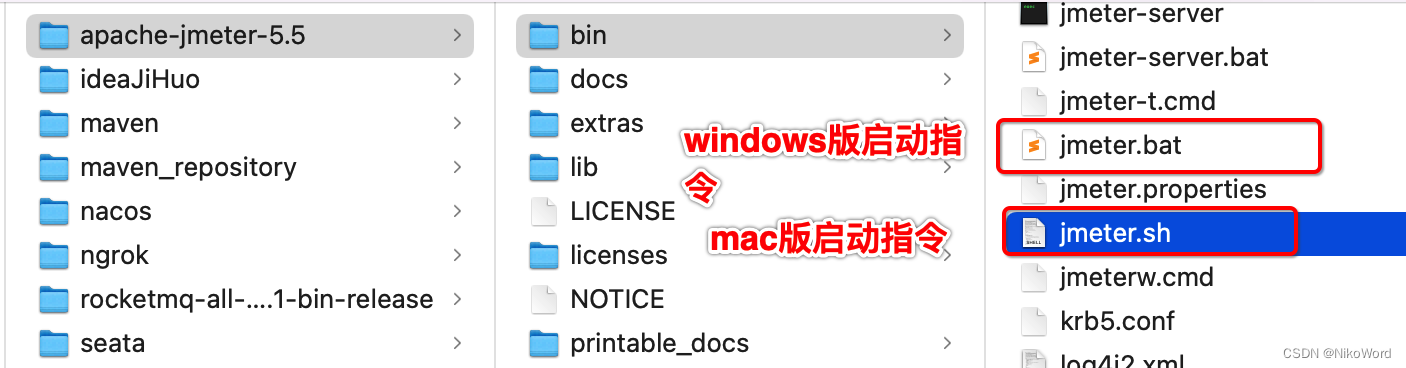
10 / 目录遍历函数

// 打开一个目录
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
参数:
- name: 需要打开的目录的名称
返回值:
DIR * 类型,理解为目录流
错误返回NULL
// 读取目录中的数据
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
- 参数:dirp是opendir返回的结果
- 返回值:
struct dirent,代表读取到的文件的信息
读取到了末尾或者失败了,返回NULL// 关闭目录
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
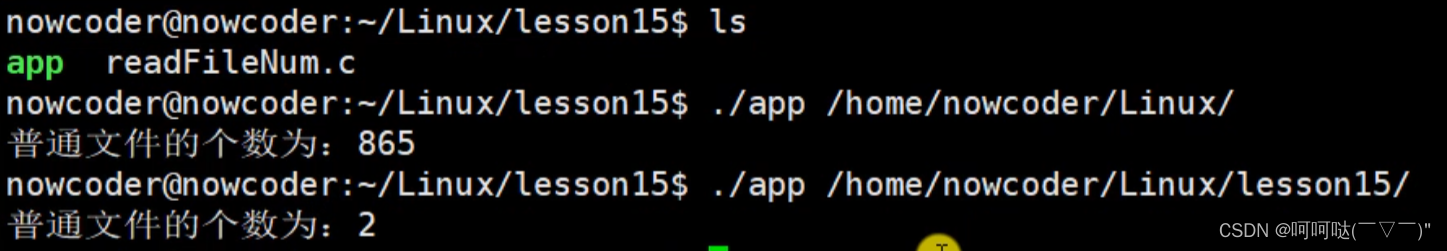
任务:读取某个目录下所有的普通文件的个数
readFileNum.c
/*
// 打开一个目录
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
参数:
- name: 需要打开的目录的名称
返回值:
DIR * 类型,理解为目录流
错误返回NULL
// 读取目录中的数据
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
- 参数:dirp是opendir返回的结果
- 返回值:
struct dirent,代表读取到的文件的信息
读取到了末尾或者失败了,返回NULL
// 关闭目录
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
*/
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int getFileNum(const char * path);
// 读取某个目录下所有的普通文件的个数
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
if(argc < 2) {
printf("%s path\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
int num = getFileNum(argv[1]);
printf("普通文件的个数为:%d\n", num);
return 0;
}
// 用于获取目录下所有普通文件的个数
int getFileNum(const char * path) {
// 1.打开目录
DIR * dir = opendir(path);
if(dir == NULL) {
perror("opendir");
exit(0);
}
struct dirent *ptr;
// 记录普通文件的个数
int total = 0;
while((ptr = readdir(dir)) != NULL) {
// 获取名称
char * dname = ptr->d_name;
// 忽略掉. 和..
if(strcmp(dname, ".") == 0 || strcmp(dname, "..") == 0) {
continue;
}
// 判断是否是普通文件还是目录
if(ptr->d_type == DT_DIR) {
// 目录,需要继续读取这个目录
char newpath[256];
sprintf(newpath, "%s/%s", path, dname);
total += getFileNum(newpath);
}
if(ptr->d_type == DT_REG) {
// 普通文件
total++;
}
}
// 关闭目录
closedir(dir);
return total;
}(1)gcc readFileNum.c -o app
![]()
(2)./app /home/nowcoder/Linux/