SpringBoot原理篇
自动配置
bean加载方式
xml方式声明bean
相关类:
domain域中的实体类:
public class Mouse {
}
public class Cat {
}
public class Dog {
}
测试:
public class App1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext1.xml");
Object cat = classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("cat");
Dog bean = classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean(Dog.class);
System.out.println(cat);
System.out.println(bean);
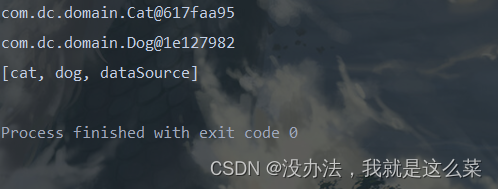
String[] names = classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
}
}
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-2.0.xsd">
<!--xml方式声明自己开发的bean-->
<bean id="cat" class="com.dc.domain.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog" class="com.dc.domain.Dog"/>
<!--xml方式声明第三方开发的bean-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"/>
</beans>
结果:
xml+注解定义bean
domain域中的实体类
@Component(value = "cat")
public class Cat {
}
@Service("jerry")
public class Mouse {
}
配置类:
//@Component
//配置类注解
@Configuration
public class DBConfig {
@Bean
public DruidDataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
return ds;
}
}
@Configuration中使用@Conponent实现的,所以两个都可以实现bean注入,建议使用前者
配置类:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--指定加载bena的位置,component-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dc"/>
</beans>
结果:
注解方式
配置扫描类(value属性值为需要使用注解的包):
@ComponentScan(value = "com.dc")
public class SpringConfig3 {
}
测试类:
public class App3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig3.class);
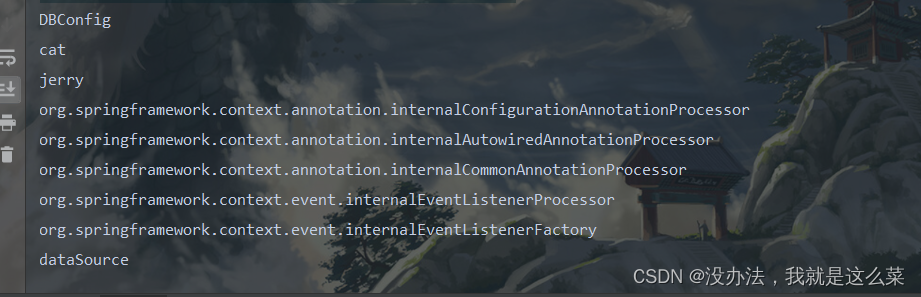
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
结果:
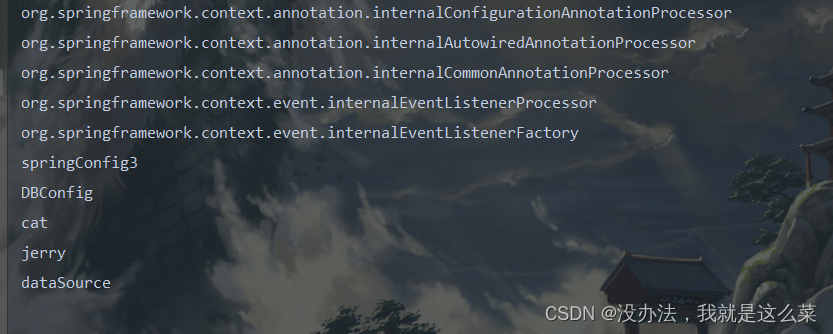
FactoryBean接口
配置类:
@ComponentScan(value = "com.dc")
public class SpringConfig3 {
@Bean
public Dog dog1() {
return new Dog();
}
@Bean
public DogFactoryBean dog(){
return new DogFactoryBean();
}
}
测试类:
public class App3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig3.class);
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("dog"));
}
}
结果:
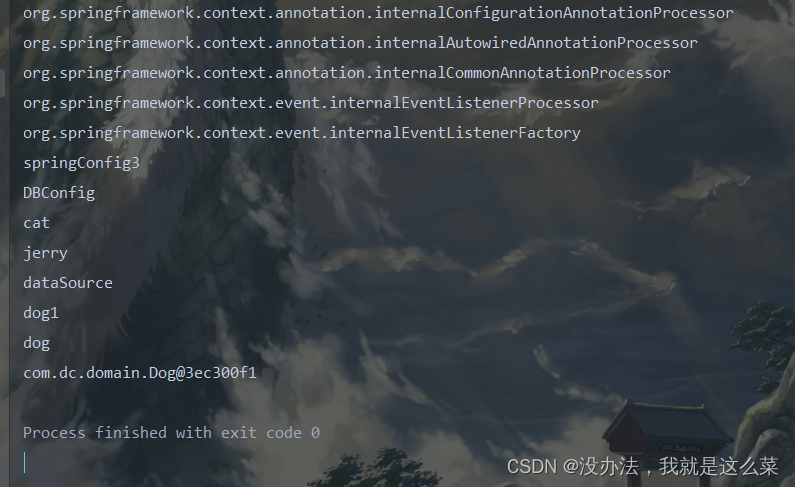
加载配置类并加载配置文件(系统迁移)
@ImportResource("applicationContext1.xml")
public class SpringConfig32 {
}
只需要@ImportResource注解就可以了
测试类
public class App32 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig32.class);
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
结果:
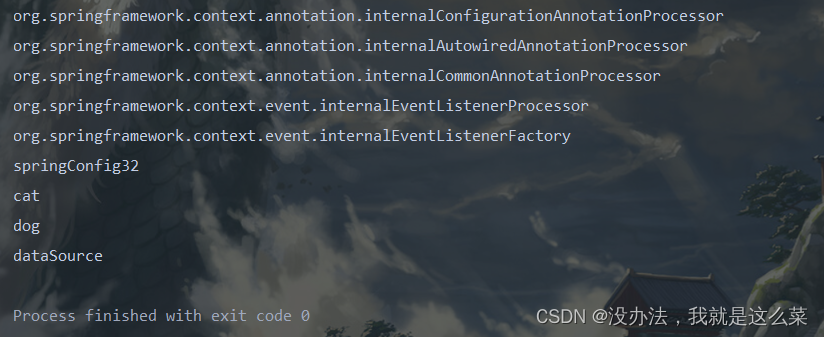
@Import()注解导入要注入的bean对应的字节码
作用:能够有效的降低源代码与Spring技术的耦合度,在Spring技术底层及诸多框架的整合中大量使用。导入时是全路径类名
配置类:
@Import(Dog.class)
public class SpringConfig4 {
}
实体类:
public class Dog {
}
测试:
public class App4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig4.class);
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
结果:
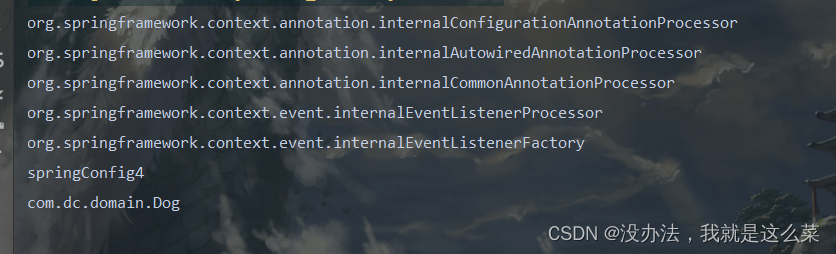
使用registerBean方法注册bean对象
使用这个方法会以键值对的方式加载bean对象,如果要以同一个key记载bean对象时,会以最后一次导入的值覆盖原来的值
实体类:
public class Cat {
private int age;
public Cat() {
}
public Cat(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类:
public class App4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig4.class);
// 上下文容器对象已经初始化完毕后,手动加载bean
annotationConfigApplicationContext.registerBean("tom", Cat.class, 0);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.registerBean("tom", Cat.class, 1);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.registerBean("tom", Cat.class, 3);
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Cat.class));
}
}
结果:
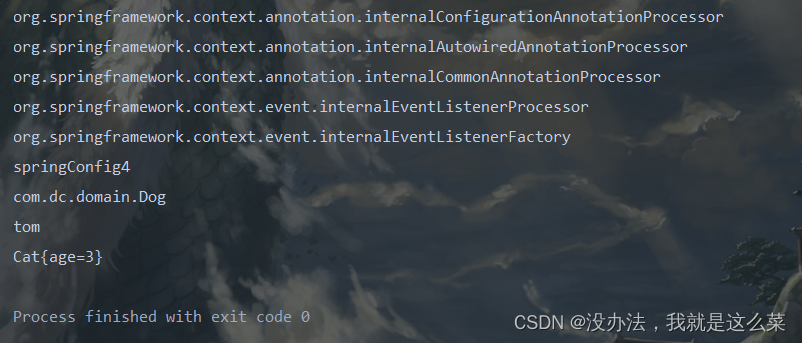
@Register注解bean对象的名字为类名首字母小写
ImportSelector接口
作用:各种条件判定,判定完毕后,决定是否加载指定的bean
MyimportSelector类:
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
boolean b = metadata.hasAnnotation("org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration");
if (b) {
// 若SpringConfig6有@Configuration注解,就加载Dog的bean对象
return new String[]{"com.dc.domain.Dog"};
}
// 否则就加载Cat的bean对象
return new String[]{"com.dc.domain.Cat"};
}
}
SpringConfig6:
//@Configuration
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
public class SpringConfig6 {
}
测试:
public class App6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig6.class);
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
结果:
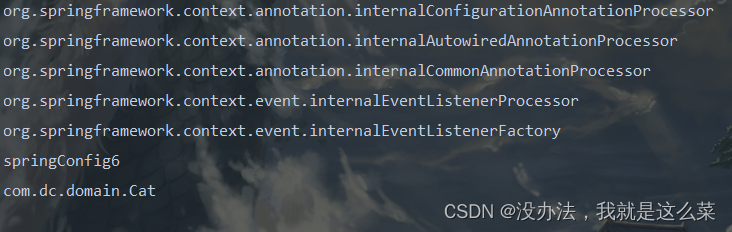
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
导入实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口的类,通过BeanDefinition的注册器注册实名bean,实现对容器中bean的裁定。例如对现有bean的覆盖,进而达成不修改源代码的情况下更换实现的效果
MyRegistrar类:
public class MyRegistar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 1、使用元数据进行判定
// 2、注册相应的实名bean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(Dog.class).getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition("yellow", beanDefinition);
}
}
SpringConfig7:
@Import(MyRegistar.class)
public class SpringConfig7 {
}
测试:
public class App7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig7.class);
String[] naems = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : naems) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
结果:
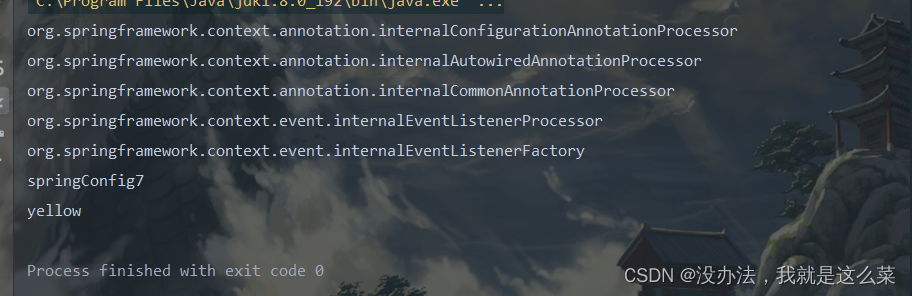
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
导入实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类,通过BeanDefinition的注册器注册实名的bean,实现对容器中bean的最终裁定
MyBeanProcessor类:
public class MyBeanProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(BookServiceImpl4.class).getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition("bookService", beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
MyRegistar类:
public class MyRegistar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 1使用元数据进行判定
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(BookServiceImpl2.class).getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition("bookService", beanDefinition);
}
}
SpringConfig8:
@Import({BookServiceImpl1.class, MyRegistar.class, MyBeanProcessor.class})
public class SpringConfig8 {
}
BookServiceImpl
@Service("bookService")
public class BookServiceImpl1 implements BookService {
@Override
public void check() {
System.out.println("book service1..");
}
}
测试:
public class App8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig8.class);
BookService bookService = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
bookService.check();
}
}
结果:
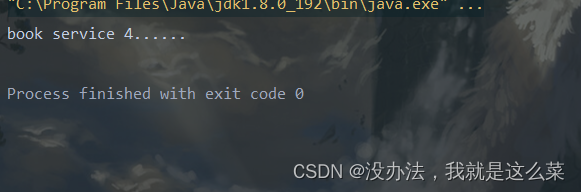 !
!
bean加载控制
编程式
根据任意条件确认是否加载bean
MyImportSelector类:
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
try {
Class<?> clzz = Class.forName("com.dc.bean.Mouse");
if (clzz !=null){
return new String[]{"com.dc.bean.Cat"};
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
return new String[0];
}
return null;
}
}
配置类:
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
public class SpringConfig {
}
测试:
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
String[] names = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
结果:
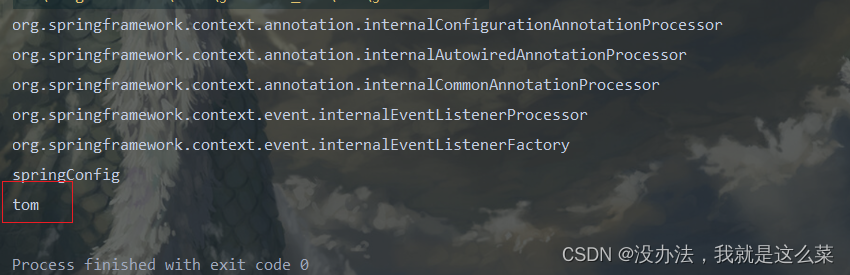
如果mouse类不存在,容器中就没有bean对象
如果存在结果如下:
注解式
使用@Conditional注解的派生注解设置各种组合条件控制bean的加载(要在SpringBoot环境下)
匹配指定环境
//@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
@Import(Mouse.class)
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "com.dc.bean.Cat") // 容器中有cat的bean对象就加载
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("com.dc.bean.Mouse") // 容器中没有mouse的bean对象就不加载
@ConditionalOnBean(Mouse.class) // 按类型匹配
@ConditionalOnWebApplication // 是web文件就加载
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication // 不是web文件就加载
public Cat tom() {
return new Cat();
}
}
bean依赖属性配置
将业务功能bean运行需要的资源抽取成独立的属性类,设置读取配置文件信息
实体类:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Mouse {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Cat {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
CatAndMouse:
@Data
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CartoonProperties.class)// 当加载该类的时候用CartoonProperties字字节码
public class CatAndMouse {
private Cat cat;
private Mouse mouse;
private CartoonProperties cartoonProperties;
public CatAndMouse(CartoonProperties cartoonProperties){
cat = new Cat();
cat.setName(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && StringUtils.hasText(cartoonProperties.getCat().getName()) ? "奥特曼" : cartoonProperties.getCat().getName());
cat.setAge(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && cartoonProperties.getCat().getAge() != null ? 2 : cartoonProperties.getCat().getAge());
mouse = new Mouse();
mouse.setName(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && StringUtils.hasText(cartoonProperties.getMouse().getName()) ? "葫芦娃" : cartoonProperties.getMouse().getName());
mouse.setAge(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && cartoonProperties.getMouse().getAge() != null ? 4 : cartoonProperties.getMouse().getAge());
}
public void play() {
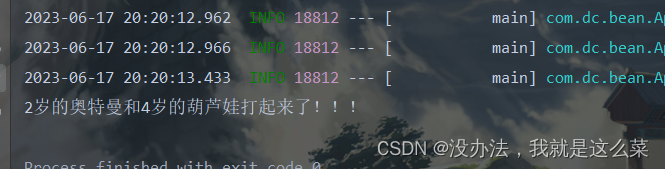
System.out.println(cat.getAge() + "岁的" + cat.getName()
+ "和" + mouse.getAge() + "岁的" + mouse.getName() + "打起来了!!!");
}
}
属性类:
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cartoon")// 读取配置文件信息
public class CartoonProperties {
private Cat cat;
private Mouse mouse;
}
测试类:
@Import(CatAndMouse.class) //定义业务功能bean,解耦强制加载bean
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(App.class);
CatAndMouse bean = run.getBean(CatAndMouse.class);
bean.play();
}
}
配置文件:
cartoon:
cat:
name: tom
age: 3
mouse:
name: jerry
age: 4
结果:
自动配置
思想
阶段一:准备阶段
- 收集Spring开发者的编程习惯,整理开发过程使用的常用技术列表–>(技术集A)
- 收集常用技术(技术集A)的使用参数,整理开发过程中每个技术常用设置列表–>(设计集B)
阶段二:加载阶段
- 初始化SpringBoot基础环境,加载用户自定义的bean和导入的其他坐标,形成初始化环境
- 将技术集A包含的所有技术在SpringBoot启动时默认全部加载,这时肯定加载的东西有一些是无效的,没有用的
- SpringBoot会对技术集A中每一个技术约定出启动这个技术对应的条件,并设置成按条件加载,由于开发者导入了一些bean和其他坐标,也就是初始化环境,这个时候就可以根据这个初始化环境与SpringBoot的技术集A进行比对,哪个匹配上记载哪个
- 因为有些技术不做配置就无法工作,所以SpringBoot开始对设置集B下手。他统计出各个国家各个行业的开发者使用某个技术时最长用的设置,然后把这些设置作为默认值直接设置好,并告诉开发者当前设置已经搞了一套,可以直接用,这样可以减少开发者配置参数的工作量
- 但是默认配置并不一定能解决问题,于是SpringBoot开发修改设置集B的接口,可以由开发者根据需要决定是否覆盖默认配置
代码展示
首先指定一个技术X,让技术X具备自动配置的功能,这个技术X可以是任意功能,这个技术隶属于上面描述的技术集A
@Data
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CartoonProperties.class)// 当加载该类的时候用CartoonProperties字字节码
public class CatAndMouse implements ApplicationContextAware {
private Cat cat;
private Mouse mouse;
private CartoonProperties cartoonProperties;
public CatAndMouse(CartoonProperties cartoonProperties){
cat = new Cat();
cat.setName(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && StringUtils.hasText(cartoonProperties.getCat().getName()) ? "奥特曼" : cartoonProperties.getCat().getName());
cat.setAge(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && cartoonProperties.getCat().getAge() != null ? 2 : cartoonProperties.getCat().getAge());
mouse = new Mouse();
mouse.setName(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && StringUtils.hasText(cartoonProperties.getMouse().getName()) ? "葫芦娃" : cartoonProperties.getMouse().getName());
mouse.setAge(cartoonProperties.getCat() != null && cartoonProperties.getMouse().getAge() != null ? 4 : cartoonProperties.getMouse().getAge());
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(cat.getAge() + "岁的" + cat.getName()
+ "和" + mouse.getAge() + "岁的" + mouse.getName() + "打起来了!!!");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
}
}
配置文件application.yml
cartoon:
cat:
name: "图多盖洛"
age: 5
mouse:
name: "泰菲"
age: 1
定义一个读取配置文件的类
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cartoon")// 当加载该类的时候用CartoonProperties字字节码
public class CartoonProperties {
private Cat cat;
private Mouse mouse;
}
在配置目录resouurce下创建META-INF目录,并创建spring.factories文件,在其中添加配置,说明哪些类要启动自动配置即可
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.dc.bean.CatAndMouse
结果:
自动配置其实是一个小的生态
思想:
- 自动配置从根本上来说就是一个bean的加载
- 通过bean的加载条件的控制给开发者一种感觉,自动配置是自适应的,可以根据情况自己判定,但是实际上就是最普通的分支语句的应用
- 使用bean的时候,如果不设置属性,就有默认值。如果不想用默认值就可以自己设置,也就是可以修改部分或者全部参数,也是一种自适应的形式,其实还是需要使用分支语句来做判断的
- SpringBoot技术提前将大量开发者有可能使用的技术提前做好了,条件也写好了,用的时候导入一个坐标,对应的技术就可以使用了,其实就是提前把spring.factories文件写好
总结
- SpringBoot启动时先加载spring.factories文件中的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration配置,将其中配置的所有的类都加载成bean
- 在加载的时候,bean对应的类定义上都设置有加载条件,因此又可能加载成功,也可能条件检测失败不加载bean
- 对于可以正常加载成bean的类,通常会通过@EnableConfigurationProperties注解初始化对应的配置属性类并加载对应的配置
- 配置属性类上通常会通过@ConfigurationProperties加载指定前缀的配置,当然这些配置会有默认值。如果没有默认值,就强制必须配置后使用
变更自动配置
方式一:通过yaml配置设置排除指定的自动配置类
spring:
autoconfigure:
exclude:
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration
方式二:通过注解参数排除自动配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration(excludeName = "",exclude = {})
@SpringBootApplication注解中已经包含@EnableAutoConfiguration注解,也可以直接使用@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication(excludeName = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration")
方式三:排除坐标(应用面较窄)
如果当前自动配置中包含有更多的自动配置功能,也就是一个套娃的效果。此时可以通过检测条件的控制来管理自动配置是否启动。如web程序启动时会自动启动tomcat服务器,可以通过排除坐标的方式,让加载的tomcat服务器的条件失效。不过需要再加一种可以运行的服务器
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!--web起步依赖环境中,排除Tomcat起步依赖,匹配自动配置条件-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--添加Jetty起步依赖,匹配自动配置条件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
总结
SpringBoot的自动配置并不是必然运行的,可以通过配置的形式干预是否启用对应的自动配置功能
自定义starter开发
案例:记录系统访客独立ip访问次数
本案例的功能是统计网站独立ip访问次数的功能,并将访问信息在后台持续输出。整体功能是在后台每10秒输出一次监控信息
具体分析:
-
数据记录在什么位置
最终记录的数据是一个字符串(IP地址)对应一个数字(访问次数),此处可以选择的数据存储模型可以使用map,也就是key-value的键值对模型,或者具有key-value键值对模型的存储技术,如redis
-
统计功能运行位置,因为每次web请求都需要进行统计,因此使用拦截器会是比较好的方案
-
为了提升统计数据展示的灵活度,为统计功能添加配置项。输出频度,输出的数据格式,统计数据的显示模式均可以通过配置实现调整
- 输出频度,默认10秒
- 数据特征:累计数据 / 阶段数据,默认累计数据
- 输出格式:详细模式 / 极简模式
Ip计数业务功能开发(自定义starter)
此功能最终实现的效果是在现有的项目中导入一个starter,对应的功能就添加上了,删除对应的starter,功能就消失了。要求功能要与原始项目完全解耦。因此需要开发一个独立的模块,制作对应功能
创建全新的模块,定义业务功能类
定义一个业务类,声明一个Map对象,用于记录ip访问次数,key是ip地址,value是访问次数
@Slf4j
public class IpCountService {
private Map<String,Integer> ipCountMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest;
public void count() {
// 每次调用当前操作,就记录当前访问的IP,然后累加访问次数
// 1、获取当前操作的Ip地址
String ip = httpServletRequest.getRemoteAddr();
log.info("ip地址为:{}", ip);
// 2、根据ip地址从Map取值,并递增
Integer count = ipCountMap.get(ip);
if (count == null) {
ipCountMap.put(ip, 1);
} else {
ipCountMap.put(ip, count + 1);
}
log.info("访问次数:{}", ipCountMap.get(ip));
}
}
定义自动配置类
@Configuration
public class IpAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public IpCountService ipCountService(){
return new IpCountService();
}
}
自动配置类需要在spring.factories文件中做配置方可自动运行
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.dc.service.IpAutoConfiguration
测试:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private IpCountService ipCountService;
@GetMapping("/find")
public String hello() {
ipCountService.count();
return "hello";
}
}
定时任务报表开发
当前已经实现了在业务功能类中记录访问数据,但是还没有输出监控的信息到控制台。由于监控信息需要每10秒输出1次,因此需要使用定时器功能。可以选取第三方技术Quartz实现,也可以选择Spring内置的task来完成此功能
开启定时任务功能
定时任务功能开启需要在当前功能的总配置中设置,结合现有业务设定,比较合理的位置是设置在自动配置类上。加载自动配置类即启用定时任务功能。
@Configuration
@EnableScheduling
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(IpProperties.class)
@Import(IpProperties.class)
public class IpAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public IpCountService ipCountService(){
return new IpCountService();
}
}
制作显示统计数据功能
定义显示统计功能的操作print(),并设置定时任务,当前设置每5秒运行一次统计数据
public class IpCountService {
private Map<String,Integer> ipCountMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
public void print(){
System.out.println(" IP访问监控");
System.out.println("+-----ip-address-----+--num--+");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : ipCountMap.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(String.format("|%18s |%5d |",key,value));
}
System.out.println("+--------------------+-------+");
}
}
其中关于统计报表的显示信息拼接可以使用各种形式进行
使用属性配置设置功能参数
由于当前报表显示的信息格式固定,为提高报表信息显示的灵活性,需要通过yml文件设置参数,控制报表的显示格式
定义参数格式
设置3个属性,分别用来控制显示周期(cycle),阶段数据是否清空(cycleReset),数据显示格式(model)
server:
port:
80
logging:
charset:
console: utf-8
tools:
ip:
cycle: 10
cycleReset: false
model: "detail"
为防止项目组定义的参数种类过多,产生冲突,通常设置属性前缀会至少使用两级属性作为前缀尽心区分
日志输出模式是在若干个类别选项中选择某一项,对于此种分类性数据建议制作枚举定义分类数据,当然使用字符串也可以
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "tools.ip")
@Component("ipProperties")
@Data
public class IpProperties {
/**
* 日志显示周期
* @param
* @return
*/
private Long cycle = 5L;
/**
* 是否周期内重置数据
* @param
* @return
*/
private Boolean cycleReset = false;
/**
* 日志输出模式 detail:详细模式 simple:极简模式
* @param
* @return
*/
private String model = LogModel.DETAIL.value;
public enum LogModel {
DETAIL("detail"),
SIMPLE("simple");
public String value;
LogModel(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}
加载属性类
@EnableScheduling
@EnableConfigurationProperties(IpProperties.class)
public class IpAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public IpCountService ipCountService(){
return new IpCountService();
}
}
应用配置属性
在应用配置属性的功能类中,使用自动装配加载对应的配置bean,然后使用配置信息做分支处理
注意
清除数据的功能一定要在输出后运行,否则每次查询的数据均为空白数据
public class IpCountService {
private Map<String,Integer> ipCountMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
@Autowired
private IpProperties ipProperties;
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
public void print(){
if(ipProperties.getModel().equals(IpProperties.LogModel.DETAIL.getValue())){
System.out.println(" IP访问监控");
System.out.println("+-----ip-address-----+--num--+");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : ipCountMap.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(String.format("|%18s |%5d |",key,value));
}
System.out.println("+--------------------+-------+");
}else if(ipProperties.getModel().equals(IpProperties.LogModel.SIMPLE.getValue())){
System.out.println(" IP访问监控");
System.out.println("+-----ip-address-----+");
for (String key: ipCountMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(String.format("|%18s |",key));
}
System.out.println("+--------------------+");
}
//阶段内统计数据归零
if(ipProperties.getCycleReset()){
ipCountMap.clear();
}
}
}
使用属性配置设置定时器参数
@Scheduled注解使用#{}读取bean属性的值
此处读取bean名称为ipProperties的bean的cycle属性值
package com.dc.service;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* -----在希望中绽放,在苦难中坚持------
*
* @author 暮辰
*/
@Slf4j
public class IpCountService {
private Map<String,Integer> ipCountMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest;
@Autowired
private IpProperties ipProperties;
public void count() {
// 每次调用当前操作,就记录当前访问的IP,然后累加访问次数
// 1、获取当前操作的Ip地址
String ip = httpServletRequest.getRemoteAddr();
log.info("ip地址为:{}", ip);
// 2、根据ip地址从Map取值,并递增
Integer count = ipCountMap.get(ip);
if (count == null) {
ipCountMap.put(ip, 1);
} else {
ipCountMap.put(ip, count + 1);
}
log.info("访问次数:{}", ipCountMap.get(ip));
}
@Scheduled(cron = "0/#{ipProperties.cycle} * * * * ?")
public void print(){
if (ipProperties.getModel().equals(IpProperties.LogModel.DETAIL.getValue())){
System.out.println("IP访问监控");
System.out.println("+-----ip-address-----+--num--+");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : ipCountMap.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(String.format("|%18s |%5d |",key,value));
}
System.out.println("+--------------------+-------+");
} else if(ipProperties.getModel().equals(IpProperties.LogModel.SIMPLE.getValue())){
System.out.println(" IP访问监控");
System.out.println("+-----ip-address-----+");
for (String key: ipCountMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(String.format("|%18s |",key));
}
System.out.println("+--------------------+");
}
//阶段内统计数据归零
if(ipProperties.getCycleReset()){
ipCountMap.clear();
}
}
}
导入bean的形式加载配置属性类
@EnableScheduling
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(IpProperties.class)
@Import(IpProperties.class)
public class IpAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public IpCountService ipCountService(){
return new IpCountService();
}
}
拦截器开发
开发拦截器
使用自动装配加载统计功能的业务类,并在拦截器中调用对应的功能
public class IpCountInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private IpCountService ipCountService;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
ipCountService.count();
return true;
}
}
配置拦截器
配置mvc拦截器,设置拦截对应的请求路径。此处拦截所有请求,用户可以根据使用需要设置要拦截的请求。甚至可以在此处加载IpCountProperties中的属性,通过配置设置拦截器拦截的要求
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(ipCountInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
@Bean
public IpCountInterceptor ipCountInterceptor(){
return new IpCountInterceptor();
}
}
开启yml提示功能
在使用SpringBoot的配置属性时,都可以看到提示,尤其是导入了对应的starter后,也会有对应的提示信息出现。SpringBoot提供有专用的工具实现此功能,仅需要导入下列坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
程序编译后会在taiget的META-INF中生成对应的提示文件
{
"groups": [
{
"name": "tools.ip",
"type": "com.dc.service.IpProperties",
"sourceType": "com.dc.service.IpProperties"
}
],
"properties": [
{
"name": "tools.ip.cycle",
"type": "java.lang.Long",
"description": "日志显示周期 @param @return",
"sourceType": "com.dc.service.IpProperties"
},
{
"name": "tools.ip.cycle-reset",
"type": "java.lang.Boolean",
"description": "是否周期内重置数据 @param @return",
"sourceType": "com.dc.service.IpProperties"
},
{
"name": "tools.ip.model",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"description": "日志输出模式 detail:详细模式 simple:极简模式 @param @return",
"sourceType": "com.dc.service.IpProperties"
}
],
"hints": []
}
总结
- 自定义starter其实就是做一个独立的功能模块,核心技术是利用自动配置的效果在加载模块后加载对应的功能
- 通常会为自定义starter的自动配置功能添加足够的条件控制,而不会卓成100%加载对应的starter
- 对于配置属性务必开启提示功能,否则使用者无法感知配置应该如何书写