Java 语言基础练习题
Key Point
●包的基本语法
●Java 语言中的标识符,命名规范
●八种基本类型
●基本操作符
●if 语句和switch 语句
练习
1.(标识符命名)下面几个变量中,那些是对的?那些是错的?错的请说明理由
Java中的命名规则:
字母 数字和美元和_组成
数字不能开头
区分大小写
任意长度
关键字不可以
遵循大驼峰。每个单词的首字母都是需要大写的
小驼峰:除了第一个单词其余的单词的首字母都是需要大写的
A. ILoveJava 正确。驼峰式的,首字母大写。
B. $20 正确。$能开头。
C. learn@java 错误。出现了特殊的字符@
D. antony.lee 错误。出现了特殊的字符.
E. Hello_World 可以。但是不太符合命名的规范
F. 2tigers 错误。数字不能开头。
2.(Java 程序的编译与运行)假设有如下程序:
package com.corejava.chp1;
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}问:
1)假设这个代码存在hello.java 文件中,那这个程序能够编译通过?为什么?如果编译不通过,应该如何改进?
解答:不能。文件名必须和类名是相同的,将文件名改为HelloWorld.java或者是把类名hello。
2)假设这个.java 文件放在C:\javafile\目录下,CLASSPATH=.,则生成
的.class文件应该放在什么目录下?如何运行?
解答:CLASSPATH=. 表示的是当前的目录。生成的class文件会保存到C:\javafile\目录下。因为classpath指定的是类文件查找的路径所以要运行这个成功需要按照下面的步骤进行运行。
- 打开Terminal争端
- 进入到C:\javafile\目录下
- 使用javac HelloWorld.java 命令,此时会生成一个HelloWorld.class文件保存到当前的目录下。
- 编译完成之后使用java HelloWorld可以运行当前的程序,在控制台上会输出 Hello World 的内容。
3.(if 语句)读入一个整数,判断其是奇数还是偶数
%运算出的结果和0之间的关系
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(number + " 是偶数。");
} else {
System.out.println(number + " 是奇数。");
}
}
}
4.(操作符)有如下代码:
自增运算
int a = 5;
int b = (a++) + (--a) +(++a);
问执行完之后,b 的结果是多少?
解答:
b=5+...+... 此时a=6
b=5+5+... 此时a=5
b=5+5+6 此时a=6
最后
b=5+5+6=16
5.(基本类型的运算)
一家商场在举行打折促销,所有商品都进行8 折优惠。一位程序员把这个逻辑写成:
short price = ...; // 先计算出原价
short realPrice = price * 8 / 10; //再计算出打折之后的价格
问:这段代码是否正确?如果正确,假设price 为100,那计算之后的
realPrice值为多少?如果不正确,应该怎么改正?
解答:
short的取值范围-32768 到 32767
realPrice的返回值应该采用int的类型,因为Java中的默认的运算是int
使用short还有可能导致溢出
short price = 100; // 先计算出原价
int realPrice = price * 8 / 10; //再计算出打折之后的价格
System.out.println(realPrice);6. (操作符)请说明>>与>>>之间的区别。
解答:
都是右移操作但是 >> 是有符号右移操作符,在右移时保留符号位。>>> 是无符号右移操作符,不考虑符号位,用零填充左侧空位。
两个> 右移的时候采用的是符号位进行填充的。跟原先的有的符号是相关的。
三个> 右移的时候采用的是0进行填充的不管原先是什么符号的
7. (操作符)有如下代码:
a = (a>b)?a:b;
请问这段代码完成了什么功能。
解答:三目运算符比较。
当a>b为true 返回a
反之返回b
8. (if 语句)
读入一个整数,表示一个人的年龄。如果小于6 岁,则输出“儿 童”,
6 岁到13 岁,输出“少儿”;14 岁到18 岁,输出“青少年”;18 岁到35 岁,
输出“青年”;35 岁到50 岁,输出“中年”;50 岁以上输出“中老年”。
解答:
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年龄:");
int age = scanner.nextInt();
if (age < 6) {
System.out.println("儿童");
} else if (age >= 6 && age <= 13) {
System.out.println("少儿");
} else if (age >= 14 && age <= 18) {
System.out.println("青少年");
} else if (age > 18 && age <= 35) {
System.out.println("青年");
} else if (age > 35 && age <= 50) {
System.out.println("中年");
} else {
System.out.println("中老年");
}
}
}
9. (switch 语句)
读入一个整数,如果是1~5 之间,则分别输出5 个福娃的名字,否则输出“北京欢迎你”。
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入一个整数!");
int a=scanner.nextInt();
switch (a){
case 1:
System.out.println("Beibei");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Jingjing");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Huanhuan");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Yingying");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("Nini");
break;
default:
System.out.println("北京欢迎你");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
10. (if 语句,赋值操作)
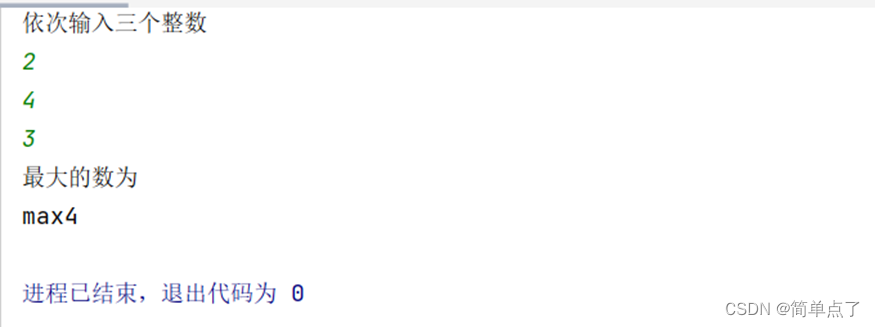
读入三个整数,输出这三个整数中最大的一个。
解答:
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("依次输入三个整数");
int num[]=new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
num[i]=scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("最大的数为");
if (num[0]>=num[1]){
if (num[0]>=num[2]){
System.out.println("max"+num[0]);
}
else {
System.out.println("max"+num[2]);
}
}
else {
if (num[1]>=num[2]){
System.out.println("max"+num[1]);
}
else {
System.out.println("max"+num[2]);
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}效果图:
11. (if 语句) 判断是不是闰年
*读入一个表示年份的整数,判断这一年是否是闰年。如何判断 一个年份是否是闰年:
- 如果这个年份能够被4 整除,且不能被100 整除,则这一年是闰年。例
如,1996 年是闰年,而相应的,1993 年就不是闰年。 - 如果这个年份能够被100 整除,则这个数必须要能被400 整除,才是闰
年。例如,2000 年是闰年,1900 年不是闰年。
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入一个年份");
int year=scanner.nextInt();
boolean isLeapYear = false;//是不是闰年
if ((year % 4 == 0&&year % 100 != 0)
||(year % 100 == 0&&year % 400 == 0)) {
isLeapYear = true;
}
if (isLeapYear) {
System.out.println(year + " 是闰年");
} else {
System.out.println(year + " 不是闰年");
}
scanner.close();
}
}效果图:

12. (switch 语句)*完成一个简单的计算器程序。程序要求如下:
- 读入两个整数
- 提示用户选择对这两个整数的操作,即输出
1 : +
2 : -
3 : *
4 : /
请输入您的选择:
读入用户的选择,输出运算结果。
public class Test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");
int number1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");
int number2 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请选择对这两个整数的操作:"+
"\n1:+"+
"\n2:-"+
"\n3:*"+
"\n4:/");
System.out.print("请输入您的选择:");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
double result = 0;
switch (choice) {
case 1:
result = number1 + number2;
break;
case 2:
result = number1 - number2;
break;
case 3:
result = number1 * number2;
break;
case 4:
if (number2 != 0) {
result = (double) number1 / number2;
} else {
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
return;
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("无效的选择");
return;
}
System.out.println("运算结果:" + result);
}
}效果图:

13. (if 语句)*托运计费问题:
- 当货物重量小于20公斤的时候,收费5元,
- 大于20 公斤小于100 公斤的时候超出20 公斤的部分按每0.2 元每公斤计费,
- 如果超出100 公斤的时候,超出的部分按照每公斤0.15 元计算。
- 读入货物的重量,输出计算之后货物的运费。
解答:
public class Test13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入货物的重量(单位:公斤):");
Scanner scanner
= new Scanner(System.in);
//重量
double weight = scanner.nextDouble();
double fee=0;
//判断
if (weight<=20){
fee=5;
}
else if (weight<=100){
fee=5+(100-20)*0.2;
}
else {
fee=5+(100-20)*0.2+(weight-100)*0.15;
}
System.out.println("货物的运费为:"+fee+"元");
}
}效果图:

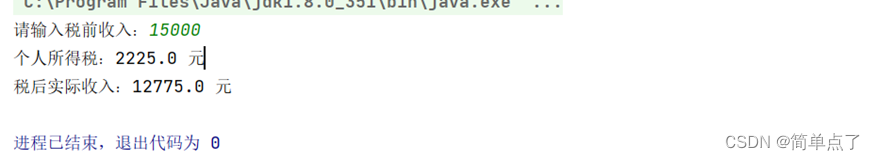
14. (if 语句)*中国的个税计算方法:
应税所得为税前收入扣除2000 元(起征点),然后超出部分,按照以下税率
收税:
500 5%
500-2000 10%
2000-5000 15%
5000-20000 20%
20000-40000 25%
40000-60000 30%
60000-80000 35%
80000-100000 40%
100000 - ? 45%
例:若月收入15000,则应税所得为15000-2000=13000;总的个人所得税为
(13000-5000)*20% + (5000-2000)*15% + (2000-500)*10% + 500*5%= 2225
要求:读入一个整数,表示税前收入,输出应当缴纳的个人所得税和税后实
际收入。
解答:
public class Test14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入税前收入:");
double income = scanner.nextDouble();
double threshold = 2000; // 起征点
double taxableIncome = income - threshold; // 应税所得
double tax = 0; // 个人所得税
if (taxableIncome <= 0) {
tax = 0;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 500) {
tax = taxableIncome * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 2000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 5000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 20000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 5000) * 0.2 + (5000 - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 40000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 20000) * 0.25 + (20000 - 5000) * 0.2 + (5000 - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 60000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 40000) * 0.3 + (40000 - 20000) * 0.25 + (20000 - 5000) * 0.2 + (5000 - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 80000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 60000) * 0.35 + (60000 - 40000) * 0.3 + (40000 - 20000) * 0.25 + (20000 - 5000) * 0.2 + (5000 - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else if (taxableIncome <= 100000) {
tax = (taxableIncome - 80000) * 0.4 + (80000 - 60000) * 0.35 + (60000 - 40000) * 0.3 + (40000 - 20000) * 0.25 + (20000 - 5000) * 0.2 + (5000 - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
} else {
tax = (taxableIncome - 100000) * 0.45 + (100000 - 80000) * 0.4 + (80000 - 60000) * 0.35 + (60000 - 40000) * 0.3 + (40000 - 20000) * 0.25 + (20000 - 5000) * 0.2 + (5000 - 2000) * 0.15 + (2000 - 500) * 0.1 + 500 * 0.05;
}
double afterTaxIncome = income - tax; // 税后实际收入
System.out.println("个人所得税:" + tax + " 元");
System.out.println("税后实际收入:" + afterTaxIncome + " 元");
}
}
效果:
15. (if 语句,操作符)**读入一个三位数,计算其各位数字之和。
例如:123 各位数字之和为6
解答:
public class Test15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个三位数:");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
int digit1 = number / 100; // 百位数字
int digit2 = (number / 10) % 10; // 十位数字
int digit3 = number % 10; // 个位数字
int sum = digit1 + digit2 + digit3; // 各位数字之和
System.out.println("各位数字之和:" + sum);
}
}效果:

16. (if 语句)**读入三个整数,把这三个整数按照由大到小的顺序输出。
解答:
public class Test16 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入三个整数,用空格分隔:");
int num1 = scanner.nextInt();
int num2 = scanner.nextInt();
int num3 = scanner.nextInt();
if (num1 >= num2 && num1 >= num3) {
if (num2 >= num3) {
System.out.println(num1 + " " + num2 + " " + num3);
} else {
System.out.println(num1 + " " + num3 + " " + num2);
}
} else if (num2 >= num1 && num2 >= num3) {
if (num1 >= num3) {
System.out.println(num2 + " " + num1 + " " + num3);
} else {
System.out.println(num2 + " " + num3 + " " + num1);
}
} else {
if (num1 >= num2) {
System.out.println(num3 + " " + num1 + " " + num2);
} else {
System.out.println(num3 + " " + num2 + " " + num1);
}
}
}
}效果: