参考资料:《VRP问题分类》
相关文章:
《[基因遗传算法]原理思想和python代码的结合理解之(一) :单变量》
《[基因遗传算法]进阶之二:最优规划问题–多种编码方式+多变量》
文章目录
- 一. GA的用法
- 1.1 help(sko.GA)
- 1.2 目标函数的书写
- A. 单变量的书写
- B. 多变量的书写
- C. 变量的范围
- 1.3 (不)等式约束的书写
- 二、实践TSP
- A. 读取城市坐标,获得相关信息
- B.定义目标函数
- C . 执行`GA_TSP`算法,输出结果
一. GA的用法
1.1 help(sko.GA)
GA(func, n_dim, size_pop=50, max_iter=200, prob_mut=0.001, lb=-1, ub=1, constraint_eq=(),
constraint_ueq=(), precision=1e-07, early_stop=None)
|
| genetic algorithm
|
| Parameters
| ----------------
| func : function
| The func you want to do optimal 优化的目标函数
| n_dim : int
| number of variables of func目标函数的变量
| lb : array_like
| The lower bound of every variables of func每个变量的下限
| ub : array_like
| The upper bound of every variables of func每个变量的上限
| constraint_eq : tuple,
| equal constraint 等式约束
| constraint_ueq : tuple,
| unequal constraint不等式约束
| precision : array_like
| The precision of every variables of func 函数每个变量的精度
| size_pop : int
| Size of population种群数量
| max_iter : int
| Max of iter迭代次数
| prob_mut : float between 0 and 1
| Probability of mutation 突变概率
1.2 目标函数的书写
A. 单变量的书写
目标函数 y = 10 ⋅ s i n ( 5 x ) + 7 ⋅ c o s ( 4 x ) y=10 \cdot sin(5x)+7\cdot cos(4x) y=10⋅sin(5x)+7⋅cos(4x)
def aim(p):
x= p[0]
return -(10*np.sin(5*x)+7*np.cos(4*x))
B. 多变量的书写
目标函数 Z = 2 a + x 2 − a c o s 2 π x + y 2 − a c o s 2 π y Z=2a+x^2-acos2πx+y^2-acos2πy Z=2a+x2−acos2πx+y2−acos2πy求最小值为例. x ∈ [ 0 , 5 ] , y ∈ [ − 5 , 5 ] , a = 10 x \in [0,5], y\in [-5,5],a=10 x∈[0,5],y∈[−5,5],a=10.
def aim(p):
a = 10
pi = np.pi
x,y=p
return 2 * a + x ** 2 - a * np.cos(2 * pi * x) + y ** 2 - a * np.cos(2 * 3.14 * y)
C. 变量的范围
x
∈
[
0
,
5
]
,
y
∈
[
−
5
,
10
]
x \in [0,5], y\in [-5,10]
x∈[0,5],y∈[−5,10]
lb:low lb=[0,-5]
ub: upub=[5,10]
1.3 (不)等式约束的书写

二、实践TSP
这里应用的是GA_TSP算法.与GA算法不同.主要区分在目标函数的意义.
- GA的目标函数的变量是:(多个)自变量
- GA_TSP的目标函数的变量:是某个路径(环)
参考资料:《Python调用scikit-opt工具箱中的遗传算法求解TSP问题》
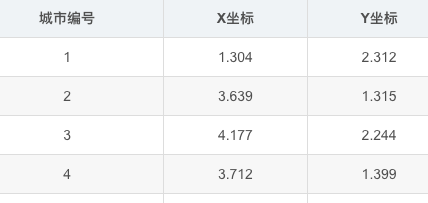
本案例以31个城市为例,假定31个城市的位置坐标如表1所列。寻找出一条最短的遍历31个城市的路径.城市列表见参考链接.
# 导入常用库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import spatial #计算空间的
from sko.GA import GA
from sko.GA import GA_TSP
from time import perf_counter
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
参考《scipy.spatial 距离计算模块》
A. 读取城市坐标,获得相关信息
读取.xlsx数据
file_name = 'cities.xlsx'#31座城市坐标数据文件
df = pd.read_excel(file_name)
points_coordinate=df.values
读取.csv或.txt数据
file_name = 'data.csv' #31座城市坐标数据文件
points_coordinate = np.loadtxt(file_name, delimiter=',')
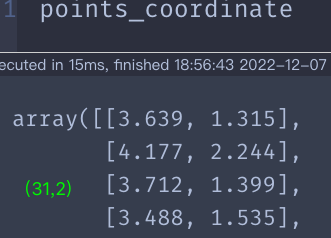
计算城市间的欧式距离
num_points = points_coordinate.shape[0]
distance_matrix = spatial.distance.cdist(points_coordinate, points_coordinate, metric='euclidean')
☀️ 注意到,distance_matrix如果没有定义,则GA_TSP则执行的时候会报错.虽然GA_TSP中美有distance_matrix这个参数变量.
B.定义目标函数
即路线距离函数
路线routine举例为: 共31个城市的路线顺序.起点与终点的为同一个city.
def cal_total_distance(routine):
'''计算总距离:输入路线,返回总距离.
cal_total_distance(np.arange(num_points))
'''
num_points, = routine.shape
return sum([distance_matrix[routine[i % num_points], routine[(i + 1) % num_points]] for i in range(num_points)])
C . 执行GA_TSP算法,输出结果
路径输出函数
def print_route(best_points):
result_cur_best=[]
for i in best_points:
result_cur_best+=[i]
for i in range(len(result_cur_best)):
result_cur_best[i] += 1
result_path = result_cur_best
result_path.append(result_path[0])
return result_path
执行算法
start=perf_counter() #计时开始
# 执行遗传(GA)算法
ga_tsp = GA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points, size_pop=300, max_iter=1000, prob_mut=1) #调用工具箱
# 结果输出
best_points, best_distance = ga_tsp.run()
print("运行时间是: {:.5f}s".format(perf_counter()-start)) #计时结束
print("最优距离为:",best_distance)
print("最优路线:", print_route(best_points))
运行结果一:
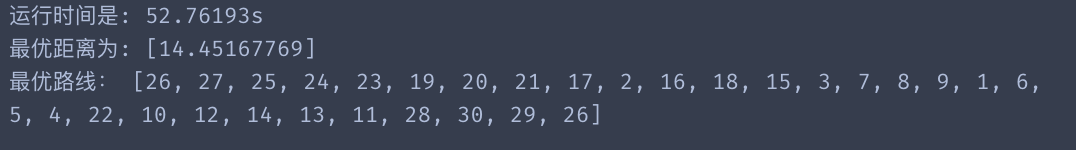
缺city: 30
运行结果二:
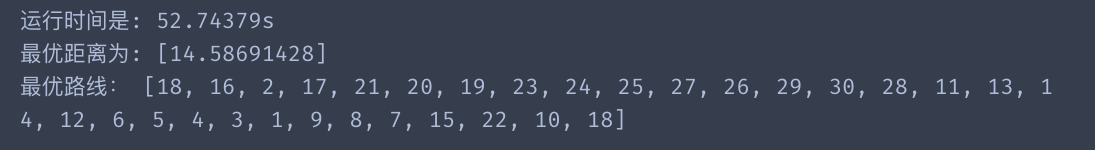
缺city:0
运行结果三:

缺City:30
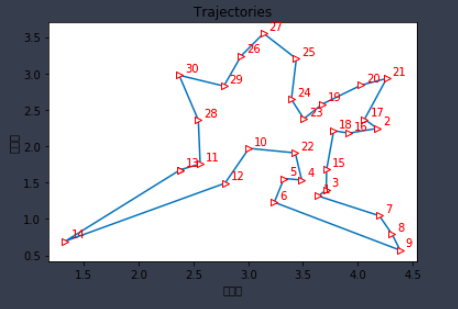
绘图展示
best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_points, [best_points[0]]])
#列表尾部添加起点城市
best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :]#升维
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax1.set_title('Trajectories', loc='center')#轨迹图
line=ax1.plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1], marker='>', mec='r', mfc='w')
for i in range(num_points):
plt.text(best_points_coordinate[:, 0][i] + 0.05, best_points_coordinate[:, 1][i] + 0.05, str(best_points[i]+1), color='red')
ax1.set_xlabel("横坐标")
ax1.set_ylabel("纵坐标")
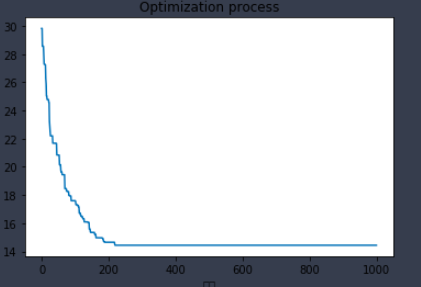
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax2.set_title('Optimization process', loc='center')#优化过程
ax2.plot(ga_tsp.generation_best_Y)
ax2.set_xlabel("代数")
ax2.set_ylabel("最优值")
plt.show()