文章目录
- TypeScript 总结
- 概述
- 运行ts文件
- 方式一
- 方式二
- 基础
- 声明变量
- 类型
- 数组
- 元组
- 联合类型
- 取值限制
- 枚举类型
- any & unknown
- void & undefined
- 类型适配
- 面向对象
- 函数
- 普通函数
- 箭头函数
- 可选参数
- 默认参数
- 对象
- 创建对象
- 对象的类型限制
- 类和接口
- 泛型
- 简单使用
- 多个泛型
- 默认泛型类型
- 进阶
- 类型守卫
- 自定义类型守卫
- 函数重载
- 调用签名
TypeScript 总结
概述
TypeScript 是一种基于 JavaScript 构建的强类型编程语言,可为你提供任何规模的更好工具。
官方文档
中文文档
TypeScript资料
运行ts文件
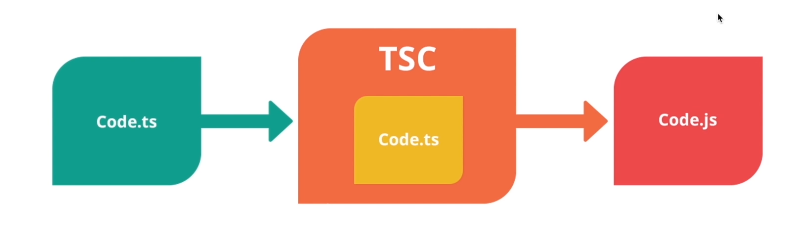
方式一
一、安卓typescript:
npm install -g typescript
二、将ts文件编译为js文件:
tsc code.ts
三、运行js文件:
node code.js
查看tsc版本:
tsc -v
使用ES5编译ts代码:
tsc -t es5 demo.ts
方式二
一、安装ts-node:
npm install -g typescript ts-node
二、运行ts文件:
ts-node code.ts
基础
声明变量
var a = 1;
let b = 2;
const c = 3;
类型
TypeScript是JavaScript的一个超集,它添加了静态类型和一些其他的特性。
类型:boolean 布尔值、number 数字、string 字符串、array 数组、tuple 元组、enum 元组、any 任意类型、void、null、undefined、never、object。
数组
let arr1: number[] = [1, 2, 3, 4];
let arr2: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3, 4];
let arr3 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
元组
let person: [string, number] = ["小明", 18];
console.log(person[0]); //小明
console.log(person[1]); //18
联合类型
let union1: string | number;
union1 = 2;
union1 = "hello";
取值限制
let union2: 10 | 20 | 30;
// union2 = 1; //报错
union2 = 10;
枚举类型
enum Color {
red,
green,
blue,
}
let color = Color.red;
console.log(color); //0
自定义值:
enum Sports {
football = "足球",
basketball = "篮球",
pingpong = "乒乓球",
}
let s = Sports.football;
console.log(s); //足球
any & unknown
- any:任意类型,没有类型检查。
- unknown:未知类型,会进行类型检查。
let a: any;
a = 123;
a = "abc";
a.eat(); //不会提示报错
let a: unknown;
a = 123;
a = "abc";
a.eat(); //提示报错
void & undefined
- void:表示没有返回值,主要用于函数。
- undefined:表示值未定义。
function fun1(): void {
}
console.log(fun1()); //undefined
function fun2(): undefined {
let a;
return a;
}
console.log(fun2()); //undefined
类型适配
类型适配:也称为类型断言,将某个值强转为指定类型。
无类型适配:
let msg: any;
msg = "hello";
let result = msg.endsWith("o");
console.log(result); //true
说明:调用endsWidth方法时没有提示。
适配方式一:
let msg: any;
msg = "hello";
let result = (<string>msg).endsWith("o");
说明:通过<string>将any转为string类型,调用endsWidth方式有提示。
适配方式二:
let msg: any;
msg = "hello";
let result = (msg as string).endsWith("o");
说明:通过as string将any转为string类型。
面向对象
函数
普通函数
function fun(msg: string) {
console.log(msg);
}
箭头函数
let fun = (msg: string) => console.log(msg);
可选参数
let fun = (msg: string, code?: number) => console.log(msg);
默认参数
let fun = (msg: string, code: number = 0) => console.log(msg, code);
对象
创建对象
const user = {
name: "小明",
age: 18,
address: "北京市",
};
console.log(user.name);
// console.log(user.nickname); //提示报错
对象的类型限制
let user: { name: string; age: number; address: string };
user = {
name: "小明",
age: 18,
address: "北京市",
};
console.log(user.name);
类和接口
interface IPoint {
x: number;
y: number;
}
const drawPoint = (point: IPoint) => {
console.log({ x: point.x, y: point.y });
};
drawPoint({ x: 100, y: 200 });
// drawPoint({ x: "abc", y: true }); //提示报错
interface IPoint {
x: number;
y: number;
drawPoint: () => void;
}
class Point implements IPoint {
x: number;
y: number;
constructor(x: number, y: number) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
drawPoint() {
console.log({ x: this.x, y: this.y });
}
}
let p = new Point(2, 3);
p.drawPoint();
泛型
简单使用
// 普通泛型函数
function lastInArray<T>(arr: T[]) {
return arr[arr.length - 1];
}
console.log(lastInArray(["a", "b", "c", "d"])); //d
// 箭头泛型函数
const lastInArray = <T>(arr: T[]) => arr[arr.length - 1];
// 联合类型
console.log(lastInArray<string | number>(["a", "b", "c", 1])); //d
多个泛型
let makeArray = <T, Y>(x: T, y: Y) => [x, y];
let result = makeArray("a", true);
console.log(result); //[ 'a', true ]
默认泛型类型
let makeArray = <T, Y = number>(x: T, y: Y) => [x, y];
let result = makeArray<string>("a", 1);
console.log(result); //[ 'a', 1 ]
进阶
类型守卫
在 TypeScript 中,类型守卫是一种表达式,它在编译时期检查某个变量的类型,以确保在某个特定的代码块中,该变量的类型是已知的。这对于避免类型错误非常有用,因为它可以确保你在处理变量时,变量的类型是你期望的那种类型。
type Square = {
size: number;
};
type Rectangle = {
width: number;
height: number;
};
type Shape = Square | Rectangle;
function area(shape: Shape) {
if ("size" in shape) {
return shape.size * shape.size;
} else if ("width" in shape) {
return shape.width * shape.height;
}
}
let shape = { size: 20 };
console.log(area(shape)); //400
let shape2 = { width: 20, height: 30 };
console.log(area(shape2)); //600
自定义类型守卫
需要借助is表达式。
type Square = {
size: number;
};
type Rectangle = {
width: number;
height: number;
};
type Shape = Square | Rectangle;
function isSquare(shape: Shape): shape is Square {
return "size" in shape;
}
function isRectangle(shape: Shape): shape is Rectangle {
return "width" in shape;
}
function area(shape: Shape) {
if (isSquare(shape)) {
return shape.size * shape.size;
} else if (isRectangle(shape)) {
return shape.width * shape.height;
}
}
let shape = { size: 20 };
console.log(area(shape)); //400
let shape2 = { width: 20, height: 30 };
console.log(area(shape2)); //600
函数重载
在TypeScript中,函数重载是指在一个函数名下定义多个函数签名,每个函数签名对应不同的参数类型和返回值类型。通过函数重载,我们可以根据不同的参数类型和返回值类型来实现不同的函数行为。
function reverse(string: string): string;
function reverse(array: string[]): string[];
function reverse(stringOrArray: string | string[]) {
if (typeof stringOrArray == "string") {
return stringOrArray.split("").reverse().join("");
} else {
return stringOrArray.slice().reverse();
}
}
console.log(reverse("hello")); //olleh
console.log(reverse(["h", "e", "l", "l", "o"])); //[ 'o', 'l', 'l', 'e', 'h' ]
function makeDate(timestamp: number): Date;
function makeDate(year: number, month: number, day: number): Date;
function makeDate(timestampOrYear: number, month?: number, day?: number) {
if (month != null && day != null) {
return new Date(timestampOrYear, month - 1, day);
} else {
return new Date(timestampOrYear);
}
}
console.log(makeDate(1688368612562));
console.log(makeDate(2008, 9, 10));
调用签名
TypeScript调用签名是指在TypeScript中定义函数或方法时,指定函数的参数类型和返回值类型。通过调用签名,我们可以明确指定函数的输入和输出类型,以提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
type Add = (a: number, b: number) => number;
const add: Add = (a: number, b: number) => {
return a + b;
};
console.log(add(2, 3)); //5
实现函数重载:
type Add = {
(a: number, b: number): number;
(a: number, b: number, c: number): number;
};
const add: Add = (a: number, b: number, c?: number) => {
return a + b + (c != null ? c : 0);
};
console.log(add(1, 2)); //3
console.log(add(1, 2, 3)); //6
实现constructor重载: