概述:
Servlet(Server Applet)是Java Server的简称,称为小服务程序或服务网连接器,用Java编写的服务器端服务,具有独立于平台和协议的特性,主要功能在于交互式的浏览和生成数据,生成动态Web内容,这个过程为:
1.客户端发送请求到服务器端。
2。服务器将请求发送至Servlet
3.Servlet生成响应内容并将其传给服务器,响应内容动态生成,通常取决于客户端的请求。
4.服务器将响应返回给客户端。
Servlet看起来像是通常的Java程序,Servlet需要导入特定的属于Java Servlet API的包。
Servlet有三种实现方式:实现Servlet接口,继承抽象类GenericServlet。继承HttpServlet。
入门案例
创建Servlet程序
选中src-右键-New-Create New Servlet-输入Servlet类的名字和包名-ok
package
import javax.serclet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "MyServlet")
public class MyServlet extends HttpsServlet{
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletRwsponse response) throws ServletException,IOExceptikon{
//向浏览器响应指定内容
response.getWriter()write("hello servlet");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest requset,HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException ,IOException{
doPost(request,response);//调用doPost()
}}
注解方式配置Servlet程序
1、直接在Servlet类上加一个注解就可以了
//Servlet程序想要浏览器访问,使用@WebServlet规定了浏览器的访问方式
@WebServlet("/hello/Servlet1")
2、打开浏览器直接访问这个Servlet就可以了
http://localhost:8080/hello/Servlet1
配置文件方式配置Servlet程序(提供web。xml)
在Servlet3.0版本中,被@WebServlet注解代替,如@WebServlet(“/muyservlet”)括号中,就可以规定访问方式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!-- 这是Servlet程序的核心配置文件,IDEA不会自动帮我们配置,只能自己来配置的,
主要是规定浏览器的访问方式 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>myservlet</servlet-name>
<!-- Servlet类的全路径 -->
<servlet-class>package后边的到类名</servlet-calss>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>myservlet</servlet-name>
<!-- 规定了浏览器的访问方式 -->
<url-pattern>/myservlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
测试
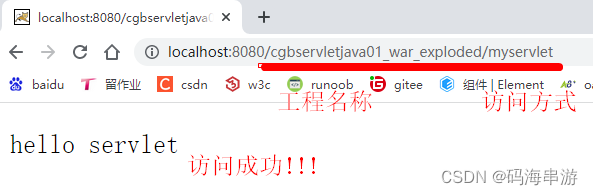
你写个HTML网页测试也可以的。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<>form action="http://localhost:8080/cgbservletjava01_war_exploded/a/b/x" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Servlet的继承结构

Servlet的生命周期
Servlet生命周期可被定义为从创建直到毁灭的整个过程,一下是Servlet重要阶段遵循的过程:
1.初始化阶段,调用init()方法
2.响应客户请求阶段,调用Service()方法。
3.终止阶段 调用destroy()方法。
最后,Servlet是由JVM的垃圾回收器进行垃圾回收的。

init()方法
init方法被设计成只调用一次,他在第一次创建Servlet时被调用,在后续每次用户请求时不在调用。因此,他是用于一次性初始化,Servlet创建于用户第一次调用对应于该Servlet的URL时,但是您也可以指定Servlet在服务器第一次启动时被加载。
当用户调用一个Servlet时,就会创建一个Servlet实例,每一个用户请求都会产生一个新的线程,适当的时候移交给doGet或dopost方法,init()方法简单的创建或加载一些数据,这些数据将被用于Servlet的整个生命周期。
Service()方法
他是Servlet的核心,每当一个客户请求一个HttpServlet对象,该对象的Service()方法就要调用,而且传递给这个方法一个请求(ServletRequest)对象和一个“响应”(ServletResponse)对象作为参数。在HttpServlet中已存在Service()方法。
service()方法会检查HTTP请求类型(GET。POST。PUT。DELETE等),并且适当的时候调用doGet。doPost。doPut。doDelete等方法。service()方法由容器调用,您只需要会根据来自客户端的请求类型来重写doGet()和doPost()即可。
doGet()和doPost()方法是每次服务请求中最常用的方法。
doGet()方法
GET请求来自于一个URL的正常请求,或者来自于一个未指定METHOD的HTML表单,他由doGet()方法处理。
doPost()方法
POST请求来自于一个特别指定了METHOD为OPST的HTML表单,它由doPost()方法处理。
destroy()方法
destroy()方法只会被调用一次,在Servlet生命周期结束时被调用,destroy()方法可以让您的Servlet关闭数据库连接。停止后台线程,把Cookie列表或点击计数器写入到磁盘,并执行其他类似的清理活动。在调用destroy()方法之后。servlet对象被标记为垃圾回收。
Request(要求)
概述
Request对象用来解析请求参数,当浏览器访问服务器时,携带者一些请求参数,可以通过Servlet提供的Request对象提供的API来解析请求参数。
请求对象有两个:
ServletRequest
httpServletRequest
常用的方法:
getParameter(“参数名”)--根据参数名获取参数的值
getParameterValues()--获取到所有参数的值并存入数组。
setCharacterEncoding()--设置请求的字符编码方式
getCharacterEncoding()--返回字符编码方式
setAttribute(String,Object)存储此请求中的属性
getAttribute(String name)返回指定属性的属性值
测试
前端HTML程序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/cgbservletjava01_war_exploded/FormServlet?name=张三&addr=北京">点我提交get数据</a>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/cgbservletjava01_war_exploded/FormServlet" method="post">
用户名:
<input type="text" name="username">
<br />
爱好:
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="篮球"/>篮球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="足球"/>足球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="乒乓球"/>乒乓球
<br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
后端java程序
package cn.tedu.req;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
@WebServlet(name = "FormServlet")
public class FormServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//请求参数中,包含中文时,post必须配置
// request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//获取请求参数
//方式1:根据参数名获取一个值
String name = request.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("name = " + name);
//方式2:根据参数名获取所有值,并返回数组
String[] likes = request.getParameterValues("hobby");
System.out.println("hobby = " + Arrays.toString(likes));
//给浏览器做出响应
response.getWriter().print("dopost..success!");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String addr = request.getParameter("addr");
System.out.println("doget..."+name+addr);
}
}
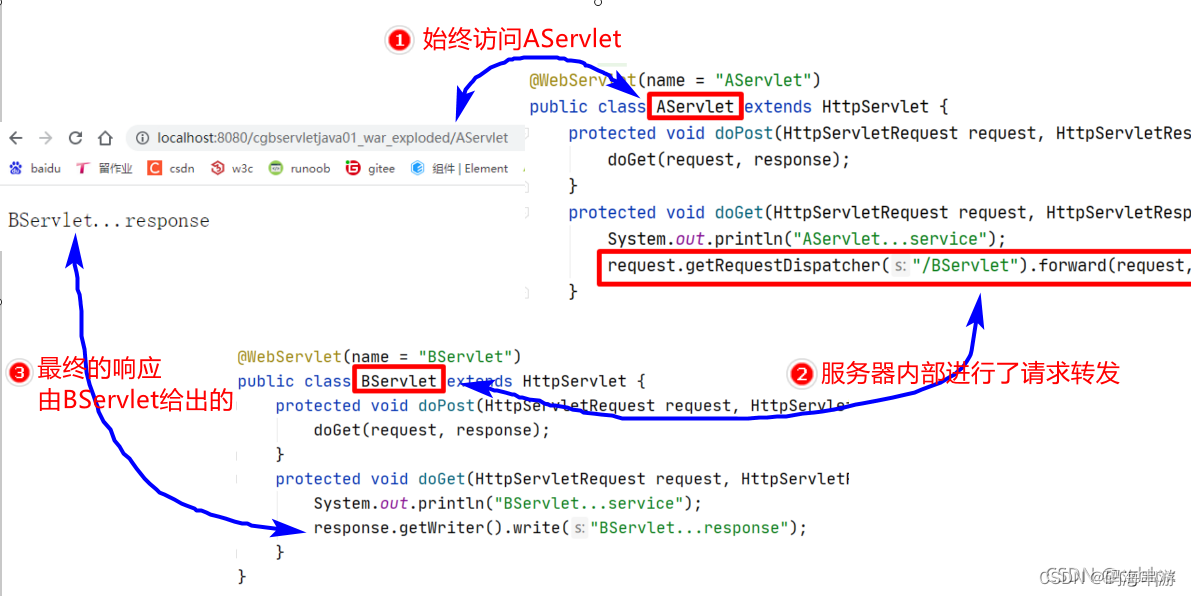
请求转发:
概述
请求转发是服务器内部资源的一种跳转方式,即当浏览器发送请求访问服务器中的某一个资源时,该资源将请求交给另外一个资源进行处理的过程,就叫做请求转发,具有以下特点。:
1.请求转发整个过程是一次请求,一次响应。
2.请求转发前后,浏览器地址栏地址不会发生变化(浏览器-访问-》A-转发-》B,地址栏地址始终指向A的地址。)
3,请求转发前后的request对象是同一个。
4.转发前后的两个资源必须属于同一个Web应用,否则将无法进行转发。
5.使用代码:request。getRequestDispatcher(访问目的资源的路径)。forward(request,response);
6.也可以使用setAttribute()/getAttribute()来验证。

测试过程
Response
概述
Response是代表Http响应信息的对象,其中将会封装服务器要发送给浏览器的响应信息,将response对象作为参数传递给service方法,在service方法执行完后,服务器负责从response对象中获取到响应信息,再按照http响应信息的格式组织成响应消息,发送给浏览器。
常用的方法。
setContentType(“参数名”)--设置响应的字符编码方式
sendRedirect()--完成重定向
getOutputStream()--获取字节输出流
getWriter()--获取字符输出流
setHeader(“Access-Control-Allow-Orgin”,"*");--专门用来解决跨域问题
测试
package
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet(name = "RespServlet")
public class RespServlet extends HttpServlet{
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws
ServletException,IOException{
doGet(request,response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException,IOException{
//响应数据中包含中文,会乱码,用以下代码指定编码,缓冲字符输出流内部有一个缓冲区,这个缓冲区的默认字符集是ISO-8859-1
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//给浏览器响应数据
resopnse。getWriter()。write(“你好123”);
}
}
重定向
概述
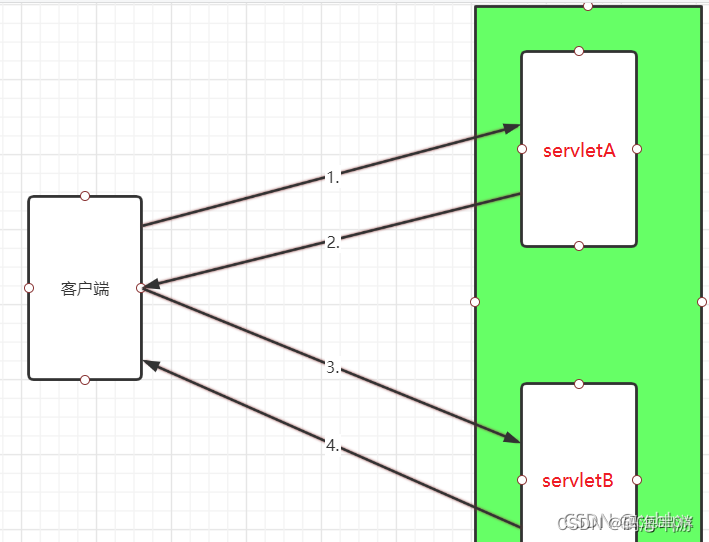
当浏览器向服务器发送请求访问某一个资源A时,资源A在响应时通知浏览器需要再进行请求才能获取到对应的资源,浏览器再次向服务器发送请求访问资源B,最终是由资源B响应浏览器要获取的数据,这个过程叫做重定向,具有以下特点。
1.重定向前后是两次请求,两次响应。
2.重定向前后,浏览器地址栏地址会发生变化(因为两次请求都是通过浏览器发起,浏览器知道这个跳转过程,因此地址栏地址会发生变化)。
3.重定向前后的request对象不是同一个(因此重定向前后是两次请求,服务器根据两次请求会创建两个request对象。因此request对象不是同一个)。
4.重定向前后的两个资源可以来自不同的Web应用,甚至可以是来自不同的虚拟主机或者服务器。
5.使用代码:response。sendRedirect(“重定向到资源的路径”);
测试
观察:一开始是访问A资源,服务器内部重定向后,地址栏已经变成了B资源的访问方式了,是两次请求两次响应。
package cn.tedu.resp;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "RedirectServlet")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//重定向的地址,可以随意设置,不是必须在同一工程中
//response.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/cgbservletjava01_war_exploded/RespServlet");
response.sendRedirect("https://www.baidu.com/");
}
}
扩展:在Web工程里使用Servlet程序
在IDEA里创建一个web工程
File-New-project-选java Enterprise并勾选右侧的Web Appliocation-next-输入工程名称-Finish,
整理web工程目录结构

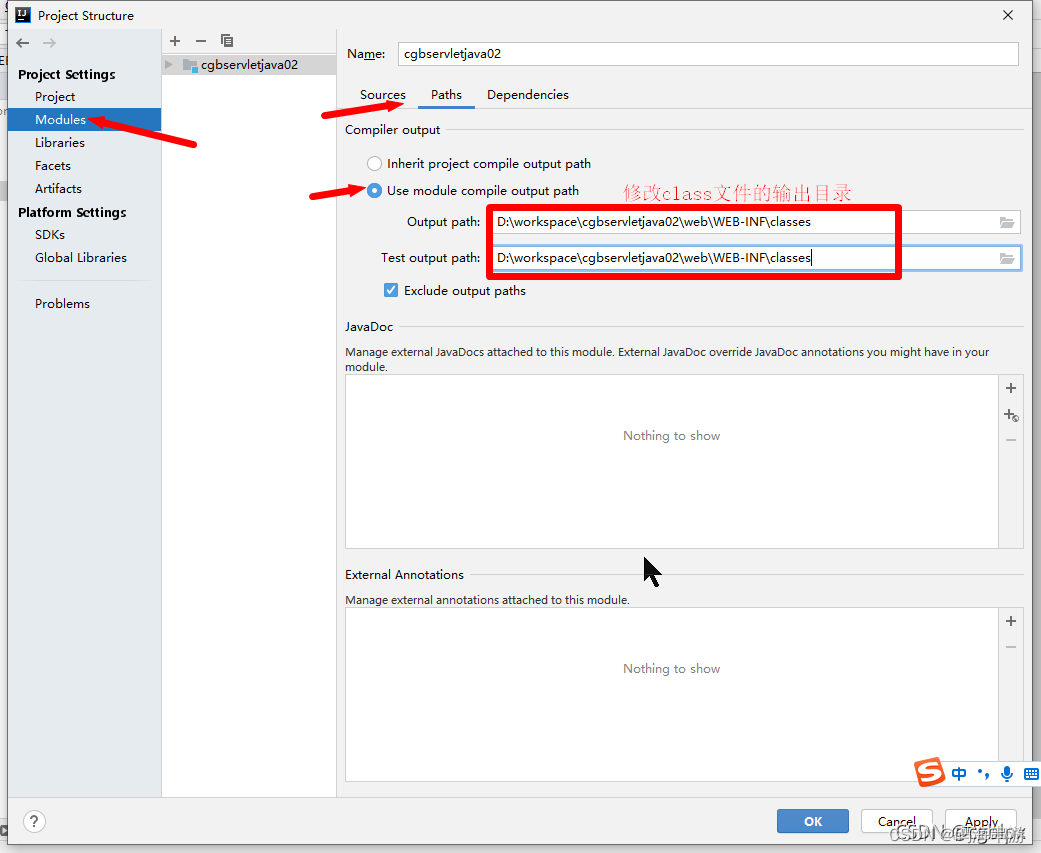
修改资源输出位置
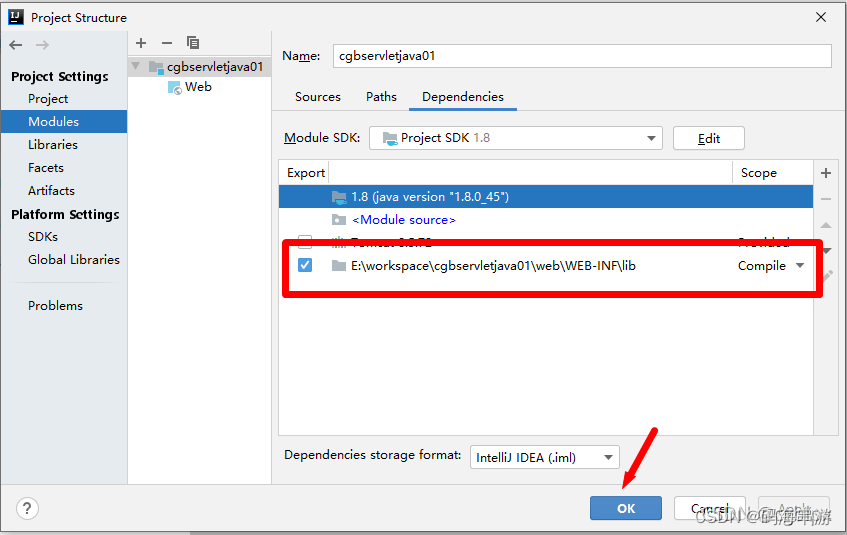
修改jar包存放位置

配置Tomcat服务器
拓展案例
创建前端页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/index.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点我</el-button>
<el-input v-model="name"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="id"></el-input>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data(){
return{
name:'',
id:''
}
},
methods:{
get(){
// axios.get("http://localhost:8080/axios/t3?id=10&name=jack").then(
axios.get("http://localhost:8080/axios/t3",{
params:{
id:10,
name:'jack'
}
}).then(
a=>{
console.log(a);
console.log(a.data);
this.id=a.data.id;
this.name=a.data.name;
}
)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
创建Servlet程序:
package cn.tedu.cgb2110boot03.test;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/axios/t3")
public class ServletT3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(111);
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
String id = request.getParameter("id");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
// {"id":"10","name":"jack"}
// "{\"id\":\"10\",\"name\":\"jack\"}"
String json="{\"id\":\""+id+"\",\"name\":\""+name+"\"}";
response.getWriter().write(json);
}
}