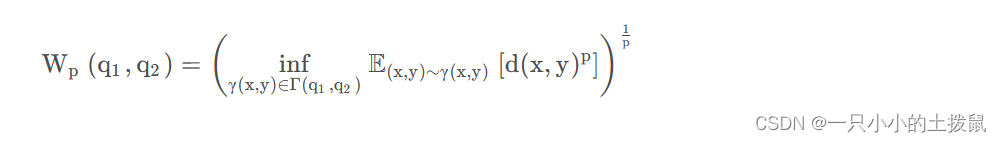背景:
在linux环境,使用shell脚本,实现对某个服务的启动、停止功能。
shell脚本的功能:
- 启动(start):通过参数
start,实现启动服务。如果该服务已经启动,给出已经启动的提示信息,避免重复启动该服务;如果未启动,启动该服务。 - 关闭(stop):通过参数
stop,实现停止服务。如果该服务已停止,给出已关闭的提示信息。如果服务已启动,停止该服务。 - 提示信息:如果没有传递任何参数,给出可用参数的提示信息。
实现:
ps:以python实现的定时任务为例,说明服务启动、关闭脚本的实现
# 服务配置
# python 项目使用的虚拟环境路径
venvPath="/home/ops/add_missing_room_detail/py36"
# python 项目的路径
projectPath="/home/ops/add_missing_room_detail/HotelGo2DelonixPmx"
# python 项目启动命令
CMD="python fix_missing_rates.py"
# 启动进程函数
start_process() {
# 判断进程是否已经在运行,如果已经在运行则不需要重复启动
start_pid=$(ps aux | grep "$CMD" | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}')
if [ -n "$start_pid" ]; then
echo "The process is already running with PID:" $start_pid
return 1
fi
# 激活python虚拟环境
echo "activate python venv3 $venvPath"
source $venvPath"/bin/activate"
cd $projectPath
# 后台运行执行命令,将日志输出到文件runoob.log
nohup $CMD >runoob.log 2>&1 &
start_pid=$!
# 判断进程是否成功启动
if [ -z "$start_pid" ]; then
echo "Fail to start process"
return 1
else
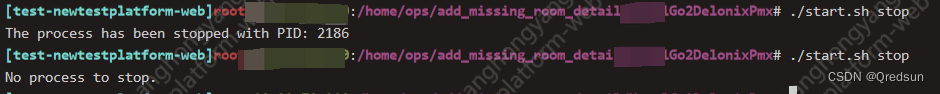
echo "The process has been started with PID:" $start_pid
return 0
fi
}
# 停止进程函数
stop_process() {
# 根据进程名过滤出进程id,并结束进程
start_pid=$(ps aux | grep "$CMD" | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}')
if [ -z "$start_pid" ]; then
echo "No process to stop."
return 1
else
kill -9 $start_pid
echo "The process has been stopped with PID:" $start_pid
return 0
fi
}
# 根据传入参数执行对应的操作
case $1 in
start)
start_process
;;
stop)
stop_process
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop}"
exit 1
;;
esac
使用
-
提示信息:
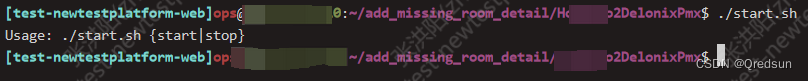
-
启动:
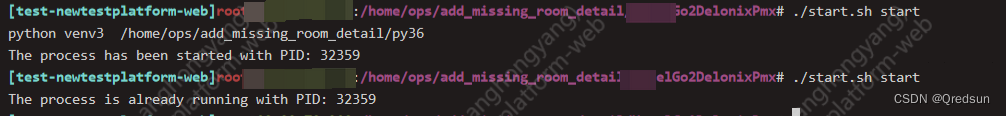
-
关闭: