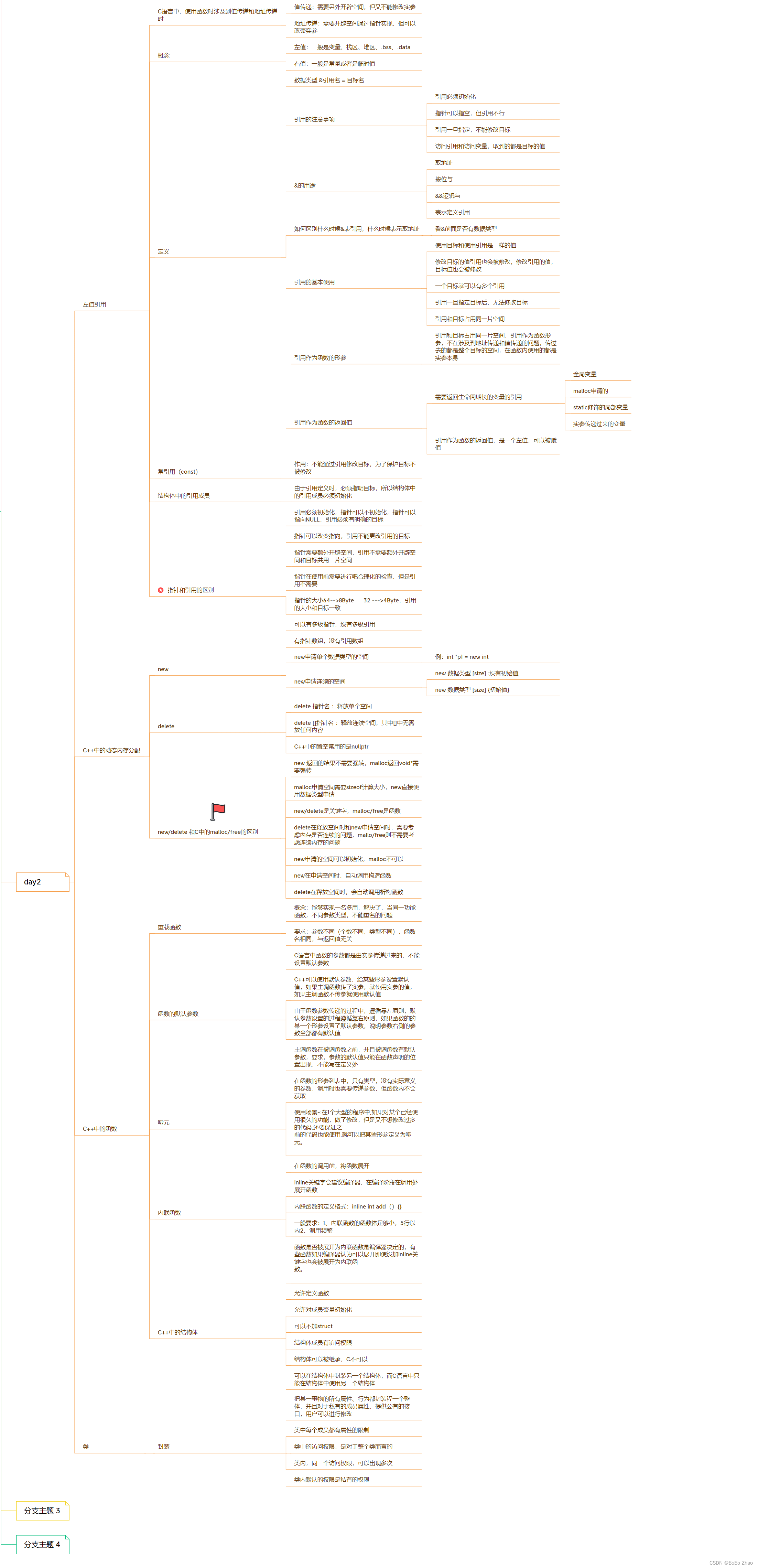
Spring 笔记记录
- 1. spring整合mybatis 注解开发
- 2. spring整合junit
- 3. IOC底层核心原理
- 3.1 层次结构
- 3.2 组件扫描器
- 3.3 自定义导入器
- 3.4 自定义注册器
- 3.5 bean初始化过程解析
- 4.AOP配置
- 4.1 AOP核心概念
- 4.2 AOP入门案例
- 4.2.1 XML方式
- 4.2.2 注解方式
- 4. 3 切入点的三种形式
- 4.4 五种通知类型
- 4.5 通知顺序
- 4.6 通知获取参数数据
- 4.7 利用AOP测接口执行时间
- 5. 静态代理 装饰着模式
- 6. 动态代理
- 7. cglib--动态代理
- 8. AOP织入时机
- 9 Spring对事物的管理
- 9.1 Spring事务核心对象
- 9.2 PlatformTransactionManager
- 9.3 TranasactionDefinition
- 9.4 TranasactionStatus
- 9.5 事务控制方式
- 1. 编程式
- 2.声明式xml
- 3.声明式 注解
1. spring整合mybatis 注解开发

1.引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.resources下编写properties文件,用于连接数据库
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db?useSSL=false
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
3.使用注解@PropertySource引入数据库配置文件,使用注解@Bean创建DruidDataSource
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class JDBCConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String Driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean("dataSource")
public DruidDataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds=new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(Driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
}
4.使用注解@Bean创建SqlSessionFactoryBean 和MapperScannerConfigurer ,分别用来配置数据源和扫描实体类bean以及mapper映射文件
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactoryBean=new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.zfz.bean");
sessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sessionFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer msc=new MapperScannerConfigurer();
msc.setBasePackage("com.zfz.mapper");
return msc;
}
}
5.使用以下注解引入上述两个配置,并指明spring扫描基础包
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.zfz")
@Import({JDBCConfig.class,MyBatisConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
6.写dao层接口
public interface AccountMapper {
@Insert(" insert into account(name, money)\n" +
" values (#{name}, #{money})")
void save(Account account);
@Delete(" delete\n" +
" from account\n" +
" where id = #{id}")
void delete(Integer id);
@Update(" update account\n" +
" set name=#{name},\n" +
" money=#{money}\n" +
" where id = #{id}")
void update(Account account);
@Select(" select *\n" +
" from account")
List<Account> findAll();
@Select(" select *\n" +
" from account\n" +
" where id = #{id}")
Account findById(Integer id);
}
7.service层接口
public interface AccountService {
void save(Account account);
void delete(Integer id);
void update(Account account);
List<Account> findAll();
Account findById(Integer id);
}
8.service实现及注入dao
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountDao;
@Override
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.save(account);
}
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
accountDao.delete(id);
}
@Override
public void update(Account account) {
accountDao.update(account);
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
@Override
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findById(id);
}
}
9.测试
public class AccountApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ctx.getBean("accountService");
List<Account> all = accountService.findAll();
for (Account account : all) {
System.out.println(account);
}
DruidDataSource dataSource = (DruidDataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
}
输出成功:

2. spring整合junit


使用注解开发
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfig.class})
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void findById(){
Account byId = accountService.findById(1);
Assert.assertEquals("Mike",byId.getName());
}
}
3. IOC底层核心原理
3.1 层次结构
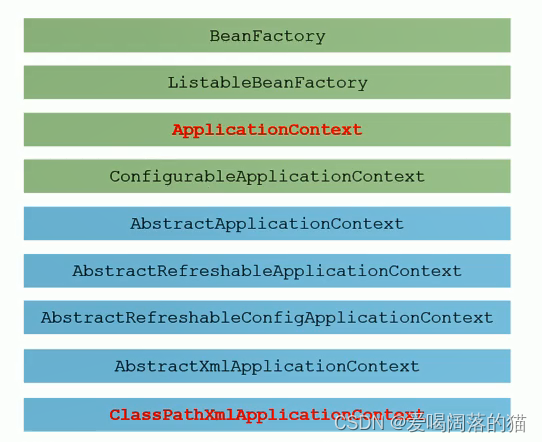
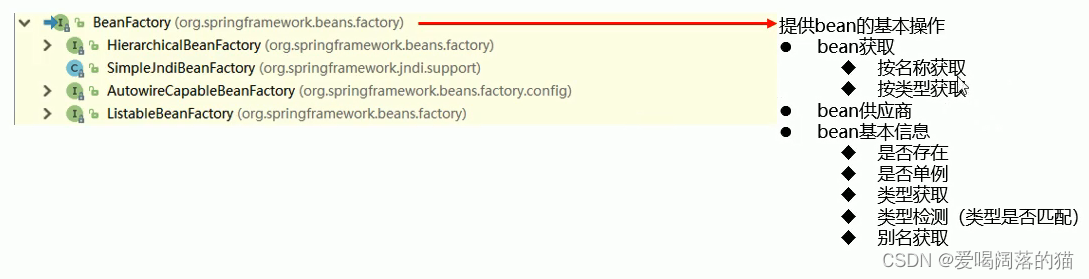
在这里插入图片描述
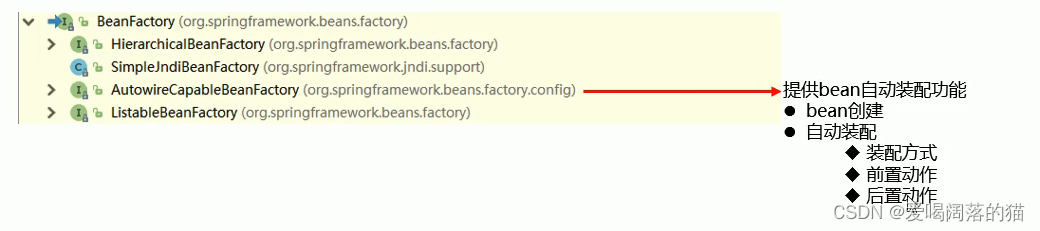
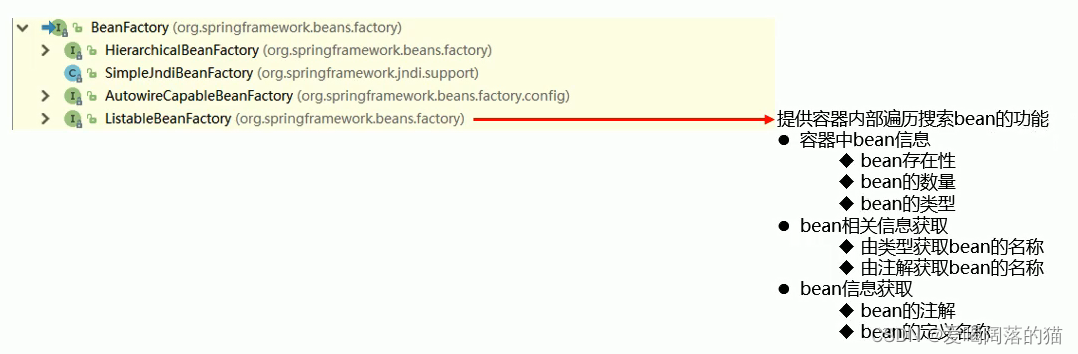
3.2 组件扫描器
在测试中排除非自己写的bean,只需要能够加载启动自己方法的bean,其他的排除;比如我只测试dao层或者service层接口,但是我不需要让他们整个都跑,只需要排除即可
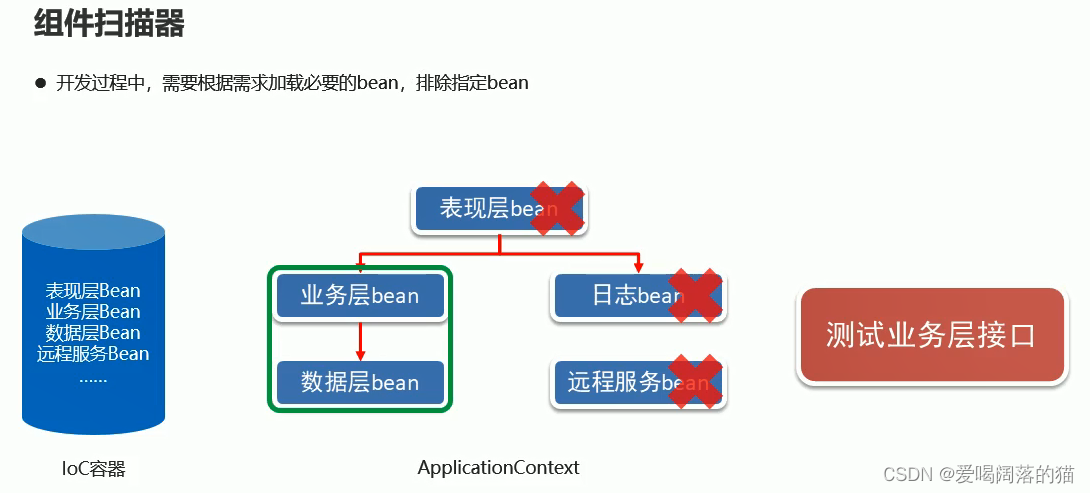

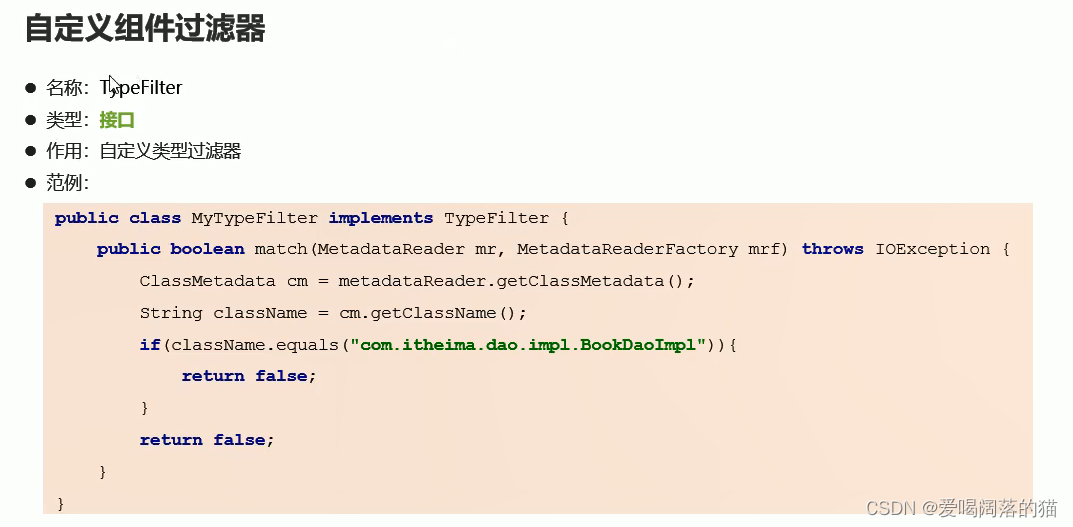
3.3 自定义导入器
应用场景:当bean很多很多时,需要自己写导入器加载bean

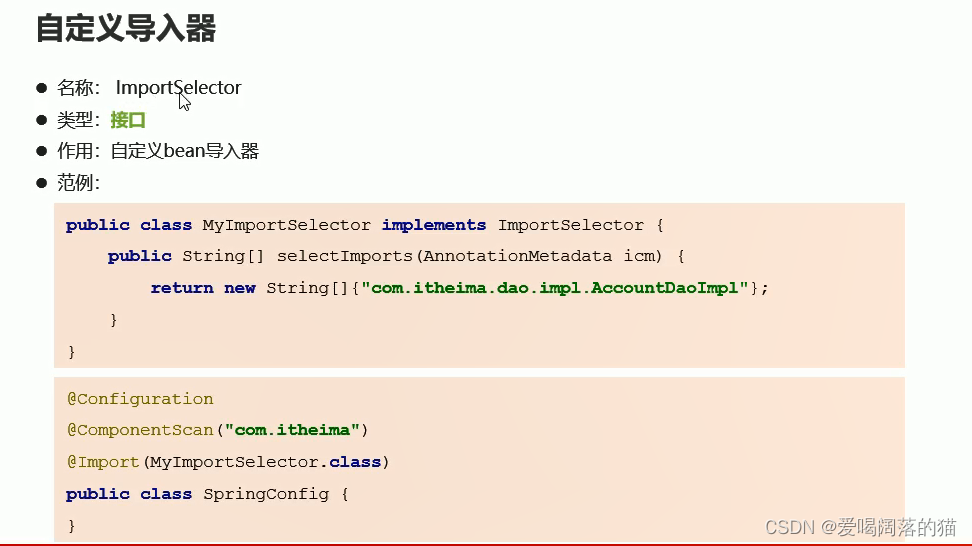
自定义导入器
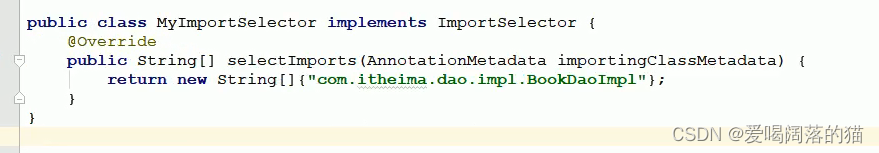
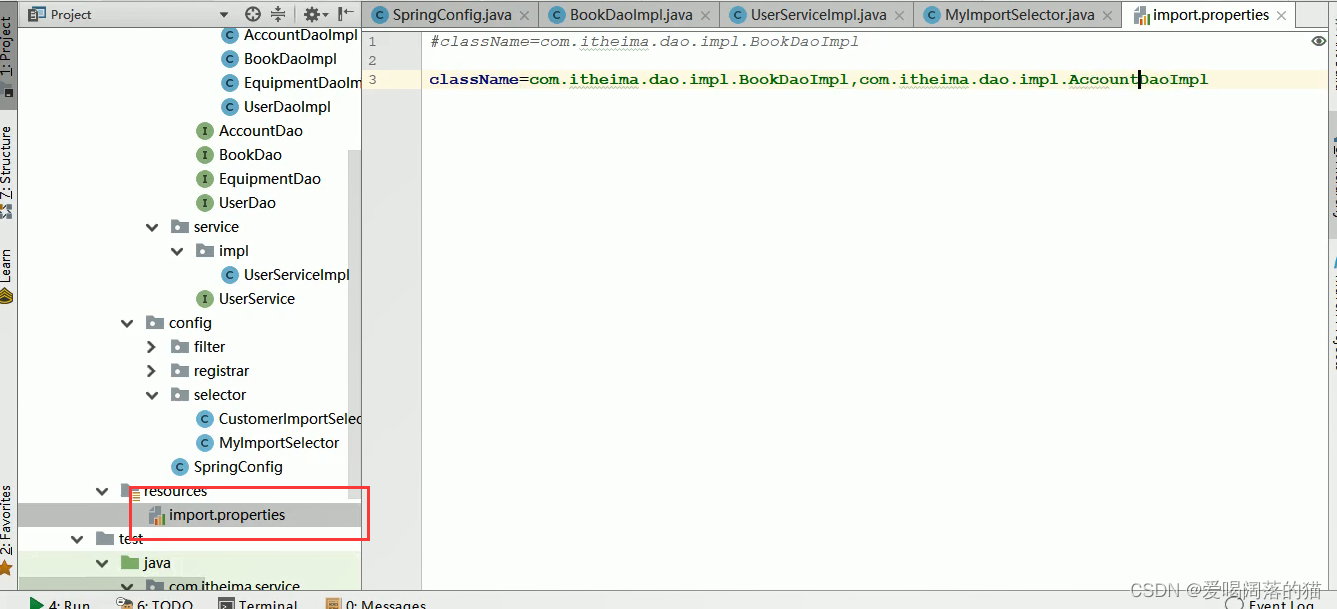
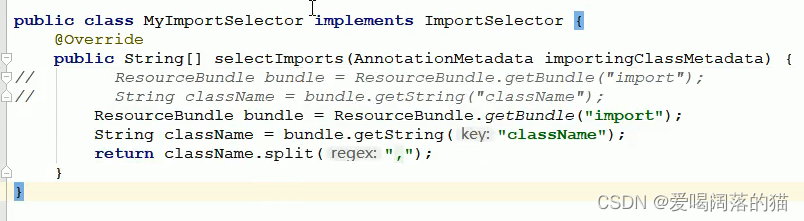
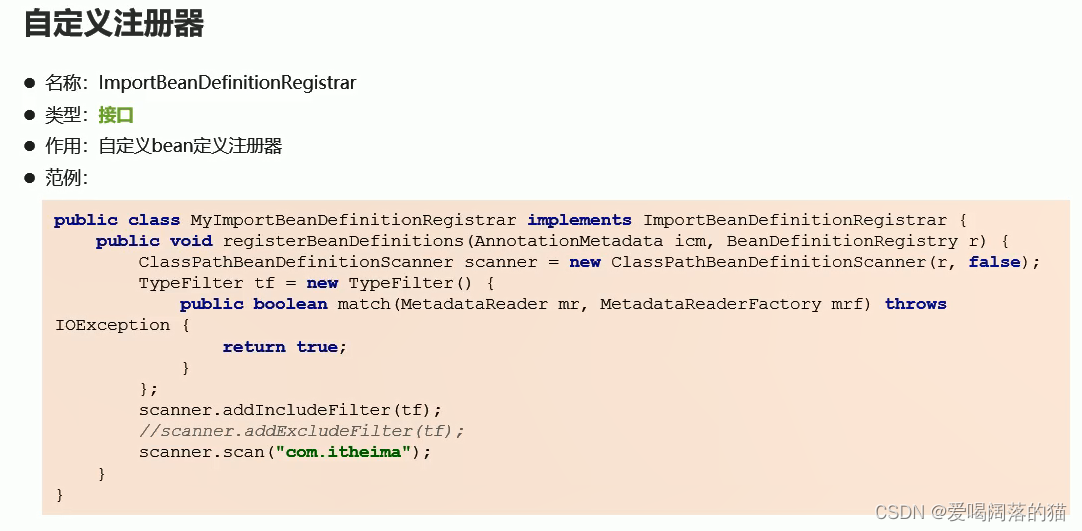
3.4 自定义注册器
为了明白ComponentScan注解的作用
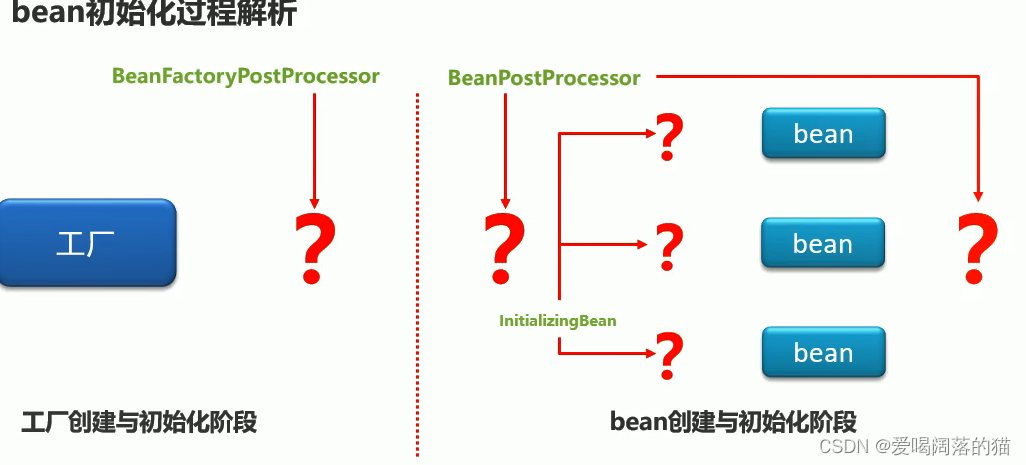
3.5 bean初始化过程解析

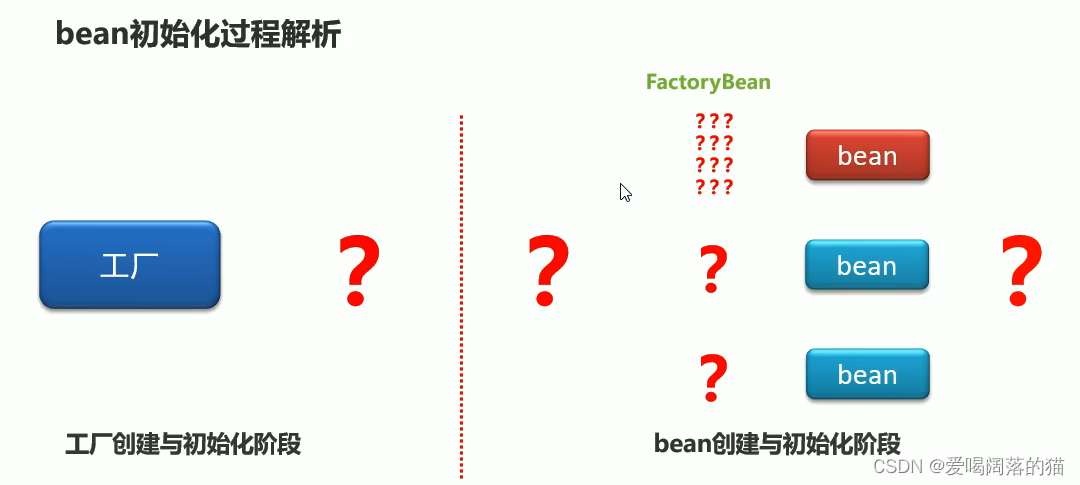
问题又来了:其中一个bean加载需要干很多事情,这个时候FcatoryBean来了

4.AOP配置


4.1 AOP核心概念
- 不论是接口中的方法还是实现的方法都叫连接点
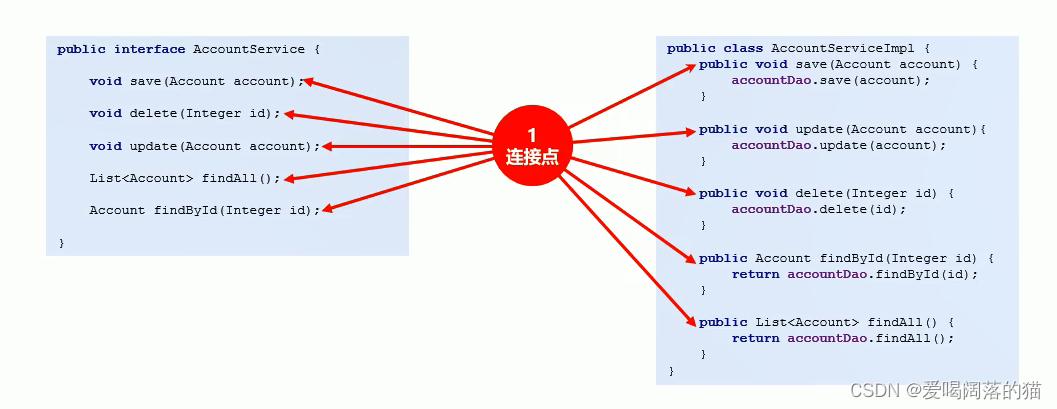
- 能被抽走共性功能的方法叫切入点
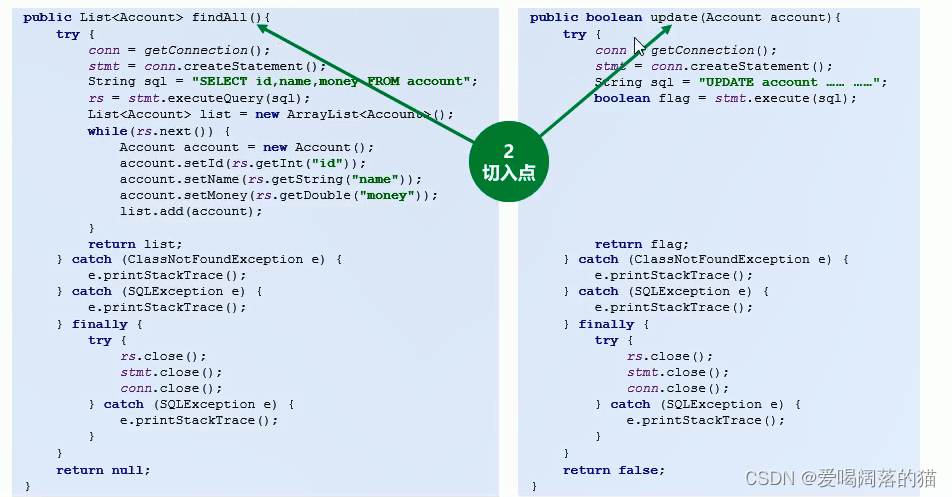
- 通知 指的是被抽走共性功能以后剩下的代码
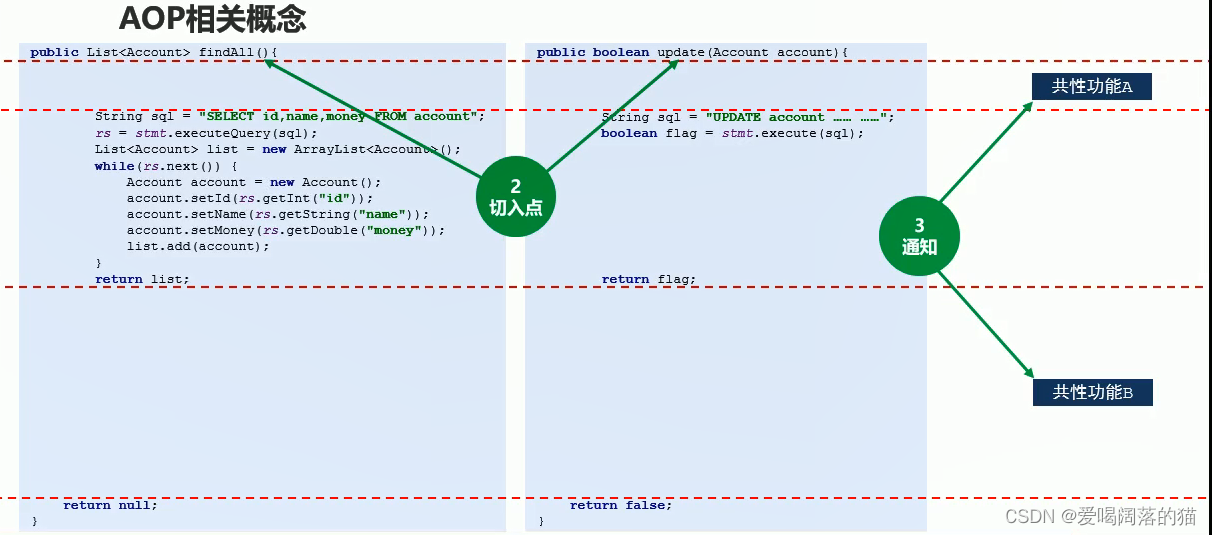
- 切面指的就是 共性代码从哪里被抽走的 与非共性代码(通知)之间的关系
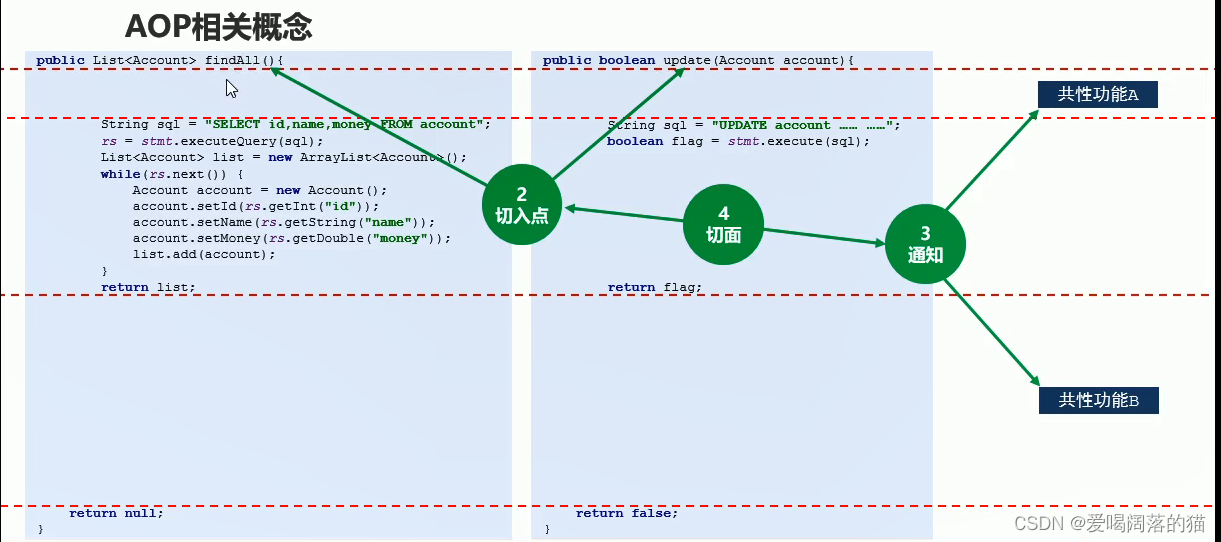
- 被简化出来的运行对象叫 目标对象,这个目标对象需要被抽走的共性代码才能运行

- 原始的共性代码放回到目标功能中的过程叫做织入

- 目标对象类变成的心得类的过程–>叫做代理
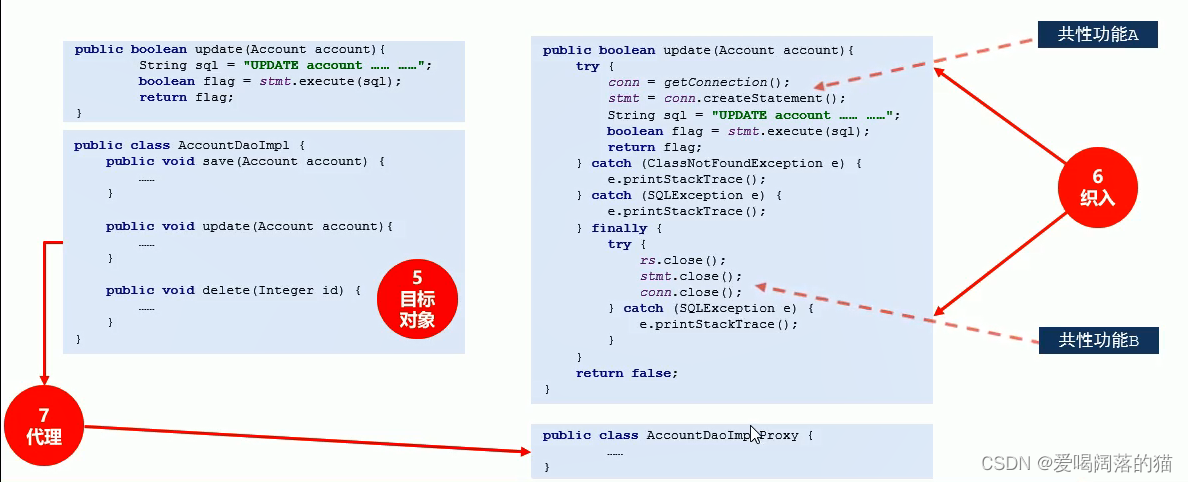
- 现在得到的类现在的类根据之前目标对象的类创建出来的东西都有,但是还可以无中生有,引入新的东西,这个代理类可以凭空出现,这个动作叫引入
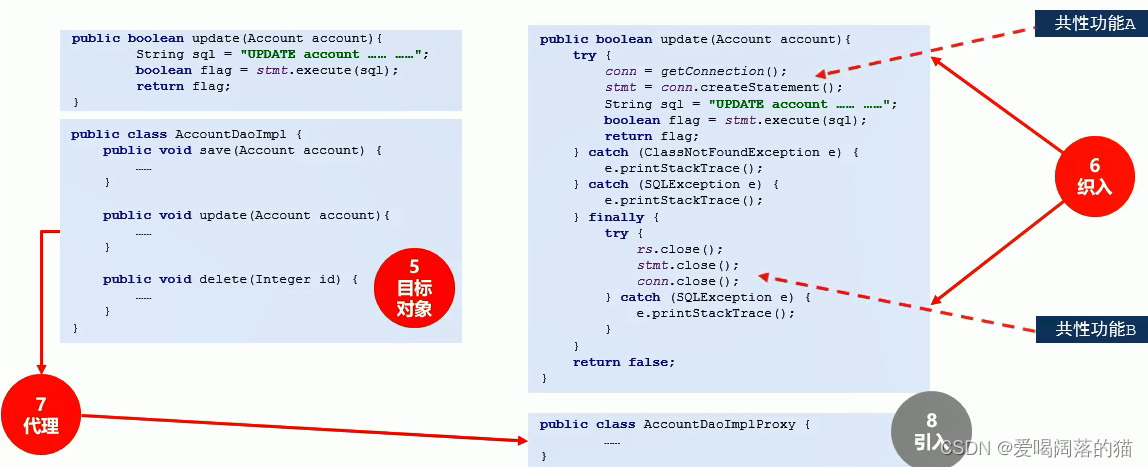

开发中需要做的是绿色的东西:
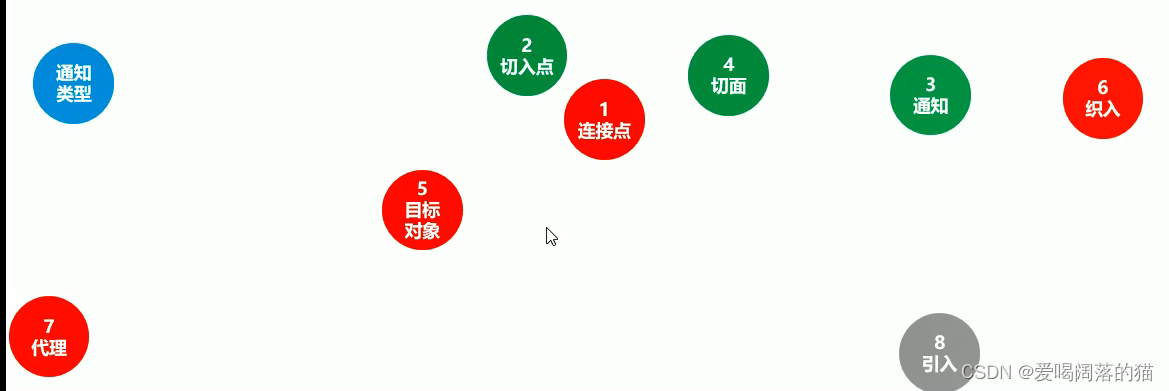

4.2 AOP入门案例
4.2.1 XML方式






1.导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
2.把共性功能抽离出来,写到一个类中
这里是接口实现的一句话抽取
@Override
public void save() {
// System.out.println("共性功能");
System.out.println("userService running");
}
3. 写抽取的代码,制作通知类,在类中定义一个方法用于完成共性功能
public class AopAdvice {
public void function(){
System.out.println("共性功能");
}
}
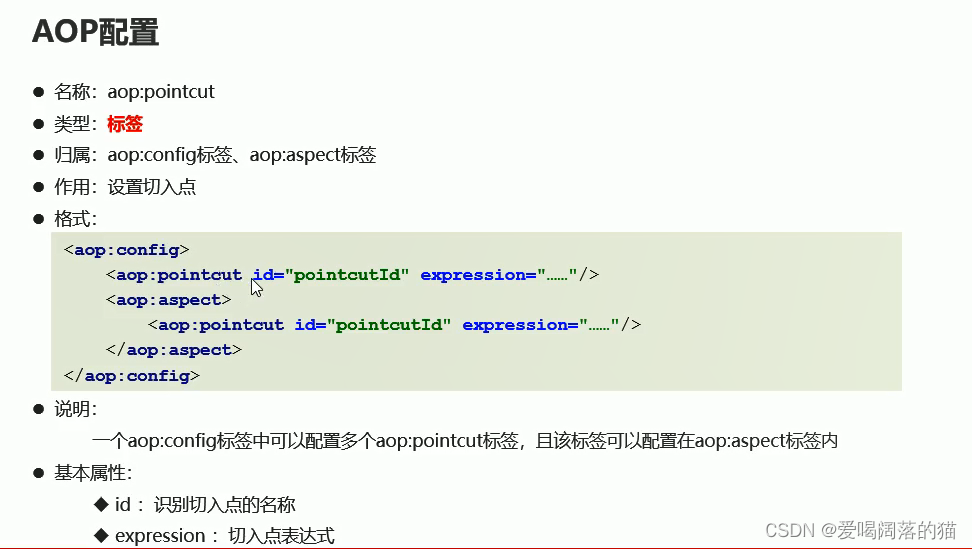
4.这时候spring还不知道这之间的关系,现在做配置,将上面抽离出的共性功能类配置成一个bean,然后开启aop的命名空间支持,然后配置AOP
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启命名空间-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.zfz.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
</bean>
<!-- 配置通知bean-->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.zfz.aop.AopAdvice"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
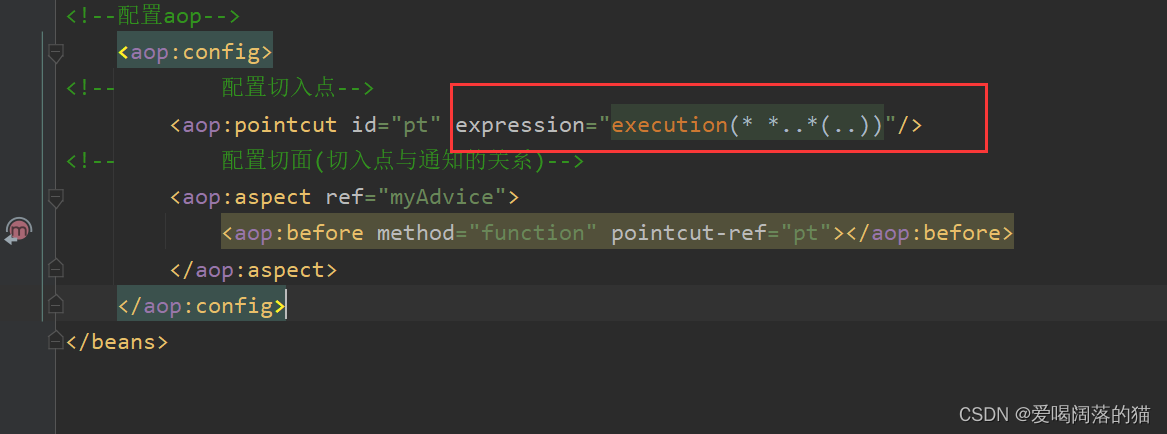
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* *..*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置切面(切入点与通知的关系)-->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<aop:before method="function" pointcut-ref="pt"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
4.2.2 注解方式

1.@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启注解配置
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.zfz")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {
}
2.切面类配置
@Component
@Aspect
public class AopAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* *(..))")
public void pt(){
}
@Before("pt()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("共性功能");
}
}
4. 3 切入点的三种形式


4.4 五种通知类型




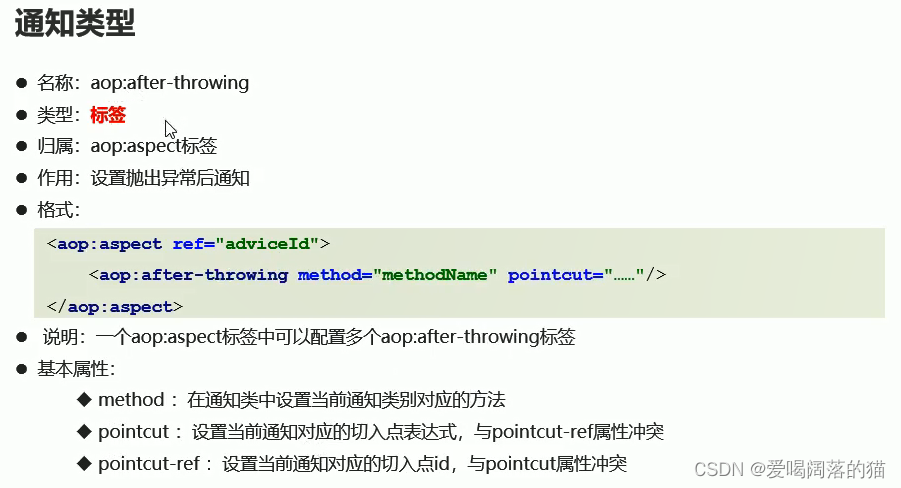

4.5 通知顺序
不论是前置还是后置,配置顺序就是它的基本顺序

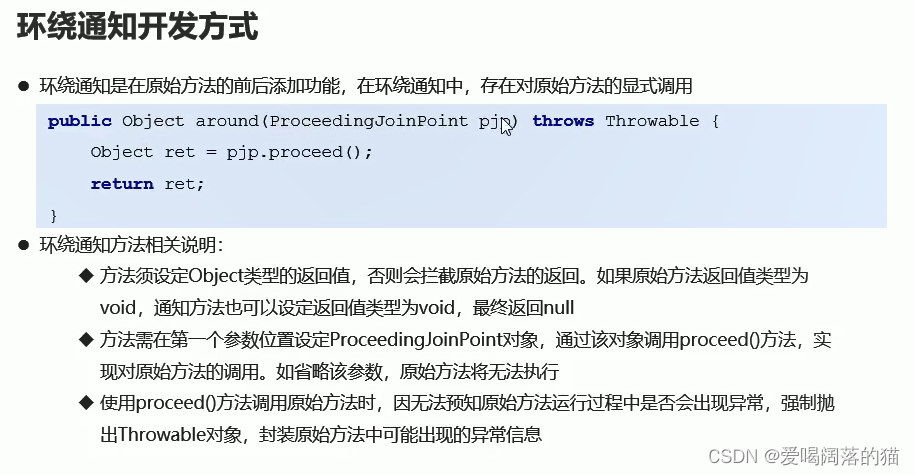
4.6 通知获取参数数据
方式一:

方式二:


只有这两种一定有返回值:



4.7 利用AOP测接口执行时间
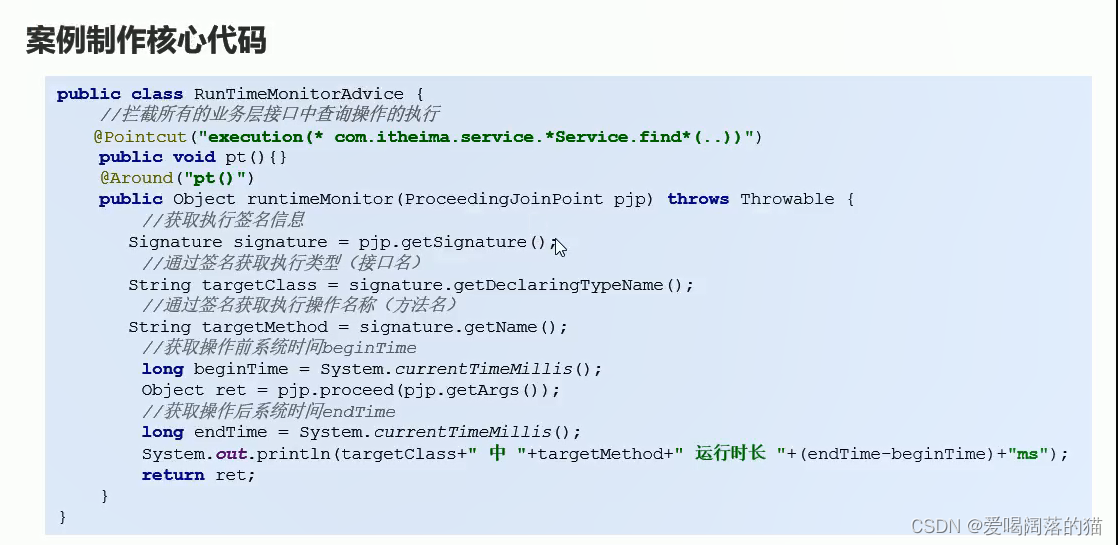
5. 静态代理 装饰着模式
@Component("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void save() {
// System.out.println("共性功能");
System.out.println("水泥墙");
}
}
public class decorator implements UserService{
private UserService userService;
public decorator(UserService userService){
this.userService=userService;
}
@Override
public void save() {
userService.save();
System.out.println("刮大白");
}
}

6. 动态代理
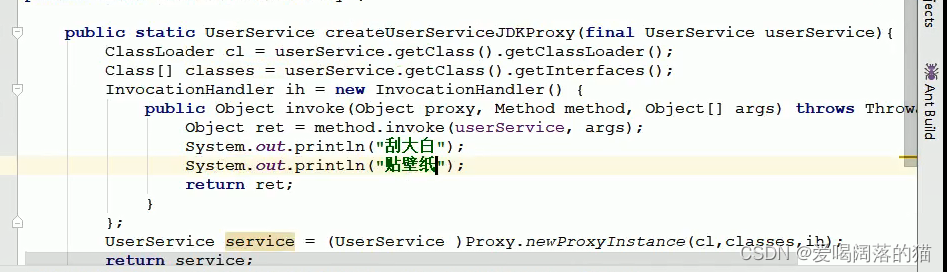
public class UserServiceProxy {
public static UserService getServiceProxy( UserService userService){
UserService service = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(userService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{UserService.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object invoke = method.invoke(userService, args);
System.out.println("刮大白22");
System.out.println("贴壁纸22");
return invoke;
}
});
return service;
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserService userService=new UserServiceImpl();
UserService userService1=UserServiceProxy.getServiceProxy(userService);
userService1.save();
}
}
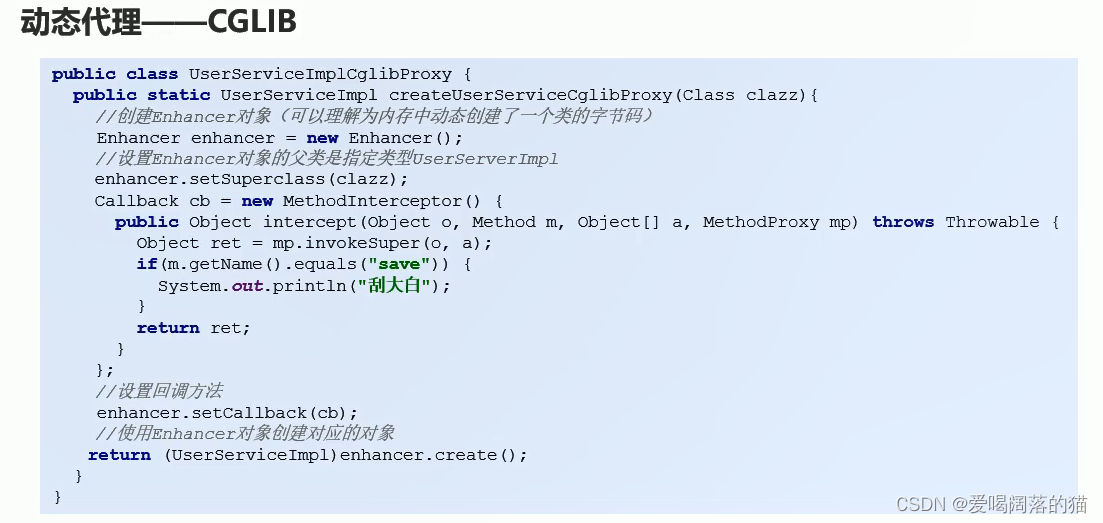
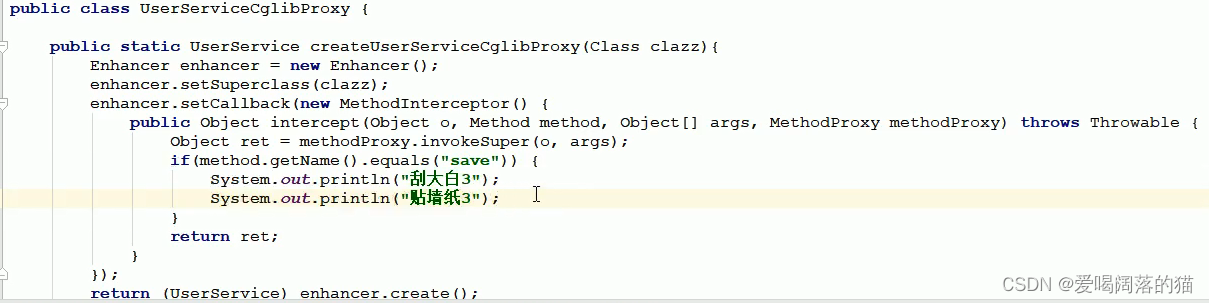
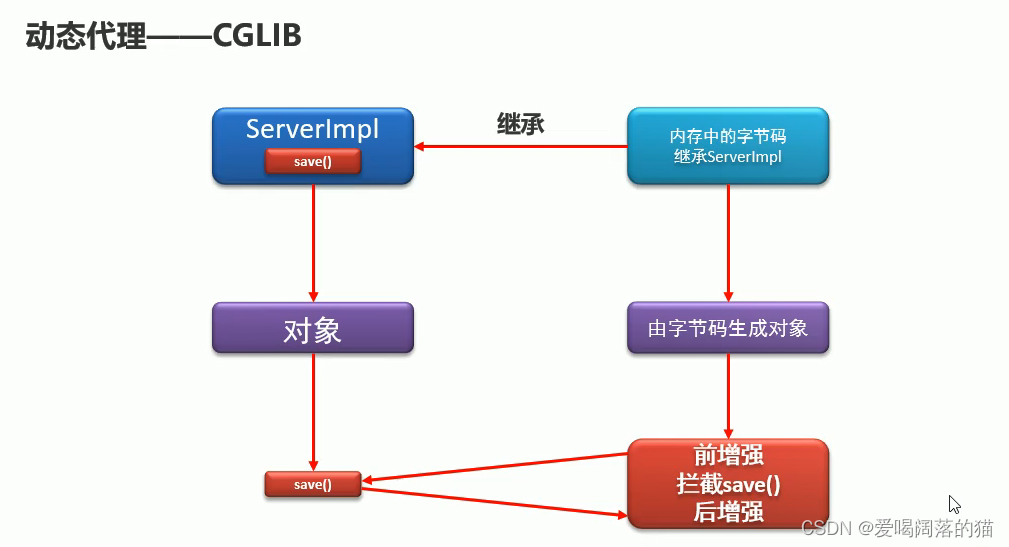
7. cglib–动态代理
动态字节码文件


8. AOP织入时机
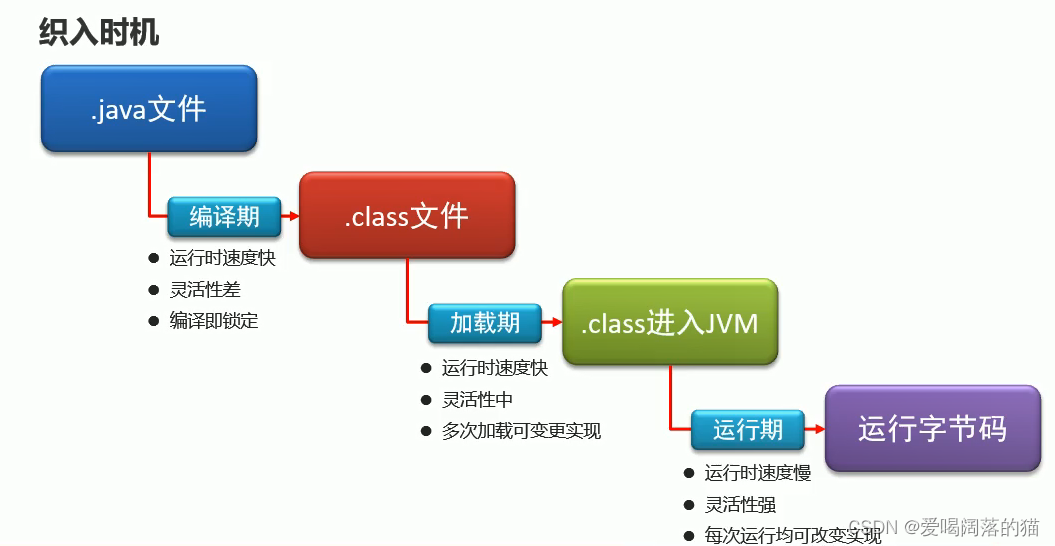
9 Spring对事物的管理


9.1 Spring事务核心对象


9.2 PlatformTransactionManager
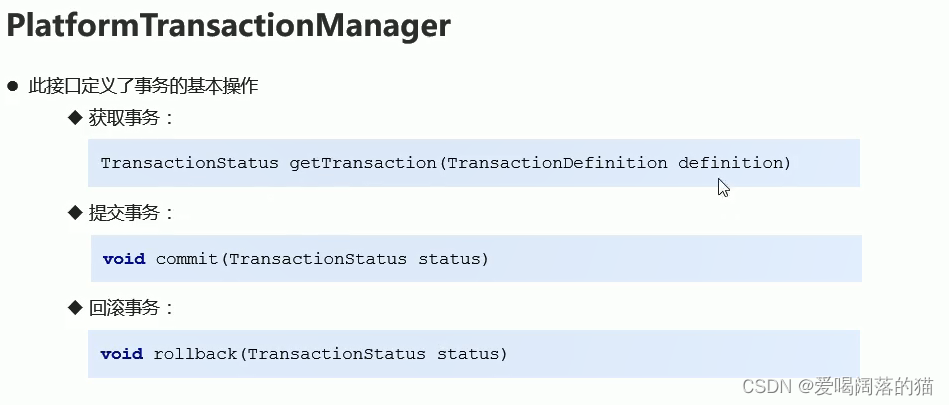
9.3 TranasactionDefinition

9.4 TranasactionStatus

9.5 事务控制方式
实现案例:

业务层实现:主要是转钱的接口实现,要么都成功要么都失败
1. 编程式

public void transfer(String outName, String inName, Double money) {
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
TransactionDefinition td = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
TransactionStatus ts = ptm.getTransaction(td);
accountMapper.inMoney(outName, money);
int i = 1 / 0;
accountMapper.outMoney(inName, money);
//提交事务
ptm.commit(ts);
}
2.声明式xml
通知类:


3.声明式 注解
记得开:@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.zfz")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Import({JDBCConfig.class,MybatisConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
//通知类
@Component
@Aspect
public class AdviceT {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Pointcut("execution(* *transfer(..))")
public void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public Object test(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
TransactionDefinition td = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
TransactionStatus ts = ptm.getTransaction(td);
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
ptm.commit(ts);
return proceed;
}
}