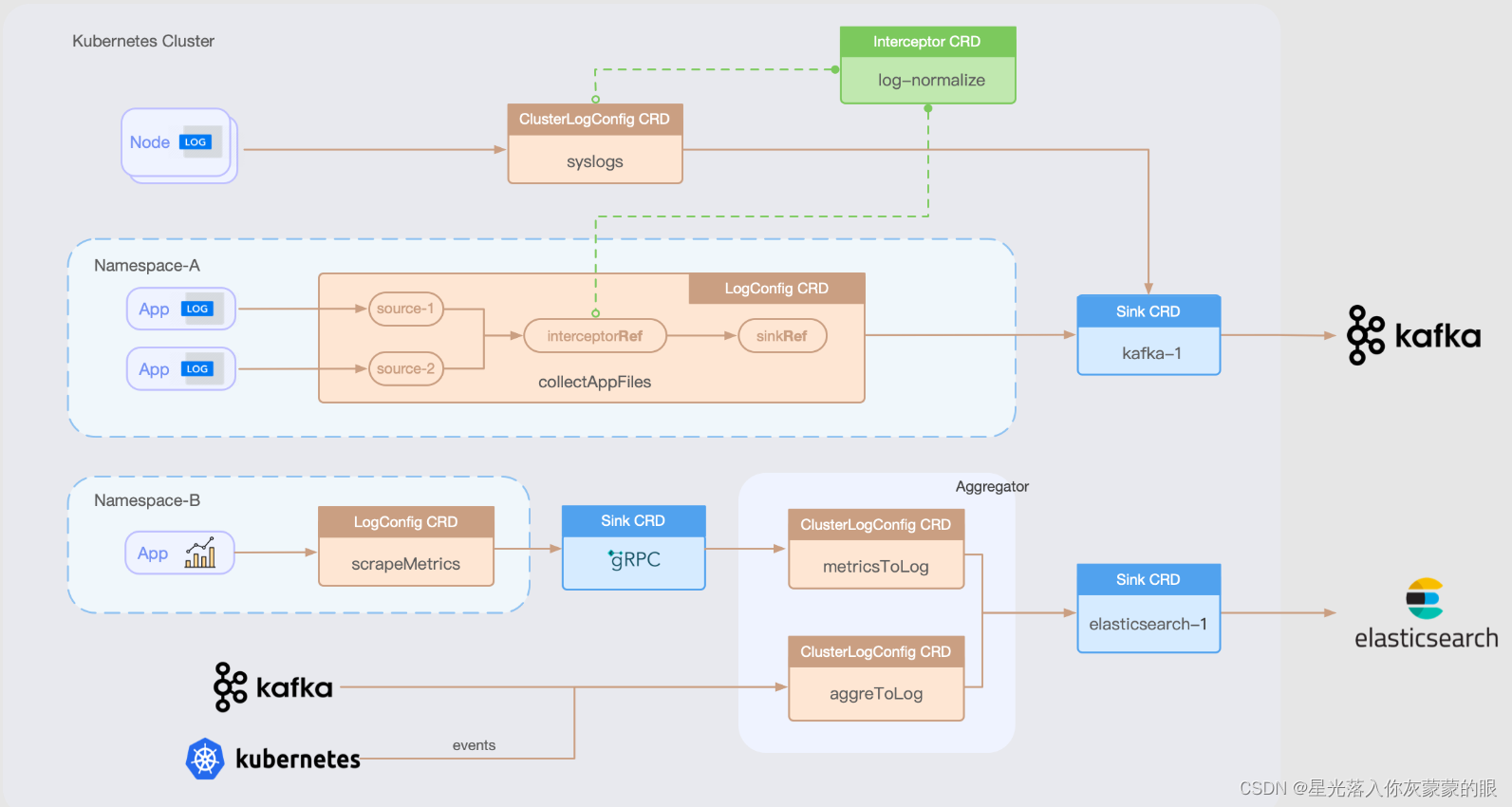
37款传感器与执行器的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止这37种的。鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器和执行器模块,依照实践出真知(一定要动手做)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里准备逐一动手尝试系列实验,不管成功(程序走通)与否,都会记录下来—小小的进步或是搞不掂的问题,希望能够抛砖引玉。
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
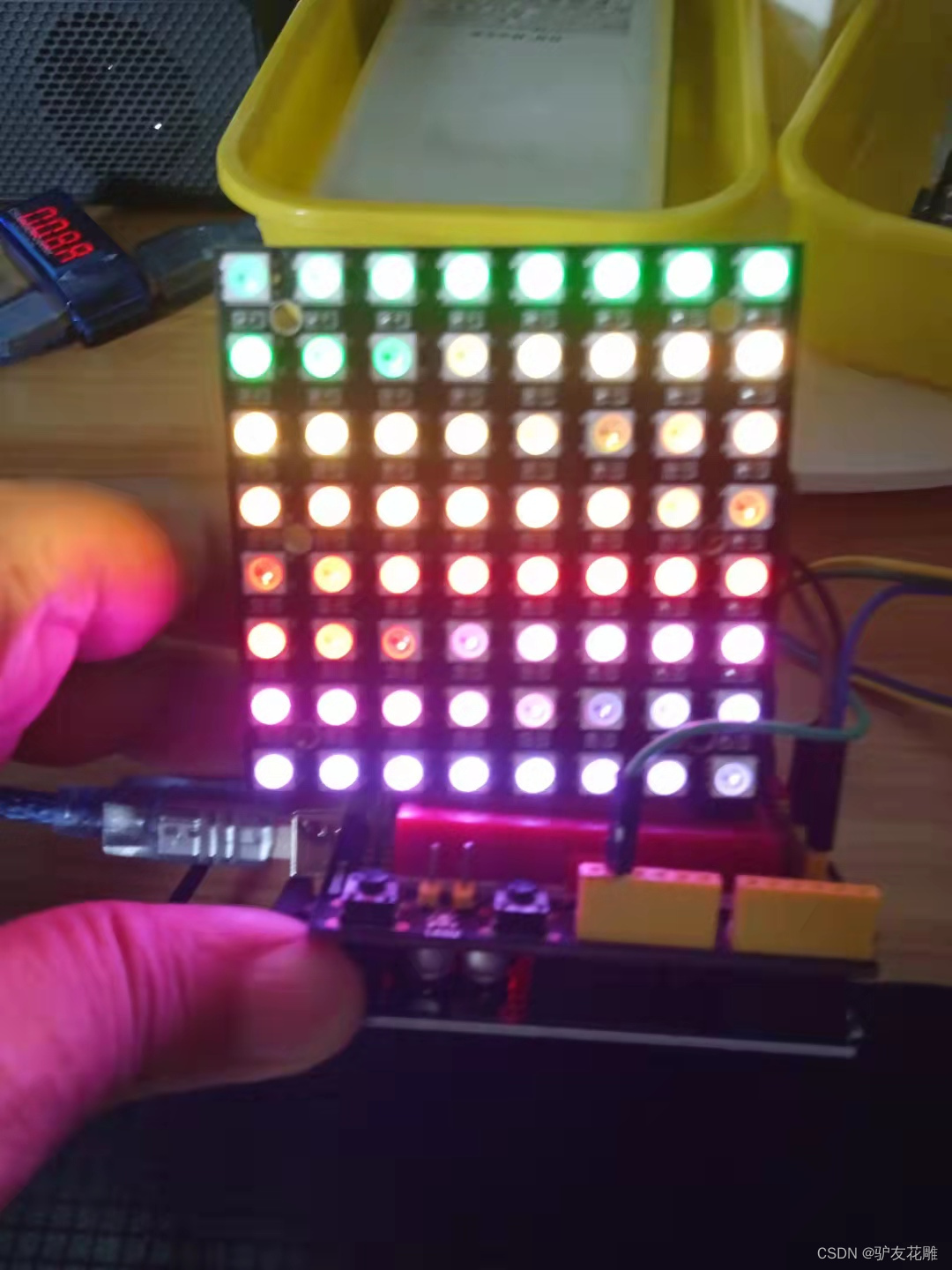
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏

【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
安装NeoPixel库,工具—管理库—搜索NeoPixel—安装
安装Adafruit_NeoPixel库,
下载https://learn.adafruit.com/adafr … ibrary-installation
程序之六:复合流水彩虹灯
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
安装NeoPixel库,工具—管理库—搜索NeoPixel—安装
安装Adafruit_NeoPixel库,
下载https://learn.adafruit.com/adafr ... ibrary-installation
程序之六:复合流水彩虹灯
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 6
#define BRIGHTNESS 64
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(64, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.setBrightness(BRIGHTNESS);
strip.begin();
strip.show();
}
void loop() {
colorWipe(strip.Color(150, 0, 0), 50); // Red
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 150, 0), 50); // Green
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 150), 50); // Blue
colorWipe(strip.Color(150, 150, 150), 50); // BlueWite
rainbowCycle(1);
}
void colorWipe(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
void rainbow(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for (j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
for (i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel((i + j) & 255 ));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
void rainbowCycle(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for (j = 0; j < 256 * 5; j++) { // 5 cycles of all colors on wheel
for (i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos) {
if (WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color(WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3, 0);
} else if (WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color(255 - WheelPos * 3, 0, WheelPos * 3);
} else {
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(0, WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3);
}
}
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
程序之七:复合飘逸彩虹满屏灯
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
安装NeoPixel库,工具—管理库—搜索NeoPixel—安装
安装Adafruit_NeoPixel库,
下载https://learn.adafruit.com/adafr ... ibrary-installation
程序之七:复合飘逸彩虹满屏灯
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h>
#endif
#define PIN 6
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = Arduino pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
// NEO_RGBW Pixels are wired for RGBW bitstream (NeoPixel RGBW products)
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(64, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
// IMPORTANT: To reduce NeoPixel burnout risk, add 1000 uF capacitor across
// pixel power leads, add 300 - 500 Ohm resistor on first pixel's data input
// and minimize distance between Arduino and first pixel. Avoid connecting
// on a live circuit...if you must, connect GND first.
void setup() {
// This is for Trinket 5V 16MHz, you can remove these three lines if you are not using a Trinket
#if defined (__AVR_ATtiny85__)
if (F_CPU == 16000000) clock_prescale_set(clock_div_1);
#endif
// End of trinket special code
strip.begin();
strip.setBrightness(50);
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
// Some example procedures showing how to display to the pixels:
colorWipe(strip.Color(255, 0, 0), 50); // Red
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 255, 0), 50); // Green
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 255), 50); // Blue
//colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 0, 255), 50); // White RGBW
// Send a theater pixel chase in...
theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 127, 127), 50); // White
theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 0, 0), 50); // Red
theaterChase(strip.Color(0, 0, 127), 50); // Blue
rainbow(20);
rainbowCycle(20);
theaterChaseRainbow(50);
}
// Fill the dots one after the other with a color
void colorWipe(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
void rainbow(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256; j++) {
for(i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel((i+j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
// Slightly different, this makes the rainbow equally distributed throughout
void rainbowCycle(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256*5; j++) { // 5 cycles of all colors on wheel
for(i=0; i< strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
//Theatre-style crawling lights.
void theaterChase(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
for (int j=0; j<10; j++) { //do 10 cycles of chasing
for (int q=0; q < 3; q++) {
for (uint16_t i=0; i < strip.numPixels(); i=i+3) {
strip.setPixelColor(i+q, c); //turn every third pixel on
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
for (uint16_t i=0; i < strip.numPixels(); i=i+3) {
strip.setPixelColor(i+q, 0); //turn every third pixel off
}
}
}
}
//Theatre-style crawling lights with rainbow effect
void theaterChaseRainbow(uint8_t wait) {
for (int j=0; j < 256; j++) { // cycle all 256 colors in the wheel
for (int q=0; q < 3; q++) {
for (uint16_t i=0; i < strip.numPixels(); i=i+3) {
strip.setPixelColor(i+q, Wheel( (i+j) % 255)); //turn every third pixel on
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
for (uint16_t i=0; i < strip.numPixels(); i=i+3) {
strip.setPixelColor(i+q, 0); //turn every third pixel off
}
}
}
}
// Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
// The colours are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos) {
WheelPos = 255 - WheelPos;
if(WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color(255 - WheelPos * 3, 0, WheelPos * 3);
}
if(WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color(0, WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3);
}
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3, 0);
}
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
程序之八:复合彩虹滚动流水灯
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
安装NeoPixel库,工具—管理库—搜索NeoPixel—安装
安装Adafruit_NeoPixel库,
下载https://learn.adafruit.com/adafr ... ibrary-installation
程序之八:复合彩虹滚动流水灯
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h> // Required for 16 MHz Adafruit Trinket
#endif
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
// On a Trinket or Gemma we suggest changing this to 1:
#define LED_PIN 6
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino?
#define LED_COUNT 64
// Declare our NeoPixel strip object:
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
// Argument 1 = Number of pixels in NeoPixel strip
// Argument 2 = Arduino pin number (most are valid)
// Argument 3 = Pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
// NEO_RGBW Pixels are wired for RGBW bitstream (NeoPixel RGBW products)
// setup() function -- runs once at startup --------------------------------
void setup() {
// These lines are specifically to support the Adafruit Trinket 5V 16 MHz.
// Any other board, you can remove this part (but no harm leaving it):
#if defined(__AVR_ATtiny85__) && (F_CPU == 16000000)
clock_prescale_set(clock_div_1);
#endif
// END of Trinket-specific code.
strip.begin(); // INITIALIZE NeoPixel strip object (REQUIRED)
strip.show(); // Turn OFF all pixels ASAP
strip.setBrightness(50); // Set BRIGHTNESS to about 1/5 (max = 255)
}
// loop() function -- runs repeatedly as long as board is on ---------------
void loop() {
// Fill along the length of the strip in various colors...
colorWipe(strip.Color(255, 0, 0), 50); // Red
colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 255, 0), 50); // Green
colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 0, 255), 50); // Blue
// Do a theater marquee effect in various colors...
theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 127, 127), 50); // White, half brightness
theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 0, 0), 50); // Red, half brightness
theaterChase(strip.Color( 0, 0, 127), 50); // Blue, half brightness
rainbow(10); // Flowing rainbow cycle along the whole strip
theaterChaseRainbow(50); // Rainbow-enhanced theaterChase variant
}
// Some functions of our own for creating animated effects -----------------
// Fill strip pixels one after another with a color. Strip is NOT cleared
// first; anything there will be covered pixel by pixel. Pass in color
// (as a single 'packed' 32-bit value, which you can get by calling
// strip.Color(red, green, blue) as shown in the loop() function above),
// and a delay time (in milliseconds) between pixels.
void colorWipe(uint32_t color, int wait) {
for(int i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) { // For each pixel in strip...
strip.setPixelColor(i, color); // Set pixel's color (in RAM)
strip.show(); // Update strip to match
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
}
}
// Theater-marquee-style chasing lights. Pass in a color (32-bit value,
// a la strip.Color(r,g,b) as mentioned above), and a delay time (in ms)
// between frames.
void theaterChase(uint32_t color, int wait) {
for(int a=0; a<10; a++) { // Repeat 10 times...
for(int b=0; b<3; b++) { // 'b' counts from 0 to 2...
strip.clear(); // Set all pixels in RAM to 0 (off)
// 'c' counts up from 'b' to end of strip in steps of 3...
for(int c=b; c<strip.numPixels(); c += 3) {
strip.setPixelColor(c, color); // Set pixel 'c' to value 'color'
}
strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
}
}
}
// Rainbow cycle along whole strip. Pass delay time (in ms) between frames.
void rainbow(int wait) {
// Hue of first pixel runs 5 complete loops through the color wheel.
// Color wheel has a range of 65536 but it's OK if we roll over, so
// just count from 0 to 5*65536. Adding 256 to firstPixelHue each time
// means we'll make 5*65536/256 = 1280 passes through this outer loop:
for(long firstPixelHue = 0; firstPixelHue < 5*65536; firstPixelHue += 256) {
for(int i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) { // For each pixel in strip...
// Offset pixel hue by an amount to make one full revolution of the
// color wheel (range of 65536) along the length of the strip
// (strip.numPixels() steps):
int pixelHue = firstPixelHue + (i * 65536L / strip.numPixels());
// strip.ColorHSV() can take 1 or 3 arguments: a hue (0 to 65535) or
// optionally add saturation and value (brightness) (each 0 to 255).
// Here we're using just the single-argument hue variant. The result
// is passed through strip.gamma32() to provide 'truer' colors
// before assigning to each pixel:
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.gamma32(strip.ColorHSV(pixelHue)));
}
strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
}
}
// Rainbow-enhanced theater marquee. Pass delay time (in ms) between frames.
void theaterChaseRainbow(int wait) {
int firstPixelHue = 0; // First pixel starts at red (hue 0)
for(int a=0; a<30; a++) { // Repeat 30 times...
for(int b=0; b<3; b++) { // 'b' counts from 0 to 2...
strip.clear(); // Set all pixels in RAM to 0 (off)
// 'c' counts up from 'b' to end of strip in increments of 3...
for(int c=b; c<strip.numPixels(); c += 3) {
// hue of pixel 'c' is offset by an amount to make one full
// revolution of the color wheel (range 65536) along the length
// of the strip (strip.numPixels() steps):
int hue = firstPixelHue + c * 65536L / strip.numPixels();
uint32_t color = strip.gamma32(strip.ColorHSV(hue)); // hue -> RGB
strip.setPixelColor(c, color); // Set pixel 'c' to value 'color'
}
strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
firstPixelHue += 65536 / 90; // One cycle of color wheel over 90 frames
}
}
}
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
程序之九:按键控制进入下段彩灯程序
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
ws —— D2
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
安装NeoPixel库,工具—管理库—搜索NeoPixel—安装
安装Adafruit_NeoPixel库,
下载https://learn.adafruit.com/adafr ... ibrary-installation
程序之九:按键控制进入下段彩灯程序
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
ws —— D2
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h> // Required for 16 MHz Adafruit Trinket
#endif
// Digital IO pin connected to the button. This will be driven with a
// pull-up resistor so the switch pulls the pin to ground momentarily.
// On a high -> low transition the button press logic will execute.
#define BUTTON_PIN 2
#define PIXEL_PIN 7 // Digital IO pin connected to the NeoPixels.
#define PIXEL_COUNT 64 // Number of NeoPixels
// Declare our NeoPixel strip object:
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip(PIXEL_COUNT, PIXEL_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
// Argument 1 = Number of pixels in NeoPixel strip
// Argument 2 = Arduino pin number (most are valid)
// Argument 3 = Pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
// NEO_RGBW Pixels are wired for RGBW bitstream (NeoPixel RGBW products)
boolean oldState = HIGH;
int mode = 0; // Currently-active animation mode, 0-9
void setup() {
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
strip.begin(); // Initialize NeoPixel strip object (REQUIRED)
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
// Get current button state.
boolean newState = digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN);
// Check if state changed from high to low (button press).
if ((newState == LOW) && (oldState == HIGH)) {
// Short delay to debounce button.
delay(20);
// Check if button is still low after debounce.
newState = digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN);
if (newState == LOW) { // Yes, still low
if (++mode > 8) mode = 0; // Advance to next mode, wrap around after #8
switch (mode) { // Start the new animation...
case 0:
colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 0, 0), 50); // Black/off
break;
case 1:
colorWipe(strip.Color(255, 0, 0), 50); // Red
break;
case 2:
colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 255, 0), 50); // Green
break;
case 3:
colorWipe(strip.Color( 0, 0, 255), 50); // Blue
break;
case 4:
theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 127, 127), 50); // White
break;
case 5:
theaterChase(strip.Color(127, 0, 0), 50); // Red
break;
case 6:
theaterChase(strip.Color( 0, 0, 127), 50); // Blue
break;
case 7:
rainbow(10);
break;
case 8:
theaterChaseRainbow(50);
break;
}
}
}
// Set the last-read button state to the old state.
oldState = newState;
}
// Fill strip pixels one after another with a color. Strip is NOT cleared
// first; anything there will be covered pixel by pixel. Pass in color
// (as a single 'packed' 32-bit value, which you can get by calling
// strip.Color(red, green, blue) as shown in the loop() function above),
// and a delay time (in milliseconds) between pixels.
void colorWipe(uint32_t color, int wait) {
for (int i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) { // For each pixel in strip...
strip.setPixelColor(i, color); // Set pixel's color (in RAM)
strip.show(); // Update strip to match
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
}
}
// Theater-marquee-style chasing lights. Pass in a color (32-bit value,
// a la strip.Color(r,g,b) as mentioned above), and a delay time (in ms)
// between frames.
void theaterChase(uint32_t color, int wait) {
for (int a = 0; a < 10; a++) { // Repeat 10 times...
for (int b = 0; b < 3; b++) { // 'b' counts from 0 to 2...
strip.clear(); // Set all pixels in RAM to 0 (off)
// 'c' counts up from 'b' to end of strip in steps of 3...
for (int c = b; c < strip.numPixels(); c += 3) {
strip.setPixelColor(c, color); // Set pixel 'c' to value 'color'
}
strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
}
}
}
// Rainbow cycle along whole strip. Pass delay time (in ms) between frames.
void rainbow(int wait) {
// Hue of first pixel runs 3 complete loops through the color wheel.
// Color wheel has a range of 65536 but it's OK if we roll over, so
// just count from 0 to 3*65536. Adding 256 to firstPixelHue each time
// means we'll make 3*65536/256 = 768 passes through this outer loop:
for (long firstPixelHue = 0; firstPixelHue < 3 * 65536; firstPixelHue += 256) {
for (int i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) { // For each pixel in strip...
// Offset pixel hue by an amount to make one full revolution of the
// color wheel (range of 65536) along the length of the strip
// (strip.numPixels() steps):
int pixelHue = firstPixelHue + (i * 65536L / strip.numPixels());
// strip.ColorHSV() can take 1 or 3 arguments: a hue (0 to 65535) or
// optionally add saturation and value (brightness) (each 0 to 255).
// Here we're using just the single-argument hue variant. The result
// is passed through strip.gamma32() to provide 'truer' colors
// before assigning to each pixel:
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.gamma32(strip.ColorHSV(pixelHue)));
}
strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
}
}
// Rainbow-enhanced theater marquee. Pass delay time (in ms) between frames.
void theaterChaseRainbow(int wait) {
int firstPixelHue = 0; // First pixel starts at red (hue 0)
for (int a = 0; a < 30; a++) { // Repeat 30 times...
for (int b = 0; b < 3; b++) { // 'b' counts from 0 to 2...
strip.clear(); // Set all pixels in RAM to 0 (off)
// 'c' counts up from 'b' to end of strip in increments of 3...
for (int c = b; c < strip.numPixels(); c += 3) {
// hue of pixel 'c' is offset by an amount to make one full
// revolution of the color wheel (range 65536) along the length
// of the strip (strip.numPixels() steps):
int hue = firstPixelHue + c * 65536L / strip.numPixels();
uint32_t color = strip.gamma32(strip.ColorHSV(hue)); // hue -> RGB
strip.setPixelColor(c, color); // Set pixel 'c' to value 'color'
}
strip.show(); // Update strip with new contents
delay(wait); // Pause for a moment
firstPixelHue += 65536 / 90; // One cycle of color wheel over 90 frames
}
}
}
视频——程序之六:复合流水彩虹灯
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNDU2ODUwMTE2NA==.html
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十三:颜色调色板
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十三:颜色调色板
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <FastLED.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define NUM_LEDS 64
#define BRIGHTNESS 23
#define LED_TYPE WS2811
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define UPDATES_PER_SECOND 100 //定义每秒更新数
// This example shows several ways to set up and use 'palettes' of colors
// with FastLED.
//
// These compact palettes provide an easy way to re-colorize your
// animation on the fly, quickly, easily, and with low overhead.
//
// USING palettes is MUCH simpler in practice than in theory, so first just
// run this sketch, and watch the pretty lights as you then read through
// the code. Although this sketch has eight (or more) different color schemes,
// the entire sketch compiles down to about 6.5K on AVR.
//
// FastLED provides a few pre-configured color palettes, and makes it
// extremely easy to make up your own color schemes with palettes.
//
// Some notes on the more abstract 'theory and practice' of
// FastLED compact palettes are at the bottom of this file.
CRGBPalette16 currentPalette;
TBlendType currentBlending;
extern CRGBPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette;
extern const TProgmemPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette_p PROGMEM;
void setup() {
delay( 3000 ); // power-up safety delay
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
currentPalette = RainbowColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
void loop()
{
ChangePalettePeriodically();
static uint8_t startIndex = 0;
startIndex = startIndex + 1; /* motion speed */
FillLEDsFromPaletteColors( startIndex);
FastLED.show();
FastLED.delay(1000 / UPDATES_PER_SECOND);
}
void FillLEDsFromPaletteColors( uint8_t colorIndex)
{
uint8_t brightness = 255;
for ( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; ++i) {
leds[i] = ColorFromPalette( currentPalette, colorIndex, brightness, currentBlending);
colorIndex += 3;
}
}
// There are several different palettes of colors demonstrated here.
//
// FastLED provides several 'preset' palettes: RainbowColors_p, RainbowStripeColors_p,
// OceanColors_p, CloudColors_p, LavaColors_p, ForestColors_p, and PartyColors_p.
//
// Additionally, you can manually define your own color palettes, or you can write
// code that creates color palettes on the fly. All are shown here.
void ChangePalettePeriodically()
{
uint8_t secondHand = (millis() / 1000) % 60;
static uint8_t lastSecond = 99;
if ( lastSecond != secondHand) {
lastSecond = secondHand;
if ( secondHand == 0) {
currentPalette = RainbowColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 10) {
currentPalette = RainbowStripeColors_p;
currentBlending = NOBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 15) {
currentPalette = RainbowStripeColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 20) {
SetupPurpleAndGreenPalette();
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 25) {
SetupTotallyRandomPalette();
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 30) {
SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette();
currentBlending = NOBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 35) {
SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette();
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 40) {
currentPalette = CloudColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 45) {
currentPalette = PartyColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 50) {
currentPalette = myRedWhiteBluePalette_p;
currentBlending = NOBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 55) {
currentPalette = myRedWhiteBluePalette_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
}
}
// This function fills the palette with totally random colors.
void SetupTotallyRandomPalette()
{
for ( int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
currentPalette[i] = CHSV( random8(), 255, random8());
}
}
// This function sets up a palette of black and white stripes,
// using code. Since the palette is effectively an array of
// sixteen CRGB colors, the various fill_* functions can be used
// to set them up.
void SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette()
{
// 'black out' all 16 palette entries...
fill_solid( currentPalette, 16, CRGB::Black);
// and set every fourth one to white.
currentPalette[0] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[4] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[8] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[12] = CRGB::White;
}
// This function sets up a palette of purple and green stripes.
void SetupPurpleAndGreenPalette()
{
CRGB purple = CHSV( HUE_PURPLE, 255, 255);
CRGB green = CHSV( HUE_GREEN, 255, 255);
CRGB black = CRGB::Black;
currentPalette = CRGBPalette16(
green, green, black, black,
purple, purple, black, black,
green, green, black, black,
purple, purple, black, black );
}
// This example shows how to set up a static color palette
// which is stored in PROGMEM (flash), which is almost always more
// plentiful than RAM. A static PROGMEM palette like this
// takes up 64 bytes of flash.
const TProgmemPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette_p PROGMEM =
{
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray, // 'white' is too bright compared to red and blue
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Black
};
// Additional notes on FastLED compact palettes:
//
// Normally, in computer graphics, the palette (or "color lookup table")
// has 256 entries, each containing a specific 24-bit RGB color. You can then
// index into the color palette using a simple 8-bit (one byte) value.
// A 256-entry color palette takes up 768 bytes of RAM, which on Arduino
// is quite possibly "too many" bytes.
//
// FastLED does offer traditional 256-element palettes, for setups that
// can afford the 768-byte cost in RAM.
//
// However, FastLED also offers a compact alternative. FastLED offers
// palettes that store 16 distinct entries, but can be accessed AS IF
// they actually have 256 entries; this is accomplished by interpolating
// between the 16 explicit entries to create fifteen intermediate palette
// entries between each pair.
//
// So for example, if you set the first two explicit entries of a compact
// palette to Green (0,255,0) and Blue (0,0,255), and then retrieved
// the first sixteen entries from the virtual palette (of 256), you'd get
// Green, followed by a smooth gradient from green-to-blue, and then Blue.
实验场景图