import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"]=["SimHei"] #设置字体
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"]=False #该语句解决图像中的“-”负号的乱码问题
# 创建初始种群
def create_initial_population():
population = []
for _ in range(population_size):
chromosome = list(cities.keys())
random.shuffle(chromosome)
population.append(chromosome)
return population
# 计算两个城市之间的距离
def distance(city1, city2):
x1, y1 = cities[city1]
x2, y2 = cities[city2]
return ((x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2) ** 0.5
# 计算适应度(路径长度)
def calculate_fitness(chromosome):
total_distance = 0
for i in range(len(chromosome) - 1):
city1, city2 = chromosome[i], chromosome[i + 1]
total_distance += distance(city1, city2)
return total_distance
# 选择精英个体
def select_elite(population):
elite = []
sorted_population = sorted(population, key=lambda chromosome: calculate_fitness(chromosome))
for i in range(elite_size):
elite.append(sorted_population[i])
return elite
# 进化过程(交叉和变异)
def evolve_population(population):
# 选择精英种群
elite = select_elite(population)
new_population = elite.copy()
# 初始种群数量, population_size = 50
while len(new_population) < population_size:
parent1 = random.choice(elite)
parent2 = random.choice(elite)
# 交叉操作
child = crossover(parent1, parent2)
mutate(child)
# 交叉操作后的种群添加到新的种群里面去
new_population.append(child)
# 返回新的种群
return new_population
# 交叉操作
def crossover(parent1, parent2):
child = ['-'] * len(parent1)
start = random.randint(0, len(parent1) - 1)
end = random.randint(start, len(parent1) - 1)
child[start:end+1] = parent1[start:end+1]
for city in parent2:
if city not in child:
index = child.index('-')
child[index] = city
return child
# 变异操作
def mutate(chromosome):
for i in range(len(chromosome)):
if random.random() < mutation_rate:
j = random.randint(0, len(chromosome) - 1)
# 染色体的两个片段进行交互
chromosome[i], chromosome[j] = chromosome[j], chromosome[i]
# 主函数
def run():
# 创建初始种群, 随机生成n个种群
population = create_initial_population()
best_distance = float('inf')
best_chromosome = []
# 进化一百次
for _ in range(generations):
# 把随机生成的种群放进去进化
population = evolve_population(population)
# 计算当前的适应度,并选出最小的(路径)的一组
current_best = min(population, key=lambda chromosome: calculate_fitness(chromosome))
current_distance = calculate_fitness(current_best)
# 比较当前的最小距离和全局最优的距离
if current_distance < best_distance:
best_distance = current_distance
best_chromosome = current_best
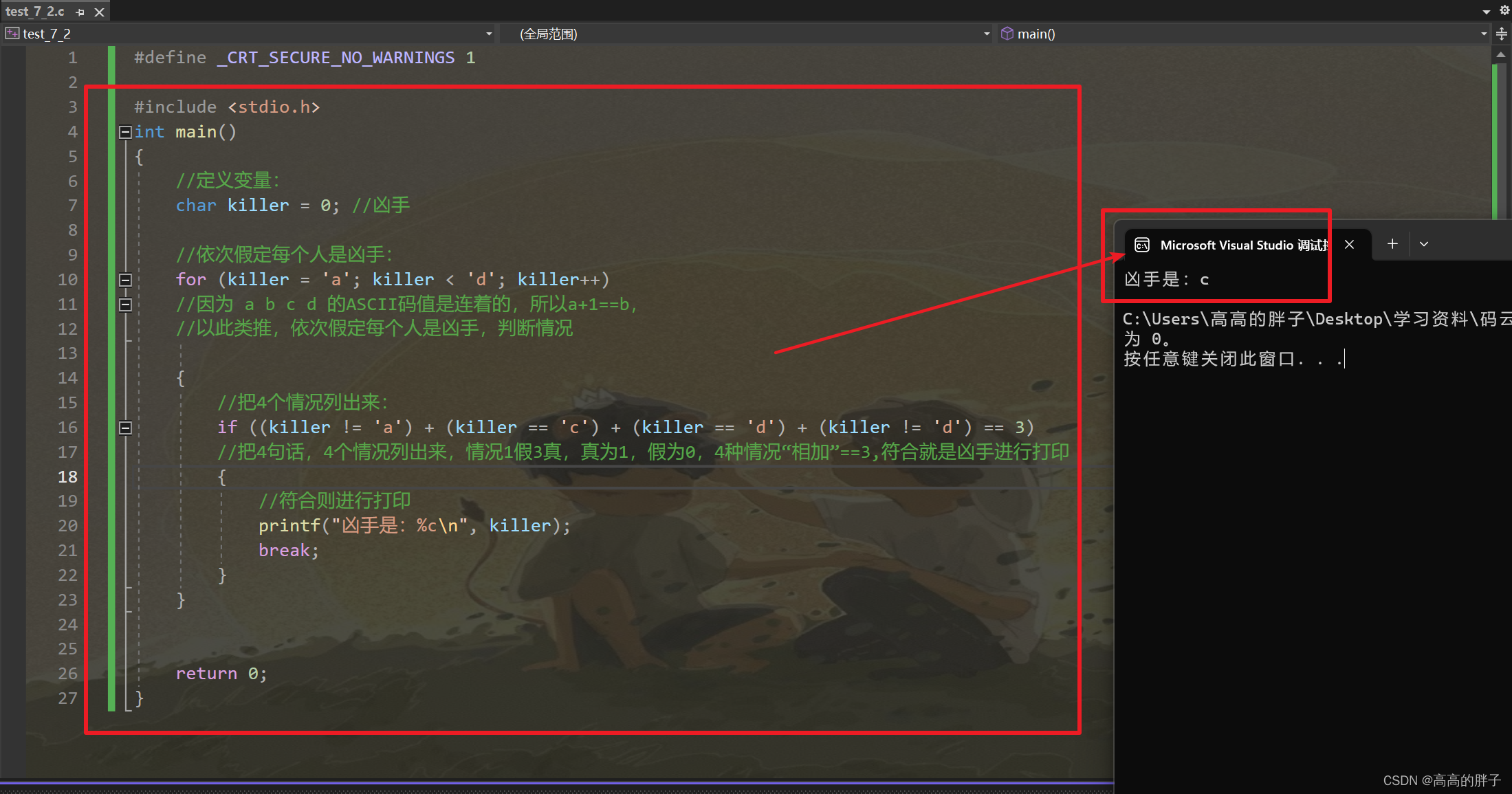
print("最短路径:", best_chromosome)
print("最短路径长度:", best_distance)
return best_chromosome
# 运行主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
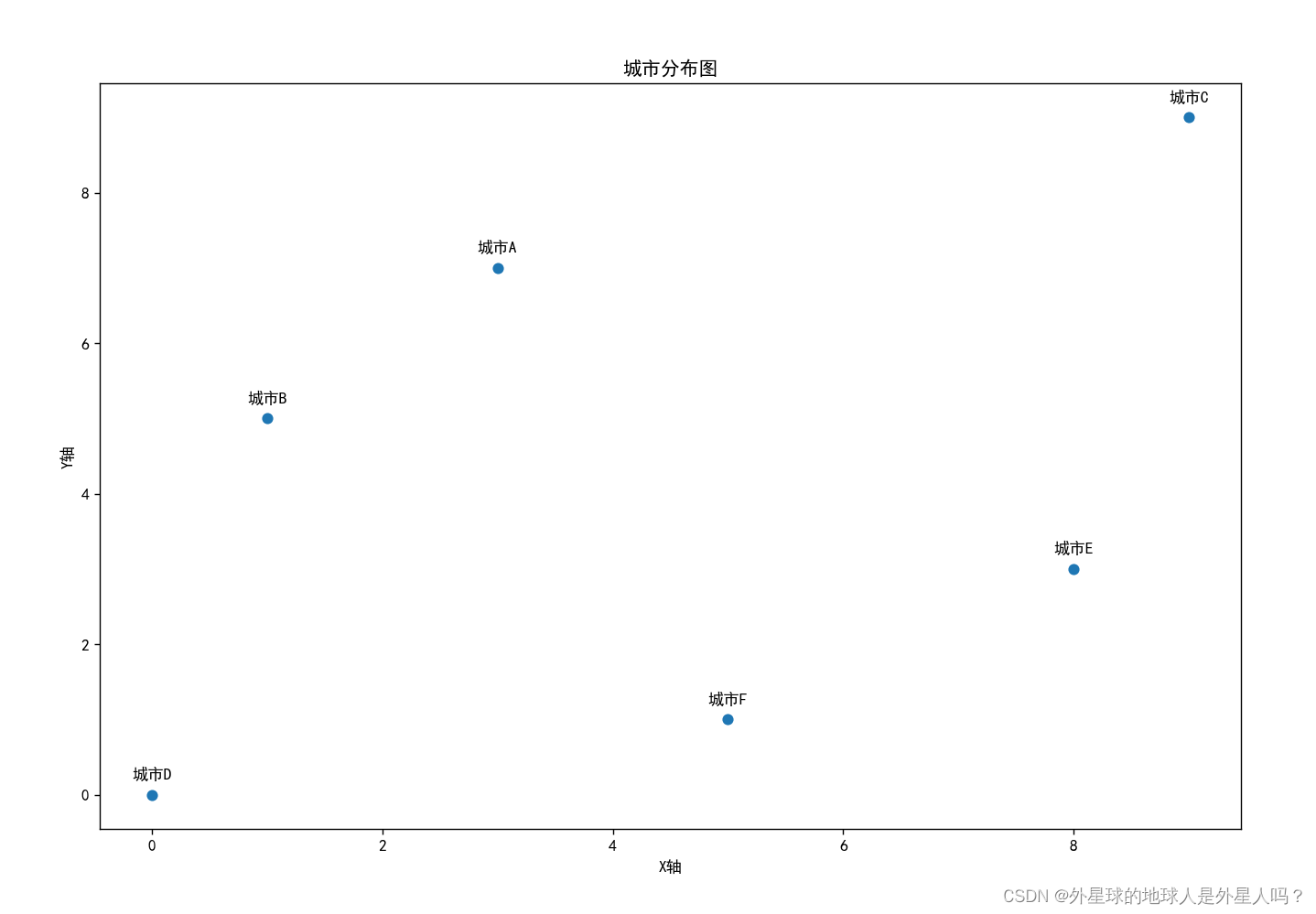
# 城市坐标
cities = {
'城市A': (3, 7),
'城市B': (1, 5),
'城市C': (9, 9),
'城市D': (0, 0),
'城市E': (8, 3),
'城市F': (5, 1)
}
x = [cities[k][0] for k in cities]
y = [cities[k][1] for k in cities]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('X轴')
ax.set_ylabel('Y轴')
ax.set_title('城市分布图')
for i, txt in enumerate(cities.keys()):
ax.annotate(txt, (x[i], y[i]), textcoords='offset points', xytext=(0, 10), ha='center')
# 显示图形
plt.show()
# 遗传算法参数
# 初始种群数量
population_size = 50
# 精英个体数量,即每次进化,筛选出来的数量
elite_size = 10
# mutation_rate(变异率),表示在交叉操作后发生基因变异的概率
mutation_rate = 0.01
# 进化次数
generations = 100
res = run()
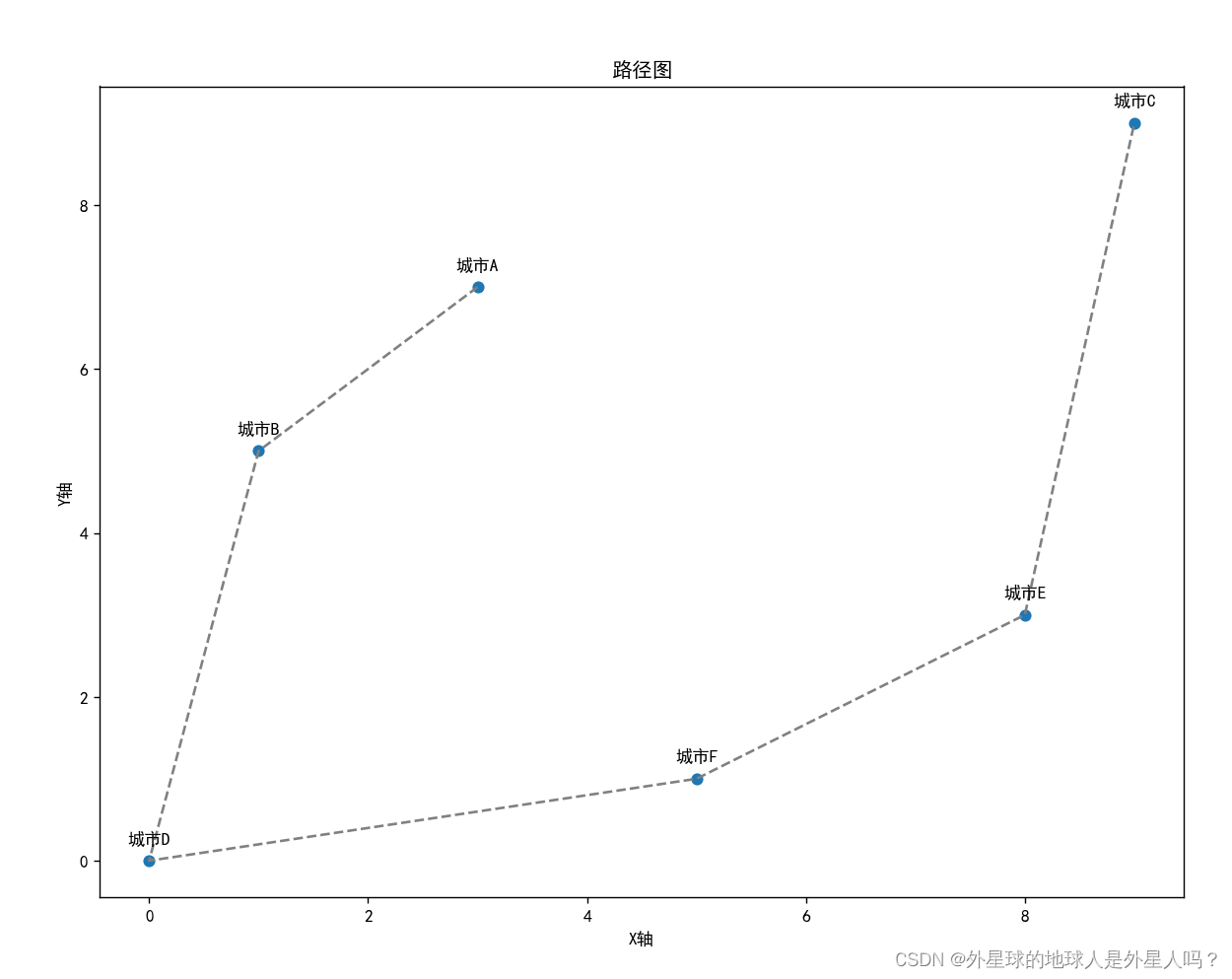
res_x = [cities[r][0] for r in res]
res_y = [cities[r][1] for r in res]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
scatter = ax.scatter(res_x, res_y)
path = ax.plot(res_x, res_y, '--', color='gray')
ax.set_xlabel('X轴')
ax.set_ylabel('Y轴')
ax.set_title('路径图')
for i, txt in enumerate(res):
ax.annotate(txt, (res_x[i], res_y[i]), textcoords='offset points', xytext=(0, 10), ha='center')
plt.show()