1 链表
链表是线性数据结构(数据元素之间存在着“一对一”关系),链表中的每个元素是一个包含数据data和引用字段的对象,引用字段只有next为单向链表,同时又prev和next为双向链表。
1.1 链表基本操作
链表读取第 i 个节点或查找指定值的节点,均需要从头遍历,时间复杂度为O(n)。
在不考虑查找节点的过程的情况下,更新(替换data),插入(新节点next指针指向插入位置节点,前一节点的next指针指向新节点)、删除(前一节点next指针指向下一节点,当前节点置空),时间复杂度均为O(1)。
1.2 设计链表
设计单向链表的实现。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0 ~ size - 1 的。
class LinkNode<T> {
val: T;
next: LinkNode<T> | null;
constructor(val: T, next?: LinkNode<T> | null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next ?? null;
}
}
class MyLinkedList<T> {
size: number; // 链表长度
head: LinkNode<T> | null; // 头结点
constructor() {
this.size = 0;
this.head = null;
}
/**
* 获取链表中 index 位置的节点。如果索引无效,则返回 null。
* @param index
*/
getNode(index: number): LinkNode<T> | null {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return null;
}
// index 有效,所以 node.next 和 node.val 是存在的。
let node = this.head as LinkNode<T>;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
node = node.next as LinkNode<T>;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 获取链表中 index 位置的节点值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
* @param index
*/
get(index: number): T | -1 {
const node = this.getNode(index);
return node?.val ?? -1;
}
/**
* 在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
* @param val
*/
addAtHead(val: T): void {
const newHead = new LinkNode(val);
newHead.next = this.head;
this.head = newHead;
this.size = this.size + 1;
}
/**
* 将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
* @param val
*/
addAtTail(val: T): void {
const oldTailNode = this.getNode(this.size - 1);
const newTailNode = new LinkNode(val);
this.size = this.size + 1;
if (oldTailNode === null) {
this.head = new LinkNode(val);
return;
}
oldTailNode.next = newTailNode;
}
/**
* 在链表中的 index 位置之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果 index 小于0,则在头部插入节点。
* @param index
* @param val
*/
addAtIndex(index: number, val: T): void {
if (index > this.size) return;
// 尾插
if (index === this.size) {
this.addAtTail(val);
return;
}
// 头插
if (index < 0) {
this.addAtHead(val);
return;
}
const prevNode = this.getNode(index - 1) as LinkNode<T>;
const node = new LinkNode(val);
node.next = prevNode.next;
prevNode.next = node;
this.size = this.size + 1;
}
/**
* 如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
* @param index
*/
deleteAtIndex(index: number): void {
// index 无效
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size || this.size === 0) return;
this.size = this.size - 1;
// 删除头节点
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head?.next as LinkNode<T> | null;
return;
}
const prevNode = this.getNode(index - 1) as LinkNode<T>;
const deleteNode = prevNode.next as LinkNode<T>;
prevNode.next = deleteNode.next;
}
}1.3 剑指 offer 链表算法题(typescript 版)
从尾到头打印链表
链表倒数第k个节点
反转链表
合并两个排序链表
复杂链表的复制
删除链表中的重复节点
两个链表的第一个公共节点
链表中环的入口节点
2 树
2.1 基本概念
树是非线性逻辑结构,是n(n≥0)个节点的有限集。当n=0时,称为空树。树的每个节点有一个节点值和包含所有子节点的列表,从图的角度看,即N个节点的N - 1条边的有向无环图。树的最大层级数,被称为树的高度或深度。树中最多子节点数称为树的度。
而最常用且典型的是二叉树,即每个节点最多只有两个子节点。两个孩子节点的顺序是固定的(与二度树不同)。
满二叉树的所有非叶子节点都存在左右孩子,并且所有叶子节点都在同一层级上。
完全二叉树是具有与同深度的按层级顺序1 到 n 编号的满二叉树完全对应的节点编号的二叉树。
二叉树是逻辑结构,物理结构可以是链式存储结构,或者是数组。
链式存储结构:存储数据的data变量、指向左孩子的left指针、指向右孩子的right指针。
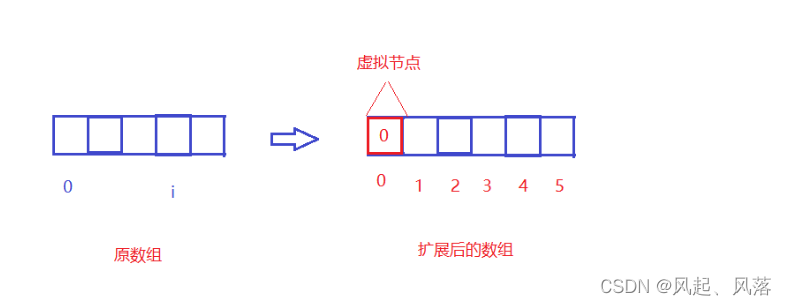
数组:按层级顺序把二叉树的节点放到数组中对应的位置上。如果某一个节点的左孩子或右孩子空缺,则数组的相应位置也空出来:
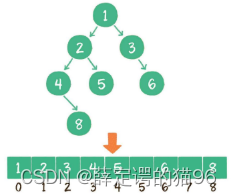
如上图,当前节点的下标是parent,那么它的左孩子节点下标就是2 × parent + 1;右孩子节点下标就是2 × parent + 2。反过来,假设一个左孩子节点的下标是lChild,那么它的父节点下标就是(lChild - 1)/ 2,同理,假设一个右孩子节点的下标是rChild,那么它的父节点下标就是(rChild - 2)/ 2,因此任何一个节点下标为child,其父节点下标为 Math.floor((child - 1) / 2)。数组存储更适合完全二叉树和满二叉树,对于稀疏二叉树,无疑是浪费空间的。
二叉树的应用主要是查找和维持相对顺序,比如二叉查找树(二叉搜索树)(左孩子 < 父节点 < 右孩子)和二叉堆(大根堆:左孩子 < 父节点 > 右孩子,小根堆:左孩子 > 父节点 < 右孩子)。对于一个节点分布相对均衡的二叉查找树来说,如果节点总数是n,那么搜索节点的时间复杂度就是O(logn),和树的深度是一样的。而如果考虑插入有序的序列,树的高度和搜索时间都会退化成O(n),就需要采用二叉树的自平衡,其应用有:红黑树、AVL树(二叉平衡树)等 。
2.2 二叉树的实现与遍历
二叉树遍历包括前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,层序遍历。实现方法为递归遍历和迭代遍历。
二叉树的实现和递归遍历:
class BinaryTreeNode {
key: string | number; // 节点的键
parent: BinaryTreeNode | null; // 节点的父节点
value: any; // 节点的值
left: BinaryTreeNode | null; // 指向节点左孩子的指针
right: BinaryTreeNode | null; // 指向节点右孩子的指针
constructor(key: string | number, value = key, parent = null) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
get isLeaf() {
return this.left === null && this.right === null;
}
get hasChildren() {
return !this.isLeaf;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// 根节点
root: BinaryTreeNode;
constructor(key: string, value = key) {
this.root = new BinaryTreeNode(key, value);
}
/**
* 中序遍历 (首先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树)
* @param node
*/
*inOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
const { left, right } = node;
if (left) yield* this.inOrderTraversal(left);
yield node;
if (right) yield* this.inOrderTraversal(right);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历 (首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点)
* @param node
*/
*postOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
const { left, right } = node;
if (left) yield* this.postOrderTraversal(left);
if (right) yield* this.postOrderTraversal(right);
yield node;
}
}
/**
* 前序遍历 (首先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树)
* @param node
*/
*preOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
const { left, right } = node;
yield node;
if (left) yield* this.preOrderTraversal(left);
if (right) yield* this.preOrderTraversal(right);
}
}
/**
* 插入一个节点作为给定父节点的子节点
* @param parentNodeKey
* @param key
* @param value
* @param param3
* @returns
*/
insert(parentNodeKey: any, key: string, value = key, { left, right } = { left: true, right: true }) {
for (const node of this.preOrderTraversal()) {
if (node.key === parentNodeKey) {
// 插入到某父节点下,如果不指定则插入到左右孩子中的空的那个
const canInsertLeft = left && node.left === null;
const canInsertRight = right && node.right === null;
if (!canInsertLeft && !canInsertRight) return false; // 该父节点孩子节点不空余
if (canInsertLeft) {
node.left = new BinaryTreeNode(key, value, node);
return true;
}
if (canInsertRight) {
node.right = new BinaryTreeNode(key, value, node);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 从二叉树中删除一个节点及其子节点
* @param key
* @returns
*/
remove(key: string) {
for (const node of this.preOrderTraversal()) {
if (node.left.key === key) {
node.left = null;
return true;
}
if (node.right.key === key) {
node.right = null;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 检索给定节点
* @param key
* @returns
*/
find(key: string) {
for (const node of this.preOrderTraversal()) {
if (node.key === key) return node;
}
return undefined;
}
}前序遍历(迭代):
/**
* 前序遍历 (首先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树)
*/
function preOrderTraversal(root: BinaryTreeNode | null) {
if (root === null) return [];
const result: number[] = [];
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length !== 0) {
const current = stack.pop()!;
result.push(current.value);
const lChild = current.left;
const rChild = current.right;
// 栈后进先出,因此先右孩子入栈,然后左孩子入栈
if (rChild !== null) stack.push(rChild);
if (lChild !== null) stack.push(lChild);
}
return result;
}中序遍历(迭代):
/**
* 中序遍历 (首先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树)
*/
function inOrderTraversal(root: BinaryTreeNode | null) {
if (root === null) return [];
const result: number[] = [];
const stack: BinaryTreeNode[] = [];
let current: BinaryTreeNode | null = root;
while (stack.length !== 0 || current !== null) {
while (current !== null) {
// 一直遍历到最左孩子节点
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
if (stack.length !== 0) {
// 栈非空
const node = stack.pop()!;
result.push(node.value);
current = node.right; // 当前 -> 右
}
}
return result;
}后序遍历(迭代):
/**
* 后序遍历 (首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点)
* @param node
*/
function postOrderTraversal(root: BinaryTreeNode | null) {
if (root === null) return [];
const result: number[] = [];
// 转变成遍历 根节点 -> 右节点 -> 左节点
// 遍历结果数组进行reverse, 即得到左节点 -> 右节点 -> 根节点
let stack = [root];
while (stack.length !== 0) {
let current = stack.pop()!;
result.push(current.value);
let lChild = current.left;
let rChild = current.right;
// 交换和前序的顺序
if (lChild !== null) stack.push(lChild);
if (rChild !== null) stack.push(rChild);
}
return result.reverse(); // 反转即可
}层序遍历:
/**
* 层序遍历 (逐层遍历树结构,借助队列实现)
* @param node
*/
function leverOrderTraversal(root: BinaryTreeNode | null) {
if (root === null) return [];
const result: number[] = [];
const queue = [root]; // 队列(先入先出)
while (queue.length !== 0) {
// 队列非空
const current = queue.shift()!; // 队首出队
result.push(current.value);
const leftChild = current.left;
const rightChild = current.right;
if (leftChild !== null) queue.push(leftChild);
if (rightChild !== null) queue.push(rightChild);
}
return result;
}2.3 剑指offer树算法题(typescript 版)
二叉树的深度
重建二叉树
从上到下打印二叉树
镜像二叉树
平衡二叉树
二叉树中和为某一值的路径
对称二叉树
二叉搜索树的后序遍历
二叉搜索树的第k个节点
树的子结构
二叉树的下一个节点
序列化二叉树
二叉搜索树与双向链表
3 图
3.1 图的基本操作
图是一种非线性逻辑结构,由一组节点或顶点以及一组表示这些节点之间连接的边组成。图可以是有向的或无向的,而它们的边可以分配数字权重。
3.2 图的设计与实现
interface Edge {
a: GraphNode; // 边的起始节点
b: GraphNode; // 边的目标节点
weight?: number; // 边的可选数字权重值
}
interface GraphNode {
key: string; // 节点的键
value: any; // 节点的值
}
class Graph {
directed: boolean;
nodes: GraphNode[];
edges: Map<string, Edge>;
constructor(directed = true) {
this.directed = directed;
this.nodes = [];
this.edges = new Map();
}
/**
* 插入具有特定键和值的新节点
* @param key
* @param value
*/
addNode(key: string, value = key) {
this.nodes.push({ key, value });
}
/**
* 在两个给定节点之间插入一条新边,可选择设置其权重
* @param a
* @param b
* @param weight
*/
addEdge(a: GraphNode, b: GraphNode, weight?: number) {
this.edges.set(JSON.stringify([a, b]), { a, b, weight });
if (!this.directed) this.edges.set(JSON.stringify([b, a]), { a: b, b: a, weight });
}
/**
* 删除具有指定键的节点
* @param key
*/
removeNode(key: string) {
this.nodes = this.nodes.filter((n: { key: string }) => n.key !== key);
[...this.edges.values()].forEach(({ a, b }) => {
if (a.key === key || b.key === key) this.edges.delete(JSON.stringify([a, b]));
});
}
/**
* 删除两个给定节点之间的边
* @param a
* @param b
*/
removeEdge(a: any, b: any) {
this.edges.delete(JSON.stringify([a, b]));
if (!this.directed) this.edges.delete(JSON.stringify([b, a]));
}
/**
* 检索具有给定键的节点
* @param key
* @returns
*/
findNode(key: string) {
return this.nodes.find((x: { key: string }) => x.key === key);
}
/**
* 检查图在两个给定节点之间是否有边
* @param a
* @param b
* @returns
*/
hasEdge(a: any, b: any) {
return this.edges.has(JSON.stringify([a, b]));
}
/**
* 设置给定边的权重
* @param a
* @param b
* @param weight
*/
setEdgeWeight(a: any, b: any, weight: any) {
this.edges.set(JSON.stringify([a, b]), { a, b, weight });
if (!this.directed) this.edges.set(JSON.stringify([b, a]), { a: b, b: a, weight });
}
/**
* 获取给定边的权重
* @param a
* @param b
* @returns
*/
getEdgeWeight(a: any, b: any) {
return this.edges.get(JSON.stringify([a, b]))?.weight;
}
/**
* 从给定节点查找存在边的所有节点
* @param key
* @returns
*/
adjacent(key: string) {
return [...this.edges.values()].reduce((acc, { a, b }) => {
if (a.key === key) acc.push(b);
return acc;
}, [] as GraphNode[]);
}
/**
* 计算给定节点的总边数
* @param key
* @returns
*/
inDegree(key: string) {
return [...this.edges.values()].reduce((acc, { a, b }) => (b.key === key ? acc + 1 : acc), 0);
}
/**
* 计算给定节点的总边数
* @param key
* @returns
*/
outDegree(key: string) {
return [...this.edges.values()].reduce((acc, { a, b }) => (a.key === key ? acc + 1 : acc), 0);
}
}3.3 深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索
深度优先搜索 (DFS) 是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图数据结构的算法。一个从根开始(在图的情况下选择某个任意节点作为根)并在回溯之前沿着每个分支尽可能地探索。
广度优先搜索 (BFS) 则是从树根(或图的某个任意节点,有时称为“搜索key”)开始,首先探索邻居节点,然后再移动到下一级邻居。
3.4 剑指 offer 搜索题(typescript 版)
矩阵中的路径
机器人的运动范围
4 堆
4.1 堆的基本操作
堆是具有以下性质的完全二叉树,有两种堆:
大顶堆(大根堆):每个节点值大于等于左、右孩子节点的值,大根堆的堆顶是整个堆中的最大元素。
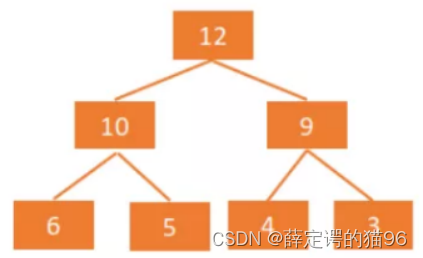
小顶堆(小根堆):每个节点值小于等于左、右孩子节点的值,小根堆的堆顶是整个堆中的最小元素。
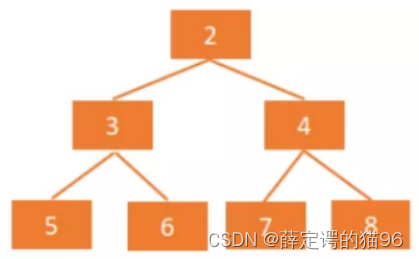
存储形式:数组
应用:优先级队列(多个定时器任务问题)、求前n个最大/最小的数。
堆的基本操作包括(均依赖于堆的自我调整使其满足大/小根堆特性):
- 插入节点:插入位置是在堆的末尾,然后对该节点进行上浮操作(上浮即和它的父节点比较大小);
- 删除节点:删除位置在堆顶,然后将堆尾元素放到堆顶,对此元素进行下沉操作(下沉即和它的左、右孩子比较大小),不断递归,直到无法下沉;
- 构建堆:把一个无序的完全二叉树调整为大/小根堆,从下往上、从左往右的对所有非叶子节点进行下沉操作。
4.2 设计堆
利用数组,实现具有插入,删除操作的大根或小根堆。
class Heap {
container: number[];
cmp: Function;
/**
* 默认是大顶堆
* @param type
*/
constructor(type: 'max' | 'min' = 'max') {
this.container = [];
this.cmp = type === 'max' ? (x, y) => x > y : (x, y) => x < y;
}
/**
* 对堆中的两个节点进行交换
* @param i
* @param j
*/
swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.container[i], this.container[j]] = [this.container[j], this.container[i]];
}
/**
* 插入节点,在堆末尾插入,并对节点进行上浮操作
* @param data
* @returns
*/
insert(data: number) {
this.container.push(data);
// 上浮操作
let index = this.container.length - 1;
while (index) {
// 直到遍历到堆顶
// 父节点位置
const parent = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (!this.cmp(this.container[index], this.container[parent])) {
// 大顶堆:当前节点不大于父节点,到达最终位置
return;
}
// 交换
this.swap(index, parent);
index = parent;
}
}
/**
* 删除节点,删除堆顶元素与堆尾元素后的堆尾所在元素,再对堆顶元素执行下沉操作
* @returns
*/
delete(): number {
if (this.isEmpty()) return NaN;
// 将堆顶元素与堆尾元素进行交换,并删除堆尾元素
const size = this.getSize();
this.swap(0, size - 1);
const top = this.container.pop()!;
// 当前节点位置
let index = 0;
// 交换节点位置,大顶堆:子节点中的较大者
let exchange = index * 2 + 1;
while (exchange < size) {
// 右子节点位置
let right = index * 2 + 2;
if (right < length && this.cmp(this.container[right], this.container[exchange])) {
// 大顶堆:存在右节点且右节点较大
exchange = right;
}
if (!this.cmp(this.container[exchange], this.container[index])) {
// 大顶堆:子节点较大者小于当前节点
return NaN;
}
// 交换
this.swap(exchange, index);
index = exchange;
exchange = index * 2 + 1;
}
return top;
}
/**
* 获取堆顶元素,堆空则返回 NaN
* @returns
*/
top(): number {
if (this.isEmpty()) return NaN;
return this.container[0];
}
/**
* 判断堆是否为空
* @returns
*/
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.getSize() === 0;
}
/**
* 堆中元素个数
* @returns
*/
getSize(): number {
return this.container.length;
}
}
4.3 剑指 offer 堆算法题( typescript 版)
数据流中的中位数
5 散列表
5.1 Hash表的基本操作
Hash表是一种是使用哈希函数来组织数据,支持快速插入和搜索的线性数据结构。关键是通过哈希函数将键映射到存储桶。哈希函数的选取取决于键的值范围和桶的数量。
a) 插入新的键,哈希函数计算被存储的桶;
b) 搜索一个键,使用相同的哈希函数计算所在桶, 然后在桶中搜索。
5.2 设计Hash表
关键是选择哈希函数和进行冲突处理
哈希函数:分配一个地址存储值。理想情况下,每个键都应该有一个对应唯一的散列值。
冲突处理:哈希函数的本质就是从 A 映射到 B。但是多个 A 键可能映射到相同的 B。
将哈希key转换为字符串的函数如下:
/**
* @description: 将 item 也就是 key 统一转换为字符串
*/
export function defaultToString(item: any): string {
// 对于 null undefined和字符串的处理
if (item === null) {
return 'NULL';
} else if (item === undefined) {
return 'UNDEFINED';
} else if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`;
}
// 其他情况时调用数据结构自带的 toString 方法
return item.toString();
}冲突解决策略:
1) 单独链接法(链表法):对于相同的散列值,我们将它们放到一个桶中,每个桶是相互独立的
// 单独链接法(链表)
export class HashTableSeparateChaining<K, V> {
protected table: Map<number, MyLinkedList<{ key: K; value: V }>>;
constructor(protected toStrFn: (key: K) => string = defaultToString) {
this.table = new Map();
}
/**
* @description: 哈希函数(djb2函数(或者loselose函数)
*/
private hashCodeHelper(key: K): number {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 5381;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash = hash * 33 + tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 1013;
}
/**
* @description: 哈希函数封装
*/
hashCode(key: K): number {
return this.hashCodeHelper(key);
}
/**
* @description: 更新散列表
*/
put(key: K, value: V): boolean {
if (key !== null && value !== null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 当该 hashcode 不存在时,先创建一个链表
if (this.table.get(position) == null) {
this.table.set(position, new MyLinkedList<{ key: K; value: V }>());
}
// 再给链表push值
this.table.get(position)!.addAtTail({ key, value });
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* @description: 根据键获取值
*/
get(key: K): V | undefined {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
const linkedList = this.table.get(position);
if (linkedList && linkedList.size !== 0) {
let current = linkedList.head;
// 去链表中迭代查找键值对
while (current !== null) {
if (current.val.key === key) {
return current.val.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 根据键移除值
*/
remove(key: K): boolean {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
const linkedList = this.table.get(position);
if (linkedList && linkedList.size !== 0) {
let current = linkedList.head;
let index = 0;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.val.key === key) {
break;
}
index = index + 1;
current = current.next;
}
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(index);
// 关键的一点,当链表为空以后,需要在 table 中删除掉 hashcode
if (linkedList.size === 0) {
this.table.delete(position);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* @description: 返回是否为空散列表
*/
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.size() === 0;
}
/**
* @description: 散列表的大小
*/
size(): number {
let count = 0;
// 迭代每个链表,累计求和
for (const [hashCode, linkedList] of this.table) {
count += linkedList.size;
}
return count;
}
/**
* @description: 清空散列表
*/
clear() {
this.table.clear();
}
/**
* @description: 返回内部table
*/
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
/**
* @description: 替代默认的toString
*/
toString(): string {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
let objStringList: string[] = [];
for (const [hashCode, linkedList] of this.table) {
let node = linkedList.head;
while (node) {
objStringList.push(`{${node.val.key} => ${node.val.value}}`);
node = node.next;
}
}
return objStringList.join(',');
}
}2) 开放地址法(线性探测):每当有碰撞,则根据我们探查的策略找到一个空的槽为止。
// 开放地址法(线性探测)
export default class HashTableLinearProbing<K, V> {
protected table: Map<number, { key: K; value: V }>;
constructor(protected toStrFn: (key: K) => string = defaultToString) {
this.table = new Map();
}
/**
* @description: 哈希函数(djb2函数(或者loselose函数))
*/
private hashCodeHelper(key: K): number {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 5381;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash = hash * 33 + tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 1013;
}
/**
* @description: 哈希函数封装
*/
hashCode(key: K): number {
return this.hashCodeHelper(key);
}
/**
* @description: 更新散列表
*/
put(key: K, value: V): boolean {
if (key !== null && value !== null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table.get(position) == null) {
// 当hashcode位置为空时,可以直接添加
this.table.set(position, { key, value });
} else {
// 否则需要迭代查找最近的空位置再添加
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table.get(index) !== null) {
index++;
}
this.table.set(index, { key, value });
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* @description: 根据键获取值
*/
get(key: K): V | undefined {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table.get(position)) {
// 如果查到的hashcode位置就是要查的key,则直接返回
if (this.table.get(position)!.key === key) {
return this.table.get(position)!.value;
}
// 否则需要迭代着向下查找
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table.get(index) != null && this.table.get(index)!.key !== key) {
index++;
}
if (this.table.get(index) !== null && this.table.get(index)!.key === key) {
return this.table.get(position)!.value;
}
}
// 最后也没查到,就返回 undefined
return undefined;
}
/**
* @description: 根据键移除值
*/
remove(key: K): boolean {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table.get(position)) {
// 同理,如果hashcode对应位置就是要查的key,则直接删除
if (this.table.get(position)!.key === key) {
this.table.delete(position);
// 删除后处理副作用
this.verifyRemoveSideEffect(key, position);
return true;
}
// 同理,如果hashcode对应的位置不是要查的key,就迭代查到
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table.get(index) !== null && this.table.get(index)!.key !== key) {
index++;
}
if (this.table.get(index) !== null && this.table.get(index)!.key === key) {
this.table.delete(index);
// 同样在删除后处理副作用
this.verifyRemoveSideEffect(key, index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* @description: 处理移除键值对后的副作用
*/
private verifyRemoveSideEffect(key: K, removedPosition: number) {
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
let index = removedPosition + 1;
// 迭代着处理后面的每一个键值对
while (this.table.get(index) !== null) {
const posHash = this.hashCode(this.table.get(index)!.key);
// 挨个向前挪动,关键点在于,hashcode值比较小的键值对尽量先向前补位
// 详细的说:如果当前元素的 hash 值小于或等于原始的 hash 值
// 或者当前元素的 hash 值小于或等于 removedPosition(也就是上一个被移除 key 的 hash 值),
// 表示我们需要将当前元素移动至 removedPosition 的位置
if (posHash <= hash || posHash <= removedPosition) {
this.table.set(removedPosition, this.table.get(index)!);
this.table.delete(index);
removedPosition = index;
}
index++;
}
}
/**
* @description: 返回是否为空散列表
*/
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.size() === 0;
}
/**
* @description: 散列表的大小
*/
size(): number {
return this.table.size;
}
/**
* @description: 清空散列表
*/
clear() {
this.table.clear();
}
/**
* @description: 返回内部table
*/
getTable(): Map<number, { key: K; value: V }> {
return this.table;
}
/**
* @description: 替代默认的toString
*/
toString(): string {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
let objStringList: string[] = [];
for (const [hashCode, { key, value }] of this.table) {
objStringList.push(`{${key} => ${value}}`);
}
return objStringList.join(',');
}
}上述实现中使用到的 djb2函数(或者loselose函数),原理是借助字符串各个位上的 UTF-16 Unicode 值进行计算,然后对 特定值取余即为哈希值。
3) 双散列法:使用两个哈希函数计算散列值,选择碰撞更少的地址。
JavaScript内置哈希表的典型设计是:
键值可以是任何具有可哈希码(映射函数获取存储区索引)的可哈希化的类型。每个桶包含一个数组,用于在初始时将所有值存储在同一个桶中。 如果在同一个桶中有太多的值,这些值将被保留在一个高度平衡的二叉树搜索树(BST)中。
插入和搜索的平均时间复杂度仍为 O(1)。最坏情况下插入和搜索的时间复杂度是 O(logN)。使用高度平衡的 BST是在插入和搜索之间的一种权衡。