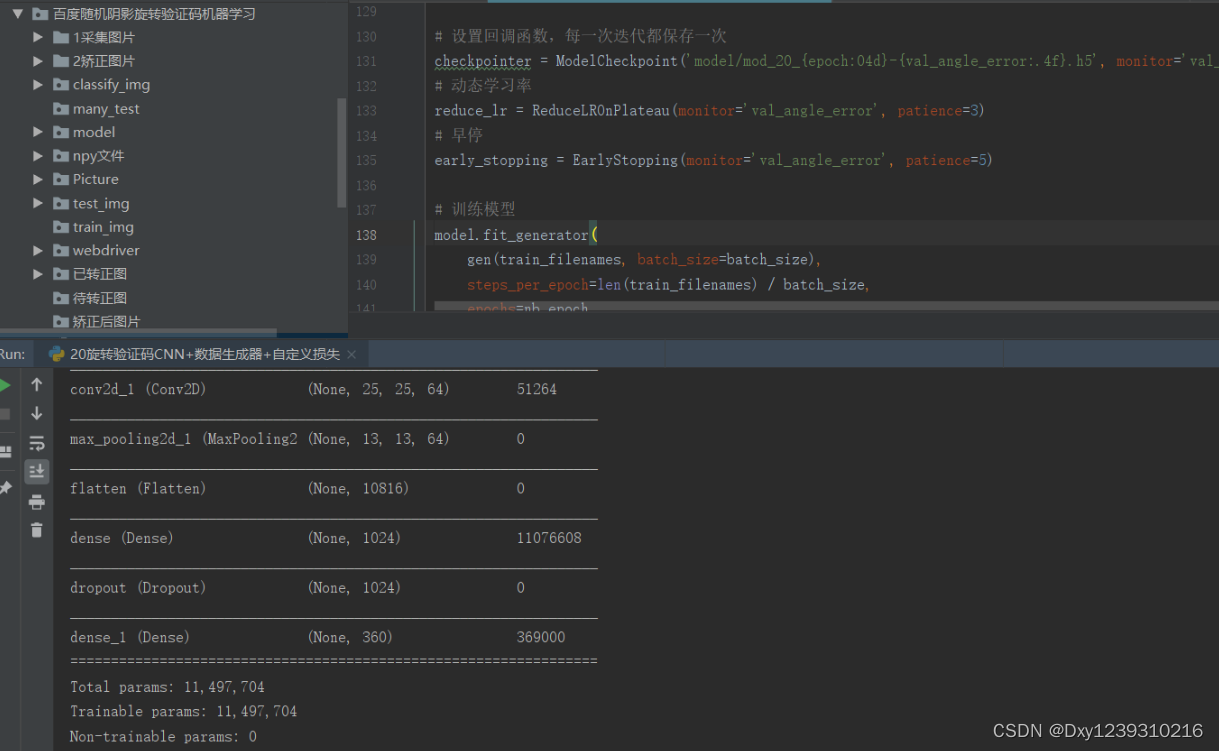
导致问题出现的demo代码
#define SH_DEV_MEM "/dev/mem"
#define myerror printf
// 获取由mmap映射的设备物理内存
static void *mymmap(u32 offset, u32 size, u8 is_rd_only, u8 is_clear)
{
void *ptr;
s32 fd;
offset = 0x45E00000;
size = 0x1000;
is_rd_only = 0;
is_clear = 1;
/* open the shared memory object */
// SH_DEV_MEM is "/dev/mem"
if (is_rd_only)
fd = open(SH_DEV_MEM, O_RDONLY | O_SYNC);
else
fd = open(SH_DEV_MEM, O_RDWR | O_SYNC);
if (fd == -1)
{
myerror("Open %s: %s\n", SH_DEV_MEM, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
// get a pointer to a piece of the shared memory, note that we only map in the amount we need to
// void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset)
if (is_rd_only)
ptr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, offset);
else
ptr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, offset);
问题现象
在用户态通过mmap映射一段物理地址到用户空间,执行memset(ptr , 0, 0x100)时会导致Bus error:
...
fd = open("/dev/mem", O_RDONLY | O_SYNC);
ptr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0x45e00000);
memset(ptr , 0, 0x100);

但以下情况不会:
- memset(ptr , val , size),如果val非0,不会出现Bus error
- memset(ptr , val , size),如果val为0,size<0x100,不会出现Bus error
- 0x45e00000地址如果添加到memory节点,不会出现Bus error

问题分析
通过gdb分析,发现程序停在dc zva指令

查看arm v8官方文档发现,如果memory的类型是device type,执行dc zva时会有对齐错误产生,
(ps:dc zva cache zero by vir address)

在内核加打印追踪,发现确实产生了alignment fault

然后分析/driver/char/mem.c驱动,在mmap的时候,会设置内存的属性,当mmap的物理地址在memblock memory范围内,会设置内存属性为PTE_ATTRINDX(MT_NORMAL_NC) | PTE_PXN | PTE_UXN),即normal memory,如果不在memblock memory范围,则设置为PTE_ATTRINDX(MT_DEVICE_nGnRnE) | PTE_PXN | PTE_UXN),即device memory,这解释了,为什么0x45e00000添加到memory节点则不会出现Bus error的原因
static int mmap_mem(struct file *file, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
size_t size = vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start;
phys_addr_t offset = (phys_addr_t)vma->vm_pgoff << PAGE_SHIFT;
/* It's illegal to wrap around the end of the physical address space. */
if (offset + (phys_addr_t)size - 1 < offset)
return -EINVAL;
if (!valid_mmap_phys_addr_range(vma->vm_pgoff, size))
return -EINVAL;
if (!private_mapping_ok(vma))
return -ENOSYS;
if (!range_is_allowed(vma->vm_pgoff, size))
return -EPERM;
if (!phys_mem_access_prot_allowed(file, vma->vm_pgoff, size,
&vma->vm_page_prot))
return -EINVAL;
vma->vm_page_prot = phys_mem_access_prot(file, vma->vm_pgoff,
size,
vma->vm_page_prot);
vma->vm_ops = &mmap_mem_ops;
/* Remap-pfn-range will mark the range VM_IO */
if (remap_pfn_range(vma,
vma->vm_start,
vma->vm_pgoff,
size,
vma->vm_page_prot)) {
return -EAGAIN;
}
return 0;
}
// arch/arm64/mm/mmu.c
pgprot_t phys_mem_access_prot(struct file *file, unsigned long pfn,
unsigned long size, pgprot_t vma_prot)
{
if (!pfn_valid(pfn)){
return pgprot_noncached(vma_prot);
}
else if (file->f_flags & O_SYNC)
{
return pgprot_writecombine(vma_prot);
}
return vma_prot;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(phys_mem_access_prot);
#define pgprot_noncached(prot) \
__pgprot_modify(prot, PTE_ATTRINDX_MASK, PTE_ATTRINDX(MT_DEVICE_nGnRnE) | PTE_PXN | PTE_UXN)
#define pgprot_writecombine(prot) \
__pgprot_modify(prot, PTE_ATTRINDX_MASK, PTE_ATTRINDX(MT_NORMAL_NC) | PTE_PXN | PTE_UXN)
#define pgprot_device(prot) \
__pgprot_modify(prot, PTE_ATTRINDX_MASK, PTE_ATTRINDX(MT_DEVICE_nGnRE) | PTE_PXN | PTE_UXN)
#define __HAVE_PHYS_MEM_ACCESS_PROT
int pfn_valid(unsigned long pfn)
{
return (pfn & PFN_MASK) == pfn && memblock_is_map_memory(pfn << PAGE_SHIFT);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pfn_valid);
考虑到val为非0,不会出现Bus error,怀疑是glibc的memset,对val为0而且cout > 0x100的操作做了特殊的处理,查看glibc的源码,发现如果set的val,如果等于0,确实会做不同的操作,执行了dc zva指令,这解释了为什么非0的val会没问题,且size<0x100,也不会出现Bus error
// sysdeps/aarch64/memset.S
ENTRY_ALIGN (MEMSET, 6)
DELOUSE (0)
DELOUSE (2)
dup v0.16B, valw
add dstend, dstin, count
cmp count, 96
b.hi L(set_long)
cmp count, 16
b.hs L(set_medium)
mov val, v0.D[0]
...
L(set_long):
and valw, valw, 255
bic dst, dstin, 15
str q0, [dstin]
cmp count, 256//
ccmp valw, 0, 0, cs //cout > 0x100,并且val是0,则会使用zva指令,
b.eq L(try_zva)
L(no_zva):
sub count, dstend, dst /* Count is 16 too large. */
sub dst, dst, 16 /* Dst is biased by -32. */
sub count, count, 64 + 16 /* Adjust count and bias for loop. */
1: stp q0, q0, [dst, 32]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 64]!
L(tail64):
subs count, count, 64
b.hi 1b
2: stp q0, q0, [dstend, -64]
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -32]
ret
L(try_zva):
#ifdef ZVA_MACRO
zva_macro
#else
.p2align 3
mrs tmp1, dczid_el0
tbnz tmp1w, 4, L(no_zva)
and tmp1w, tmp1w, 15
cmp tmp1w, 4 /* ZVA size is 64 bytes. */
b.ne L(zva_128)
/* Write the first and last 64 byte aligned block using stp rather
than using DC ZVA. This is faster on some cores.
*/
L(zva_64):
str q0, [dst, 16]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 32]
bic dst, dst, 63
stp q0, q0, [dst, 64]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 96]
sub count, dstend, dst /* Count is now 128 too large. */
sub count, count, 128+64+64 /* Adjust count and bias for loop. */
add dst, dst, 128
nop
1: dc zva, dst
add dst, dst, 64
subs count, count, 64
b.hi 1b
stp q0, q0, [dst, 0]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 32]
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -64]
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -32]
ret
.p2align 3
L(zva_128):
cmp tmp1w, 5 /* ZVA size is 128 bytes. */
b.ne L(zva_other)
str q0, [dst, 16]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 32]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 64]
stp q0, q0, [dst, 96]
bic dst, dst, 127
sub count, dstend, dst /* Count is now 128 too large. */
sub count, count, 128+128 /* Adjust count and bias for loop. */
add dst, dst, 128
1: dc zva, dst
add dst, dst, 128
subs count, count, 128
b.hi 1b
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -128]
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -96]
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -64]
stp q0, q0, [dstend, -32]
ret
...
#endif
END (MEMSET)
处理建议
把需要mmap的那段内存添加到memory和reserved-memory节点,以0x45E00000例:
memory@50000000 {
device_type = "memory";
reg = <HIGH32(AP1_REE_MEMBASE) LOW32(AP1_REE_MEMBASE) HIGH32(AP1_REE_MEMSIZE) LOW32(AP1_REE_MEMSIZE) \
HIGH32(AP1_2ND_MEMBASE) LOW32(AP1_2ND_MEMBASE) HIGH32(AP1_2ND_MEMSIZE) LOW32(AP1_2ND_MEMSIZE) \
0x0 (VDSP_MEMBASE+0x4000) 0x0 (VDSP_SHARE_MEMSIZE + VDSP_MEMSIZE -0x4000)
0x0 LOW32(0x45E00000) 0 0x200000>;
};
reserved-memory {
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
mmap_test {
/* reserve mem for mmap*/
compatible = "mmap_test";
//no-map;//注意不能用no-map标志
reg = <0x0 LOW32(0x45E00000) 0 0x100000>;
};
};