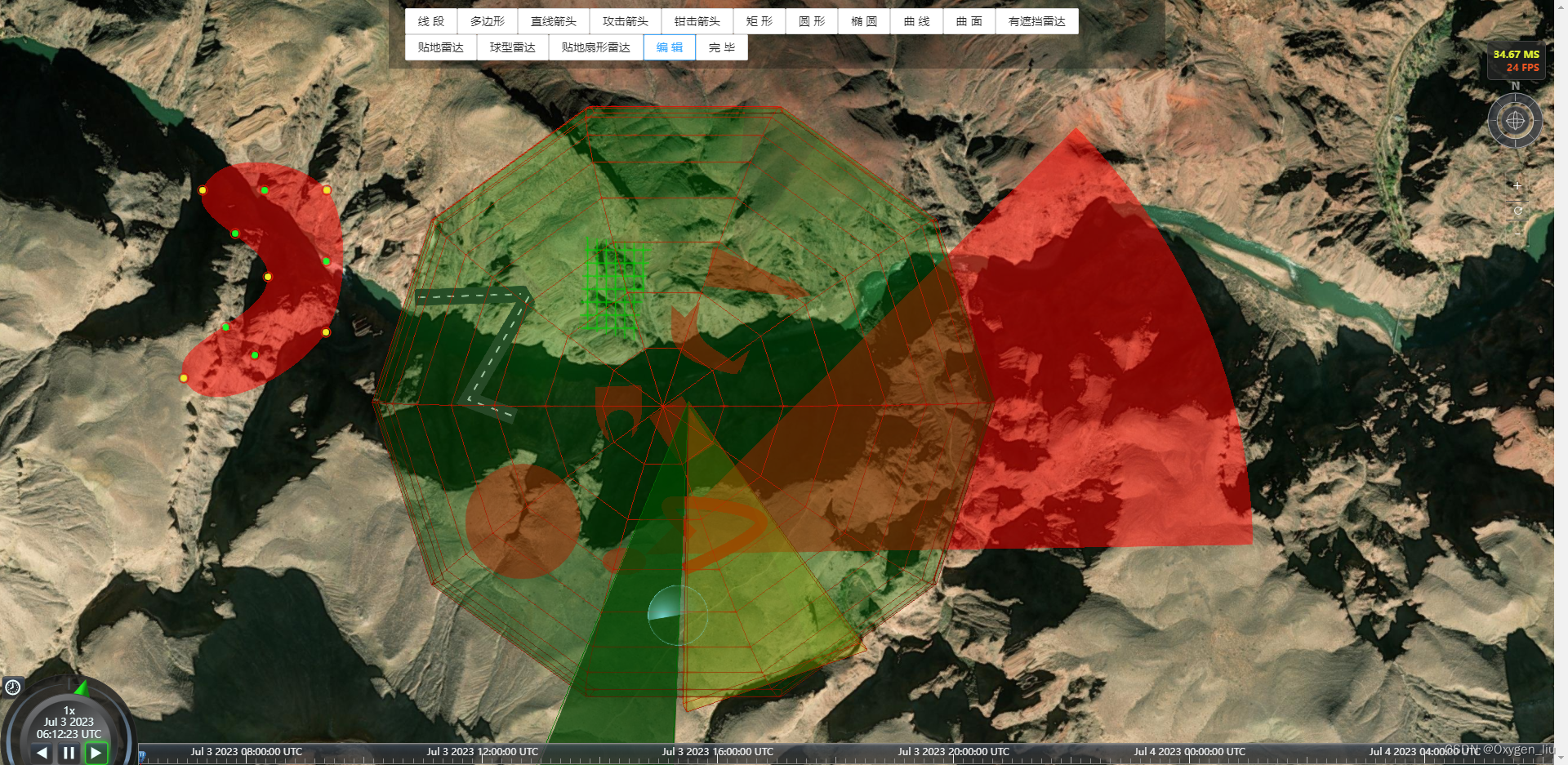
前言:直接放效果图,符合就往下看,不符合出门右转。
由于篇幅有限,只贴出各个标绘的关键代码。
1、线段
- 基于坐标点,加载不同的材质。
//动态加载
const entity = this._viewer.entities.add({
polyline: {
positions: new CallbackProperty(() => {
return this._positions;
}, false),
show: true,
material: Color.RED,
width: 3,
clampToGround: true //是否贴地
}
});
//静态
const primitive = scene.groundPrimitives.add(
new GroundPolylinePrimitive({
geometryInstances: new GeometryInstance({
geometry: new GroundPolylineGeometry({
positions: line,
width: this._width,
}),
id: this.id
}),
appearance: new PolylineMaterialAppearance({
material:
Material.fromType("Image", {
image: this._imageUrl,
repeat: this._repeat
})
}),
})
);
2、多边形
- 基于做坐标点,加载不同的材质
//动态
const entity = this._viewer.entities.add({
polygon: {
hierarchy: new CallbackProperty(() => {
return new PolygonHierarchy(this._positions)
}, false),
show: true,
fill: true,
material: Color.RED.withAlpha(0.5),
//@ts-ignore
clampToGround: true,
width: 3,
outlineColor: Color.BLACK,
outlineWidth: 1,
outline: true
}
});
//静态
const primite = scene.groundPrimitives.add(
new GroundPrimitive({
geometryInstances: new GeometryInstance({
id: this._id,
geometry: new PolygonGeometry({
polygonHierarchy: {
positions: positions,
holes: []
},
}),
}),
appearance: new EllipsoidSurfaceAppearance({
material: Material.fromType("Grid", this._grid)
}),
classificationType: ClassificationType.TERRAIN,
})
)
3、绘制直线箭头
- 根据箭头算法,提供两个点的坐标
//动态
const arrowEntity = this._viewer.entities.add({
polygon: {
hierarchy: new CallbackProperty(() => {
const length = this._positions.length;
const p1 = this._positions[0];
const p2 = this._positions[length - 1];
const firstPoint = this.cartesianToLatlng(p1);
const endPoints = this.cartesianToLatlng(p2);
let arrow = [];
let res = this.fineArrow([firstPoint[0], firstPoint[1]], [endPoints[0], endPoints[1]]);
if (res) {
for (let i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
let cart3 = new Cartesian3(res[i].x, res[i].y, res[i].z);
arrow.push(cart3);
}
return new PolygonHierarchy(arrow);
}
}, false),
show: true,
fill: true,
material: Color.RED.withAlpha(0.5)
}
})
- 箭头算法
/**
*
* @param t 二维坐标
* @param o 二维坐标
* @returns 两点之间的距离
*/
export function distance(t: number[], o: number[]) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(t[0] - o[0], 2) + Math.pow(t[1] - o[1], 2));
}
/**
*
* @param positionArr 点坐标数组
* @returns 距离
*/
export function wholeDistance(positionArr: number[][]) {
let dis = 0;
const length = positionArr.length - 1;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
dis += distance(positionArr[i], positionArr[i + 1]);
}
return dis;
}
export function getBaseLength(positionArr: number[][]) {
return Math.pow(wholeDistance(positionArr), 0.99);
}
/**
*
* @param t
* @param o
* @param e
* @param r
* @param n
* @returns 获取第三个点的坐标
*/
export function getThirdPoint(
t: number[],
o: number[],
e: number,
r: number,
n: boolean = false
) {
let g = getAzimuth(t, o),
i = n ? g + e : g - e,
s = r * Math.cos(i),
a = r * Math.sin(i);
return [o[0] + s, o[1] + a];
}
/**
*
* @param t
* @param o
* @returns 获取方位角
*/
export function getAzimuth(t: number[], o: number[]): number {
let e = 0,
r = Math.asin(Math.abs(o[1] - t[1]) / distance(t, o));
o[1] >= t[1] && o[0] >= t[0]
? (e = r + Math.PI)
: o[1] >= t[1] && o[0] < t[0]
? (e = 2 * Math.PI - r)
: o[1] < t[1] && o[0] < t[0]
? (e = r)
: o[1] < t[1] && o[0] >= t[0]
? (e = Math.PI - r)
: 0;
return e;
}
fineArrowDefualParam() {
return {
tailWidthFactor: 0.15,
neckWidthFactor: 0.2,
headWidthFactor: 0.25,
headAngle: Math['PI'] / 8.5,
neckAngle: Math['PI'] / 0xd
};
}
fineArrow(po1: number[], po2: number[]) {
if ((po1.length < 2) || (po2.length < 2)) return;
//画箭头的函数
let tailWidthFactor = this.fineArrowDefualParam().tailWidthFactor;
let neckWidthFactor = this.fineArrowDefualParam().neckWidthFactor;
let headWidthFactor = this.fineArrowDefualParam().headWidthFactor;
let headAngle = this.fineArrowDefualParam().headAngle;
let neckAngle = this.fineArrowDefualParam().neckAngle;
let o = [];
o[0] = po1;
o[1] = po2;
var e = o[0],
r = o[1],
n = getBaseLength(o),
g = n * tailWidthFactor,
//尾部宽度因子
i = n * neckWidthFactor,
//脖子宽度银子
s = n * headWidthFactor,
//头部宽度因子
a = getThirdPoint(r, e, Math.PI / 2, g, !0),
l = getThirdPoint(r, e, Math.PI / 2, g, !1),
u = getThirdPoint(e, r, headAngle, s, !1),
c = getThirdPoint(e, r, headAngle, s, !0),
p = getThirdPoint(e, r, neckAngle, i, !1),
h = getThirdPoint(e, r, neckAngle, i, !0),
d = [];
d.push(a[0], a[1], p[0], p[1], u[0], u[1], r[0], r[1], c[0], c[1], h[0], h[1], l[0], l[1], e[0], e[1]);
return Cartesian3.fromDegreesArray(d)
}
4、攻击箭头
- 提供坐标点 绘制攻击箭头也叫燕尾箭头
import initXp from 'algorithm.js'
//动态
const xp = initXp()
const update = () => {
//计算面
if (positions.length < 3) {
return null;
}
let lnglatArr = [], lnglat;
for (var i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
lnglat = this.cartesianToLatlng(positions[i]);
lnglatArr.push(lnglat)
}
const res = xp.algorithm.tailedAttackArrow(lnglatArr);
const returnData = res.polygonalPoint;
return new PolygonHierarchy(returnData);
}
this._viewer.entities.add({
polygon: new PolygonGraphics({
hierarchy: new CallbackProperty(update, false),
show: true,
fill: true,
material: this.fillMaterial
})
});
function cartesianToLatlng(position: Cartesian3) {
const latlng =
this._viewer.scene.globe.ellipsoid.cartesianToCartographic(position);
const lat = CesiumMath.toDegrees(latlng.latitude);
const lng = CesiumMath.toDegrees(latlng.longitude);
return [lng, lat];
}
5、钳击箭头
- 一共需要提供五个点
const update = () => {
//计算面
if (positions.length < 3) {
return null;
}
var lnglatArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
var lnglat = this.cartesianToLatlng(positions[i]);
lnglatArr.push(lnglat)
}
const xp = initXp()
let res = xp.algorithm.doubleArrow(lnglatArr);
const returnData = res.polygonalPoint;
return new PolygonHierarchy(returnData);
}
return this._viewer.entities.add({
polygon: new PolygonGraphics({
hierarchy: new CallbackProperty(update, false),
show: true,
fill: true,
material: this.fillMaterial
})
});
function cartesianToLatlng(position: Cartesian3) {
const latlng =
this._viewer.scene.globe.ellipsoid.cartesianToCartographic(position);
const lat = CesiumMath.toDegrees(latlng.latitude);
const lng = CesiumMath.toDegrees(latlng.longitude);
return [lng, lat];
}
6、矩形
- 提供两个点
import { point } from "@turf/helpers"
import rhumbBearing from "@turf/rhumb-bearing"
import distance from "@turf/distance"
import destination from "@turf/destination"
const entity = this._viewer.entities.add({
polygon: {
hierarchy: new CallbackProperty(() => {
if (this._positions[0] && this._positions[1] && this._positions[2]) {
const r0 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[0])
const r1 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[1]) // 辅助点
const r2 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[2])
const p0 = point([r0.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r0.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
const p1 = point([r1.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r1.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
const p2 = point([r2.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r2.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
const bearing1 = rhumbBearing(p0, p1)
const bearing2 = rhumbBearing(p0, p2)
const angle1 = bearing2 - bearing1
// 对角长度
const length = distance(p0, p2, { units: 'miles' })
const len1 = Math.cos(angle1 / 180 * Math.PI) * length
const dest1 = destination(p0, len1, bearing1, { units: 'miles' })
const angle2 = 90 - angle1
const len2 = Math.cos(angle2 / 180 * Math.PI) * length
const dest2 = destination(p0, len2, 90 + bearing1, { units: 'miles' })
//@ts-ignore
const coordinates = [this._positions[0], Cartesian3.fromDegrees(...dest1.geometry.coordinates), this._positions[2], Cartesian3.fromDegrees(...dest2.geometry.coordinates)]
return new PolygonHierarchy(coordinates)
}
}, false),
material: this._color
},
})
7、绘制椭圆
- 绘制椭圆需要两个点,注意长轴必须大于短轴,长短轴一致时为圆
import { point } from "@turf/helpers"
import distance from "@turf/distance"
const entity = this._viewer.entities.add({
//@ts-ignore
position: new CallbackProperty(() => {
return this._positions[0]
}, false),
ellipse: {
// 半短轴(画圆:半短轴和半长轴一致即可)
semiMinorAxis: new CallbackProperty(() => {
const r0 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[0])
const r1 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[1])
const p0 = point([r0.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r0.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
let p3 = point([r1.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r1.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
if (this._isEllipse) {
let p1 = point([r1.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r0.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
let p2 = point([r0.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r1.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
let len1, len2
len1 = distance(p0, p1, { units: 'kilometers' }) * 1000
len2 = distance(p0, p2, { units: 'kilometers' }) * 1000
return len1 < len2 ? len1 : len2
} else return distance(p0, p3, { units: 'kilometers' }) * 1000
}, false),
// 半长轴
semiMajorAxis: new CallbackProperty(() => {
const r0 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[0])
const r1 = Cartographic.fromCartesian(this._positions[1])
const p0 = point([r0.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r0.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
let p3 = point([r1.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r1.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
if (this._isEllipse) {
let p1 = point([r1.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r0.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
let p2 = point([r0.longitude * 180 / Math.PI, r1.latitude * 180 / Math.PI])
let len1, len2
len1 = distance(p0, p1, { units: 'kilometers' }) * 1000
len2 = distance(p0, p2, { units: 'kilometers' }) * 1000
return len1 > len2 ? len1 : len2
} else return distance(p0, p3, { units: 'kilometers' }) * 1000
}, false),
// 填充色
material: this._color,
},
});
8、绘制曲线
- 绘制曲线利用bezier算法
import { lineString, bezierSpline } from '@turf/turf'
const entity = this._viewer.entities.add({
polyline: {
positions: new CallbackProperty(() => {
const lngLatPoints = this._positions.map(i => this.cartesianToLatlng(i))
const pos = bezierSpline(lineString(lngLatPoints)).geometry.coordinates
return Cartesian3.fromDegreesArray(pos.flat())
}, false),
show: true,
material: Color.RED,
width: 3,
clampToGround: true //是否贴地
}
});
9、绘制封闭曲面
- 根据turf
const entity = this._viewer.entities.add({
polygon: {
hierarchy: new CallbackProperty(() => {
if (this._positions.length < 2) return []
let pnts = []
for (let p = 0; p < this._positions.length; p++) {
pnts.push(this.cartesianToLatlng(this._positions[p]))
}
pnts.push(pnts[0], pnts[1])
let normals: number[][] = []
let pList: Cartesian3[] = []
for (let i = 0; i < pnts.length - 2; i++) {
let normalPoints = this.getBisectorNormals(this._t, pnts[i], pnts[i + 1], pnts[i + 2])
normals = normals.concat(normalPoints)
}
let count = normals.length
normals = [normals[count - 1]].concat(normals.slice(0, count - 1))
for (let i = 0; i < pnts.length - 2; i++) {
let pnt1 = pnts[i]
let pnt2 = pnts[i + 1]
pList.push(this.latlngTocartesian(pnt1))
for (let t = 0; t <= this._FITTING_COUNT; t++) {
let pnt = this.getCubicValue(t / this._FITTING_COUNT, pnt1, normals[i * 2], normals[i * 2 + 1], pnt2)
pList.push(this.latlngTocartesian(pnt))
}
pList.push(this.latlngTocartesian(pnt2))
}
return new PolygonHierarchy(pList)
}, false),
show: true,
fill: true,
material: Color.RED.withAlpha(0.5),
//@ts-ignore
clampToGround: true,
width: 3,
outlineColor: Color.BLACK,
outlineWidth: 1,
outline: true
}
});
function getBisectorNormals(t: number, pnt1: number[], pnt2: number[], pnt3: number[]): number[][] {
let normal = this.getNormal(pnt1, pnt2, pnt3)
let bisectorNormalRight: number[] = []
let bisectorNormalLeft: number[] = []
let dt: number, x: number, y: number
let dist = Math.sqrt(normal[0] * normal[0] + normal[1] * normal[1])
let uX = normal[0] / dist
let uY = normal[1] / dist
let d1 = this.mathDistance(pnt1, pnt2)
let d2 = this.mathDistance(pnt2, pnt3)
if (dist > this._ZERO_TOLERANCE) {
if (this.isClockWise(pnt1, pnt2, pnt3)) {
dt = t * d1
x = pnt2[0] - dt * uY
y = pnt2[1] + dt * uX
bisectorNormalRight = [x, y]
dt = t * d2
x = pnt2[0] + dt * uY
y = pnt2[1] - dt * uX
bisectorNormalLeft = [x, y]
} else {
dt = t * d1
x = pnt2[0] + dt * uY
y = pnt2[1] - dt * uX
bisectorNormalRight = [x, y]
dt = t * d2
x = pnt2[0] - dt * uY
y = pnt2[1] + dt * uX
bisectorNormalLeft = [x, y]
}
} else {
x = pnt2[0] + t * (pnt1[0] - pnt2[0])
y = pnt2[1] + t * (pnt1[1] - pnt2[1])
bisectorNormalRight = [x, y]
x = pnt2[0] + t * (pnt3[0] - pnt2[0])
y = pnt2[1] + t * (pnt3[1] - pnt2[1])
bisectorNormalLeft = [x, y]
}
return [bisectorNormalRight, bisectorNormalLeft]
}
getNormal(pnt1: number[], pnt2: number[], pnt3: number[]) {
let dX1 = pnt1[0] - pnt2[0]
let dY1 = pnt1[1] - pnt2[1]
let d1 = Math.sqrt(dX1 * dX1 + dY1 * dY1)
dX1 /= d1
dY1 /= d1
let dX2 = pnt3[0] - pnt2[0]
let dY2 = pnt3[1] - pnt2[1]
let d2 = Math.sqrt(dX2 * dX2 + dY2 * dY2)
dX2 /= d2
dY2 /= d2
let uX = dX1 + dX2
let uY = dY1 + dY2
return [uX, uY]
}
function mathDistance(pnt1: number[], pnt2: number[]) {
return (Math.sqrt(Math.pow((pnt1[0] - pnt2[0]), 2) + Math.pow((pnt1[1] - pnt2[1]), 2)))
}
function isClockWise(pnt1: number[], pnt2: number[], pnt3: number[]) {
return ((pnt3[1] - pnt1[1]) * (pnt2[0] - pnt1[0]) > (pnt2[1] - pnt1[1]) * (pnt3[0] - pnt1[0]))
}
- 雷达在我之前博客中