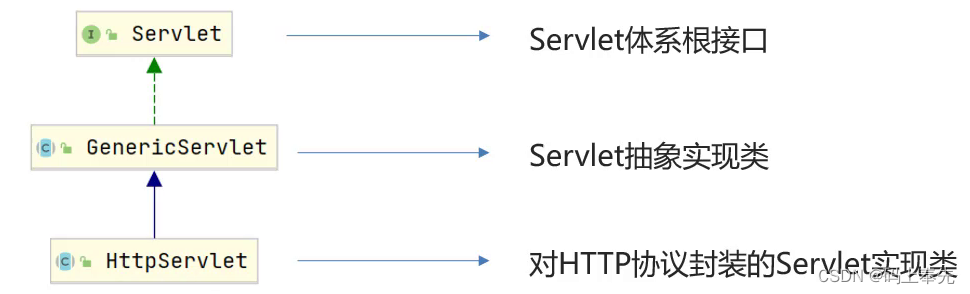
1.简述
计算概率分布律及密度函数值
matlab直接提供了通用的计算概率密度函数值的函数,它们是pdf 和namepdf函数,使用方式如下:
Y=pdf(‘name’,K,A,B)或者:namepdf (K,A,B)
上述函数表示返回在X=K处、参数为A、B、C的概率值或密度值,对于不同的分布,参数个数是不同;name为分布函数名,使用时需要按照对应分布进行改动。函数名总结如下表:
name的取值 函数说明
‘beta’ 或 ‘Beta’ Beta分布
‘bino’ 或 ‘Binomial’ 二项分布
‘chi2’ 或 ‘Chisquare’ 卡方分布
‘exp’ 或 ‘Exponential’ 指数分布
‘f’ 或 ‘F’ F分布
‘gam’ 或 ‘Gamma’ GAMMA分布
‘geo’ 或 ‘Geometric’ 几何分布
‘hyge’ 或 ‘Hypergeometric’ 超几何分布
‘logn’ 或 ‘Lognormal’ 对数正态分布
‘nbin’ 或 ‘Negative Binomial’ 负二项式分布
‘ncf’ 或 ‘Noncentral F’ 非中心F分布
‘nct’ 或 ‘Noncentral t’ 非中心t分布
‘ncx2’ 或 ‘Noncentral Chi-square’ 非中心卡方分布
‘norm’ 或 ‘Normal’ 正态分布
‘poiss’ 或 ‘Poisson’ 泊松分布
‘rayl’ 或 ‘Rayleigh’ 瑞利分布
‘t’ 或 ‘T’ T分布
‘unif’ 或 ‘Uniform’ 连续均匀分布
‘unid’ 或 ‘Discrete Uniform’ 离散均匀分布
‘weib’ 或 ‘Weibull’ Weibull分布
2.代码及运行结果
%% 二项分布的密度函数
clear all;
x=1:20;
y=binopdf(x,200,0.06);
figure;
plot(x,y,'r*');
title('二项分布(n=200,p=0.06)');

%% 泊松分布的密度函数
clear all;
x=1:20;
y=poisspdf(x,20); %泊松分布
figure;
plot(x,y,'r+');
title('泊松分布');

%% 几何分布
clear all;
x=1:10;
y=geopdf(x,0.4); %几何分布
figure;
plot(x,y,'rx');
title('几何分布');

%% 均匀分布(离散)
clear all;
n=10;
x=1:n;
y=unidpdf(x,n); %均匀分布(离散)
figure;
plot(x,y,'ro');
title('均匀分布(离散)');
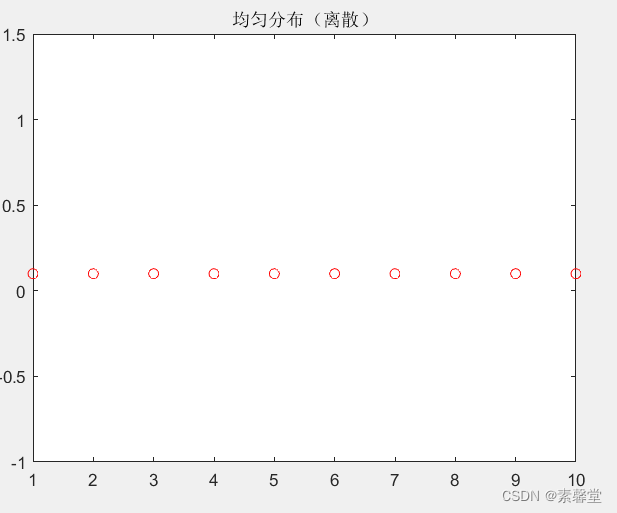
%% 均匀分布(连续)
clear all;
x=-2:0.1:15;
y=unifpdf(x,0,6); %均匀分布(连续) 0到6之间
figure;
plot(x,y,'r:');
title('均匀分布(连续)');
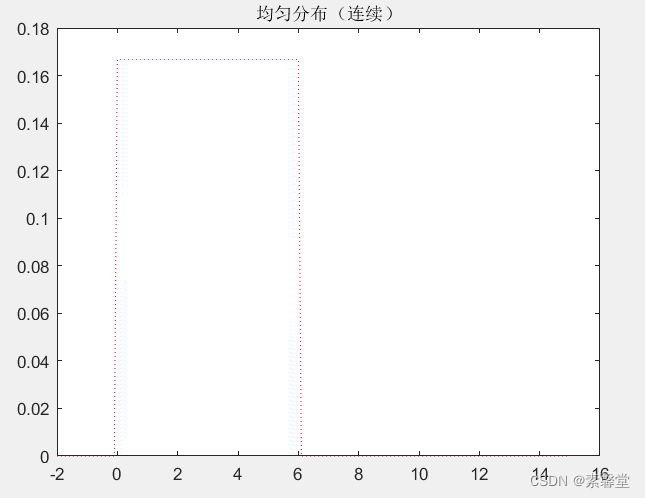
%% 指数分布
clear all;
x=0:0.1:10;
y=exppdf(x,2); %指数分布
figure;
plot(x,y,'r:');
title('指数分布');
%% 正态分布
clear all;
x=-5:0.1:5;
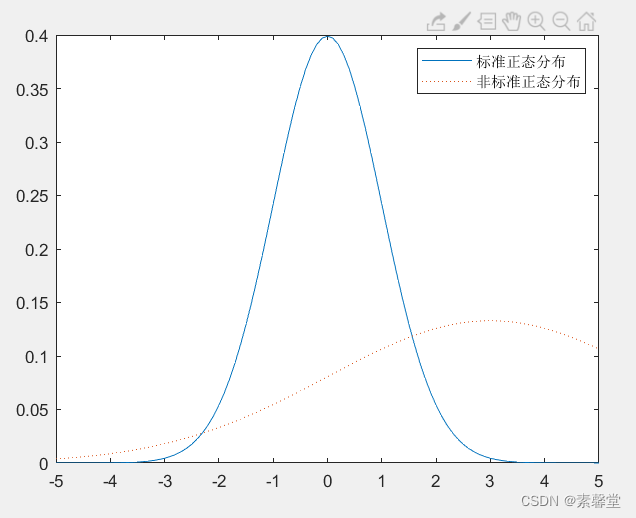
y1=normpdf(x,0,1); %标准正态分布
y2=normpdf(x,3,3); %非标准正态分布
figure;
plot(x,y1,x,y2,':');
legend('标准正态分布','非标准正态分布');
x1=-5:0.1:5;
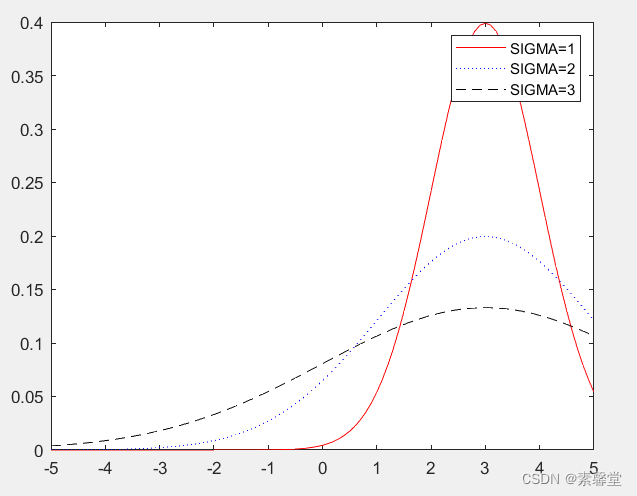
y3=normpdf(x1,3,1); %SIGMA=1
y4=normpdf(x1,3,2); %SIGMA=2
y5=normpdf(x1,3,3); %SIGMA=3
figure;
plot(x1,y3,'r-',x1,y4,'b:',x1,y5,'k--');
legend('SIGMA=1','SIGMA=2','SIGMA=3');
y6=normpdf(x1,0,2); %MU=0
y7=normpdf(x1,2,2); %MU=2
y8=normpdf(x1,4,2); %MU=4
figure;
plot(x1,y6,'r-',x1,y7,'b:',x1,y8,'k--');
legend('MU=0','MU=2','MU=4');

%% 三大抽样分布的概率密度函数
%% 卡方分布
clear all;
x=0:0.1:15;
y1=chi2pdf(x,2); %卡方分布n=2
y2=chi2pdf(x,3); %卡方分布n=3
figure;
hold on;
plot(x,y1);
plot(x,y2,':');
legend('n=2','n=3');
title('卡方分布');

%% t分布
clear all;
x=-5:0.1:5;
y1=tpdf(x,2); %t分布(n=2)
y2=tpdf(x,10); %t分布(n=10)
figure;
plot(x,y1,'r:',x,y2,'b-');
legend('n=2','n=10');
title('t分布');

%% F分布
clear all;
x=0.1:0.1:5;
y=fpdf(x,2,5); %F分布
figure;
plot(x,y,'r:');
title('F分布(m=2,n=5)');





![[已解决]Running setup.py install for MinkowskiEngine ... error](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6030787cf4f54dcd810ae5ea3fd00827.png)