目录
〇、简介
0.1 ScheduledExecutorService 和 Timer 的区别
一、什么是ScheduledExecutorService?
二、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor中的方法
2.1 构造方法
2.2 schedule方法
2.3 scheduleAtFixedRate方法
2.4 scheduleWithFixedDelay方法
2.5 setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy方法
2.6 setExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy方法
2.7 scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay的区别
三、练习
3.1 schedule练习1
3.2 schedule练习2
3.3 scheduleAtFixedRate练习1
3.4 scheduleAtFixedRate练习2
3.5 scheduleWithFixedDelay练习
3.6 setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy练习
〇、简介
在实现定时调度功能的时候,我们往往会借助于第三方类库来完成,比如:quartz、Spring Schedule等等。JDK从1.3版本开始,就提供了基于Timer的定时调度功能。在Timer中,任务的执行是串行的。这种特性在保证了线程安全的情况下,往往带来了一些严重的副作用,比如任务间相互影响、任务执行效率低下等问题。为了解决Timer的这些问题,JDK从1.5版本开始,提供了基于ScheduledExecutorService的定时调度功能。
虽然Java的定时调度可以通过Timer&TimerTask来实现。但是由于其实现的方式为单线程,因此从JDK1.3发布之后就一直存在一些问题,大致如下:
- 多个任务之间会相互影响
- 多个任务的执行是串行的,性能较低
ScheduledExecutorService在设计之初就是为了解决Timer&TimerTask的这些问题。因为天生就是基于多线程机制,所以任务之间不会相互影响(只要线程数足够。当线程数不足时,有些任务会复用同一个线程)。
除此之外,因为其内部使用的延迟队列,本身就是基于等待/唤醒机制实现的,所以CPU并不会一直繁忙。同时,多线程带来的CPU资源复用也能极大地提升性能。
0.1 ScheduledExecutorService 和 Timer 的区别
- Timer 对系统时钟的变化敏感,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor不是;
- Timer 内部只有一个执行线程,因此长时间运行的任务会延迟其他任务,而且如果有多个任务的话就会顺序执行,这样我们的延迟时间和循环时间就会出现问题。 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 可以配置任意数量的线程。 此外,如果你想(通过提供 ThreadFactory),你可以完全控制创建的线程。所以在多线程环境下对延迟任务和循环任务要求严格的时候,就需要考虑使用ScheduledExecutorService了;
- 在TimerTask 中抛出的运行时异常会杀死一个线程,从而导致 Timer 死机,即计划任务将不再运行。ScheduledThreadExecutor 不仅捕获运行时异常,还允许您在需要时处理它们(通过重写 afterExecute 方法ThreadPoolExecutor)。抛出异常的任务将被取消,但其他任务将继续运行。
综上,在 JDK1.5 之后,你没有理由再使用 Timer 进行任务调度了。当然,在实际项目中基本也不会用到ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,所以对这部分大家只需要简单了解一下它的思想。
备注: Quartz 是一个由 Java 编写的任务调度库,由 OpenSymphony 组织开源出来。在实际项目开发中使用 Quartz 的还是居多,比较推荐使用 Quartz。因为 Quartz 理论上能够同时对上万个任务进行调度,拥有丰富的功能特性,包括任务调度、任务持久化、可集群化、插件等等。
一、什么是ScheduledExecutorService?
ScheduledExecutorService接口是基于ExecutorService的功能实现的延迟和周期执行任务的功能。每个任务以及每个任务的每个周期都会提交到线程池中由线程去执行,所以任务在不同周期内执行它的线程可能是不同的。ScheduledExecutorService接口的默认实现类是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。在周期执行的任务中,如果任务执行时间大于周期时间,则会以任务时间优先,等任务执行完毕后才会进入下一次周期
ScheduledExecutorService接口中定义了一些方法:
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService {
// 在指定延时后执行一次
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
// 在指定延时后执行一次
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
// 在指定延时后开始执行,并在之后以指定时间间隔重复执行(间隔不包含任务执行的时间)
// 相当于之后的延时以任务开始计算
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
// 在指定延时后开始执行,并在之后以指定延时重复执行(间隔包含任务执行的时间)
// 相当于之后的延时以任务结束计算
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
}
二、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor中的方法
之前我们讲的ThreadPoolExecutor是java的普通线程池。而ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是java提供的定时任务线程池。
因为ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类继承了ThreadPoolExecutor类,所以有很多方法都是来自ThreadPoolExecutor类,其本身是支持线程池的所有功能,它自己还额外提供了一些关于延迟执行和定时任务的方法。我们常用的有如下几种:
/**
* 带延迟时间的调度,只执行一次
* 调度之后可通过Future.get()阻塞直至任务执行完毕
*/
1. public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* 带延迟时间的调度,只执行一次
* 调度之后可通过Future.get()阻塞直至任务执行完毕,并且可以获取执行结果
*/
2. public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* 带延迟时间的调度,循环执行,固定频率
*/
3. public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
/**
* 带延迟时间的调度,循环执行,固定延迟
*/
4. public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
2.1 构造方法
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize)
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)- corePoolSize:线程池核心线程数
- threadFactory:线程工厂
- handler:任务拒绝策略
构造一个Schedule线程池,最大线程数为Integer的最大值,线程的空闲时间为0,队列采用的是DelayedWorkQueue。
2.2 schedule方法
// 延迟执行无返回值单个任务,该方法返回ScheduledFuture,就可以理解普通线程池中返回的Future
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
// 延迟执行有返回值单个任务,该方法返回ScheduledFuture
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
- command:要延迟执行的任务(Runnable / Callable)
- delay:延时的时间
- unit:时间单位
延时delay时长执行Runnable或者Callable任务,只会执行一次。执行Runnable任务时是没有结果返回的,那为什么还会返回ScheduledFuture,因为我们可以通过Future做一些取消任务等操作。该方法会使任务在delay时间之后去执行。
调度之后还可以通过Future.get()阻塞直至任务执行完毕。
2.3 scheduleAtFixedRate方法
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
- command:Runnable任务
- initialDelay:任务首次执行前的延迟时间
- period:周期时间
- unit:时间单位
固定周期性执行任务,当任务的执行时长大于周期,那么下一个周期任务将在上一个执行完毕之后马上执行。
作用:指定的延迟时间( initialDelay)调度第一次,后续以 period为一个时间周期进行调度,该方法并不 care 每次任务执行的耗时,如果某次耗时超过调度周期(period),则下一次调度从上一次任务结束时开始,然后接着按照period的间隔严格执行任务。
也就是说这个方法会严格按照周期间隔去执行,并不会管任务的执行时间。
任务的第一次会在 initialDelay 后开始执行,然后在 initialDelay+period 后执行,接着在 initialDelay + 2 * period 后执行,依此类推。意思是下一次执行任务的时间与任务执行过程花费的时间无关,只与period有关!
如果此任务的任何一个执行要花费比其周期更长的时间,则将推迟后续执行,但不会同时执行。
如果任务的任何一个执行遇到异常,则后续执行都会被取消。否则,只能通过执行程序的取消或终止方法来终止该任务。
2.4 scheduleWithFixedDelay方法
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
- command:Runnable任务
- initialDelay:任务首次执行前的延迟时间
- delay:延时时间
- unit:时间单位
固定延时执行任务,也是周期性任务,和scheduleAtFixedRate不同的是:scheduleAtFixedRate当任务执行时间小于周期时间时,此时周期时间到了的时候会进入下一周期,这一点和scheduleWithFixedDelay是没有区别的;但是如果任务执行时间大于周期时间时,scheduleAtFixedRate的任务结束后会立即进入下一周期;而scheduleWithFixedDelay是无论你任务时间是否超过,都将会在你任务执行完毕后延迟固定时间(delay),才会进入下一周期。
作用:在指定的延迟时间( delay)调度第一次,后续以 period 为一个时间周期进行调度,该方法非常 care 上一次任务执行的耗时,如果某次耗时超过调度周期(period),则下一次调度时间为 上一次任务结束时间 + 调度周期时间
也就是说使用scheduleWithFixedDelay可以实现在每一次执行终止和下一次执行开始之间都存在给定的延迟(delay)。
2.5 setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy方法
void setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(boolean value)
默认为false。在线程池执行shutdown方法后是否继续执行scheduleAtFixedRate方法和scheduleWithFixedDelay方法提交的任务
2.6 setExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy方法
void setExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(boolean value)默认为true,在线程池执行shutdown方法后,需要等待当前正在等待的任务的和正在运行的任务被执行完,然后进程被销毁。为false时,表示放弃等待的任务,正在运行的任务一旦完成,则进程被销毁。
2.7 scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay的区别
直白地讲,scheduleAtFixedRate()为固定频率,scheduleWithFixedDelay()为固定延迟。固定频率是相对于任务执行的开始时间,而固定延迟是相对于任务执行的结束时间,这就是他们最根本的区别!
三、练习
3.1 schedule练习1
本次练习中除了schedule的练习外,还包含了如何取消任务。
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ScheduledExecutorServiceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建定时任务线程池,核心线程数为2
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
// 2秒后执行Runnable任务
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(() -> {
System.out.println("This is runable1 task");
}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 再提交一个2秒后才执行的Runnable任务
// 既然Runnable无法返回结果,为什么还要有Future呢,因为我们可以通过Future进行取消任务等操作
ScheduledFuture<?> runnableFuture = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(() -> {
System.out.println("This is runable2 task");
}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 取消任务
runnableFuture.cancel(true);
// 休眠3秒,确保上面的任务都被执行完
mySleep(3);
System.out.println("========================");
}
private static void mySleep(int seconds){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
This is runable1 task
========================
3.2 schedule练习2
@Test public void test_schedule4Runnable() throws Exception {
// 创建定时任务线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
// 延迟执行任务
ScheduledFuture future = service.schedule(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task finish time: " + format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("schedule finish time: " + format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 通过get方法阻塞当前线程,直到任务执行完毕
System.out.println("Runnable future's result is: " + future.get() +
", and time is: " + format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}
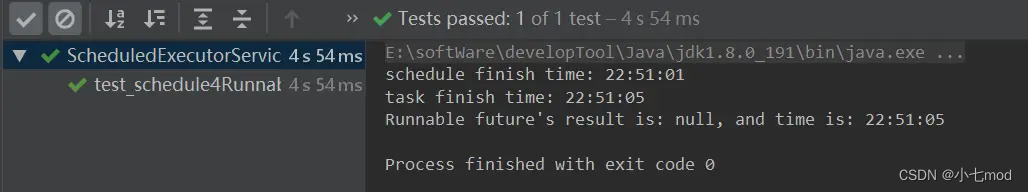
上述代码达到的效果应该是这样的:延迟执行时间为1秒,任务执行3秒,任务只执行一次,同时通过Future.get()阻塞直至任务执行完毕。
我们运行看到的效果的确和我们猜想的一样,如下图所示。
在schedule Runnable的基础上,我们将Runnable改为Callable来看一下。
@Test public void test_schedule4Callable() throws Exception {
// 创建定时任务线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
// 提交一个带返回值的Callable任务,延迟1秒执行
ScheduledFuture<String> future = service.schedule(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task finish time: " + format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
return "success";
}, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("schedule finish time: " + format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 通过future.get()方法获取任务执行结果,如果任务还没执行完,则会阻塞等待
System.out.println("Callable future's result is: " + future.get() +
", and time is: " + format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}
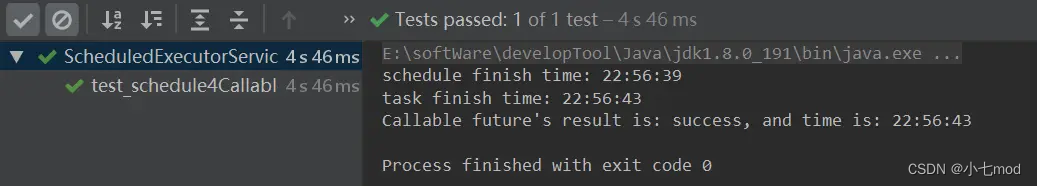
运行看到的结果和Runnable基本相同,唯一的区别在于future.get()能拿到Callable返回的真实结果。
3.3 scheduleAtFixedRate练习1
周期性执行某个任务,执行到一定时间后取消任务
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ScheduledExecutorServiceExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建定时任务线程池
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
// 提交延迟1秒执行,周期为2秒的runnable任务,虽然Runnable没有返回结果,但是可以通过runnableFuture取消任务
ScheduledFuture<?> runnableFuture = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
System.out.println("This is runable task running "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, 1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 休眠8秒
mySleep(8);
// 取消该循坏任务
runnableFuture.cancel(true);
}
private static void mySleep(int seconds){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
- 可以看出每个周期执行的任务并不是同一个线程,周期时间到的时候只是将任务扔到线程池的任务队列中由空闲线程获取它的执行权。
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-2
3.4 scheduleAtFixedRate练习2
超时的周期性任务
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class ScheduledExecutorServiceExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建定时任务线程池
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
// 创建一个原子计数器
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0L);
// 提交初始延迟1秒执行,固定周期为2秒的Runnable任务
ScheduledFuture<?> runnableFuture = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
// 记录当前时间
Long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 判断是否为第一次运行
if (atomicLong.get()==0) {
atomicLong.set(current);
System.out.printf("first running [%d]\n",atomicLong.get());
} else {
// 记录与上次的间隔时间
System.out.printf("running time:[%d]\n",current-atomicLong.get());
}
// 将当前时间保存
atomicLong.set(current);
// 模拟超过固定周期时间,故意让任务晚结束,导致超过本轮周期时长了
mySleep(5);
}, 1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private static void mySleep(int seconds){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
- 可以看出,超出周期时间时,任务完成后立即就进入了下一周期
first running [1597659726690]
running time:[5042]
running time:[5001]
running time:[5000]
running time:[5001]
3.5 scheduleWithFixedDelay练习
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class ScheduledExecutorServiceExample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建定时任务线程池
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
// 创建原子计数器
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0L);
// 提交初始延迟1秒执行,延迟为2秒的runnable任务
ScheduledFuture<?> runnableFuture = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
// 记录当前时间
Long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 判断是否为第一次运行
if (atomicLong.get() == 0){
atomicLong.set(current);
System.out.printf("first running [%d]\n",atomicLong.get());
}else{
//记录与上次的间隔时间
System.out.printf("running time:[%d]\n",current-atomicLong.get());
}
// 将当前时间保存
atomicLong.set(current);
// 模拟超过固定周期时间 使其运行时间超过周期时间
mySleep(5);
}, 1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private static void mySleep(int seconds){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
- 可以看出来,无论你的任务执行多久,在任务执行完毕之后都会延迟一个调度周期时间才进入下一周期。
first running [1597659862349]
running time:[7047]
running time:[7002]
running time:[7023]
running time:[7002]
running time:[7003]
3.6 setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy练习
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ScheduledExecutorServiceExample5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建定时任务线程池
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
// 提交固定周期任务
ScheduledFuture<?> runnableFuture = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
System.out.println("This is runable task running "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, 1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 默认情况关闭线程池后是不允许继续执行固定周期任务的,所有输出false
System.out.println(scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.getContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy());
// 设置为true
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(true);
// 休眠1200毫秒,确保任务被执行
mySleep(1200);
// 关闭线程池
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
// 休眠2000毫秒后查看线程池状态
mySleep(2000);
// 线程池的状态
System.out.println("isShutdown:"+scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.isShutdown());
System.out.println("isTerminating:"+scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.isTerminating());
System.out.println("isTerminated:"+scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.isTerminated());
}
private static void mySleep(int milliSeconds){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(milliSeconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
- 可以看出来,设置为true之后,即使线程池关闭了,定时任务仍然在执行
false
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
isShutdown:true
isTerminating:true
isTerminated:false
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
This is runable task running pool-1-thread-1
...
相关文章:【线程池】Java的线程池
【线程池】Java线程池的核心参数
【线程池】Executors框架创建线程池