目录
1.关于逻辑回归的原理解析和准备工作
2.关于激活函数
3.关于数据集
4.编写LogisticsRegression类
5.逻辑回归测试
6.结果
1.关于逻辑回归的原理解析和准备工作
逻辑回归原理相关内容,请参考博主的另一篇文章:机器学习(二)逻辑回归。在本文中的逻辑回归算法实现,不调用sklearn中的相关API,通过纯手写的方式,帮助学习理解逻辑回归的过程。
2.关于激活函数
本文采用Sigmoid函数作为激活函数(也叫逻辑斯谛函数),sigmoid的函数的公式如下:
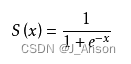
sigmoid函数可以用于处理二分类问题,其函数图像如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class Sigmoid:
@staticmethod
def sigmoid(matrix):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-matrix))
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
y = Sigmoid.sigmoid(x)
plt.plot(x, y, "b.", label="sigmoid")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
3.关于数据集
本文采用sklearn中自带数据集iris,iris数据集数据分布状态如下:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
# 载入数据
iris = load_iris()
data = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
data["class"] = iris.target_names[iris["target"]]
x_axis = "petal length (cm)"
y_axis = "petal width (cm)"
for iris_type in iris.target_names:
plt.scatter(data[x_axis][data["class"] == iris_type],
data[y_axis][data["class"] == iris_type],
label=iris_type)
plt.show()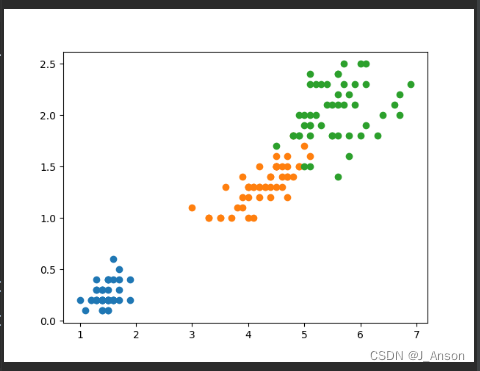
4.编写LogisticsRegression类
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from utils.features import pre_for_training
from utils.hypothesis.sigmoid import Sigmoid
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self,
data,
labels,
polynomial_degree=0,
sinusoid_degree=0,
normalize_data=True):
"""
对数据预处理,获取所有特征个数,初始化参数矩阵
:param data: 训练特征集
:param labels: 训练目标值
:param polynomial_degree: 特征变换
:param sinusoid_degree: 特征变换
:param normalize_data: 标准化数据处理
"""
(data_processed, features_mean, features_deviation) = \
pre_for_training.prepare(data=data,
polynomial_degree=polynomial_degree,
sinusoid_degree=sinusoid_degree,
normalize_data=normalize_data)
self.data = data_processed
self.labels = labels
self.unique_lables = np.unique(self.labels)
self.features_mean = features_mean
self.features_deviation = features_deviation
self.polynomial_degree = polynomial_degree
self.sinusoid_degree = sinusoid_degree
self.normalize_data = normalize_data
num_unique_labels = np.unique(self.labels).shape[0]
num_features = self.data.shape[1]
self.theta = np.zeros((num_unique_labels, num_features))
def train(self, max_iterations=1000):
loss_histories = []
num_features = self.data.shape[1]
for label_index, unique_label in enumerate(self.unique_lables):
current_init_theta = np.copy(self.theta[label_index].reshape(num_features, 1))
current_labels = (self.labels == unique_label).astype(float)
(
current_theta,
loss_history
) = LogisticRegression.gradient_descent(data=self.data,
labels=current_labels,
current_init_theta=current_init_theta,
max_iterations=max_iterations)
self.theta[label_index] = current_theta.T
loss_histories.append(loss_history)
return self.theta, loss_histories
@staticmethod
def gradient_descent(data, labels, current_init_theta, max_iterations):
loss_history = []
num_features = data.shape[1]
result = minimize(
fun=lambda current_theta:
LogisticRegression.loss_function(data=data,
labels=labels,
theta=current_theta.reshape(num_features, 1)),
x0=current_init_theta.reshape(num_features, ),
method="CG",
jac=lambda current_theta:
LogisticRegression.gradient_step(data=data,
labels=labels,
theta=current_theta.reshape(num_features, 1)),
callback=lambda current_theta:
loss_history.append(LogisticRegression.loss_function(data=data,
labels=labels,
theta=current_theta.reshape(num_features, 1)),
options={"maxiter": max_iterations}
)
if not result.success:
raise ArithmeticError(f"[Cannot minimize loss function],msg:{result.message},res:{result.x}")
optimized_theta = result.x.reshape(num_features, 1)
return optimized_theta, loss_history
@staticmethod
def loss_function(data, labels, theta):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
predictions = LogisticRegression.hypothesis(data, theta)
y_is_set_loss = np.dot(labels[labels == 1].T, np.log(predictions[labels == 1]))
y_is_not_set_loss = np.dot(1 - labels[labels == 0].T, np.log(1 - predictions[labels == 0]))
loss = (-1 / num_examples) * (y_is_set_loss + y_is_not_set_loss)
return loss
@staticmethod
def gradient_step(data, labels, theta):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
predictions = LogisticRegression.hypothesis(data, theta)
label_diff = predictions - labels
gradients = (1 / num_examples) * np.dot(data.T, label_diff)
return gradients.T.flatten()
@staticmethod
def hypothesis(data, theta):
predictions = Sigmoid.sigmoid(np.dot(data, theta))
return predictions
def predict(self, data):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
(
data_processed,
features_mean,
features_deviation
) = pre_for_training.prepare(data=data,
polynomial_degree=self.polynomial_degree,
sinusoid_degree=self.sinusoid_degree,
normalize_data=self.normalize_data)
prob = LogisticRegression.hypothesis(data_processed, self.theta.T)
max_prb_index = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
class_prediction = np.empty(max_prb_index.shape, dtype=object)
for index, label in enumerate(self.unique_lables):
class_prediction[max_prb_index == index] = label
return class_prediction.reshape((num_examples, 1))
5.逻辑回归测试
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from logistic_regression import logical_regression
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
# 载入数据
iris = load_iris()
data = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
data["class"] = iris.target_names[iris["target"]]
x_axis = "petal length (cm)"
y_axis = "petal width (cm)"
for iris_type in iris.target_names:
plt.scatter(data[x_axis][data["class"] == iris_type],
data[y_axis][data["class"] == iris_type],
label=iris_type)
plt.show()
num_examples = data.shape[0]
x_train = data[[x_axis, y_axis]].values.reshape(num_examples, 2)
y_train = data["class"].values.reshape(num_examples, 1)
max_iterations = 1000
polynomial_degree = 0
sinusoid_degree = 0
logi_reg = logical_regression.LogisticRegression(data=x_train,
labels=y_train,
polynomial_degree=polynomial_degree,
sinusoid_degree=sinusoid_degree,
normalize_data=False) # 不标准化
thetas, loss_histories = logi_reg.train(max_iterations=max_iterations)
plt.plot(range(len(loss_histories[0])), loss_histories[0], label=logi_reg.unique_lables[0])
plt.plot(range(len(loss_histories[1])), loss_histories[1], label=logi_reg.unique_lables[1])
plt.plot(range(len(loss_histories[2])), loss_histories[2], label=logi_reg.unique_lables[2])
plt.show()
y_train_predictions = logi_reg.predict(x_train)
precision = np.sum((y_train_predictions == y_train) / y_train.shape[0]) * 100
print("precision:", precision)
x_min = np.min(x_train[:, 0])
x_max = np.max(x_train[:, 0])
y_min = np.min(x_train[:, 1])
y_max = np.max(x_train[:, 1])
samples = 150
X = np.linspace(x_min, x_max, samples)
Y = np.linspace(y_min, y_max, samples)
Z_SETOSA = np.zeros((samples, samples))
Z_VERSICOLOR = np.zeros((samples, samples))
Z_VIRGINICA = np.zeros((samples, samples))
predictions = np.zeros((samples, samples))
for x_index, x in enumerate(X):
for y_index, y in enumerate(Y):
data = np.array([[x, y]])
prediction = logi_reg.predict(data=data)[0][0]
if prediction == "setosa":
Z_SETOSA[x_index][y_index] = 1
elif prediction == "versicolor":
Z_VERSICOLOR[x_index][y_index] = 1
elif prediction == "virginica":
Z_VIRGINICA[x_index][y_index] = 1
for iris_type in ["setosa", "versicolor", "virginica"]:
plt.scatter(
x_train[(y_train == iris_type).flatten(), 0],
x_train[(y_train == iris_type).flatten(), 1],
label=iris_type
)
plt.contour(X, Y, Z_SETOSA)
plt.contour(X, Y, Z_VERSICOLOR)
plt.contour(X, Y, Z_VIRGINICA)
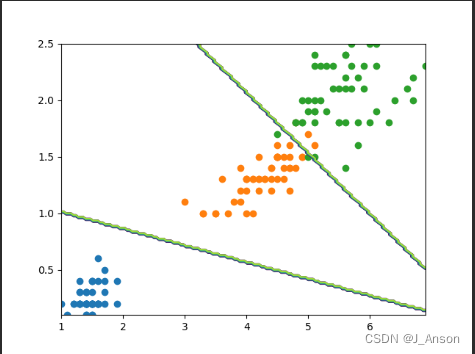
plt.show()6.结果
通过测试,可得到分类的准确率,如下:
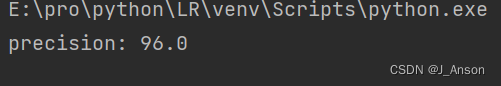
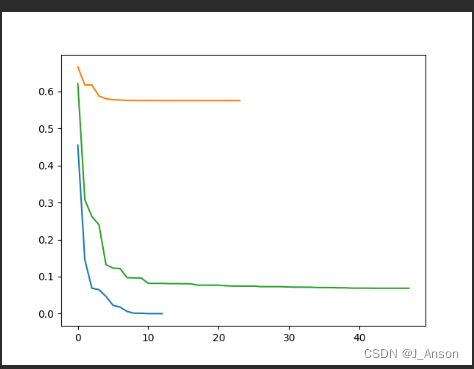
预测的损失,如下:
分类的边界线,如下: