螺牙缺陷检测
- 简述
- 去噪
- 椒盐噪声
- 高斯噪声
- 小波变换
- 引导滤波
- 求最大凸包
- 判断曲直
- 全部代码
简述
- 今天收到了一个检测螺牙缺陷的问题,当复习opencv练个手,记录一下基础知识。
- 这里的代码是检测弯曲的,其他缺陷用yolo处理。
- 东家给的图片有的是有干扰的(红框标识),所以要求一下最大凸包。
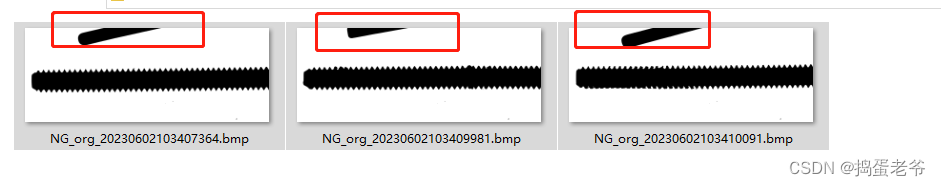
- 里面很多知识是复习用,最终代码在最后一行,给的101张图片,有2个弯曲度超过0.25,来到了0.33以上
- 有个小技巧可以提高弯直的区分度,这里就不介绍了,需要的私信。
去噪
椒盐噪声
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg')
median = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
cv2.imshow('Median filter', median)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
高斯噪声
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg')
gaussian = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5,5), 0)
cv2.imshow('Gaussian filter', gaussian)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
小波变换
import cv2
import pywt
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0)
coeffs = pywt.dwt2(img, 'haar')
cA, (cH, cV, cD) = coeffs
cv2.imshow('Wavelet denoising', pywt.idwt2((cA, (None, None, None)), 'haar'))
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
引导滤波
import numpy as np
import cv2
main_path="D:/Handletiling/NG_org_20230602103406819.bmp"
def guideFilter(I, p, winSize, eps):
mean_I = cv2.blur(I, winSize)
mean_p = cv2.blur(p, winSize)
mean_II = cv2.blur(I * I, winSize)
mean_Ip = cv2.blur(I * p, winSize)
var_I = mean_II - mean_I * mean_I
cov_Ip = mean_Ip - mean_I * mean_p
a = cov_Ip / (var_I + eps)
b = mean_p - a * mean_I
mean_a = cv2.blur(a, winSize)
mean_b = cv2.blur(b, winSize)
q = mean_a * I + mean_b
return q
if __name__ == '__main__':
eps = 0.01
winSize = (5,5)
image = cv2.imread(main_path, cv2.IMREAD_ANYCOLOR)
image = cv2.resize(image, None,fx=0.7, fy=0.7, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
I = image/255.0 #将图像归一化
p =I
guideFilter_img = guideFilter(I, p, winSize, eps)
# 保存导向滤波结果
guideFilter_img = guideFilter_img * 255
guideFilter_img [guideFilter_img > 255] = 255
guideFilter_img = np.round(guideFilter_img )
guideFilter_img = guideFilter_img.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow("image",image)
cv2.imshow("winSize_5", guideFilter_img )
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
求最大凸包
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
from skimage.measure import label
main_path="D:\Handletiling\luoya/NG/NG_org_20230602103407364.bmp"
##method1 --opencv
def get_lagrest_connect_component1(img):
# rgb->gray
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# gaussian filter
img_gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_gray, (5, 5), 0)
# binary exp-threshold=0
_, img_gray = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV) # ret==threshold
# find contour
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(img_gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# cv2.drawContours(img_gray, contours, -1, 255, 3)
# find the area_max region
area = []
for i in range(len(contours)):
area.append(cv2.contourArea(contours[i]))
if len(area) >= 1:
max_idx = np.argmax(area)
max_contour_area = area[max_idx]
for k in range(len(contours)):
if k != max_idx:
cv2.fillPoly(img_gray, [contours[k]], 0)
else:
max_contour_area = 0
return max_contour_area, img_gray
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.imread(main_path)
max_area, img_gray = get_lagrest_connect_component1(img)
print(max_area)
cv2.imwrite('img_gray.jpg', img_gray)
判断曲直
1.查找轮廓,提取凸包
2.获得点集
3.计算导数方差
4.比较阈值
def calccurl(str,thresh):
img = cv2.imread(str)
# cv2.imshow('src',img)
#提取凸包
max_area, img_gray =get_lagrest_connect_component1(img)
gray = img_gray
#阈值处理
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,0)
#查找轮廓,提取凸包
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
cv2.polylines(img_gray,[hull],True,(255,255,0),2)
min_x=min(hull[:,0,0])
max_x=max(hull[:,0,0])
topList=[]
bottomList=[]
thresh_left=220
thresh_right=30
count=hull.shape[0]
isthesame=False
for i in range(hull.shape[0]):
point = tuple(hull[i][0]) #
# cv2.circle(img, point, 1, (0, 255, 0) , 12)
if point[0]<(max_x-thresh_right) and point[0]>(min_x+thresh_left):
length=binary.shape[0]
x1 = np.linspace(start=0, stop=length-1, num=length)
temp=x1 * (binary[:, point[0]] / 255)
n = np.sum(temp > 0)
index=temp.sum()/(n*1.)
# if i in[0,count-1]:
# if not isthesame:
# isthesame=True
# else:
# continue
if point[1]>index:
bottomList.append(point)
# cv2.putText(img, str(i), point, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# print(str(i) + ":", point)
else:
topList.append(point)
# cv2.putText(img, str(i), point, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# print(str(i) + ":", point)
space = np.linspace(start=min_x+thresh_left, stop=max_x-thresh_right, num=15)
space= np.ceil(space)
length = img_gray.shape[0]
x1 = np.linspace(start=0, stop=length - 1, num=length)
tempM = (img_gray / 255.)* x1[:,None]
if len(topList) >len(bottomList):
topList.clear()
for x in space:
temp=tempM[:, int(x)]
temp = temp[temp != 0]
topList.append([x,temp.min()])
# cv2.circle(img, (int(x),int(temp.min())), 1, (0, 255, 0), 12)
# cv2.putText(img, str(x), (int(x),int(temp.min())), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
line = np.array(topList, dtype=float)
else:
bottomList.clear()
for x in space:
temp = tempM[:, int(x)]
temp = temp[temp != 0]
bottomList.append([x, temp.max()])
# cv2.circle(img, (int(x), int(temp.max())), 1, (0, 255, 0), 12)
# cv2.putText(img, str(x), (int(x),int(temp.max())), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
line = np.array(bottomList, dtype=float)
if line.size > 0:
#method1
slopend=(line[-1,1]-line[0,1])/(line[-1,0]-line[0,0])
slop=(line[1:,1]-line[:-1,1])/((line[1:,0]-line[:-1,0])+0.0001)
dis=slop-slopend
std = np.std(dis)
if std>thresh:
return 0,std
return 1,0
# method2
# std= np.std(slop)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filesPath = os.listdir(main_path)
threshstd=0.025
files = tqdm(filesPath)
for file in files:
absolute_file_path = os.path.join(main_path, file)
if '.bmp' in absolute_file_path.lower():
result,std=calccurl(absolute_file_path,threshstd)
if result:
print(absolute_file_path+":", std)
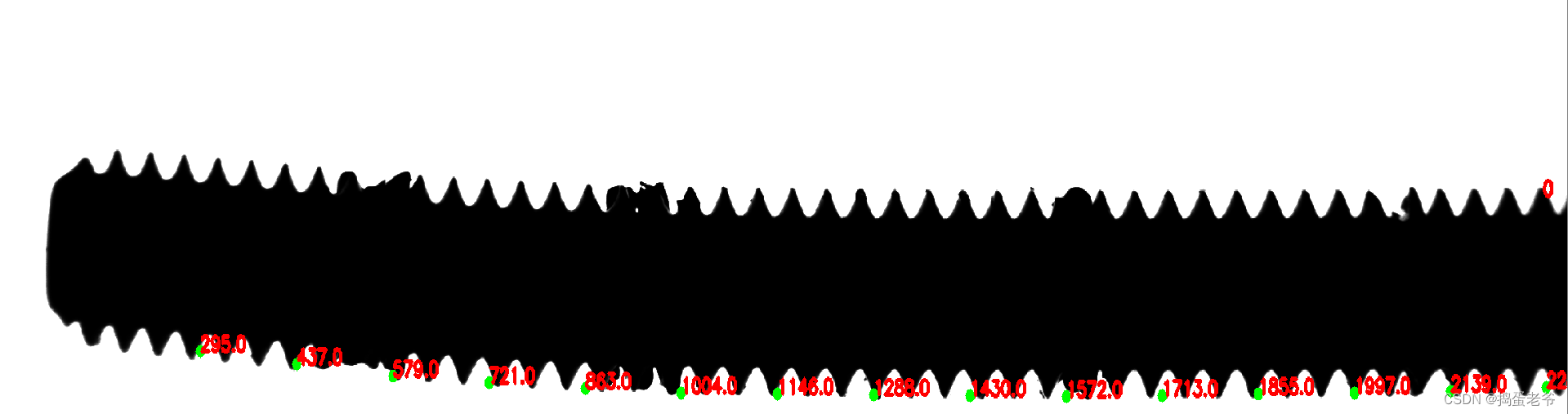
结果
--------------------
std: 0.037498851806574245
全部代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
import shutil
#需要检测弯曲的图片的文件夹地址
main_path="D:\Handletiling\src"
def get_lagrest_connect_component1(img):
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_gray, (5, 5), 0)
_, img_gray = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV) # ret==threshold
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(img_gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
area = []
for i in range(len(contours)):
area.append(cv2.contourArea(contours[i]))
if len(area) >= 1:
max_idx = np.argmax(area)
max_contour_area = area[max_idx]
for k in range(len(contours)):
if k != max_idx:
cv2.fillPoly(img_gray, [contours[k]], 0)
else:
max_contour_area = 0
return max_contour_area, img_gray
def calccurl(str,thresh):
img = cv2.imread(str)
#提取凸包
max_area, img_gray =get_lagrest_connect_component1(img)
gray = img_gray
#阈值处理
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,0)
#查找轮廓
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
cv2.polylines(img_gray,[hull],True,(255,255,0),2)
min_x=min(hull[:,0,0])
max_x=max(hull[:,0,0])
topList=[]
bottomList=[]
thresh_left=220
thresh_right=30
count=hull.shape[0]
isthesame=False
for i in range(hull.shape[0]):
point = tuple(hull[i][0]) #
# cv2.circle(img, point, 1, (0, 255, 0) , 12)
if point[0]<(max_x-thresh_right) and point[0]>(min_x+thresh_left):
length=binary.shape[0]
x1 = np.linspace(start=0, stop=length-1, num=length)
temp=x1 * (binary[:, point[0]] / 255)
n = np.sum(temp > 0)
index=temp.sum()/(n*1.)
# if i in[0,count-1]:
# if not isthesame:
# isthesame=True
# else:
# continue
if point[1]>index:
bottomList.append(point)
# cv2.putText(img, str(i), point, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# print(str(i) + ":", point)
else:
topList.append(point)
# cv2.putText(img, str(i), point, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# print(str(i) + ":", point)
space = np.linspace(start=min_x+thresh_left, stop=max_x-thresh_right, num=15)
space= np.ceil(space)
length = img_gray.shape[0]
x1 = np.linspace(start=0, stop=length - 1, num=length)
tempM = (img_gray / 255.)* x1[:,None]
if len(topList) >len(bottomList):
topList.clear()
for x in space:
temp=tempM[:, int(x)]
temp = temp[temp != 0]
topList.append([x,temp.min()])
# cv2.circle(img, (int(x),int(temp.min())), 1, (0, 255, 0), 12)
# cv2.putText(img, str(x), (int(x),int(temp.min())), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
line = np.array(topList, dtype=float)
else:
bottomList.clear()
for x in space:
temp = tempM[:, int(x)]
temp = temp[temp != 0]
bottomList.append([x, temp.max()])
# cv2.circle(img, (int(x), int(temp.max())), 1, (0, 255, 0), 12)
# cv2.putText(img, str(x), (int(x),int(temp.max())), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 255), 3)
line = np.array(bottomList, dtype=float)
if line.size > 0:
#method1
slopend=(line[-1,1]-line[0,1])/(line[-1,0]-line[0,0])
slop=(line[1:,1]-line[:-1,1])/((line[1:,0]-line[:-1,0])+0.0001)
dis=slop-slopend
std = np.std(dis)
if std>thresh:
return 0,std
return 1,0
# method2
# std= np.std(slop)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filesPath = os.listdir(main_path)
threshstd=0.025
files = tqdm(filesPath)
for file in files:
absolute_file_path = os.path.join(main_path, file)
if '.bmp' in absolute_file_path.lower():
result,std=calccurl(absolute_file_path,threshstd)
if not result:
print(absolute_file_path+"-图片弯曲:", std)
#结果
[00:00<00:01, 44.18it/s]D:\Handletiling\src\NG_org_20230602103409544.bmp-图片弯曲: 0.0334415572613885
[00:00<00:01, 44.24it/s]D:\Handletiling\src\NG_org_20230602103410530.bmp-图片弯曲: 0.037498851806574245