参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/476351994
1、Mediapipe 人像分割
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import numpy as np
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
mp_selfie_segmentation = mp.solutions.selfie_segmentation
# 图片人物抠图:
IMAGE_FILES = []
BG_COLOR = (0, 255, 0) # 背景颜色也可以使用其他的照片,要求与原照片尺寸一致
#bg_image = cv2.imread('6.jpg')
MASK_COLOR = (255, 255, 255) # mask图片颜色
file = '1.jpg'
with mp_selfie_segmentation.SelfieSegmentation(model_selection=0) as selfie_segmentation:
image = cv2.imread(file)
image_height, image_width, _ = image.shape
# 在处理之前需要转换图片到RGB颜色空间
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
results = selfie_segmentation.process(image)
# 在背景图像上绘制分割图
#为了改善边界周围的分割,可以考虑在 results.segmentation_mask进行双边过滤
condition = np.stack((results.segmentation_mask,) * 3, axis=-1) > 0.1
#生成纯色图像,白色的mask图纸
#fg_image = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
#fg_image[:] = MASK_COLOR
fg_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
bg_image = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
bg_image[:] = BG_COLOR
output_image = np.where(condition, fg_image, bg_image)
cv2.imshow('output_image',output_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
#cv2.imwrite('selfie0.png', output_image)
2、实时更换背景
准备了三张背景图,按键盘键1,2,3分别更换对应背景图
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import numpy as np
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
mp_selfie_segmentation = mp.solutions.selfie_segmentation
selfie_segmentation = mp_selfie_segmentation.SelfieSegmentation(model_selection=0)
# 加载视频
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 预加载所有背景图像
backgrounds = {
'1': cv2.resize(cv2.imread('1.jpg'), (640, 480)),
'2': cv2.resize(cv2.imread('2.jpg'), (640, 480)),
'3': cv2.resize(cv2.imread('3.jpg'), (640, 480))
}
# 初始化使用的背景
use_bg_1 = False
use_bg_2 = False
use_bg_3 = False
while True:
ret, image = cap.read()
# image = cv2.imread(frame)
image_height, image_width, _ = image.shape
# 在处理之前需要转换图片到RGB颜色空间
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
results = selfie_segmentation.process(image)
# 在背景图像上绘制分割图
#为了改善边界周围的分割,可以考虑在 results.segmentation_mask进行双边过滤
condition = np.stack((results.segmentation_mask,) * 3, axis=-1) > 0.7 ##值高点好像分割效果会好点,但不要超过1
#生成纯色图像,白色的mask图纸
#fg_image = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
#fg_image[:] = MASK_COLOR
fg_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
output_image = fg_image
# bg_image = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
# bg_image[:] = BG_COLOR
# output_image = np.where(condition, fg_image, bg_image)
# cv2.imshow('output_image',fg_image)
#cv2.imwrite('selfie0.png', output_image)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('1'):
use_bg_1 = True
use_bg_2 = False
use_bg_3 = False
elif key == ord('2'):
use_bg_2 = True
use_bg_1 = False
use_bg_3 = False
elif key == ord('3'):
use_bg_3 = True
use_bg_1 = False
use_bg_2 = False
if use_bg_1:
output_image = np.where(condition, fg_image,backgrounds['1']).astype(np.uint8)
if use_bg_2:
output_image = np.where(condition, fg_image, backgrounds['2']).astype(np.uint8)
if use_bg_3:
output_image = np.where(condition, fg_image, backgrounds['3']).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('output_image',output_image)
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3、人脸添加特效
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40062244/article/details/128409286
cv2保存和读取中文路径异常解决:
读取:
img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(file_path, dtype=np.uint8), 1)
file_path为图片路径
保存:
cv2.imencode('.jpg', src)[1].tofile(save_path)
第一个’.jpg’为保存文件格式,save_path为保存图片路径
cv2.imencode('.jpg', img)[1].tofile(‘C:\1.jpg’)
代码,添加胡子特效,根据检测关键点计算对应区域

# 导入所需库
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import numpy as np
##解决cv2读取中文路径问题
def cv_img(file_path):
cv_img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(file_path,dtype=np.uint8),-1)
return cv_img
# 获取人脸关键点
def get_landmarks(image, face_mesh):
"""
:param image: ndarray图像
:param face_mesh: 人脸检测模型
:return:人脸关键点列表,如[{0:(x,y),1:{x,y},...},{0:(x,y),1:(x,y)}]
"""
landmarks = []
height, width = image.shape[0:2]
# 人脸关键点检测
results = face_mesh.process(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 解释检测结果
if results.multi_face_landmarks:
for face_landmarks in results.multi_face_landmarks:
i = 0
points = {}
# 根据图像的高度和宽度还原关键点位置
for landmark in face_landmarks.landmark:
x = math.floor(landmark.x * width)
y = math.floor(landmark.y * height)
points[i] = (x, y)
i += 1
landmarks.append(points)
return landmarks
def process_effects(landmarks,icon_path, icon_name):
"""
:param landmarks: 检测到的人脸关键点列表
:param icon_path: 特效图像地址
:param icon_name: 特效名称
:return:处理好的特效图像、特效宽、特效高
"""
# 特效关键点,用于调整特效的尺寸
effect_landmarks = {"beard": ((landmarks[132][0], landmarks[5][1]), (landmarks[361][0], landmarks[0][1])),
"eyeglass": ((landmarks[127][0], landmarks[151][1]), (landmarks[356][0], landmarks[195][1])),
"halfmask": ((landmarks[162][0]-50, landmarks[10][1]-50), (landmarks[389][0]+50, landmarks[195][1]+50))}
# 读取特效图像
icon = cv2.imread(icon_path)
print("icon:",icon.shape)
# 选择特效关键点
pt1, pt2 = effect_landmarks[icon_name]
x, y, x_w, y_h = pt1[0], pt1[1], pt2[0], pt2[1]
# 调整特效的尺寸
w, h = x_w - x, y_h - y
effect = cv2.resize(icon, (w, h))
return effect, w, h
def swap_non_effcet2(effect, roi, threshold=240):
"""
:param effect: 特效图像
:param roi: ROI区域
:param threshold: 阈值
:return: 消除背景后的特效图像
"""
# (1)特效图像灰度化
effect2gray = cv2.cvtColor(effect, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# (2)特效图像二值化
ret, effect2wb = cv2.threshold(effect2gray, threshold, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# (3)消除特效的白色背景
effectwb = cv2.bitwise_and(roi, roi, mask=effect2wb)
# (4)反转二值化后的特效
effect2wb_ne = cv2.bitwise_not(effect2wb)
# (5)处理彩色特效
effectcolor = cv2.bitwise_and(effect, effect, mask=effect2wb_ne)
# (6) 组合彩色特效与黑色特效
effect_final = cv2.add(effectcolor, effectwb)
return effect_final
# 模型配置
mp_face_mesh = mp.solutions.face_mesh
face_mesh = mp_face_mesh.FaceMesh(static_image_mode=False, # 静态图片设置为False,视频设置为True
max_num_faces=3, # 能检测的最大人脸数
refine_landmarks=True, # 是否需要对嘴唇、眼睛、瞳孔的关键点进行定位,
min_detection_confidence=0.5, # 人脸检测的置信度
min_tracking_confidence=0.5) # 人脸追踪的置信度(检测图像时可以忽略)
# 读取图像
# 定义中文路径字符串
path_str = r"D:\opencv2\刘亦菲.jpg"
image = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(path_str, dtype=np.uint8), 1) #中文路径读取异常解决方式
print(image.shape)
# 获取关键点
face_landmarks = get_landmarks(image, face_mesh)
# ROI区域中心关键点
center = {"beard": 164, "eyeglass": 168, "halfmask": 9}
image_copy = image.copy()
icon_name = "beard"
p = 164
# 处理特效
for landmarks in face_landmarks:
effect, w, h = process_effects(landmarks, icon_name+".jpg", icon_name)
# 确定ROI
p = center[icon_name]
roi = image[landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2):landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2) + h,
landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2):landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2) + w]
if effect.shape[:2] == roi.shape[:2]:
# 消除特效图像中的白色背景区域
s = time.time()
# 第一种方法
# swap_non_effcet1(effect,roi,240)
# 第二种方法
effect = swap_non_effcet2(effect, roi,240)
print(time.time()-s) # 计算处理时间
# 将处理好的特效添加到人脸图像上
image[landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2):landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2) + h,
landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2):landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2) + w] = effect
cv2.imwrite("bread_liu.jpg", image, params=None)
# # 利用matplotlib展示
# plt.figure(figsize=(30, 10))
# plt.imshow(image[:, :, ::-1])
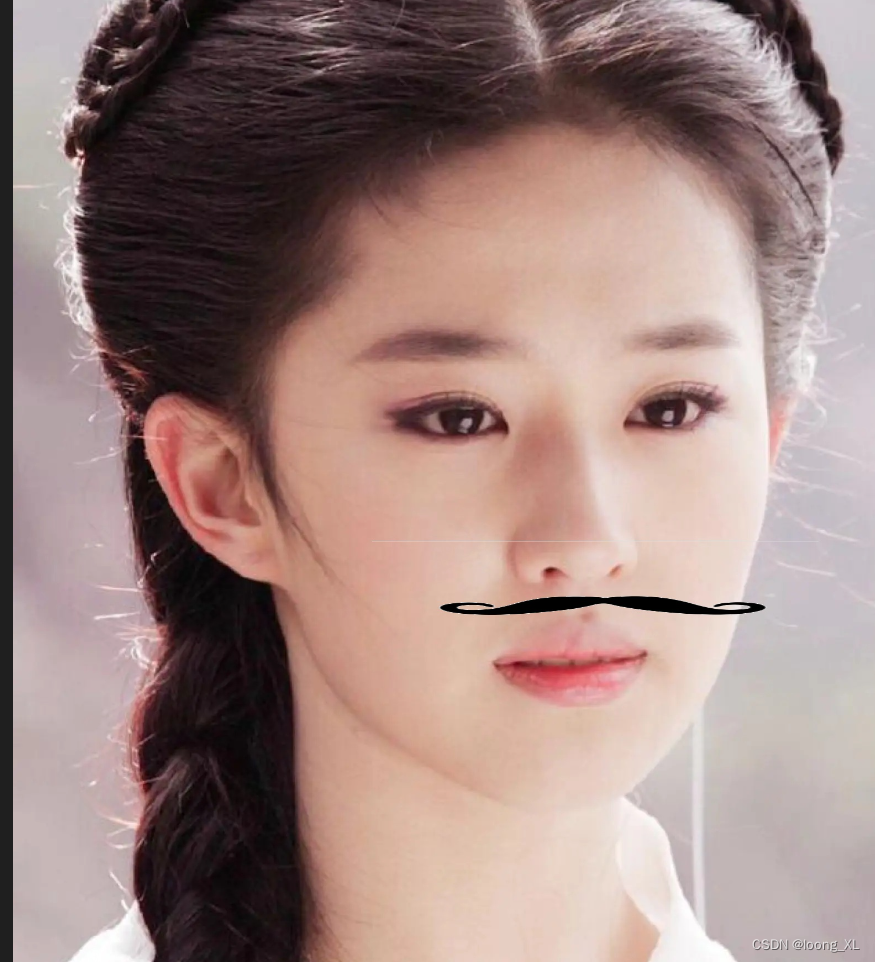

摄像头实时添加特效胡子:
# 导入所需库
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import numpy as np
##解决cv2读取中文路径问题
def cv_img(file_path):
cv_img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(file_path,dtype=np.uint8),-1)
return cv_img
# 获取人脸关键点
def get_landmarks(image, face_mesh):
"""
:param image: ndarray图像
:param face_mesh: 人脸检测模型
:return:人脸关键点列表,如[{0:(x,y),1:{x,y},...},{0:(x,y),1:(x,y)}]
"""
landmarks = []
height, width = image.shape[0:2]
# 人脸关键点检测
results = face_mesh.process(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 解释检测结果
if results.multi_face_landmarks:
for face_landmarks in results.multi_face_landmarks:
i = 0
points = {}
# 根据图像的高度和宽度还原关键点位置
for landmark in face_landmarks.landmark:
x = math.floor(landmark.x * width)
y = math.floor(landmark.y * height)
points[i] = (x, y)
i += 1
landmarks.append(points)
return landmarks
def process_effects(landmarks,icon_path, icon_name):
"""
:param landmarks: 检测到的人脸关键点列表
:param icon_path: 特效图像地址
:param icon_name: 特效名称
:return:处理好的特效图像、特效宽、特效高
"""
# 特效关键点,用于调整特效的尺寸
effect_landmarks = {"beard": ((landmarks[132][0], landmarks[5][1]), (landmarks[361][0], landmarks[0][1])),
"eyeglass": ((landmarks[127][0], landmarks[151][1]), (landmarks[356][0], landmarks[195][1])),
"halfmask": ((landmarks[162][0]-50, landmarks[10][1]-50), (landmarks[389][0]+50, landmarks[195][1]+50))}
# 读取特效图像
icon = cv2.imread(icon_path)
print("icon:",icon.shape)
# 选择特效关键点
pt1, pt2 = effect_landmarks[icon_name]
x, y, x_w, y_h = pt1[0], pt1[1], pt2[0], pt2[1]
# 调整特效的尺寸
w, h = x_w - x, y_h - y
effect = cv2.resize(icon, (w, h))
return effect, w, h
def swap_non_effcet2(effect, roi, threshold=240):
"""
:param effect: 特效图像
:param roi: ROI区域
:param threshold: 阈值
:return: 消除背景后的特效图像
"""
# (1)特效图像灰度化
effect2gray = cv2.cvtColor(effect, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# (2)特效图像二值化
ret, effect2wb = cv2.threshold(effect2gray, threshold, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# (3)消除特效的白色背景
effectwb = cv2.bitwise_and(roi, roi, mask=effect2wb)
# (4)反转二值化后的特效
effect2wb_ne = cv2.bitwise_not(effect2wb)
# (5)处理彩色特效
effectcolor = cv2.bitwise_and(effect, effect, mask=effect2wb_ne)
# (6) 组合彩色特效与黑色特效
effect_final = cv2.add(effectcolor, effectwb)
return effect_final
# 模型配置
mp_face_mesh = mp.solutions.face_mesh
face_mesh = mp_face_mesh.FaceMesh(static_image_mode=False, # 静态图片设置为False,视频设置为True
max_num_faces=3, # 能检测的最大人脸数
refine_landmarks=True, # 是否需要对嘴唇、眼睛、瞳孔的关键点进行定位,
min_detection_confidence=0.5, # 人脸检测的置信度
min_tracking_confidence=0.5) # 人脸追踪的置信度(检测图像时可以忽略)
# 加载视频
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, image = cap.read()
# 定义中文路径字符串
# path_str = r"D:\opencv2\刘亦菲.jpg"
# image = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(path_str, dtype=np.uint8), 1) #中文路径读取异常解决方式
# print(image.shape)
# 获取关键点
face_landmarks = get_landmarks(image, face_mesh)
# ROI区域中心关键点
center = {"beard": 164, "eyeglass": 168, "halfmask": 9}
image_copy = image.copy()
icon_name = "beard"
p = 164
# 处理特效
for landmarks in face_landmarks:
effect, w, h = process_effects(landmarks, icon_name+".jpg", icon_name)
# 确定ROI
p = center[icon_name]
roi = image[landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2):landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2) + h,
landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2):landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2) + w]
if effect.shape[:2] == roi.shape[:2]:
# 消除特效图像中的白色背景区域
s = time.time()
# 第一种方法
# swap_non_effcet1(effect,roi,240)
# 第二种方法
effect = swap_non_effcet2(effect, roi,240)
print(time.time()-s) # 计算处理时间
# 将处理好的特效添加到人脸图像上
image[landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2):landmarks[p][1] - int(h / 2) + h,
landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2):landmarks[p][0] - int(w / 2) + w] = effect
cv2.imshow('output_image',image)
if cv2.waitKey(20) & 0xff == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyWindow("camera")