文章目录
- 一、作用
- 二、案例
- 1.动静分离
- 将静态资源放入Nginx目录下
- 2.负载均衡
- 常见的几种负载均衡方式
- 1) 轮询(默认)
- 2)weight
- 3)ip_hash
- 4)fair(第三方)
- 5)url_hash(第三方)
- 3.ssl认证
- 1)生成证书
- 三、安装使用
- 四、属性解释
- 1.localtion
- 1)location 区段
- 2)location 前缀含义
- 3)location 配置示例
- 3.1)没有修饰符 表示:必须以指定模式开始
- 3.2) =表示:必须与指定的模式精确匹配
- 3.3) ~ 表示:指定的正则表达式要区分大小写
- 3.4) ^~
- 3.5) @
- 2. rewrite
- 1)重定向
- 2)Rewrite 相关指令
- 2.1)if 语句
- 2.2)Rewrite flag
- 2.3)Rewrite匹配参考示例
一、作用
- 保护网站安全:任何来自Internet的请求都必须先经过代理服务器
- 通过配置缓存功能加速Web请求:可以缓存真实Web服务器上的某些静态资源,减轻真实Web服务器的负载压力
- 实现负载均衡:充当负载均衡服务器均衡地分发请求,平衡集群中各个服务器的负载压力
二、案例
1.动静分离
将静态资源放入Nginx目录下
将静态资源如css,js,图片,动图等放入Nginx,让Nginx渲染资源
- 可以先在Nginx文件夹中创建存放静态资源的目录static
mkdir /static
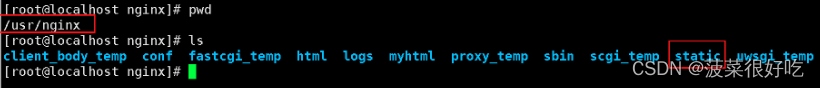
2. 将静态资源放入static文件夹
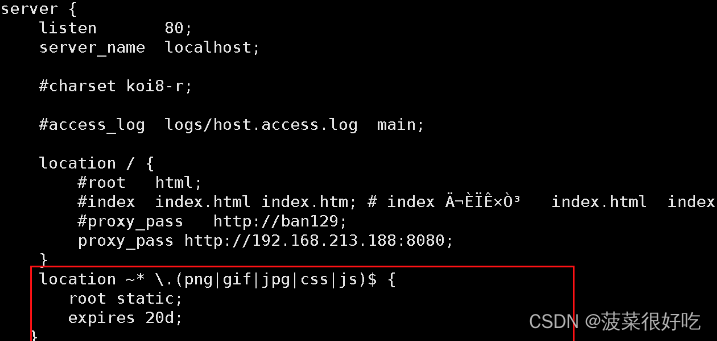
3. 修改配置文件
(1) 需要两台nginx服务器。
192.168.192.145(从 BACKUP)
192.168.192.129(主 MASTER)
(2) 需要keepalived
安装Keepalived
yum install keepalived 安装keepalived
rpm -q -a keepalived 检查是否安装keepalived
(3) 需要虚拟ip
- 实现Nginx的高可用
修改keepalived配置文件

2.负载均衡
常见的几种负载均衡方式
1) 轮询(默认)
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
upstream backserver {
server 192.168.0.14;
server 192.168.0.15;
}
2)weight
指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的
情况。
upstream backserver {
server 192.168.0.14 weight=3;
server 192.168.0.15 weight=7;
}
权重越高,在被访问的概率越大,如上例,分别是30%,70%。
3)ip_hash
每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。
upstream backserver {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.0.14:88;
server 192.168.0.15:80;
}
4)fair(第三方)
按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
upstream backserver {
server server1;
server server2;
fair;
}
5)url_hash(第三方)
按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。
upstream backserver {
server squid1:3128;
server squid2:3128;
hash $request_uri;
hash_method crc32;
}
每个设备的状态设置为:
1.down 表示单前的server暂时不参与负载
2.weight 默认为1.weight越大,负载的权重就越大。
3.max_fails:允许请求失败的次数默认为1.当超过最大次数时,返回proxy_next_upstream模块定义的错误
4.fail_timeout:max_fails次失败后,暂停的时间。
5.backup: 其它所有的非backup机器down或者忙的时候,请求backup机器。所以这台机器压力会最轻。
配置实例:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 4;
events {
# 最大并发数
worker_connections 1024;
}
http{
# 待选服务器列表
upstream myproject{
# ip_hash指令,将同一用户引入同一服务器。
ip_hash;
server 125.219.42.4 fail_timeout=60s;
server 172.31.2.183;
}
server{
# 监听端口
listen 80;
# 根目录下
location / {
# 选择哪个服务器列表
proxy_pass http://myproject;
}
}
}
3.ssl认证
1)生成证书
- 使用Linux自带ssl生成
- 阿里生成免费证书一年
server {
listen 443;
ssl on;
server_name www.681vip.com;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/ssl/8625757_www.681vip.com.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/ssl/8625757_www.681vip.com.key;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root /opt/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|ico)$ {
root /opt/;
expires 30d;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.681vip.com;
rewrite ^(.*)$ https://www.681vip.com:443/;
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
三、安装使用
# 依赖安装
yum -y install make zlib zlib-devel gcc-c++ libtool openssl openssl-devel
# 正则
wget https://jaist.dl.sourceforge.net/project/pcre/pcre/8.42/pcre-8.42.tar.gz
# 解压安装
tar -xvf pcre-8.42.tar.gz
cd pcre-8.42
./configure
make && make install
# nginx安装
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
tar -xzvf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.16.1
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-threads
make && make install
# 启动nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
# 重启
./nginx -s reload
四、属性解释
1.localtion
1)location 区段
- location 是在 server 块中配置,根据不同的 URI 使用不同的配置,来处理不同的请求。
- location 是有顺序的,会被第一个匹配的location 处理。
- 基本语法如下:
location [=||*|^~|@] pattern{……}
2)location 前缀含义
= 表示精确匹配,优先级也是最高的
^~ 表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配url路径即可
~ 表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
!~ 表示区分大小写不匹配的正则
!~* 表示不区分大小写不匹配的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到
@ 内部服务跳转
查找顺序和优先级:
= 大于 ^~ 大于 ||!|! 大于 /
多个location配置的情况下匹配顺序为:首先匹配 =,其次匹配^~, 其次是按正则匹配,最后是交给 / 通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
3)location 配置示例
3.1)没有修饰符 表示:必须以指定模式开始
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /abc {
root /home/www/nginx;
index 2.html;
}
那么,如下是对的:
http://192.168.1.10/abc
3.2) =表示:必须与指定的模式精确匹配
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
access_log /var/log/nginx/http_access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index a.html index.htm;
}
location = / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index b.html index.htm;
}
}
测试:
http://192.168.1.9
=/
http://192.168.1.9/a.html
/
3.3) ~ 表示:指定的正则表达式要区分大小写
server {
server_name localhost;
location ~ /abc {
root /home/www/nginx;
index 2.html index.html;
}
}
测试访问:
http://192.168.1.9/abc
不正确的
http://192.168.1.9/ABC
##########################
如果将配置文件修改为
location ~ /ABC {
root /home/www/nginx;
index 2.html index.html;
}
在创建目录和文件:
[root@ansible-server html]# cd /home/www/nginx/
[root@ansible-server nginx]# mkdir ABC
[root@ansible-server nginx]# vim ABC/2.html
访问:
http://192.168.1.9/ABC/
结论:~ 需要区分大小写。而且目录需要根据大小写定义。
3.4) ^~
类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模式开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了。
3.5) @
定义命名 location 区段,这些区段客户段不能访问,只可以由内部产生的请求来访问,如error_page等
location 区段匹配示例
location = / {
# 只匹配 / 的查询.
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
# 匹配任何以 / 开始的查询,但是正则表达式与一些较长的字符串将被首先匹配。
[ configuration B ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
# 匹配任何以 /images/ 开始的查询并且停止搜索,不检查正则表达式。
[ configuration C ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
# 匹配任何以gif, jpg, or jpeg结尾的文件
[ configuration D ]
}
各请求的处理如下例:
/ → configuration A
/documents/document.html → configuration B
/images/1.gif → configuration C
/documents/1.jpg → configuration D
2. rewrite
1)重定向
Rewrite对称URL Rewrite,即URL重写,就是把传入Web的请求重定向到其他URL的过程
- URL Rewrite最常见的应用是URL伪静态化,是将动态页面显示为静态页面方式的一种技术。比如http://www.123.com/news/index.php?id=123 使用URLRewrite 转换后可以显示为 http://www.123.com/news/123.html
- 从安全角度上讲,如果在URL中暴露太多的参数,无疑会造成一定量的信息泄漏,可能会被一些黑客利用,对你的系统造成一定的破坏,所以静态化的URL地址可以给我们带来更高的安全性。
- 实现网站地址跳转,例如用户访问http://360buy.com,将其跳转到http://jd.com。例如当用户访问http://tianyun.com的 80端口时,将其跳转到443端口。
2)Rewrite 相关指令
Nginx Rewrite 相关指令有 if、rewrite、set、return
2.1)if 语句
- 应用环境
server,location
语法:
if (condition) { … }
if 可以支持如下条件判断匹配符号
~ 正则匹配 (区分大小写)
~* 正则匹配 (不区分大小写)
!~ 正则不匹配 (区分大小写)
!~* 正则不匹配 (不区分大小写)
-f 和!-f 用来判断是否存在文件
-d 和!-d 用来判断是否存在目录
-e 和!-e 用来判断是否存在文件或目录
-x 和!-x 用来判断文件是否可执行
在匹配过程中可以引用一些Nginx的全局变量
$args 请求中的参数;
$document_root 针对当前请求的根路径设置值;
$host 请求信息中的"Host",如果请求中没有Host行,则等于设置的服务器名;
$limit_rate 对连接速率的限制;
$request_method 请求的方法,比如"GET"、"POST"等;
$remote_addr 客户端地址;
$remote_port 客户端端口号;
$remote_user 客户端用户名,认证用;
$request_filename 当前请求的文件路径名(带网站的主目录/usr/local/nginx/html/images /a.jpg)
$request_uri 当前请求的文件路径名(不带网站的主目录/images/a.jpg)
q u e r y s t r i n g 与 query_string 与 querystring与args相同;
$scheme 用的协议,比如http或者是https
$server_protocol 请求的协议版本,“HTTP/1.0"或"HTTP/1.1”;
$server_addr 服务器地址,如果没有用listen指明服务器地址,使用这个变量将发起一次系统调用以取得地址(造成资源浪费);
$server_name 请求到达的服务器名;
d o c u m e n t u r i 与 document_uri 与 documenturi与uri一样,URI地址;
$server_port 请求到达的服务器端口号;
2.2)Rewrite flag
- rewrite 指令根据表达式来重定向URI,或者修改字符串。可以应用于server,location, if环境下每行rewrite指令最后跟一个flag标记,支持的flag标记有: last 相当于Apache里的[L]标记,表示完成rewrite。默认为last。 break 本条规则匹配完成后,终止匹配,不再匹配后面的规则 redirect 返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址 permanent 返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后URL地址 redirect 和 permanent区别则是返回的不同方式的重定向: 对于客户端来说一般状态下是没有区别的。而对于搜索引擎,相对来说301的重定向更加友好,如果我们把一个地址采用301跳转方式跳转的话,搜索引擎会把老地址的相关信息带到新地址,同时在搜索引擎索引库中彻底废弃掉原先的老地址。 使用302重定向时,搜索引擎(特别是google)有时会查看跳转前后哪个网址更直观,然后决定显示哪个,如果它觉的跳转前的URL更好的话,也许地址栏不会更改。
2.3)Rewrite匹配参考示例
本地解析host文件
# http://www.testpm.com/a/1.html ==> http://www.testpm.com/b/2.html
location /a {
root /html;
index 1.html index.htm;
rewrite .* /b/2.html permanent;
}
location /b {
root /html;
index 2.html index.htm;
}
例2:
# http://www.testpm.com/2019/a/1.html ==> http://www.testpm.com/2018/a/1.html
location /2019/a {
root /var/www/html;
index 1.html index.hml;
rewrite ^/2019/(.*)$ /2018/$1 permanent;
}
location /2018/a {
root /var/www/html;
index 1.html index.htl;
}
例3:
# http://www.qf.com/a/1.html ==> http://jd.com
location /a {
root /html;
if ($host ~* www.qf.com ) {
rewrite .* http://jd.com permanent;
}
}
例4:
# http://www.qf.com/a/1.html ==> http://jd.com/a/1.html
location /a {
root /html;
if ( $host ~* qf.com ){
rewrite .* http://jd.com$request_uri permanent;
}
}
例5: 在访问目录后添加/ (如果目录后已有/,则不加/)
# http://www.tianyun.com/a/b/c
# $1: /a/b
# $2: c
# http://$host$1$2/
location /a/b/c {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.hml;
if (-d $request_filename) {
rewrite ^(.*)([^/])$ http://$host$1$2/ permanent;
}
}
例6:
# http://www.tianyun.com/login/tianyun.html ==> http://www.tianyun.com/reg/login.html?user=tianyun
location /login {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
rewrite ^/login/(.*)\.html$ http://$host/reg/login.html?user=$1;
}
location /reg {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index login.html;
}
例7:
#http://www.tianyun.com/qf/11-22-33/1.html ==> http://www.tianyun.com/qf/11/22/33/1.html
location /qf {
rewrite ^/qf/([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)(.*)$ /qf/$1/$2/$3$4 permanent;
}
location /qf/11/22/33 {
root /html;
index 1.html;
}