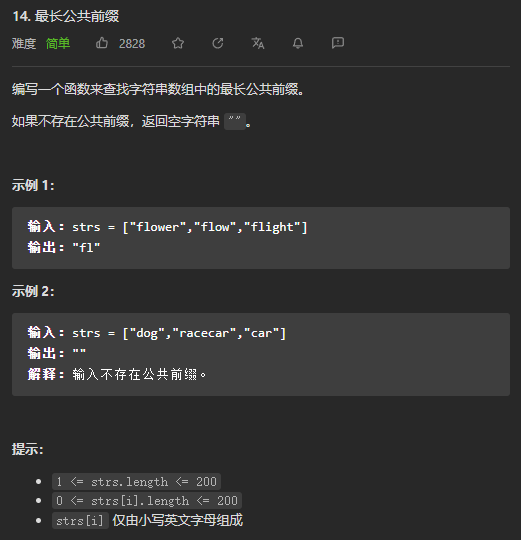
我的思路:
- 给字符串数组按照字符串的长度从长到短排序,因为最长公共前缀最长的话,也只能是字符串数组中最短的那一个字符串
- 设置一个index变量,表示当前正在检查字符数组中所有字符串的index位置
- 循环遍历字符串数组n遍,n也就是最长公共前缀的长度
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
int index = 0;
Arrays.sort(strs, Comparator.comparingInt(String::length));
while (index < strs[0].length()) {
boolean isSame = true;
char c = strs[0].charAt(index);
for (int i = 1; i < strs.length; i++) {
if (c != strs[i].charAt(index)) {
isSame = false;
break;
}
}
if (!isSame) {
return strs[0].substring(0, index);
}
index++;
}
return strs[0];
}
}
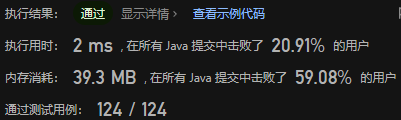
其他思路,方法一,横向扫描
用LCP(S1,S2,…,Sn)表示字符串S1,S2,…Sn的最长公共前缀。
那么,LCP(S1,S2,…,Sn) = LCP(LCP(LCP(S1,S2),S3),…Sn)
基于该结论,可以得到一种查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀的简单方法。依次遍历字符串数组中的每一个字符串,对于每个遍历到字符串,更新最长公共前缀,当遍历完所有的字符串以后,即可得到字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果在尚未遍历完所有的字符串时,最长公共前缀已经是空串,则最长公共前缀一定是空串,因此不需要继续遍历剩下的字符串,直接返回空串即可。
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
String prefix = strs[0];
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
prefix = longestCommonPrefix(prefix, strs[i]);
if (prefix.length() == 0) {
break;
}
}
return prefix;
}
public String longestCommonPrefix(String str1, String str2) {
int length = Math.min(str1.length(), str2.length());
int index = 0;
while (index < length && str1.charAt(index) == str2.charAt(index)) {
index++;
}
return str1.substring(0, index);
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(mn),其中,m是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n是字符串的数量。最坏情况下,字符串数组中的每个字符串的每个字符都会被比较一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。使用的额外空间复杂度为常数。
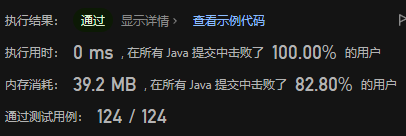
其他思路,方法二,纵向扫描
纵向扫描时,从前往后遍历所有字符串的每一列,比较相同列上的字符是否相同,如果相同则继续对下一列进行比较,如果不相同,则当前列不属于公共前缀,当前列之前的部分为最长公共前缀。
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
//字符串数组中第一个字符串的长度
int length = strs[0].length();
//字符串数组的长度
int count = strs.length;
//最长公共前缀的长度一定不会超过字符串数组中第一个字符串的长度
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//开始纵向比较
char c = strs[0].charAt(i);
for (int j = 1; j < count; j++) {
if (i == strs[j].length() || c != strs[j].charAt(i)) {
return strs[0].substring(0, i);
}
}
}
return strs[0];
}
}
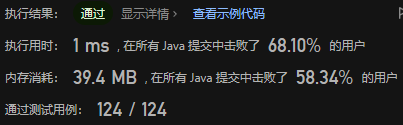
方法三,分治
注意,LCP的计算满足结合律,有以下结论:
LCP(S1…Sn) = LCP(LCP(S1…Sk),LCP(Sk+1…Sn))
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
int strsLength = strs.length;
return longestCommonPrefix(strs, 0, strsLength - 1);
}
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
return strs[start];
}
if (end - start == 1) {
return commonPrefix(strs[start], strs[end]);
}
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
String lcpLeft = longestCommonPrefix(strs, start, mid);
String lcpRight = longestCommonPrefix(strs, mid + 1, end);
return commonPrefix(lcpLeft, lcpRight);
}
public String commonPrefix(String lcpLeft, String lcpRight) {
int minLength = Math.min(lcpLeft.length(), lcpRight.length());
for (int i = 0; i < minLength; i++) {
if (lcpLeft.charAt(i) != lcpRight.charAt(i)) {
return lcpLeft.substring(0, i);
}
}
return lcpLeft.substring(0, minLength);
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(mn),其中m是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n是字符串的数量。时间复杂度的递推式是 T ( n ) = 2 ⋅ T ( n 2 ) + O ( m ) T(n)=2 \cdot T(\frac{n}{2})+O(m) T(n)=2⋅T(2n)+O(m),通过计算可得 T ( n ) = O ( m n ) T(n)=O(mn) T(n)=O(mn)
- 空间复杂度:KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \logn at position 4: O(m\̲l̲o̲g̲n̲),其中m是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n是字符串的数量。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的层数,层数最大为KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \logn at position 1: \̲l̲o̲g̲n̲,每层需要m的空间存储返回结果。
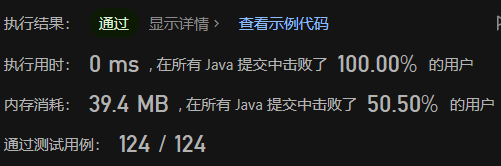
方法四,二分查找
显然,最长公共前缀的长度不会超过字符串数组中的最短字符串的长度。用minLength表示字符串数组中的最短字符串的长度,则可以在[0,minLength]的范围内通过二分查找得到最长公共前缀的长度,每次取查找范围的中间值mid,判断每个字符串的长度为mid的前缀是否相同,如果相同则最长公共前缀的长度一定大于或等于mid,如果不相同则最长公共前缀的长度一定小于mid,通过上述方式将查找范围缩小一半,直到得到最长公共前缀的长度。
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (String str : strs) {
minLength = Math.min(minLength, str.length());
}
int left = 0;
int right = minLength;
//[left,right)
while (left < right) {
//在偶数长度的区间时,mid往右边靠
int mid = (left + right + 1) / 2 ;
//int mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
if (isCommonPrefix(strs, mid)) {
//可能mid就是最长公共前缀的长度
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
//最后一次left的值,肯定是合理的
return strs[0].substring(0, left);
}
public boolean isCommonPrefix(String[] strs, int length) {
//拿到数组中的第一个字符串中的长度为length的子串
String str0 = strs[0].substring(0, length);
//获取整个字符串数组的长度
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
String str = strs[i];
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
if (str0.charAt(j) != str.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(mnlogm),其中m是字符串数组中的字符串的最小长度,n是字符串的数量。二分查找的迭代执行次数是O(logm),每次迭代最多需要比较mn个字符,因此总时间复杂度是O(mnlogm)
- 空间复杂度:O(1),使用的额外空间复杂度是常数



![[ICASSP 2019] 差分隐私压缩 K 均值](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/397bfed15be5413d87970dc020b03bef.png)