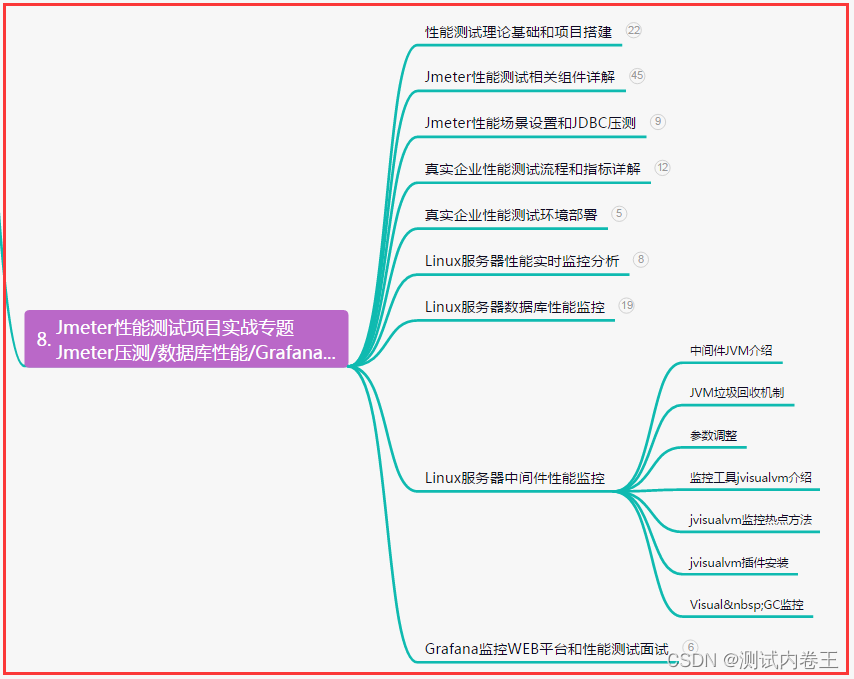
第2章-后置工厂处理器和Bean生命周期
后置工厂处理器属于后置处理器,后置处理器是Spring最核心的部分,Spring几乎所有的附加功能全由它完成。
什么是BeanPostProcessor?
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance 正在创建的bean的实例
* @param beanName the name of the bean 该bean的名称
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; 返回的bean是包装过后的bean
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
/**
* 这个方法是BeanPostProcessor接口中的一个方法,
* 用于在bean初始化回调之前(如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义init-method),
* 使用这个方法对实例化出来的bean(方法的形参)进行包装,此时这个bean的属性值已经被填充了。
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
/**
* 这个方法是BeanPostProcessor接口中的一个方法,
* 用于在bean初始化回调之后(如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义init-method),将该方法应用于当前给定的新bean实例。
* bean的属性值已经被填充。
* In case of a FactoryBean,讲的是FactoryBean生产bean对应的逻辑,暂时忽略
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
看一下各个方法的注释,如果感觉不能理解的话,就记住他们是在哪个位置执行就可以,InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义init-method的前后
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}

核心就是我们对于传进来的参数,可以修改,覆盖,添加它的东西。对于BeanPostProcessor来说,传进来的参数是(Object bean, String beanName) ,它都已经把bean传给你了,这意味着我们可以修改传进来的Bean的任何东西。不管你是事务也好,AOP也好,都是通过这些个后置处理器来添加这些额外功能的。(建议读一下上面这段话)
BeanPostProcessor:后置增强普通的Bean组件
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:后置增强BeanFactory,也就是增强Bean工厂
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的接口关系
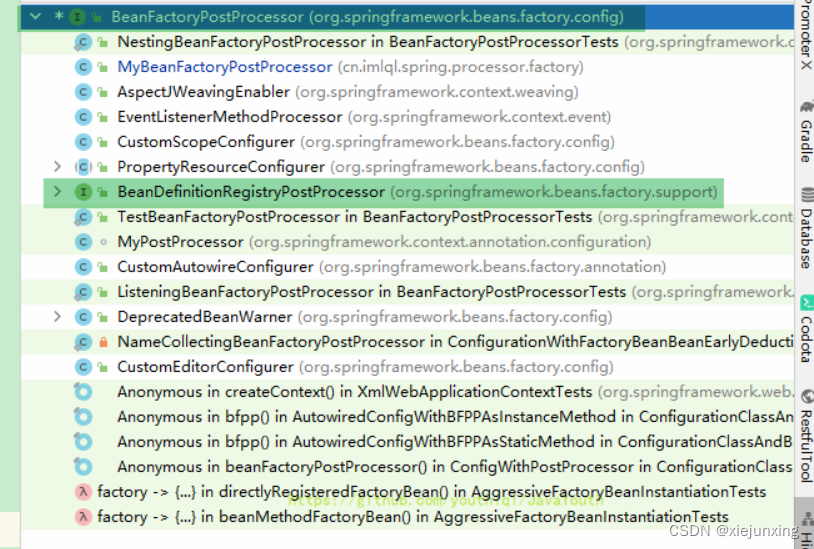
BeanPostProcessor接口关系
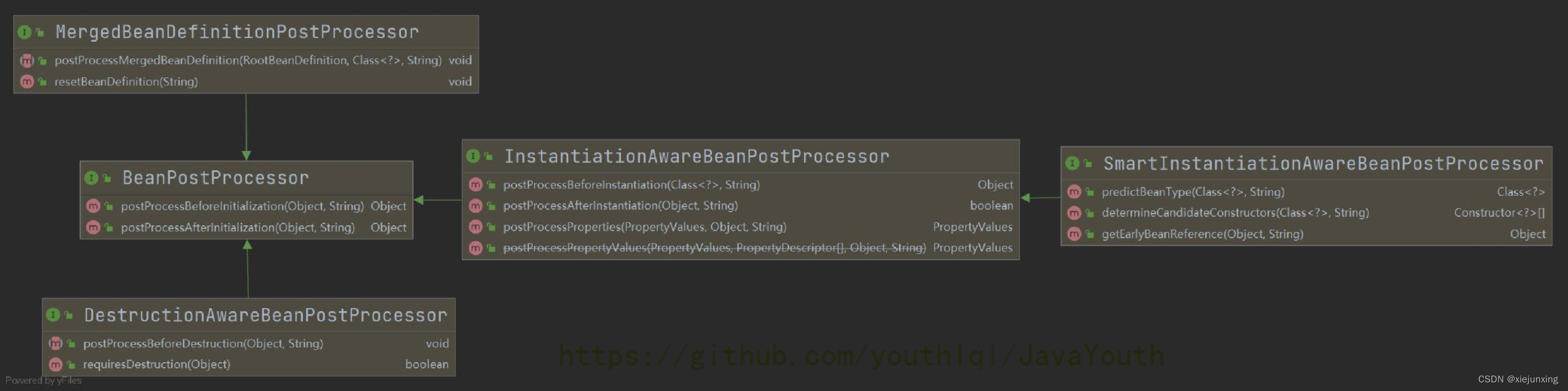
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口是跟销毁有关的,我们这里不分析
之前说过,分析源码时,优先看接口继承关系,好的框架大部分都是遵循基于接口而非实现这一设计思想。
什么是InitializingBean?
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
/**
* 这个方法是在容器设置了所有bean属性并满足BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware等接口后被调用。
* 此方法允许bean实例在其所有bean属性都已设置后对其整体配置进行验证和最终初始化。
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
- Bean组件初始化以后对组件进行后续设置,因为它没有参数传进来,它改变不了什么东西,它的目的在于额外处理。
- 后面我们会讲到BeanPostProcessor主要用于Spring中大部分组件都会用到的功能处理。而InitializingBean是单组件处理(做一些额外处理),最好的例子就是SpringMVC里的一些组件,后面讲。
测试类
MyBeanPostProcessor (几个BeanPostProcesser中间,重点学习一下BeanPostProcessor ,其他的做了解也可,都是大同小异)
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...");
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInitialization..."+bean+"==>"+beanName);
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization..."+bean+"==>"+beanName);
return bean;
}
}
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...");
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInstantiation=>"+beanClass+"--"+beanName);
return null;
}
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInstantiation=>"+bean+"--"+beanName);
return true;
}
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...postProcessProperties=>"+bean+"--"+beanName);
return null;
}
}
MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor {
public MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization...=>"+bean+"--"+beanName);
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInitialization..=>"+bean+"--"+beanName);
return null;
}
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...postProcessMergedBeanDefinition..=>"+beanName+"--"+beanType+"---"+beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void resetBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor...resetBeanDefinition.."+beanName);
}
}
MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...");
}
public Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...predictBeanType=>"+beanClass+"--"+beanName);
return null;
}
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...determineCandidateConstructors=>"+beanClass+"--"+beanName);
return null;
}
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor...getEarlyBeanReference=>"+bean+"--"+beanName);
return bean;
}
}
MyInitializingBean
/**
* 生命周期接口
*/
@Component
public class MyInitializingBean implements InitializingBean {
public MyInitializingBean(){
System.out.println("MyInitializingBean....");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInitializingBean...afterPropertiesSet...");
}
}
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor
/**
* BeanFactory的后置处理器
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor...");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor....postProcessBeanFactory==>"+beanFactory);
}
}
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor");
}
@Override //紧接着执行
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor....postProcessBeanFactory...");
}
@Override //先执行的
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor...postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry...");
//增强bean定义信息的注册中心,比如自己注册组件
}
}
Cat
@Component
public class Cat {
public Cat(){
System.out.println("cat被创建了...");
}
private String name;
@Value("${JAVA_HOME}") //自动赋值功能
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("cat....setName正在赋值调用....");
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
beans2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.imlql.spring.processor"/>
<bean class="cn.imlql.spring.bean.Cat" id="cat"/>
</beans>
MainTest
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans2.xml");
Person bean = context.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
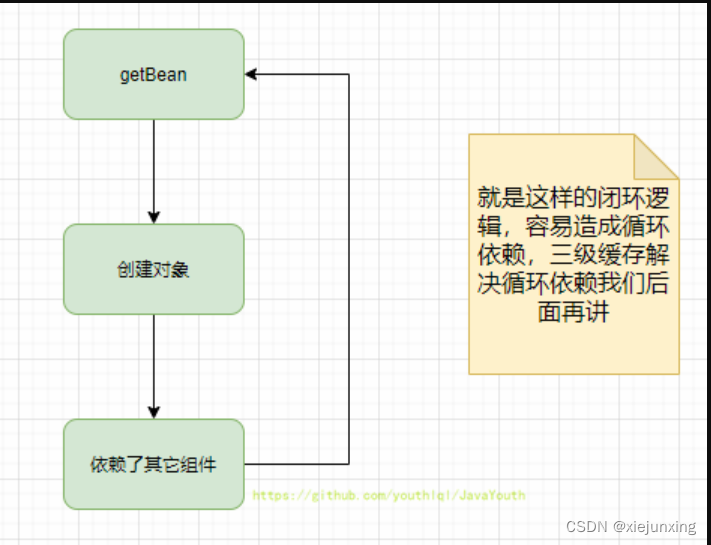
给上面的所有方法都打上断点,我们跟着调用栈一步一步看Bean的生命周期里,这些东西是什么时候参与进来的,哪个在前,哪个在后。
后置工厂处理器如何参与的Bean生命周期
标题的先后顺序就是后置处理器进入的先后顺序
流程图-Bean生命周期与后置工厂处理器

BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
执行无参构造
Debug调用栈

AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
和以前一样,目前用不到的源码都省略,最后会逐渐给一个完整的源码注释。
@Override //容器刷新的十二大步。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 工厂创建:BeanFactory第一次开始创建的时候,有xml解析逻辑。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
//工厂增强:执行所有的BeanFactory后置增强器;利用BeanFactory后置增强器对工厂进行修改或者增强,配置类会在这里进行解析。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册所有的Bean的后置处理器 Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
//...
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//bean创建;完成 BeanFactory 初始化。(工厂里面所有的组件都好了)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
}
}
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); //执行所有的工厂增强器
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
此类没有省略代码
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//先拿到底层默认有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
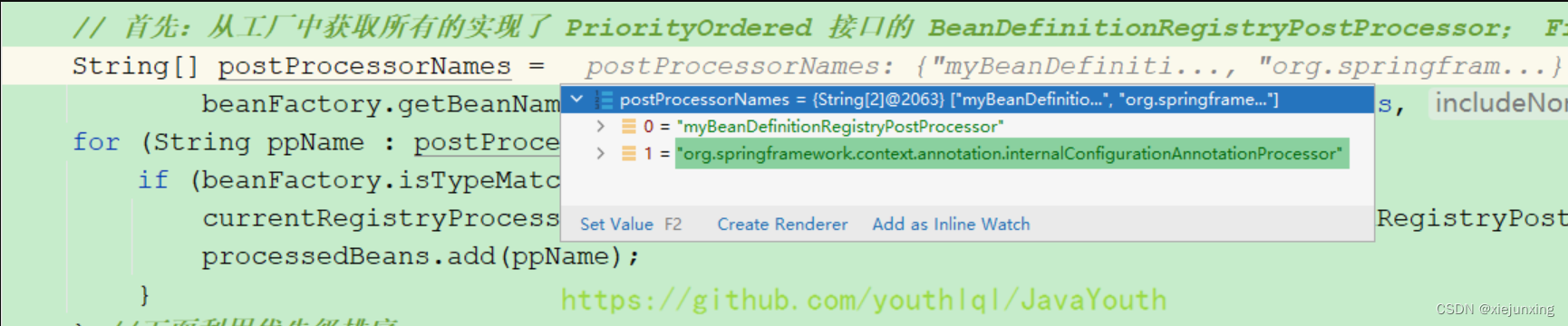
// 首先:从工厂中获取所有的实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; 之前xml解析的时候就已经注册了BeanDefinition
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//从工厂中获取这个组件【getBean整个组件创建的流程】并放到这个集合
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
} //下面利用优先级排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
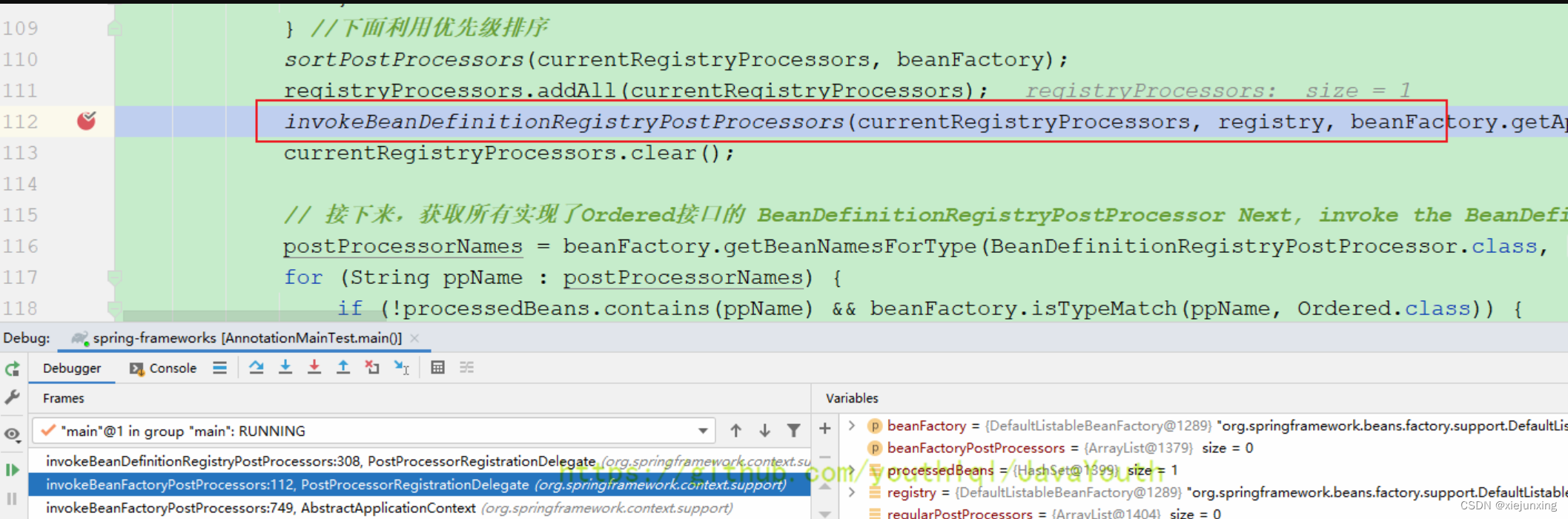
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); //执行这些BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 接下来,获取所有实现了Ordered接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName); //即使同时实现了 PriorityOrdered 和Ordered,也是以 PriorityOrdered为准
}
}//排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); //执行
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 最后,我们自定义的一般没有任何优先级和排序接口 Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);//拿到所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
//然后这里就开始走前面讲过的getBean,无参构造创建对象的流程 =====> 跳转到其它方法
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}//排序,根据类名大小写进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); //防止重复执行
}
// 接下来,再来执行postProcessBeanFactory的回调, Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
//以前在执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor ,以后来执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 首先执行所有实现了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor;First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 接下来执行,实现了 Ordered 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 最后执行没有任何优先级和排序接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); //执行所有的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
后面就是走前面讲过的getBean,无参构造创建对象的流程
Spring中所有组件的获取都是通过getBean(),容器中有就拿,没有就创建
Spring中所有组件的获取都是通过getBean(),容器中有就拿,没有就创建。
下面那个是Spring默认提供的后置处理器,我们后面再讲。
PriorityOrdered或Ordered实现排序
那么这些后置处理器的顺序Spring是如何排序的呢?我们又该怎样自定义BeanPostProcessor的顺序?我们可以通过实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered这两接口来自定义BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序。
PriorityOrdered是个空类,啥也没有
public interface PriorityOrdered extends Ordered {
}
我们只能看他的父类
public interface Ordered {
/**
* Useful constant for the highest precedence value.
* @see java.lang.Integer#MIN_VALUE
*/
int HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
/**
* Useful constant for the lowest precedence value.
* @see java.lang.Integer#MAX_VALUE
*/
int LOWEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* Get the order value of this object.
* <p>Higher values are interpreted as lower priority. As a consequence,
* the object with the lowest value has the highest priority (somewhat
* analogous to Servlet {@code load-on-startup} values).
* <p>Same order values will result in arbitrary sort positions for the
* affected objects.java
* @return the order value
* @see #HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE
* @see #LOWEST_PRECEDENCE
*/
int getOrder(); //根据注释我们可以知道返回的int值越小优先级越高,反之越低
}
- 从上面的源码中我们可以看到PriorityOrdered的代码在Ordered代码前面,获取完PriorityOrdered的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor就直接invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors执行了,所以如果有多个组件,这些组件有些实现了PriorityOrdered ,有些实现了Ordered。实现了PriorityOrdered 的组件执行顺序永远大于实现了Ordered的组件。
- 即使同时实现了 PriorityOrdered 和Ordered,也是以 PriorityOrdered为准。
执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
Debug调用栈
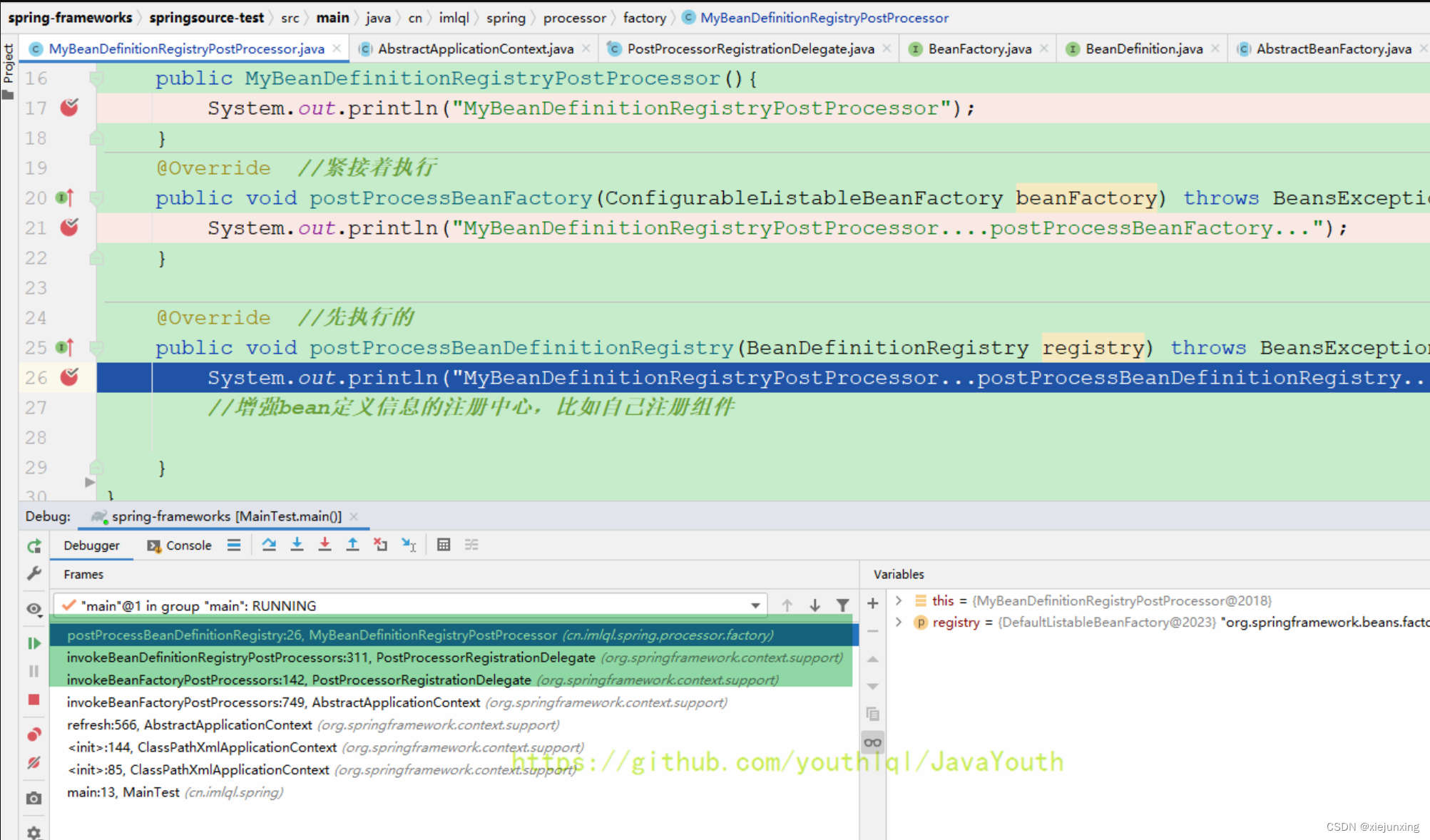
从PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 142行开始走不同的调用,代码在上面有注释
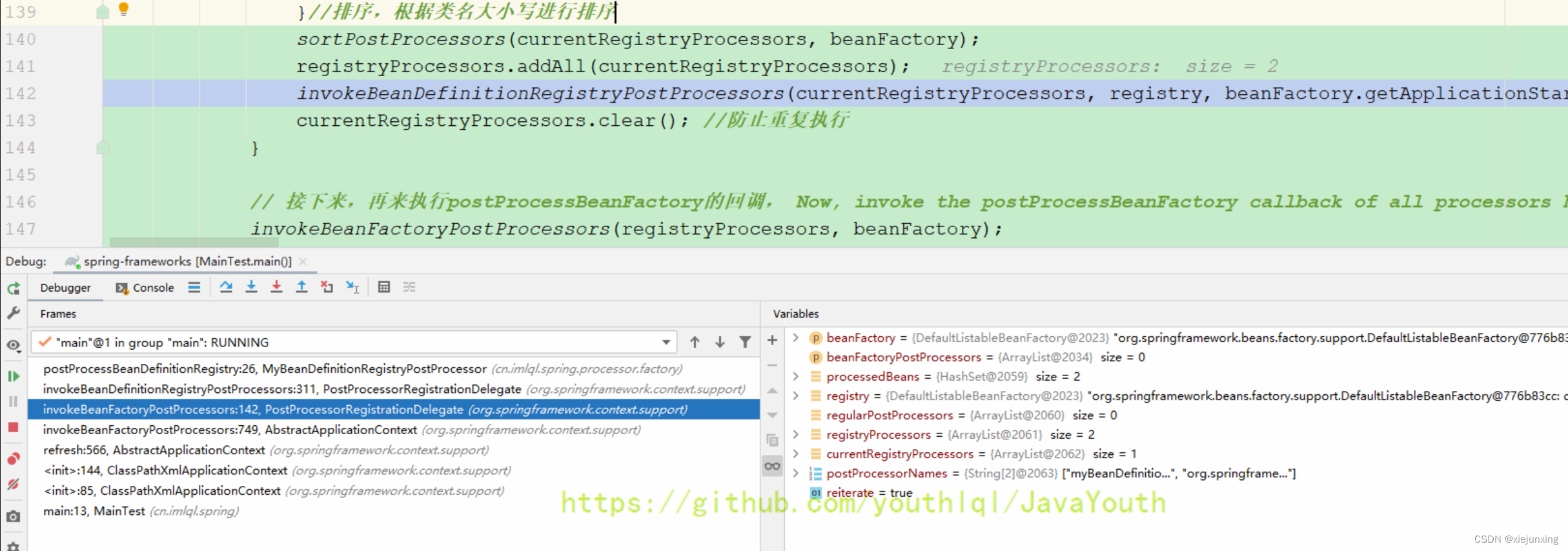
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors()
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ApplicationStartup applicationStartup) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
StartupStep postProcessBeanDefRegistry = applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beandef-registry.post-process")
.tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);//在这里就多态调用我们自定义的方法,也可以说是模板模式
postProcessBeanDefRegistry.end();
}
}
执行postProcessBeanFactory
Debug调用栈
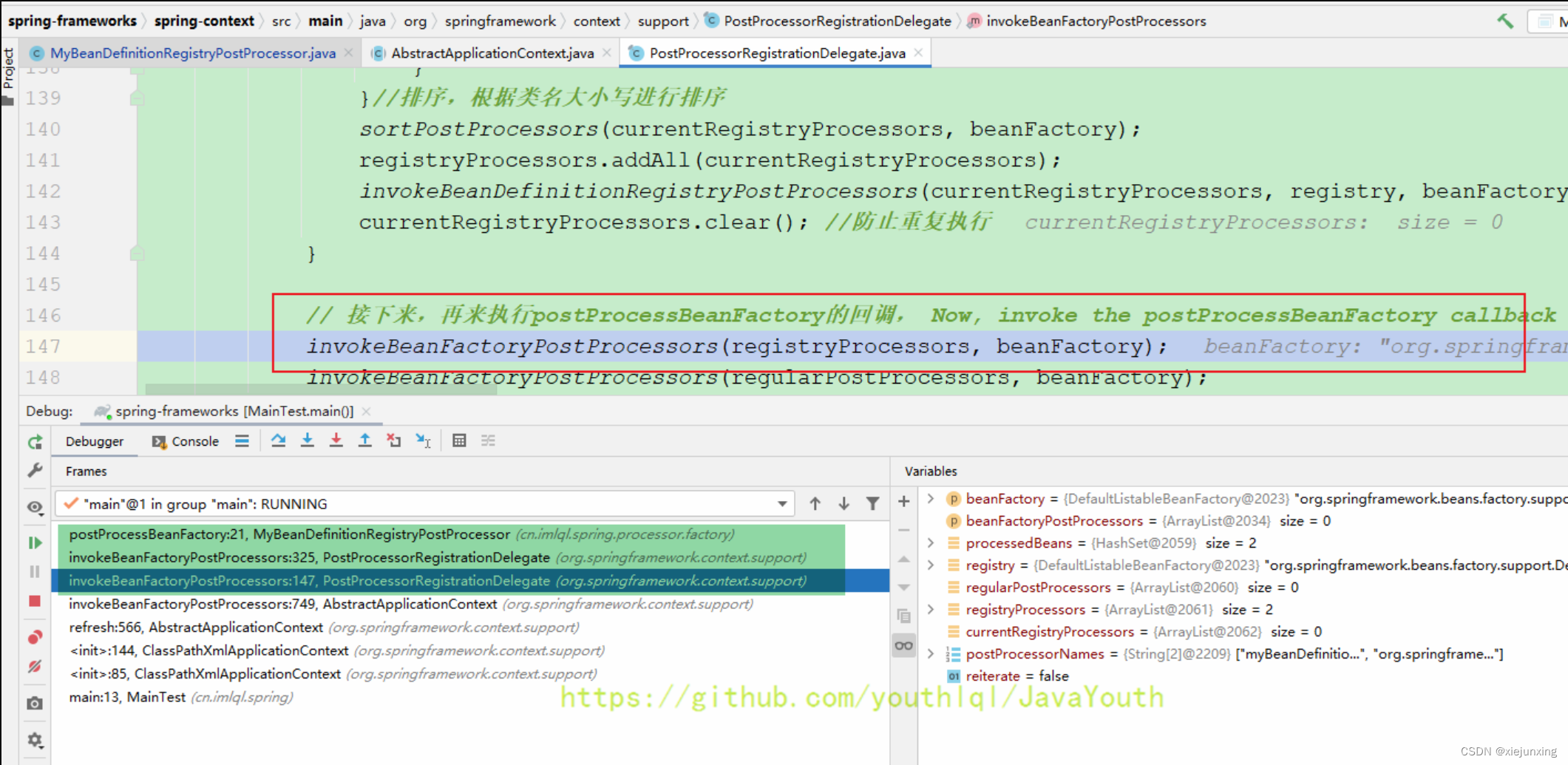
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
StartupStep postProcessBeanFactory = beanFactory.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.bean-factory.post-process")
.tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //一样的多态调用我们自定义的方法
postProcessBeanFactory.end();
}
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
执行无参构造
Debug调用栈

执行postProcessBeanFactory
Debug调用栈
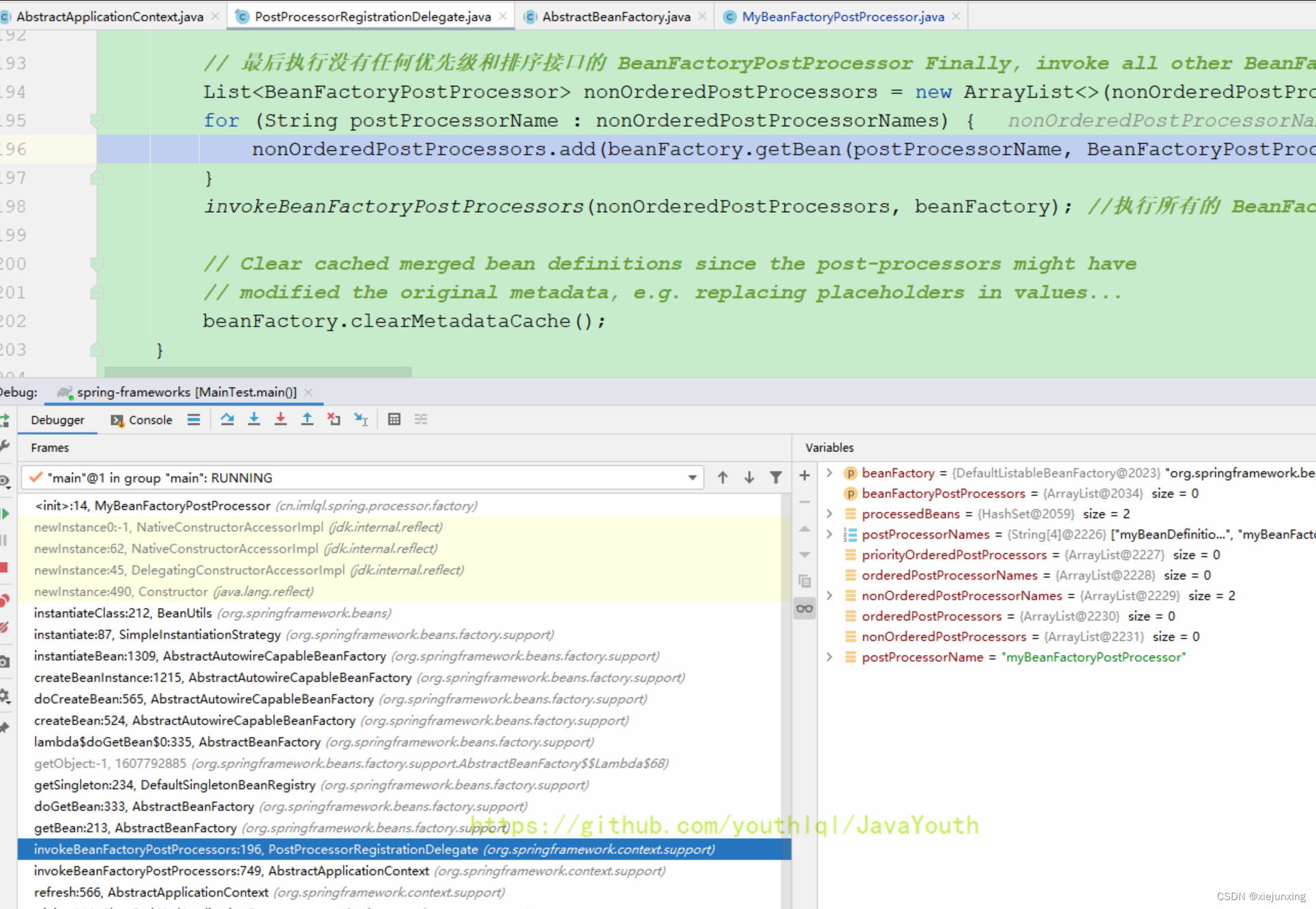
代码注释也是上面那个,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行逻辑基本一样
上面两个都是BeanFactoryPostProcessor,也就是增强Bean工厂的
Spring内部的工厂增强了什么?-简单说明
我们用注解版启动一下
public class AnnotationMainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person bean = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
ApplicationContext context = bean.getContext();
System.out.println(context == applicationContext);
}
}
@ComponentScan("cn.imlql.spring")
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
public MainConfig(){
System.out.println("MainConfig...创建了....");
}
}
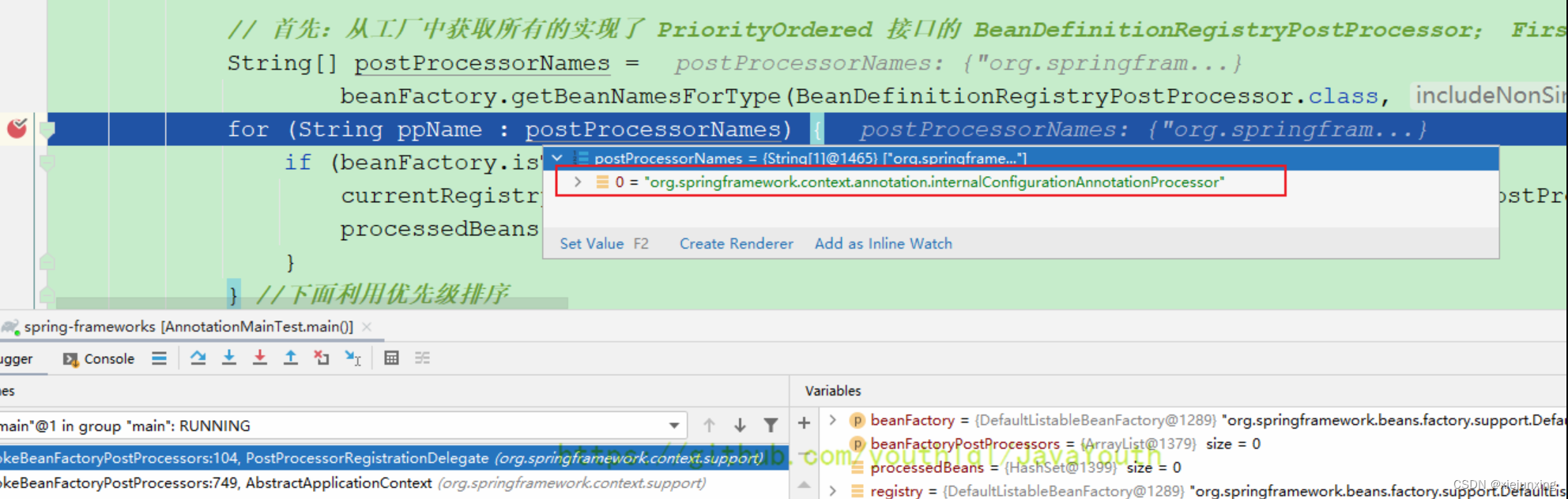
从这一步进来
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors()

F7进入
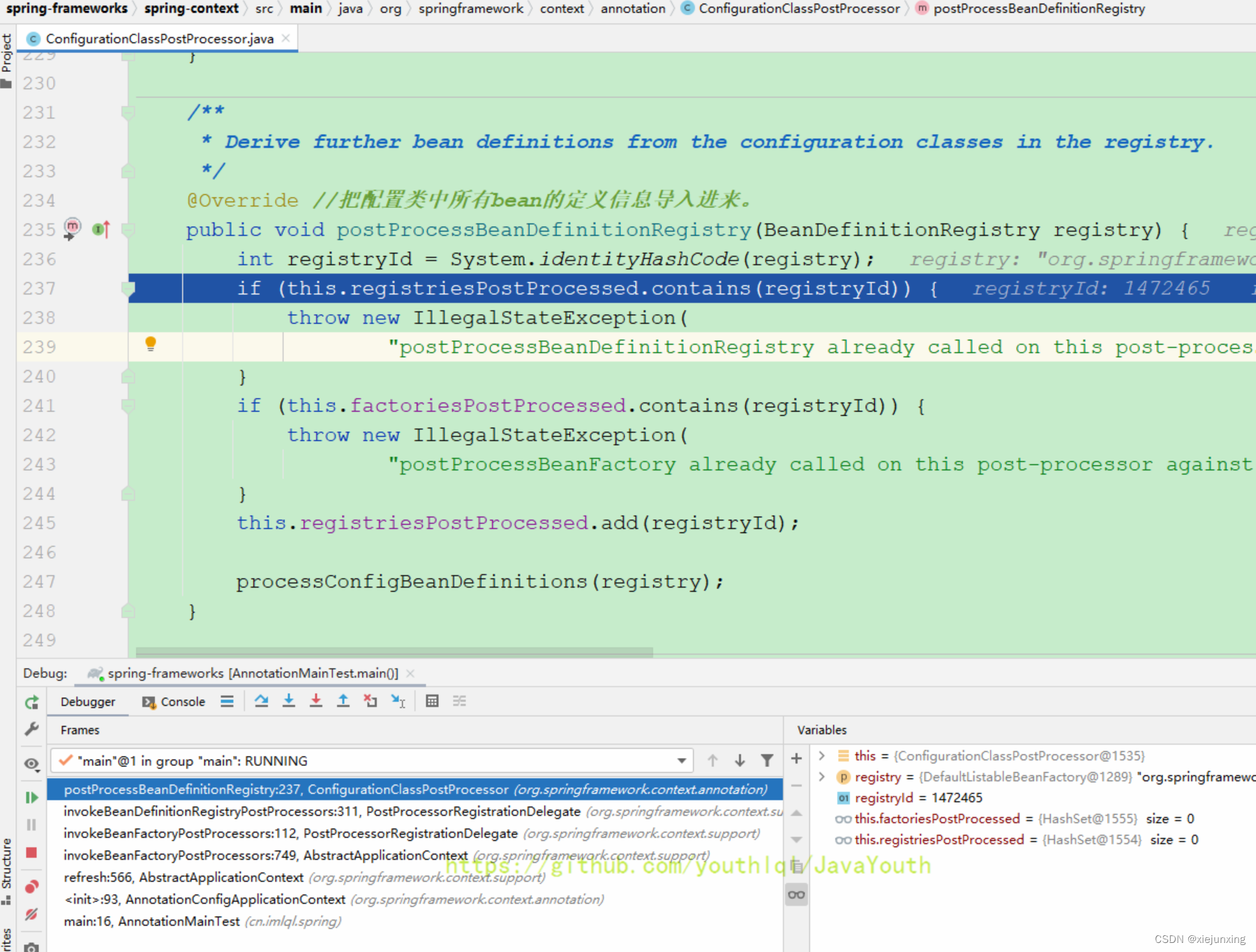
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor配置类的后置处理
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions()
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
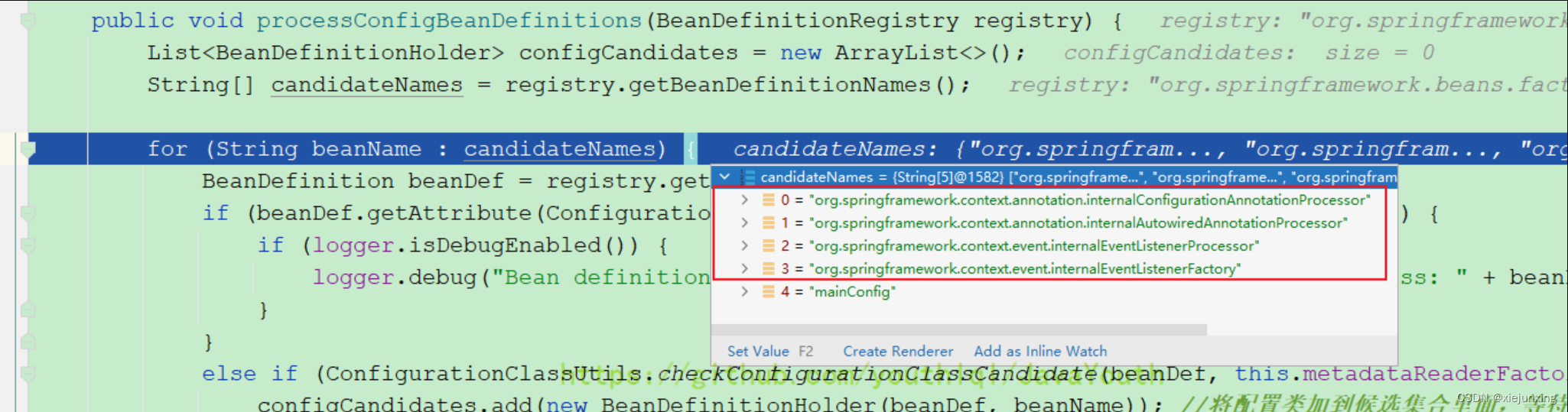
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName)); //将配置类加到候选集合里面,等待处理
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 对所有的配置类进行排序,Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// 单实例注册中心
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); //getBean--getSingleton,获取创建一个internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator来用来生成配置类的名字
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class 由ConfigurationClassParser解析每一个配置类
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
StartupStep processConfig = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.config-classes.parse");
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
processConfig.tag("classCount", () -> String.valueOf(configClasses.size())).end();
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
这几个怎么来的我们后面说
最终上面的调用栈会parser.parse(candidates); 一直调到下面的ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass(),这里也是简单过一下,后面还会再讲。
ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass()
配置类解析的核心方法
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
//Spring底层大量使用缓存来保证框架速度
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
return;
}
else {
// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);
do { //解析配置类里面的所有注解,
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
//只要这个配置类解析过,就放在已经解析好的集合中防止重复解析
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
/**
* Apply processing and build a complete {@link ConfigurationClass} by reading the
* annotations, members and methods from the source class. This method can be called
* multiple times as relevant sources are discovered.
* @param configClass the configuration class being build
* @param sourceClass a source class
* @return the superclass, or {@code null} if none found or previously processed
*/
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
//使用Scanner把ComponentScan指定的包下的所有组件都扫描进来 The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
//处理@Import注解的地方【AOP就是利用这个地方导入一个后置处理器的】 Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
//处理@ImportResource Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
//处理@Bean Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
至此,后置工厂处理器结束,后面讲后置处理器