1、什么是 Suggestion 菜单
呐,下面这个就是 Suggestion 菜单,一般出现在设置主界面最上方位置。
出现时机需要满足三个条件,1、设备不是 LowRam 设备 2、启用 settings_contextual_home 特性 3、在开机一定时间后(一般是几天,具体看 AndroidManifest.xml 中的熟悉配置)
你是不是在想我是怎么知道的这么清楚的,把加载流程搞懂你就和我一样清楚了,走起。
1.1、Suggestion 定义配置
<activity
android:name="Settings$NightDisplaySuggestionActivity"
android:enabled="@*android:bool/config_nightDisplayAvailable"
android:exported="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_suggestion_night_display">
<!-- 配置关键,可被查询到 -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="com.android.settings.suggested.category.FIRST_IMPRESSION" />
</intent-filter>
<!-- 配置显示时间 -->
<meta-data android:name="com.android.settings.dismiss"
android:value="7,1,30" />
<!-- 配置对应标题和内容 -->
<meta-data android:name="com.android.settings.title"
android:resource="@string/night_display_suggestion_title" />
<meta-data android:name="com.android.settings.summary"
android:resource="@string/night_display_suggestion_summary" />
....
2、Suggestion 菜单加载流程
先上一张经典流程图
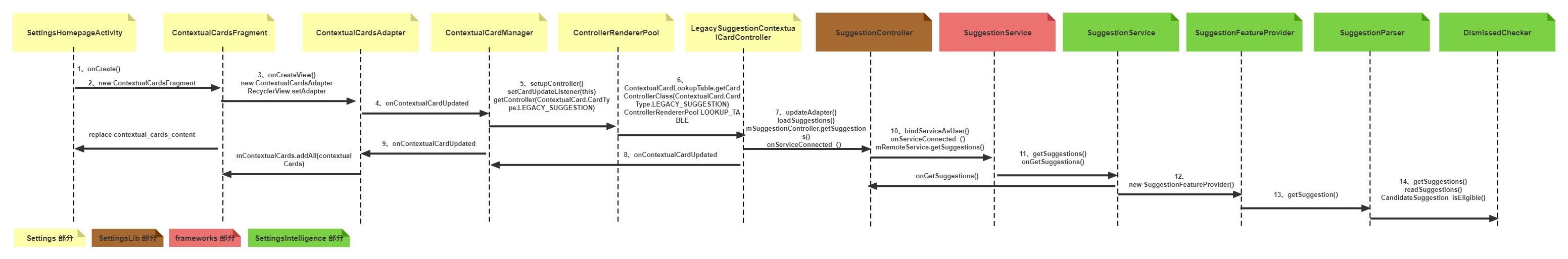
2.1 从 Settings 切入
众所周知 Settings 主入口界面在 SettingsHomepageActivity.java 中,找到我们关注代码如下
布局文件 settings_homepage_container.xml 就不说了,LinearLayout 中包含两 FrameLayout
final String highlightMenuKey = getHighlightMenuKey();
// Only allow features on high ram devices.
if (!getSystemService(ActivityManager.class).isLowRamDevice()) {
initAvatarView();
final boolean scrollNeeded = mIsEmbeddingActivityEnabled
&& !TextUtils.equals(getString(DEFAULT_HIGHLIGHT_MENU_KEY), highlightMenuKey);
showSuggestionFragment(scrollNeeded);
if (FeatureFlagUtils.isEnabled(this, FeatureFlags.CONTEXTUAL_HOME)) {
showFragment(() -> new ContextualCardsFragment(), R.id.contextual_cards_content);
((FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.main_content))
.getLayoutTransition().enableTransitionType(LayoutTransition.CHANGING);
}
}
mMainFragment = showFragment(() -> {
看到上面关键点,isLowRamDevice 和 CONTEXTUAL_HOME 进行了判断,当同时符合要求时,初始化 ContextualCardsFragment 替换 main_content
接下来跟进 ContextualCardsFragment.java 看到对应布局文件 settings_homepage.xml 中就包含了一个 FocusRecyclerView,
这就好理解为什么看到展示的 Suggestion 都是一条一条的
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final Context context = getContext();
final View rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.settings_homepage, container, false);
mCardsContainer = rootView.findViewById(R.id.card_container);
mLayoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(getActivity(), SPAN_COUNT,
GridLayoutManager.VERTICAL, false /* reverseLayout */);
mCardsContainer.setLayoutManager(mLayoutManager);
mContextualCardsAdapter = new ContextualCardsAdapter(context, this /* lifecycleOwner */,
mContextualCardManager);
mCardsContainer.setItemAnimator(null);
mCardsContainer.setAdapter(mContextualCardsAdapter);
mContextualCardManager.setListener(mContextualCardsAdapter);
mCardsContainer.setListener(this);
mItemTouchHelper = new ItemTouchHelper(new SwipeDismissalDelegate(mContextualCardsAdapter));
mItemTouchHelper.attachToRecyclerView(mCardsContainer);
return rootView;
}
既然是 RecyclerView 那我们只需要关注对应的 adapter 就知道数据来源了,跟进 ContextualCardsAdapter.java
先找 getItemCount 方法,对应数据源集合为 mContextualCards,查看是如何 add
final List<ContextualCard> mContextualCards;
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mContextualCards.size();
}
@Override
public void onContextualCardUpdated(Map<Integer, List<ContextualCard>> cards) {
final List<ContextualCard> contextualCards = cards.get(ContextualCard.CardType.DEFAULT);
final boolean previouslyEmpty = mContextualCards.isEmpty();
final boolean nowEmpty = contextualCards == null || contextualCards.isEmpty();
if (contextualCards == null) {
mContextualCards.clear();
notifyDataSetChanged();
} else {
final DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(
new ContextualCardsDiffCallback(mContextualCards, contextualCards));
mContextualCards.clear();
mContextualCards.addAll(contextualCards);
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(this);
}
if (mRecyclerView != null && previouslyEmpty && !nowEmpty) {
// Adding items to empty list, should animate.
mRecyclerView.scheduleLayoutAnimation();
}
}
找到关键点通过回调 onContextualCardUpdated() 返回 ContextualCard 集合,在 Settings 中全局搜索回调来源,找到
LegacySuggestionContextualCardController.java:174: () -> mCardUpdateListener.onContextualCardUpdated(suggestionCards));
ConditionContextualCardController.java:111: mListener.onContextualCardUpdated(conditionalCards
ContextualCardManager.java:228: mListener.onContextualCardUpdated(cardsToUpdate);
三个地方,经过分析过滤(通过 ContextualCard.CardType.DEFAULT 过滤) ,ConditionContextualCardController 不符合情况,
LegacySuggestionContextualCardController onContextualCardUpdated -> ContextualCardManager onContextualCardUpdated -> ContextualCardsAdapter onContextualCardUpdated
进入 ContextualCardManager.java,下面列出关键代码。通过 setupController 指定 type 为 LEGACY_SUGGESTION,进行初始化 LegacySuggestionContextualCardController
并设置 setCardUpdateListener,当 LegacySuggestionContextualCardController 获取到数据后直接回调 onContextualCardUpdated 进行过滤
int[] getSettingsCards() {
if (!FeatureFlagUtils.isEnabled(mContext, FeatureFlags.CONDITIONAL_CARDS)) {
return new int[] {ContextualCard.CardType.LEGACY_SUGGESTION};
}
return new int[]
{ContextualCard.CardType.CONDITIONAL, ContextualCard.CardType.LEGACY_SUGGESTION};
}
void setupController(@ContextualCard.CardType int cardType) {
final ContextualCardController controller = mControllerRendererPool.getController(mContext,
cardType);
if (controller == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Cannot find ContextualCardController for type " + cardType);
return;
}
controller.setCardUpdateListener(this);
if (controller instanceof LifecycleObserver && !mLifecycleObservers.contains(controller)) {
mLifecycleObservers.add((LifecycleObserver) controller);
mLifecycle.addObserver((LifecycleObserver) controller);
}
}
@Override
public void onContextualCardUpdated(Map<Integer, List<ContextualCard>> updateList) {
final Set<Integer> cardTypes = updateList.keySet();
// Remove the existing data that matches the certain cardType before inserting new data.
List<ContextualCard> cardsToKeep;
// We are not sure how many card types will be in the database, so when the list coming
// from the database is empty (e.g. no eligible cards/cards are dismissed), we cannot
// assign a specific card type for its map which is sending here. Thus, we assume that
// except Conditional cards, all other cards are from the database. So when the map sent
// here is empty, we only keep Conditional cards.
if (cardTypes.isEmpty()) {
final Set<Integer> conditionalCardTypes = new TreeSet<Integer>() {{
add(ContextualCard.CardType.CONDITIONAL);
add(ContextualCard.CardType.CONDITIONAL_HEADER);
add(ContextualCard.CardType.CONDITIONAL_FOOTER);
}};
cardsToKeep = mContextualCards.stream()
.filter(card -> conditionalCardTypes.contains(card.getCardType()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
} else {
cardsToKeep = mContextualCards.stream()
.filter(card -> !cardTypes.contains(card.getCardType()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
final List<ContextualCard> allCards = new ArrayList<>();
allCards.addAll(cardsToKeep);
allCards.addAll(
updateList.values().stream().flatMap(List::stream).collect(Collectors.toList()));
//replace with the new data
mContextualCards.clear();
final List<ContextualCard> sortedCards = sortCards(allCards);
mContextualCards.addAll(getCardsWithViewType(sortedCards));
loadCardControllers();
if (mListener != null) {
final Map<Integer, List<ContextualCard>> cardsToUpdate = new ArrayMap<>();
cardsToUpdate.put(ContextualCard.CardType.DEFAULT, mContextualCards);
mListener.onContextualCardUpdated(cardsToUpdate);
}
}
进入 ControllerRendererPool.java,通过 getController() 实例化 Controller
public <T extends ContextualCardController> T getController(Context context,
@ContextualCard.CardType int cardType) {
final Class<? extends ContextualCardController> clz =
ContextualCardLookupTable.getCardControllerClass(cardType);
for (ContextualCardController controller : mControllers) {
if (controller.getClass().getName().equals(clz.getName())) {
Log.d(TAG, "Controller is already there.");
return (T) controller;
}
}
final ContextualCardController controller = createCardController(context, clz);
if (controller != null) {
mControllers.add(controller);
}
return (T) controller;
}
在 ContextualCardLookupTable.java 中初始化了 Set LOOKUP_TABLE, 通过 key CardType.LEGACY_SUGGESTION 匹配
public static Class<? extends ContextualCardController> getCardControllerClass(
@CardType int cardType) {
for (ControllerRendererMapping mapping : LOOKUP_TABLE) {
if (mapping.mCardType == cardType) {
return mapping.mControllerClass;
}
}
return null;
}
static final Set<ControllerRendererMapping> LOOKUP_TABLE =
new TreeSet<ControllerRendererMapping>() {{
...
add(new ControllerRendererMapping(CardType.LEGACY_SUGGESTION,
LegacySuggestionContextualCardRenderer.VIEW_TYPE,
LegacySuggestionContextualCardController.class,
LegacySuggestionContextualCardRenderer.class));
来看下关键类 LegacySuggestionContextualCardController.java 从这里就延伸到了其它三个子模块 SettingsLib frameworks SettingsIntelligence
先看到构造方法中有个默认配置值 config_use_legacy_suggestion,是否启用 suggestion 功能,如果不需要该功能则直接改为 flase 就行
紧接着获取 ComponentName 并创建 SuggestionController,在 SuggestionController 中进行 bindService 操作
当 Service 成功绑定,回调 onServiceConnected() 通过 loadSuggestions() 解析 Suggestion 数据
public LegacySuggestionContextualCardController(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mSuggestions = new ArrayList<>();
if (!mContext.getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.config_use_legacy_suggestion)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Legacy suggestion contextual card disabled, skipping.");
return;
}
final ComponentName suggestionServiceComponent =
FeatureFactory.getFactory(mContext).getSuggestionFeatureProvider(mContext)
.getSuggestionServiceComponent();
mSuggestionController = new SuggestionController(
mContext, suggestionServiceComponent, this /* listener */);
}
private void updateAdapter() {
final Map<Integer, List<ContextualCard>> suggestionCards = new ArrayMap<>();
suggestionCards.put(ContextualCard.CardType.LEGACY_SUGGESTION, mSuggestions);
ThreadUtils.postOnMainThread(
() -> mCardUpdateListener.onContextualCardUpdated(suggestionCards));
}
private void loadSuggestions() {
ThreadUtils.postOnBackgroundThread(() -> {
if (mSuggestionController == null || mCardUpdateListener == null) {
return;
}
final List<Suggestion> suggestions = mSuggestionController.getSuggestions();
final String suggestionCount = suggestions == null
? "null"
: String.valueOf(suggestions.size());
Log.d(TAG, "Loaded suggests: " + suggestionCount);
final List<ContextualCard> cards = new ArrayList<>();
if (suggestions != null) {
// Convert suggestion to ContextualCard
for (Suggestion suggestion : suggestions) {
final LegacySuggestionContextualCard.Builder cardBuilder =
new LegacySuggestionContextualCard.Builder();
if (suggestion.getIcon() != null) {
cardBuilder.setIconDrawable(suggestion.getIcon().loadDrawable(mContext));
}
cardBuilder
.setPendingIntent(suggestion.getPendingIntent())
.setSuggestion(suggestion)
.setName(suggestion.getId())
.setTitleText(suggestion.getTitle().toString())
.setSummaryText(suggestion.getSummary().toString())
.setViewType(LegacySuggestionContextualCardRenderer.VIEW_TYPE);
cards.add(cardBuilder.build());
}
}
mSuggestions.clear();
mSuggestions.addAll(cards);
updateAdapter();
});
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected() {
loadSuggestions();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected() {
}
SuggestionFeatureProviderImpl.java 中要绑定的 Service 对应 ComponentName
@Override
public ComponentName getSuggestionServiceComponent() {
return new ComponentName(
"com.android.settings.intelligence",
"com.android.settings.intelligence.suggestions.SuggestionService");
}
packages\apps\SettingsIntelligence\AndroidManifest.xml
在 SettingsIntelligence 中声明 SuggestionService BIND_SETTINGS_SUGGESTIONS_SERVICE
<service
android:name=".suggestions.SuggestionService"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_SETTINGS_SUGGESTIONS_SERVICE" />
2.2 进入 SettingsLib
frameworks\base\packages\SettingsLib\src\com\android\settingslib\suggestions\SuggestionController.java
进行绑定服务操作,并声明回调接口 ServiceConnectionListener
public SuggestionController(Context context, ComponentName service,
ServiceConnectionListener listener) {
mContext = context.getApplicationContext();
mConnectionListener = listener;
mServiceIntent = new Intent().setComponent(service);
mServiceConnection = createServiceConnection();
}
public void start() {
mContext.bindServiceAsUser(mServiceIntent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
android.os.Process.myUserHandle());
}
public List<Suggestion> getSuggestions() {
if (!isReady()) {
return null;
}
try {
return mRemoteService.getSuggestions();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "mRemote service detached before able to query", e);
return null;
} catch (RemoteException | RuntimeException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Error when calling getSuggestion()", e);
return null;
}
}
private ServiceConnection createServiceConnection() {
return new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Service is connected");
}
mRemoteService = ISuggestionService.Stub.asInterface(service);
if (mConnectionListener != null) {
mConnectionListener.onServiceConnected();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
if (mConnectionListener != null) {
mRemoteService = null;
mConnectionListener.onServiceDisconnected();
}
}
};
}
2.3 进入 frameworks
frameworks\base\core\java\android\service\settings\suggestions\SuggestionService.java
public abstract class SuggestionService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "SuggestionService";
private static final boolean DEBUG = false;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new ISuggestionService.Stub() {
@Override
public List<Suggestion> getSuggestions() {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getSuggestions() " + getPackageName());
}
return onGetSuggestions();
}
public abstract List<Suggestion> onGetSuggestions();
2.4 进入 SettingsIntelligence
packages\apps\SettingsIntelligence\src\com\android\settings\intelligence\suggestions\SuggestionService.java
SuggestionService 继承 frameworks 中 SuggestionService
public class SuggestionService extends android.service.settings.suggestions.SuggestionService {
private static final String TAG = "SuggestionService";
@Override
public List<Suggestion> onGetSuggestions() {
final long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final List<Suggestion> list = FeatureFactory.get(this)
.suggestionFeatureProvider()
.getSuggestions(this);
final List<String> ids = new ArrayList<>(list.size());
for (Suggestion suggestion : list) {
ids.add(suggestion.getId());
}
final long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
FeatureFactory.get(this)
.metricsFeatureProvider(this)
.logGetSuggestion(ids, endTime - startTime);
return list;
}
通过 FeatureFactoryImpl.java 实例化 SuggestionFeatureProvider
@Override
public SuggestionFeatureProvider suggestionFeatureProvider() {
if (mSuggestionFeatureProvider == null) {
mSuggestionFeatureProvider = new SuggestionFeatureProvider();
}
return mSuggestionFeatureProvider;
}
其实是调用 SuggestionFeatureProvider.java 中 getSuggestions()
public List<Suggestion> getSuggestions(Context context) {
final SuggestionParser parser = new SuggestionParser(context);
final List<Suggestion> list = parser.getSuggestions();
final List<Suggestion> rankedSuggestions = getRanker(context).rankRelevantSuggestions(list);
final SuggestionEventStore eventStore = SuggestionEventStore.get(context);
for (Suggestion suggestion : rankedSuggestions) {
eventStore.writeEvent(suggestion.getId(), SuggestionEventStore.EVENT_SHOWN);
}
return rankedSuggestions;
}
SuggestionParser.java
这个名字一听就靠谱了,解析 Suggestion, 遍历 CATEGORIES 集合(默认初始化了category类型),声明在下面 SuggestionCategoryRegistry 中
readSuggestions(category, true /* ignoreDismissRule */) 从每一个 category 中获取 suggestion,看第二个参数对应显示规则,下面会讲
readSuggestions 中通过构建 intent action main category,通过 packagemanage 整个系统 query 符合对应项目,这就是为什么加了 gms 包
以后 Settings 主界面也会出现一些其它 suggestion 菜单。 category 对应匹配类型就在 CATEGORIES 中描述,在 Settings AndroidManifest.xml
中就有很多声明的类型。查询到所有 suggestion 以后,再进行对应过滤最后就返回了要显示的数据集合 suggestions
public List<Suggestion> getSuggestions() {
final SuggestionListBuilder suggestionBuilder = new SuggestionListBuilder();
for (SuggestionCategory category : CATEGORIES) {
if (category.isExclusive() && !isExclusiveCategoryExpired(category)) {
// If suggestions from an exclusive category are present, parsing is stopped
// and only suggestions from that category are displayed. Note that subsequent
// exclusive categories are also ignored.
// Read suggestion and force ignoreSuggestionDismissRule to be false so the rule
// defined from each suggestion itself is used.
final List<Suggestion> exclusiveSuggestions =
readSuggestions(category, false /* ignoreDismissRule */);
if (!exclusiveSuggestions.isEmpty()) {
suggestionBuilder.addSuggestions(category, exclusiveSuggestions);
return suggestionBuilder.build();
}
} else {
// Either the category is not exclusive, or the exclusiveness expired so we should
// treat it as a normal category.
final List<Suggestion> suggestions =
readSuggestions(category, true /* ignoreDismissRule */);
suggestionBuilder.addSuggestions(category, suggestions);
}
}
return suggestionBuilder.build();
}
List<Suggestion> readSuggestions(SuggestionCategory category, boolean ignoreDismissRule) {
final List<Suggestion> suggestions = new ArrayList<>();
final Intent probe = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN);
probe.addCategory(category.getCategory());
List<ResolveInfo> results = mPackageManager
.queryIntentActivities(probe, PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
// Build a list of eligible candidates
final List<CandidateSuggestion> eligibleCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
for (ResolveInfo resolved : results) {
final CandidateSuggestion candidate = new CandidateSuggestion(mContext, resolved,
ignoreDismissRule);
if (!candidate.isEligible()) {
continue;
}
eligibleCandidates.add(candidate);
}
android.util.Log.d("pppp","eligibleCandidates="+eligibleCandidates.size());
// Then remove completed ones
final List<CandidateSuggestion> incompleteSuggestions = CandidateSuggestionFilter
.getInstance()
.filterCandidates(mContext, eligibleCandidates);
android.util.Log.d("pppp","1111incompleteSuggestions="+incompleteSuggestions.size());
// Convert the rest to suggestion.
for (CandidateSuggestion candidate : incompleteSuggestions) {
final String id = candidate.getId();
Suggestion suggestion = mAddCache.get(id);
if (suggestion == null) {
suggestion = candidate.toSuggestion();
mAddCache.put(id, suggestion);
android.util.Log.d("pppp","suggestions ="+suggestion.getTitle().toString());
}
android.util.Log.d("pppp","suggestions size="+suggestions.size());
android.util.Log.d("pppp","suggestions ="+suggestions.contains(suggestion));
if (!suggestions.contains(suggestion)) {
suggestions.add(suggestion);
android.util.Log.d("pppp","suggestions add=");
}
}
return suggestions;
}
SuggestionCategoryRegistry.java
里面包含的 category 类型在 Settings AndroidManifest.xml 中可看到对应
static {
CATEGORIES = new ArrayList<>();
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory(CATEGORY_KEY_DEFERRED_SETUP,
true /* exclusive */, 14 * DateUtils.DAY_IN_MILLIS));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory(CATEGORY_KEY_HIGH_PRIORITY,
true /* exclusive */, 3 * DateUtils.DAY_IN_MILLIS));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory(CATEGORY_KEY_FIRST_IMPRESSION,
true /* exclusive */, 14 * DateUtils.DAY_IN_MILLIS));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.LOCK_SCREEN",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.TRUST_AGENT",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.EMAIL",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.PARTNER_ACCOUNT",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.GESTURE",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.HOTWORD",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.DEFAULT",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
CATEGORIES.add(buildCategory("com.android.settings.suggested.category.SETTINGS_ONLY",
false /* exclusive */, NEVER_EXPIRE));
}
CandidateSuggestion.java 其中有一个很关键方法 isEligible() 用于判断是否符合条件,这决定到 readSuggestions() 中能否被 add
public CandidateSuggestion(Context context, ResolveInfo resolveInfo,
boolean ignoreAppearRule) {
mContext = context;
mIgnoreAppearRule = ignoreAppearRule;
mResolveInfo = resolveInfo;
mIntent = new Intent().setClassName(
resolveInfo.activityInfo.packageName, resolveInfo.activityInfo.name);
mComponent = mIntent.getComponent();
mId = generateId();
mIsEligible = initIsEligible();
}
private boolean initIsEligible() {
if (!ProviderEligibilityChecker.isEligible(mContext, mId, mResolveInfo)) {
return false;
}
if (!ConnectivityEligibilityChecker.isEligible(mContext, mId, mResolveInfo)) {
return false;
}
if (!FeatureEligibilityChecker.isEligible(mContext, mId, mResolveInfo)) {
return false;
}
if (!AccountEligibilityChecker.isEligible(mContext, mId, mResolveInfo)) {
return false;
}
if (!DismissedChecker.isEligible(mContext, mId, mResolveInfo, mIgnoreAppearRule)) {
return false;
}
if (!AutomotiveEligibilityChecker.isEligible(mContext, mId, mResolveInfo)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
这里挑了一个 DismissedChecker.java 看一下,我们需要其中 isEligible() 返回 true
可以看到注释,META_DATA_DISMISS_CONTROL 如果配置 0,则会立即显示,配置其它数字则在对应天数后显示
parseAppearDay() 中解析 META_DATA_DISMISS_CONTROL 对应 value 值,如果是int值则直接返回,如果是字符串则取第一位
获取当前时间和解析时间比较,>= 则返回 true 对应条目就应该显示
上面提到 ignoreAppearRule ,如果为 true 则忽略 META_DATA_DISMISS_CONTROL 配置规则,直接显示
/**
* Allows suggestions to appear after a certain number of days, and to re-appear if dismissed.
* For instance:
* 0,10
* Will appear immediately, the 10 is ignored.
*
* 10
* Will appear after 10 days
*/
@VisibleForTesting
static final String META_DATA_DISMISS_CONTROL = "com.android.settings.dismiss";
// Shared prefs keys for storing dismissed state.
// Index into current dismissed state.
@VisibleForTesting
static final String SETUP_TIME = "_setup_time";
// Default dismiss rule for suggestions.
private static final int DEFAULT_FIRST_APPEAR_DAY = 0;
private static final String TAG = "DismissedChecker";
public static boolean isEligible(Context context, String id, ResolveInfo info,
boolean ignoreAppearRule) {
final SuggestionFeatureProvider featureProvider = FeatureFactory.get(context)
.suggestionFeatureProvider();
final SharedPreferences prefs = featureProvider.getSharedPrefs(context);
final long currentTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
final String keySetupTime = id + SETUP_TIME;
if (!prefs.contains(keySetupTime)) {
prefs.edit()
.putLong(keySetupTime, currentTimeMs)
.apply();
}
// Check if it's already manually dismissed
final boolean isDismissed = featureProvider.isSuggestionDismissed(context, id);
if (isDismissed) {
return false;
}
// Parse when suggestion should first appear. Hide suggestion before then.
int firstAppearDay = ignoreAppearRule
? DEFAULT_FIRST_APPEAR_DAY
: parseAppearDay(info);
Log.d(TAG, "firstAppearDay="+firstAppearDay);
long setupTime = prefs.getLong(keySetupTime, 0);
if (setupTime > currentTimeMs) {
// SetupTime is the future, user's date/time is probably wrong at some point.
// Force setupTime to be now. So we get a more reasonable firstAppearDay.
setupTime = currentTimeMs;
}
final long firstAppearDayInMs = getFirstAppearTimeMillis(setupTime, firstAppearDay);
Log.d(TAG, "currentTimeMs="+currentTimeMs+" firstAppearDayInMs="+firstAppearDayInMs);
if (currentTimeMs >= firstAppearDayInMs) {
// Dismiss timeout has passed, undismiss it.
featureProvider.markSuggestionNotDismissed(context, id);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Parse the first int from a string formatted as "0,1,2..."
* The value means suggestion should first appear on Day X.
*/
private static int parseAppearDay(ResolveInfo info) {
if (!info.activityInfo.metaData.containsKey(META_DATA_DISMISS_CONTROL)) {
return 0;
}
final Object firstAppearRule = info.activityInfo.metaData
.get(META_DATA_DISMISS_CONTROL);
if (firstAppearRule instanceof Integer) {
return (int) firstAppearRule;
} else {
try {
final String[] days = ((String) firstAppearRule).split(",");
return Integer.parseInt(days[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to parse appear/dismiss rule, fall back to 0");
return 0;
}
}
}
private static long getFirstAppearTimeMillis(long setupTime, int daysDelay) {
long days = daysDelay * DateUtils.DAY_IN_MILLIS;
return setupTime + days;
}
}
至此,整个加载流程解析完毕