一、说明
推荐系统是一种计算机程序或算法,用于预测用户对特定项目的兴趣度,并根据这些预测向用户提供个性化推荐。这种系统通常使用大量数据来分析用户的行为和偏好,以找出潜在的喜好和兴趣。推荐系统可以应用于电子商务、社交媒体、影视娱乐等领域,帮助提高用户体验、增加销售和粘性。
二、什么是推荐系统
推荐引擎是机器学习的一个子类,通常处理对产品/用户进行排名或评级。松散地定义,推荐系统是预测用户可能对特定项目给出的评级的系统。然后,这些预测将被排名并返回给用户。
它们被各种大牌公司使用,如谷歌,Instagram,Spotify,亚马逊,Reddit,Netflix等。通常是为了增加与用户和平台的互动。例如,Spotify 会推荐与您反复听或喜欢的歌曲相似的歌曲,以便您可以继续使用他们的平台听音乐。亚马逊使用推荐功能,根据用户为该用户收集的数据向各种用户推荐商品。
推荐系统通常被视为“黑匣子”,这些大公司创建的模型不太容易解释。生成的结果通常是对用户需要/想要的东西的建议,但在向他们推荐之前,他们不知道他们需要/想要它。
构建推荐系统有许多不同的方法,有些使用算法和公式化方法,如页面排名,而另一些则使用更多以建模为中心的方法,如协同过滤、基于内容、链接预测等。所有这些方法的复杂性各不相同,但复杂性并不能转化为“良好”的性能。通常,简单的解决方案和实施会产生最强的结果。例如,像Reddit,Hacker News和Google这样的大公司已经使用推荐引擎的简单公式化实现来推广其平台上的内容。在本文中,我将提供推荐系统体系结构的直观和技术概述,以及在示例生成的数据集上实现几种不同变体。
三、什么是好的推荐?
确定什么是好的推荐本身就是许多公司都在努力解决的问题。“良好”建议的这种定义有助于评估您构建的推荐器的性能。建议的质量可以通过衡量覆盖范围和准确性的各种策略来评估。准确性是正确建议占所有可能建议的比例,而覆盖范围衡量系统能够提供建议的搜索空间中对象的比例。评估建议的方法完全取决于用于生成建议的数据集和方法。推荐系统与分类和回归建模问题在概念上有几个相似之处。在理想情况下,您可能希望了解真实用户对建议的反应,并跟踪用户周围的指标以改进您的推荐,但是,这很难实现。评估推荐者准确性的常见统计准确性度量是 RMSD、MAE 和 k 折交叉验证。
3.1 K 折叠交叉验证
- 假设您已经构建了一个模型,该模型将根据一组特征预测用户对项目的评分。K折交叉验证可用于通过准确性指标推断模型的结果
- 与训练测试拆分的想法相同,除了我们创建 K 许多随机分配的训练和测试集
- 每个单独的训练集/折叠用于独立地在推荐系统上进行训练,然后根据测试集测量结果系统的准确性
- 我们取准确率分数的平均值,以了解推荐系统的学习情况
- 此方法有助于防止模型过度拟合,但这是一个计算量很大的过程
MAE(平均绝对误差)
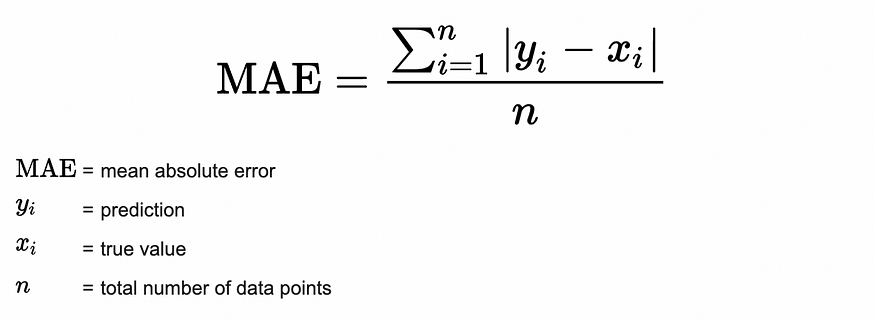
图片取自统计操作方法
- 表示评级预测中每个误差的平均绝对值
- MAE 分数越低越好
RMSD(均方根偏差)
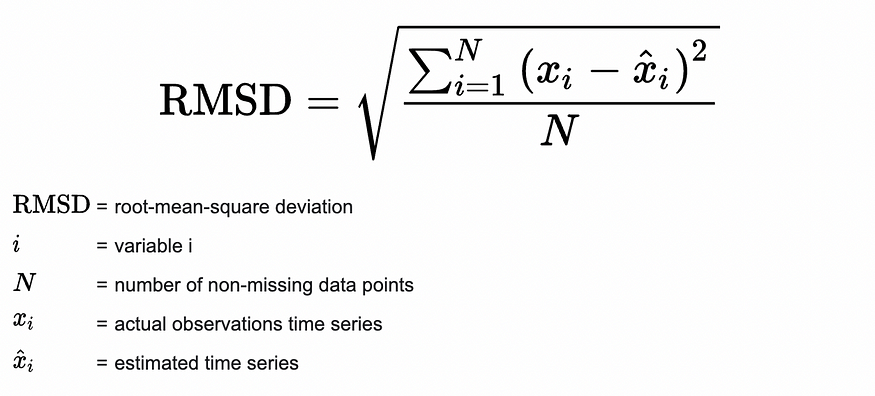
图片取自统计操作方法
- 与 MAE 类似的指标,但当预测离真实值很远时,惩罚更强,当预测更接近真实值时,惩罚较弱
- 去掉真值和预测值之差的平方,而不是绝对值的总和。这可确保结果值始终为正,并且在差值高时较大,在差值低时较小。
- RMSD 分数越低越好
这些指标通常用于评估建议的质量,但它们缺少各种组件。将用户数据与推荐相关联对于了解推荐的真实质量至关重要。能够跟踪推荐的命中率、对平台的参与度、响应能力等。将提供更清晰的推荐质量观点。其他需要注意的组件是,当用户在 X 时间内未与推荐互动时,了解何时更改推荐,或者何时根据用户的新评分或交互重新训练推荐人。您还需要注意这些建议是否将用户限制在产品的某个子部分,推荐者如何处理新颖性、多样性和选择偏见。A / B测试通常是用于跟踪这些指标的方法(查看我关于贝叶斯和频率A / B测试的文章)。
3.2 数据
在下面的部分中,我们将更深入地介绍在 Python 中创建推荐引擎和相关实现的不同方法。本节将提供一个脚本,该脚本将合成与书籍关联的数据集。该数据集将用于以下各节中推荐系统的应用,本文的目标不是获得有意义的结果,而是向用户展示各种类型的推荐引擎背后的直觉和实现。因此,这些建议的结果将毫无意义,但方法将与工业生产级环境中的方法相似。
要求
- python = 3.8.8
- pandas = 1.2.4
3.3 相关代码
import pandas as pd
from random import randint
def generate_data(n_books = 3000, n_genres = 10, n_authors = 450, n_publishers = 50, n_readers = 30000, dataset_size = 100000):
'''
This function will generate a dataset with features associated to
book data set. The dataset will have the following columns :
- book_id (String) : Unique identified for the book
- book_rating (Integer) : A value between 0 and 10
- reader_id (String) : Unique identifier for the user
- book_genre (Integer) : An integer representing a genre for the book,
value is between 1 and 15, indicating that
there are 15 unique genres. Each book can only
have 1 genre
- author_id (String) : Unique identifier for the author of the book
- num_pages (Integer) : Random value between 70 and 500
- publisher_id (String) : A unique identifier for the publisher of the book
- publish_year (Integer) : The year of book publishing
- book_price (Integer) : The sale price of the book
- text_lang (Integer) : The language of the book - returns an integer which
is mapped to some language
params:
n_books (Integer) : The number of books you want the dataset to have
n_genres (Integer) : Number of genres to be chosen from
n_authors (Integer) : Number of authors to be generated
n_publishers (Integer) : Number of publishers for the dataset
n_readers (Integer) : Number of readers for the dataset
dataset_size (Integer) : The number of rows to be generated
example:
data = generate_data()
'''
d = pd.DataFrame(
{
'book_id' : [randint(1, n_books) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'author_id' : [randint(1, n_authors) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'book_genre' : [randint(1, n_genres) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'reader_id' : [randint(1, n_readers) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'num_pages' : [randint(75, 700) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'book_rating' : [randint(1, 10) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'publisher_id' : [randint(1, n_publishers) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'publish_year' : [randint(2000, 2021) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'book_price' : [randint(1, 200) for _ in range(dataset_size)],
'text_lang' : [randint(1,7) for _ in range(dataset_size)]
}
).drop_duplicates()
return d
d = generate_data(dataset_size = 100000)
d.to_csv('data.csv', index = False)四、协同过滤系统
4.1 基于直觉
协同过滤是通过识别来自许多用户的偏好和信息来预测用户兴趣的过程。这是通过使用涉及多个代理、数据源等之间协作的技术过滤数据以获取信息或模式来完成的。协同过滤背后的潜在直觉是,如果用户A和B在产品中具有相似的品味,那么A和B在其他产品中也可能具有相似的品味。
协同过滤中有两种常见的方法,基于内存的方法和基于模型的方法。
- 基于内存的方法 - 通常也称为邻域协同过滤。从本质上讲,用户-项目组合的评级是根据其邻域预测的。这可以进一步分为基于用户的协同过滤和基于项目的协同过滤。基于用户本质上意味着志同道合的用户将产生强烈而相似的建议。基于项目的协同筛选根据使用项目的用户评分计算的项目之间的相似性来推荐项目。
- 基于模型的方法 — 是使用机器学习的预测模型。与数据集关联的特征被参数化为模型的输入,以尝试解决与优化相关的问题。基于模型的方法包括使用决策树、基于规则的方法、潜在因素模型等。
4.2 优缺点
4.2.1 优势
使用协同过滤模型的主要优点是其易于实现和它们提供的高级别覆盖率。它也是有益的,因为它捕获了微妙的特征(对于潜在因子模型来说非常正确),并且不需要理解项目内容。
4.2.2 弊端
此模型的主要缺点是它对推荐新项目不友好,这是因为没有用户/项目与之交互。这称为冷启动问题。众所周知,基于内存的算法在高度稀疏的数据集上表现不佳。
4.3 协同过滤例子
协同过滤算法的一些例子:
- 向用户推荐 YouTube 内容 — 根据与您订阅/观看过类似视频的其他用户向您推荐视频。
- CourseEra 课程推荐 — 根据已完成现有课程的其他人向您推荐课程。
4.3.1 实现
- 从generate_data功能(上面提供的功能)导入数据或从此处下载CSV
- 生成一个数据透视表,索引上有读者,列上有书籍,值是评级
- 使用 svds 计算项目和用户之间的相似性
- 根据user_id生成项目建议
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from scipy.sparse.linalg import svds
def normalize(pred_ratings):
'''
This function will normalize the input pred_ratings
params:
pred_ratings (List -> List) : The prediction ratings
'''
return (pred_ratings - pred_ratings.min()) / (pred_ratings.max() - pred_ratings.min())
def generate_prediction_df(mat, pt_df, n_factors):
'''
This function will calculate the single value decomposition of the input matrix
given n_factors. It will then generate and normalize the user rating predictions.
params:
mat (CSR Matrix) : scipy csr matrix corresponding to the pivot table (pt_df)
pt_df (DataFrame) : pandas dataframe which is a pivot table
n_factors (Integer) : Number of singular values and vectors to compute.
Must be 1 <= n_factors < min(mat.shape).
'''
if not 1 <= n_factors < min(mat.shape):
raise ValueError("Must be 1 <= n_factors < min(mat.shape)")
# matrix factorization
u, s, v = svds(mat, k = n_factors)
s = np.diag(s)
# calculate pred ratings
pred_ratings = np.dot(np.dot(u, s), v)
pred_ratings = normalize(pred_ratings)
# convert to df
pred_df = pd.DataFrame(
pred_ratings,
columns = pt_df.columns,
index = list(pt_df.index)
).transpose()
return pred_df
def recommend_items(pred_df, usr_id, n_recs):
'''
Given a usr_id and pred_df this function will recommend
items to the user.
params:
pred_df (DataFrame) : generated from `generate_prediction_df` function
usr_id (Integer) : The user you wish to get item recommendations for
n_recs (Integer) : The number of recommendations you want for this user
'''
usr_pred = pred_df[usr_id].sort_values(ascending = False).reset_index().rename(columns = {usr_id : 'sim'})
rec_df = usr_pred.sort_values(by = 'sim', ascending = False).head(n_recs)
return rec_df
if __name__ == '__main__':
# constants
PATH = '../data/data.csv'
# import data
df = pd.read_csv(PATH)
print(df.shape)
# generate a pivot table with readers on the index and books on the column and values being the ratings
pt_df = df.pivot_table(
columns = 'book_id',
index = 'reader_id',
values = 'book_rating'
).fillna(0)
# convert to a csr matrix
mat = pt_df.values
mat = csr_matrix(mat)
pred_df = generate_prediction_df(mat, pt_df, 10)
# generate recommendations
print(recommend_items(pred_df, 5, 5))