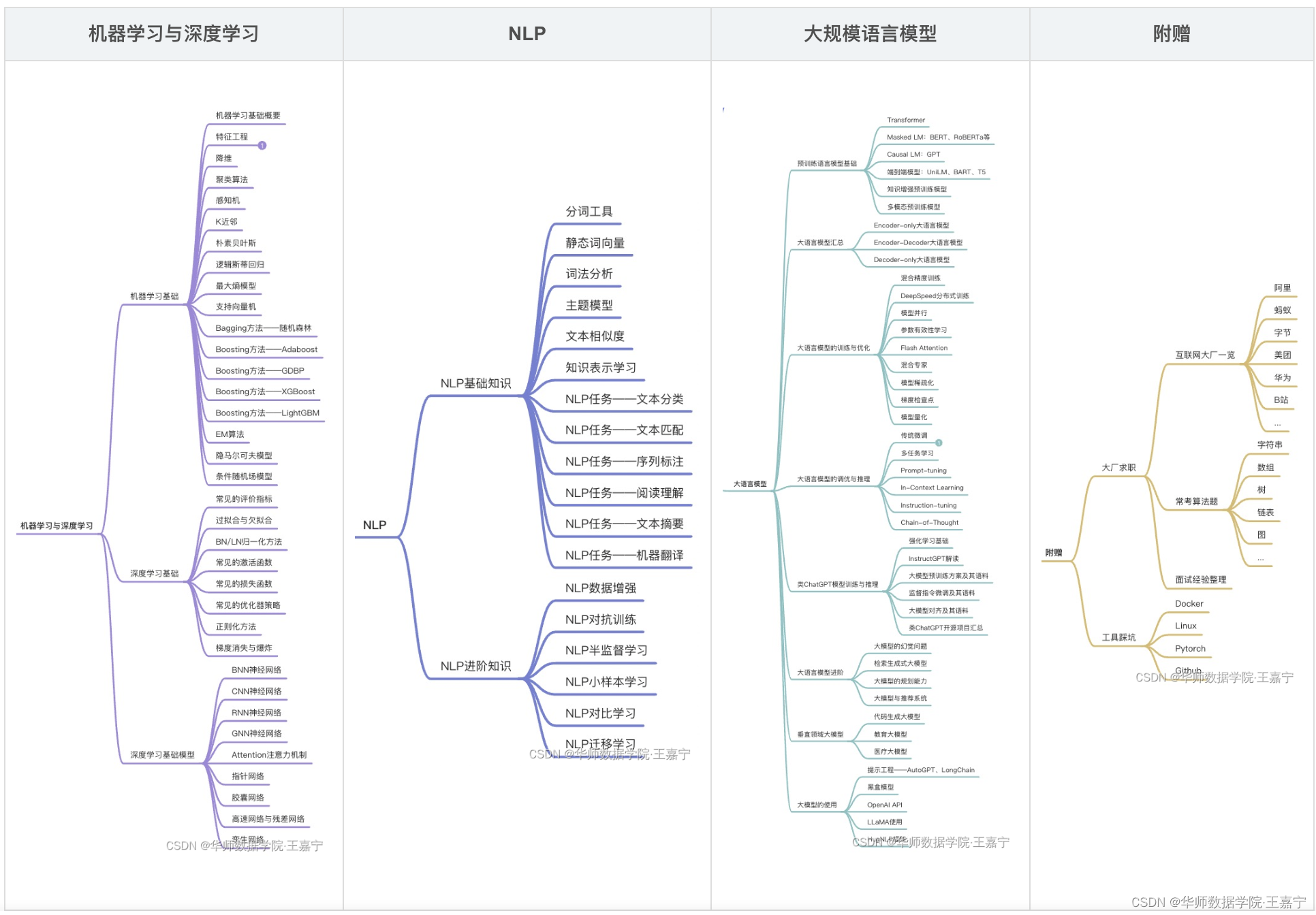
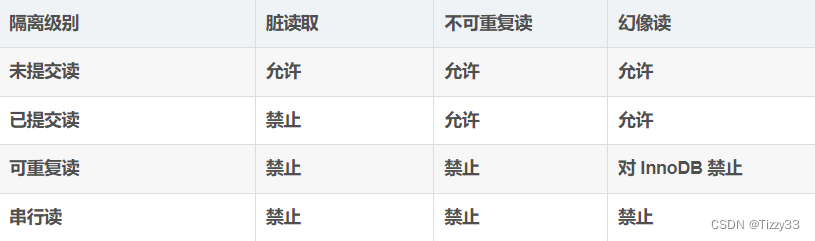
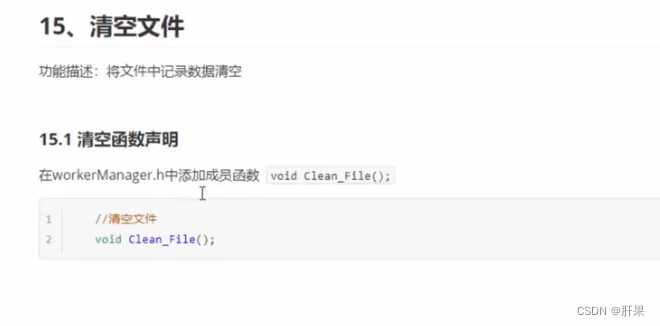
题目详情:
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
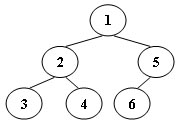
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1简单翻译:
给出一棵树按一定规律给出的节点顺序,要求复建这棵树并且输出这棵树的后序遍历结果
主要思路:
关键一点在于发现题干中给出的push顺序就是原二叉树的前序遍历结果,pop出的顺序就是原二叉树的中序遍历结果
另外,本题节点编号是从1~N,所以在利用中序和前序构造二叉树时要注意传递的实参是分割preorder数组和inorder数组的下标,函数递归返回的是下标对应的值
递归的终止条件不仅有分割起点和终点相等,还有分割起点大于分割终点这种情况,这时要返回空节点
代码实现:
/*
1.实现堆栈的数据结构
2.建树
Push入的顺序是前序遍历
Pop出的顺序是后序遍历
3.后序遍历打印
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 35
#define PUSH "Push"
#define POP "Pop"
#define NONE -1
/*实现堆栈的数据结构*/
typedef struct Stack Stack;
struct Stack {
int Data[MAX_SIZE];
int Rear;
};
void Init(Stack* stackName) {
(*stackName).Rear = -1;
return;
}
bool IsEmpty(Stack* stackName) {
if((*stackName).Rear == -1) return true;
else return false;
}
bool IsFull(Stack* stackName) {
if((*stackName).Rear == MAX_SIZE - 1) return true;
else return false;
}
void Push(Stack* stackName, int data) {
if(IsFull(stackName)) return;
(*stackName).Data[++(*stackName).Rear] = data;
return;
}
void Pop(Stack* stackName) {
if(IsEmpty(stackName)) return;
(*stackName).Rear--;
return;
}
int Top(Stack* stackName) {
if(IsEmpty(stackName)) return NONE;
return (*stackName).Data[(*stackName).Rear];
}
/*建树*/
typedef struct Tree Tree;
struct Tree {
int LeftChild, RightChild;
bool IsRoot;
};
Tree tree[MAX_SIZE];
int Preorder[MAX_SIZE];
int Inorder[MAX_SIZE];
int N;
void GetTraversal() {
Stack stack;
Init(&stack);
scanf("%d", &N);
getchar();
int preCount = 0;
int inCount = 0;
int loop = N * 2;
for(int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
char string[4];
scanf("%s", string);
if(string[1] == 'u') {
int data;
scanf("%d", &data);
Push(&stack, data);
Preorder[preCount++] = data;
}
if(string[1] == 'o') {
int data = Top(&stack);
Pop(&stack);
Inorder[inCount++] = data;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
tree[i].IsRoot = true;
tree[i].LeftChild = NONE;
tree[i].RightChild = NONE;
}
return;
}
int BuildTreeTraversal(int preStart, int preEnd, int inStart, int inEnd) {
if(preStart == preEnd) return Preorder[preEnd];
if(preStart > preEnd) return NONE; //这个说明是遍历到空节点
int root = Preorder[preStart];
int cuttingLine = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if(Inorder[i] == root) {
cuttingLine = i;
break;
}
}
int leftSubtree = (cuttingLine - 1) - inStart + 1;
int rightSubtree = inEnd - (cuttingLine + 1) + 1;
tree[root].LeftChild = BuildTreeTraversal(preStart + 1, preStart + leftSubtree, inStart, cuttingLine - 1);
tree[root].RightChild = BuildTreeTraversal(preStart + leftSubtree + 1, preEnd, cuttingLine + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
void PostPrint(int root) {
if(root == NONE) return;
PostPrint(tree[root].LeftChild);
PostPrint(tree[root].RightChild);
if(--N) printf("%d ", root);
else printf("%d", root);
return;
}
int main() {
GetTraversal();
int root = BuildTreeTraversal(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1);
PostPrint(root);
return 0;
}