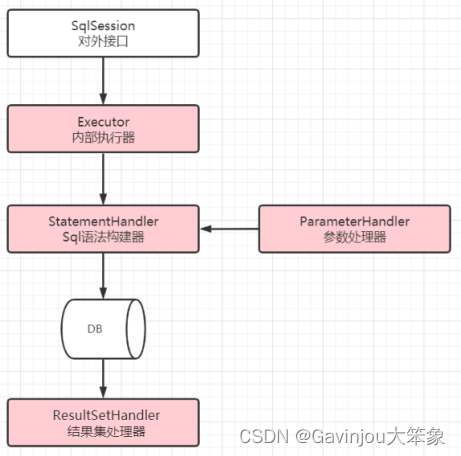
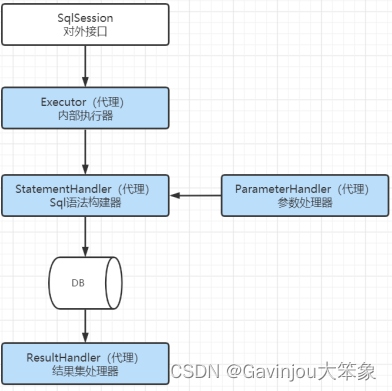
问题:什么是Mybatis插件?有什么作用? Mybatis插件本质上来说就是一个拦截器,它体现了 JDK 动态代理和责任链设计模式的综合运用 Mybatis 中所允许拦截的方法如下 Executor 【SQL执行器】【update,query,commit,rollback】 StatementHandler 【Sql语法构建器对象】【prepare,parameterize,batch,update,query 等】 ParameterHandler 【参数处理器】【getParameterObject,setParameters 等】 ResultSetHandler 【结果集处理器】【handleResultSets,handleOuputParameters 等】 用于定义插件的类 @Documented
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME)
@Target ( ElementType . TYPE)
public @interface Intercepts {
Signature [ ] value ( ) ;
}
由于一个拦截器可以同时拦截多个对象的多个方法,,所以就使用了 Signture 数组,该注解定义了拦截的完整信息 @Documented
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME)
@Target ( { } )
public @interface Signature {
Class < ? > type ( ) ;
String method ( ) ;
Class < ? > [ ] args ( ) ;
}
已经知道了该拦截哪些对象的哪些方法,拦截后要干什么就需要实现 Intercetor#intercept 方法,在这个方法里面实现拦截后的处理逻辑 public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept ( Invocation invocation) throws Throwable ;
default Object plugin ( Object target) {
return Plugin . wrap ( target, this ) ;
}
default void setProperties ( Properties properties) {
}
}
自定义插件 需求:把 Mybatis 所有执行的 sql 都记录下来 相关类
public class Invocation {
private final Object target;
private final Method method;
private final Object [ ] args;
}
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept ( Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
StatementHandler statementHandler = ( StatementHandler ) invocation. getTarget ( ) ;
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler. getBoundSql ( ) ;
String sql = boundSql. getSql ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "拦截方法,记录Sql:" + sql) ;
return invocation. proceed ( ) ;
}
@Override
public Object plugin ( Object target) {
return Plugin . wrap ( target, this ) ;
}
@Override
public void setProperties ( Properties properties) {
System . out. println ( "插件配置的初始化参数:" + properties) ;
}
}
使用 @Intercepts 注解完成插件签名 说明插件的拦截四大对象之一的哪一个对象的哪一个方法 @Intercepts ( {
@Signature ( type = StatementHandler . class ,
method = "prepare" ,
args = { Connection . class , Integer . class } )
} )
< configuration> < plugins> < plugininterceptor = " com.itheima.interceptor.MyPlugin" > < propertyname = " someProperty" value = " 100" /> </ plugin> </ plugins> </ configuration> 核心思想 使用 JDK 动态代理的方式,对这四个对象进行包装增强 具体的做法是,创建一个类实现 Mybatis 的拦截器接口,并且加入到拦截器链中 在创建核心对象的时候,不直接返回,而是遍历拦截器链,把每一个拦截器都作用于核心对象中 这么一来,Mybatis 创建的核心对象其实都是代理对象,都是被包装过的 问题: 插件对象是如何实例化的? 插件的实例对象如何添加到拦截器链中的? 组件对象的代理对象是如何产生的? 拦截逻辑的执行 为了了解清楚上述的问题,首先先看解析配置文件部分 public class MybatisTest {
. . .
@Test
public void test2 ( ) throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources . getResourceAsStream ( "sqlMapConfig.xml" ) ;
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ( ) . build ( resourceAsStream) ;
. . .
}
}
下面直接跳过读入配置文件部分,进入解析 /plugins 标签部分 public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void parseConfiguration ( XNode root) {
try {
. . .
pluginElement ( root. evalNode ( "plugins" ) ) ;
. . .
} catch ( Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException ( "Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e) ;
}
}
读取 /plugins 标签后,首先获取自定义拦截器名称,然后获取配置的属性。根据配置文件中配置的插件类的全限定名,反射实例化对象,得到 Intercepetor 对象(也就是 MyPlugin ),然后对于 Intercepetor 执行 setProperties() 方法,并把创建好的 Intercepetor 加入到 configuration 配置类中,这就解决第一个问题 public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
protected final Configuration configuration;
. . .
private void pluginElement ( XNode parent) throws Exception {
if ( parent != null ) {
for ( XNode child : parent. getChildren ( ) ) {
String interceptor = child. getStringAttribute ( "interceptor" ) ;
Properties properties = child. getChildrenAsProperties ( ) ;
Interceptor interceptorInstance = ( Interceptor ) resolveClass ( interceptor) . getDeclaredConstructor ( ) . newInstance ( ) ;
interceptorInstance. setProperties ( properties) ;
configuration. addInterceptor ( interceptorInstance) ;
}
}
}
}
接下来继续看是怎么把 Intercepetor 对象添加到插件链中,首先是由 Configuration 对象调用 addInterceptor() 方法,Configuration 对象会将 Intercepetor 对象添加到 InterceptorChain 对象中 public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain ( ) ;
. . .
public void addInterceptor ( Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain. addInterceptor ( interceptor) ;
}
}
InterceptorChain 对象会把 Intercepetor 对象添加到集合 interceptors 里面,这里就回答了第 2 个问题,将实力添加到拦截链当中public class InterceptorChain {
private final List < Interceptor > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
public void addInterceptor ( Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors. add ( interceptor) ;
}
}
通过配置完成 Configuration 对象并创建 SqlSessionFactory 后,然后执行 sqlSessionFactory.openSession() 创建 SqlSession 对象 public class MybatisTest {
@Test
public void test2 ( ) throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources . getResourceAsStream ( "sqlMapConfig.xml" ) ;
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ( ) . build ( resourceAsStream) ;
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory. openSession ( ) ;
. . .
}
}
当执行 openSession() 时,会调用 openSessionFromDataSource() 方法,交由 Configuration 对象来创建执行器对象,然后封装到 DefaultSqlSession 当中 public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
. . .
@Override
public SqlSession openSession ( ) {
return openSessionFromDataSource ( configuration. getDefaultExecutorType ( ) , null , false ) ;
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource ( ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null ;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration. getEnvironment ( ) ;
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment ( environment) ;
tx = transactionFactory. newTransaction ( environment. getDataSource ( ) , level, autoCommit) ;
final Executor executor = configuration. newExecutor ( tx, execType) ;
return new DefaultSqlSession ( configuration, executor, autoCommit) ;
} catch ( Exception e) {
closeTransaction ( tx) ;
throw ExceptionFactory . wrapException ( "Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e) ;
} finally {
ErrorContext . instance ( ) . reset ( ) ;
}
}
Configuration 对象根据传入的 ExecutorType ,创建指定类型的 Executor ,如果允许缓存的话,还会进一步装饰成 CachingExecutor 。然后基于插件链,遍历插件,通过 JDK 动态代理的方式,封装新的 Executor public class Configuration {
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType . SIMPLE;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true ;
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain ( ) ;
. . .
public Executor newExecutor ( Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType . SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if ( ExecutorType . BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor ( this , transaction) ;
} else if ( ExecutorType . REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor ( this , transaction) ;
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor ( this , transaction) ;
}
if ( cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor ( executor) ;
}
executor = ( Executor ) interceptorChain. pluginAll ( executor) ;
return executor;
}
}
InterceptorChain 会遍历 interceptors 插件链对每个对象执行 plugins() 方法public class InterceptorChain {
private final List < Interceptor > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
. . .
public Object pluginAll ( Object target) {
for ( Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor. plugin ( target) ;
}
return target;
}
}
因为只配置了一个自定义 Interceptor ,所以会调用到 MyPlugin 的 plugin() 方法 public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
. . .
@Override
public Object plugin ( Object target) {
return Plugin . wrap ( target, this ) ;
}
}
Plugin.wrap() 的执行首先会解析该拦截器所拦截的所有接口及对应拦截接口的方法,存入 signatureMap ,然后拿到目标对象所有实现的接口,判断是否命中要拦截的接口,如果是的话,进行 JDK 动态代理返回,否则就返回原目标对象。因为实现的 MyPlugin 对象主要拦截 StatementHandler 的 prepare() 方法,所以就直接返回源对象。这个地方就解答了第 3 个问题,代理对象就是这么创建public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
. . .
public static Object wrap ( Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map < Class < ? > , Set < Method > > = getSignatureMap ( interceptor) ;
Class < ? > = target. getClass ( ) ;
Class < ? > [ ] interfaces = getAllInterfaces ( type, signatureMap) ;
if ( interfaces. length > 0 ) {
return Proxy . newProxyInstance (
type. getClassLoader ( ) ,
interfaces,
new Plugin ( target, interceptor, signatureMap) ) ;
}
return target;
}
private static Class < ? > [ ] getAllInterfaces ( Class < ? > , Map < Class < ? > , Set < Method > > ) {
Set < Class < ? > > = new HashSet < > ( ) ;
while ( type != null ) {
for ( Class < ? > : type. getInterfaces ( ) ) {
if ( signatureMap. containsKey ( c) ) {
interfaces. add ( c) ;
}
}
type = type. getSuperclass ( ) ;
}
return interfaces. toArray ( new Class < ? > [ 0 ] ) ;
}
}
创建完 sqlSession 后,从 sqlSession 中获取 UserMapper 代理对象并开始执行 findByCondition() public class MybatisTest {
@Test
public void test2 ( ) throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources . getResourceAsStream ( "sqlMapConfig.xml" ) ;
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ( ) . build ( resourceAsStream) ;
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory. openSession ( ) ;
UserMapper mapperProxy = sqlSession. getMapper ( UserMapper . class ) ;
User user = mapperProxy. findByCondition ( 1 ) ;
. . .
}
}
因为返回的 UserMapper 是个代理对象,所以首先创建 MapperMethod 来构建 PlainMethodInvoker ,然后调用 MapperMethod 来执行 execute() 方法 public class MapperProxy < T > implements InvocationHandler , Serializable {
. . .
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker ( MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super ( ) ;
this . mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke ( Object proxy, Method method, Object [ ] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod. execute ( sqlSession, args) ;
}
}
}
根据 SqlCommand 的方法类型选择执行 SqlSession 指定方法,这里是执行 SelectOne() 返回结果 public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
. . .
public Object execute ( SqlSession sqlSession, Object [ ] args) {
Object result;
switch ( command. getType ( ) ) {
case INSERT: {
. . .
break ;
}
case UPDATE: {
. . .
break ;
}
case DELETE: {
. . .
break ;
}
case SELECT:
if ( method. returnsVoid ( ) && method. hasResultHandler ( ) ) {
. . .
} else if ( method. returnsMany ( ) ) {
. . .
} else if ( method. returnsMap ( ) ) {
. . .
} else if ( method. returnsCursor ( ) ) {
. . .
} else {
Object param = method. convertArgsToSqlCommandParam ( args) ;
result = sqlSession. selectOne ( command. getName ( ) , param) ;
if ( method. returnsOptional ( )
&& ( result == null || ! method. getReturnType ( ) . equals ( result. getClass ( ) ) ) ) {
result = Optional . ofNullable ( result) ;
}
}
break ;
case FLUSH:
. . .
break ;
default :
throw new BindingException ( "Unknown execution method for: " + command. getName ( ) ) ;
}
. . .
return result;
}
}
执行 SelectOne() 方法,实际是底层是调用 selectList() ,并经过多轮嵌套以后,交由 Executor 来执行查询语句 public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
. . .
@Override
public < T > T selectOne ( String statement, Object parameter) {
List < T > = this . selectList ( statement, parameter) ;
if ( list. size ( ) == 1 ) {
return list. get ( 0 ) ;
} else if ( list. size ( ) > 1 ) {
throw new TooManyResultsException ( "Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list. size ( ) ) ;
} else {
return null ;
}
}
@Override
public < E > List < E > selectList ( String statement, Object parameter) {
return this . selectList ( statement, parameter, RowBounds . DEFAULT) ;
}
@Override
public < E > List < E > selectList ( String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
return selectList ( statement, parameter, rowBounds, Executor . NO_RESULT_HANDLER) ;
}
private < E > List < E > selectList ( String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration. getMappedStatement ( statement) ;
return executor. query ( ms, wrapCollection ( parameter) , rowBounds, handler) ;
} catch ( Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory . wrapException ( "Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e) ;
} finally {
ErrorContext . instance ( ) . reset ( ) ;
}
}
}
CachingExecutor 首先生成缓存键,尝试从缓存中拿到结果,如果没有,就委派包装的 SimpleExecutor 来执行获取结果public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private final Executor delegate;
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager ( ) ;
. . .
@Override
public < E > List < E > query ( MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms. getBoundSql ( parameterObject) ;
CacheKey key = createCacheKey ( ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql) ;
return query ( ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql) ;
}
@Override
public < E > List < E > query ( MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms. getCache ( ) ;
if ( cache != null ) {
flushCacheIfRequired ( ms) ;
if ( ms. isUseCache ( ) && resultHandler == null ) {
ensureNoOutParams ( ms, boundSql) ;
@SuppressWarnings ( "unchecked" )
List < E > = ( List < E > ) tcm. getObject ( cache, key) ;
if ( list == null ) {
list = delegate. query ( ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql) ;
tcm. putObject ( cache, key, list) ;
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate. query ( ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql) ;
}
}
SimpleExecutor 尝试从一级缓存 localCache 获取数据,没有,就从数据库查询数据public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
. . .
@Override
public < E > List < E > query ( MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext . instance ( ) . resource ( ms. getResource ( ) ) . activity ( "executing a query" ) . object ( ms. getId ( ) ) ;
if ( closed) {
throw new ExecutorException ( "Executor was closed." ) ;
}
if ( queryStack == 0 && ms. isFlushCacheRequired ( ) ) {
clearLocalCache ( ) ;
}
List < E > ;
try {
. . .
list = resultHandler == null ? ( List < E > ) localCache. getObject ( key) : null ;
if ( list != null ) {
. . .
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase ( ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql) ;
}
} finally {
queryStack-- ;
}
. . .
return list;
}
private < E > List < E > queryFromDatabase ( MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List < E > ;
localCache. putObject ( key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER) ;
try {
list = doQuery ( ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
} finally {
. . .
}
. . .
return list;
}
}
SimpleExecutor 将会执行 doQuery() 方法,首先从 MappedStatement 中获取到 Configuration 对象,然后由 Configuration 对象创建 StatementHandler 来预处理 sql 语句后,再真正执行语句并返回执行结果public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
. . .
@Override
public < E > List < E > doQuery ( MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null ;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms. getConfiguration ( ) ;
StatementHandler handler = configuration. newStatementHandler ( wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
stmt = prepareStatement ( handler, ms. getStatementLog ( ) ) ;
return handler. query ( stmt, resultHandler) ;
} finally {
closeStatement ( stmt) ;
}
}
}
Configuration 对象执行newStatementHandler() 时,根据参数从中创建不同类型的 RoutingStatementHandler public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain ( ) ;
. . .
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler ( executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
statementHandler = ( StatementHandler ) interceptorChain. pluginAll ( statementHandler) ;
return statementHandler;
}
}
RoutingStatementHandler 根据 MappedStatement 类型,选择创建指定的 StatementHandler ,这里是创建 PreparedStatementHandler public class RoutingStatementHandler implements StatementHandler {
private final StatementHandler delegate;
. . .
public RoutingStatementHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch ( ms. getStatementType ( ) ) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler ( executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
break ;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler ( executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
break ;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler ( executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
break ;
default :
throw new ExecutorException ( "Unknown statement type: " + ms. getStatementType ( ) ) ;
}
}
}
PreparedStatementHandler 的构造直接交由父类 BaseStatementHandler public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler {
public PreparedStatementHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
super ( executor, mappedStatement, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
}
}
BaseStatementHandler 又会通过 Configuration 来执行创建 ParameterHandler public abstract class BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler {
protected final Configuration configuration;
protected final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
protected final ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler;
protected final ParameterHandler parameterHandler;
protected final Executor executor;
protected final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
protected final RowBounds rowBounds;
protected BoundSql boundSql;
. . .
protected BaseStatementHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this . configuration = mappedStatement. getConfiguration ( ) ;
this . executor = executor;
this . mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this . rowBounds = rowBounds;
this . typeHandlerRegistry = configuration. getTypeHandlerRegistry ( ) ;
this . objectFactory = configuration. getObjectFactory ( ) ;
if ( boundSql == null ) {
generateKeys ( parameterObject) ;
boundSql = mappedStatement. getBoundSql ( parameterObject) ;
}
this . boundSql = boundSql;
this . parameterHandler = configuration. newParameterHandler ( mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql) ;
this . resultSetHandler = configuration. newResultSetHandler ( executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
}
}
【关键 】从创建 ParameterHandler 这一刻,就会调用 interceptorChain 的 pluginAll() 来对 ParameterHandler 进行 JDK 代理配置,代理的逻辑在上面已经阐述过了,这里就不再重复 public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain ( ) ;
. . .
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler ( MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement. getLang ( ) . createParameterHandler ( mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql) ;
parameterHandler = ( ParameterHandler ) interceptorChain. pluginAll ( parameterHandler) ;
return parameterHandler;
}
}
完成 ParameterHandler 创建后,BaseStatementHandler 还需要创建 ResultSetHandler public abstract class BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler {
protected final Configuration configuration;
. . .
protected BaseStatementHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
. . .
this . parameterHandler = configuration. newParameterHandler ( mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql) ;
this . resultSetHandler = configuration. newResultSetHandler ( executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
}
}
【关键 】从创建 ResultSetHandler 这一刻,就会调用 interceptorChain 的 pluginAll() 来对 ResultSetHandler 进行 JDK 代理配置 public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain ( ) ;
. . .
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler ( executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds) ;
resultSetHandler = ( ResultSetHandler ) interceptorChain. pluginAll ( resultSetHandler) ;
return resultSetHandler;
}
}
【关键 】通过创建 ParameterHandler 、ResultSetHandler 等完成 RoutingStatementHandler 的构造并返回到 newStatementHandler() 方法,这时候也需要对 StatementHandler 核心对象进行拦截,执行 JDK 动态代理 public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain ( ) ;
. . .
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler ( Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler ( executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
statementHandler = ( StatementHandler ) interceptorChain. pluginAll ( statementHandler) ;
return statementHandler;
}
}
创建完 StatementHandler ,SimpleExecutor 需要准备处理器,包括创建 Statement 以及动态参数的设置,这时候,就会调用 StatementHandler 的 prepare() 来预处理得到 Statement 对象 public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
. . .
@Override
public < E > List < E > doQuery ( MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null ;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms. getConfiguration ( ) ;
StatementHandler handler = configuration. newStatementHandler ( wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql) ;
stmt = prepareStatement ( handler, ms. getStatementLog ( ) ) ;
return handler. query ( stmt, resultHandler) ;
} finally {
closeStatement ( stmt) ;
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement ( StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection ( statementLog) ;
stmt = handler. prepare ( connection, transaction. getTimeout ( ) ) ;
handler. parameterize ( stmt) ;
return stmt;
}
}
因为 StatementHandler 已经被代理了,这时候会调用 Plugin 的 invoke() ,然后执行 MyPlugin 的 intercept() 方法 public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
private final Interceptor interceptor;
. . .
@Override
public Object invoke ( Object proxy, Method method, Object [ ] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set < Method > = signatureMap. get ( method. getDeclaringClass ( ) ) ;
if ( methods != null && methods. contains ( method) ) {
return interceptor. intercept ( new Invocation ( target, method, args) ) ;
}
return method. invoke ( target, args) ;
} catch ( Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil . unwrapThrowable ( e) ;
}
}
}
然后执行完成后就会返回查询结果,这个查询的具体流程完整可以参考 『手撕 Mybatis 源码』05 - SqlSession 执行主流程 总结