文章目录
IO流
一、文件
1.1、文件流
文件在程序中是以流的形式来操作的
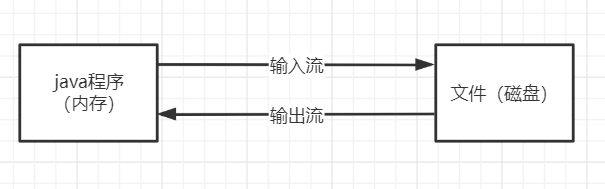
- 流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径
- 输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径
- 输入流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径
1.2、常用的文件操作
1.2.1、创建文件对象相关构造和方法
- new File(String pathname) // 根据路径构建一个File对象
- new File(File parent, String child) // 根据父目录文件+子路径构建
- new File(String parent, String child) // 根据父目录+子路径构建
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/13
* @description 实操创建文件的三种方法
*/
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 方式一 new File(String pathname) // 根据路径构建一个File对象
*/
@Test
public void create01() {
String filePath = "F:\\file\\test01.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功!!!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 方式二 new File(File parent, String child) // 根据父目录文件+子路径构建
*/
@Test
public void create02() {
File parentFile = new File("F:\\file\\");
String fileName = "test02.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功!!!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 方式三 new File(String parent, String child) // 根据父目录+子路径构建
*/
@Test
public void create03() {
String parentPath = "F:\\";
String filePath = "file\\test03.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath, filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功!!!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.2.2、获取文件的相关信息
- getName:获取文件的名字
- getAbsolutePath:获取文件的绝对路径
- getParent:获得文件的父级目录
- length:获取文件的大小(返回字节数)
- exists:判断文件是否存在
- isFile:判断是否是一个文件
- isDirectory:是不是一个目录
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/13
* @description 获取文件的基本信息
*/
public class FileInformation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 获取文件信息
*/
@Test
public void info() {
// 先创建文件对象
File file = new File("F:\\file\\test01.txt");
// 调用相应的方法,得到对应的信息
System.out.println("文件名 = " + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件绝对路径 = " + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录 = " + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节) = " + file.length());
// true
System.out.println("文件是否存在 = " + file.exists());
// true
System.out.println("是不是一个文件 = " + file.isFile());
// false
System.out.println("是不是一个目录 = " + file.isDirectory());
}
}
运行结果:

1.2.3、目录的操作和文件删除
- mkdir创建一级目录
- mkdirs创建多级目录
- delete删除空目录或文件
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/13
* @description 目录操作
*/
public class Directory_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 判断 F:\\file\\test01.txt 是否存在,如果存在就删除
*/
@Test
public void m1() {
String filePath = "f:\\file\\test01.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败");
}
} else {
System.out.println("该文件不存在...");
}
}
/**
* 判断 F:\\file1 是否存在,如果存在就删除
*/
@Test
public void m2() {
String filePath = "f:\\file1";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败");
}
} else {
System.out.println("该目录不存在...");
}
}
/**
* 判断 F:\\file1\\a\\b 是否存在,如果存在就提示已存在,否则就创建
*/
@Test
public void m3() {
String directoryPath = "f:\\file1\\a\\b";
File file = new File(directoryPath);
if (file.exists()) {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "该目录已存在!!!");
} else {
if (file.mkdirs()) {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "该目录创建成功!!!");
} else {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "该目录创建失败!!!");
}
}
}
}
二、IO流原理及流的分类
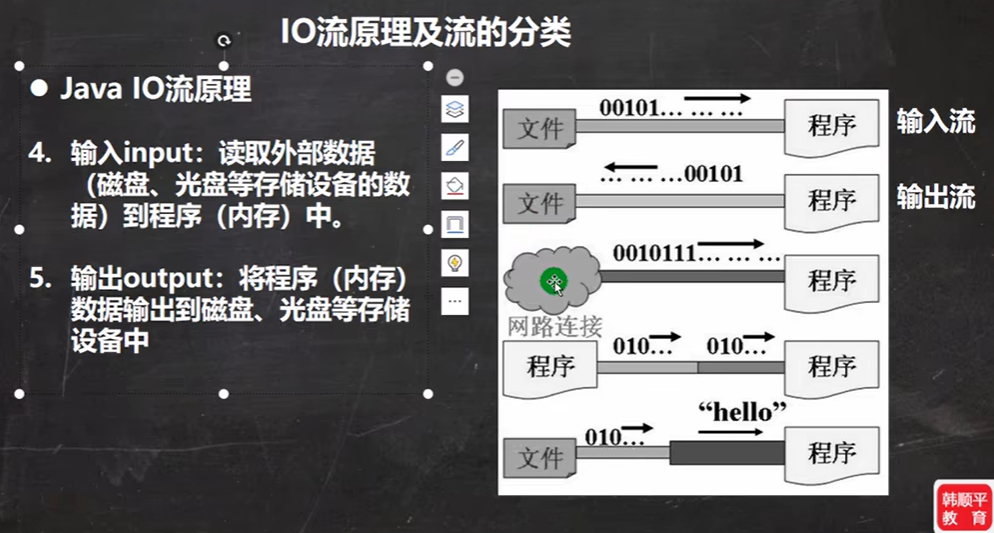
2.1、Java IO流的原理
- I/O 是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常使用的技术,用于处理数据传输。
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以”流(stream)“的方式进行
- java.io包下提供了各种”流“类接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入或输出数据
2.2、流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8bit),字符流(按字符)
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流
| (抽象基类) | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
2.3、IO流常用的类
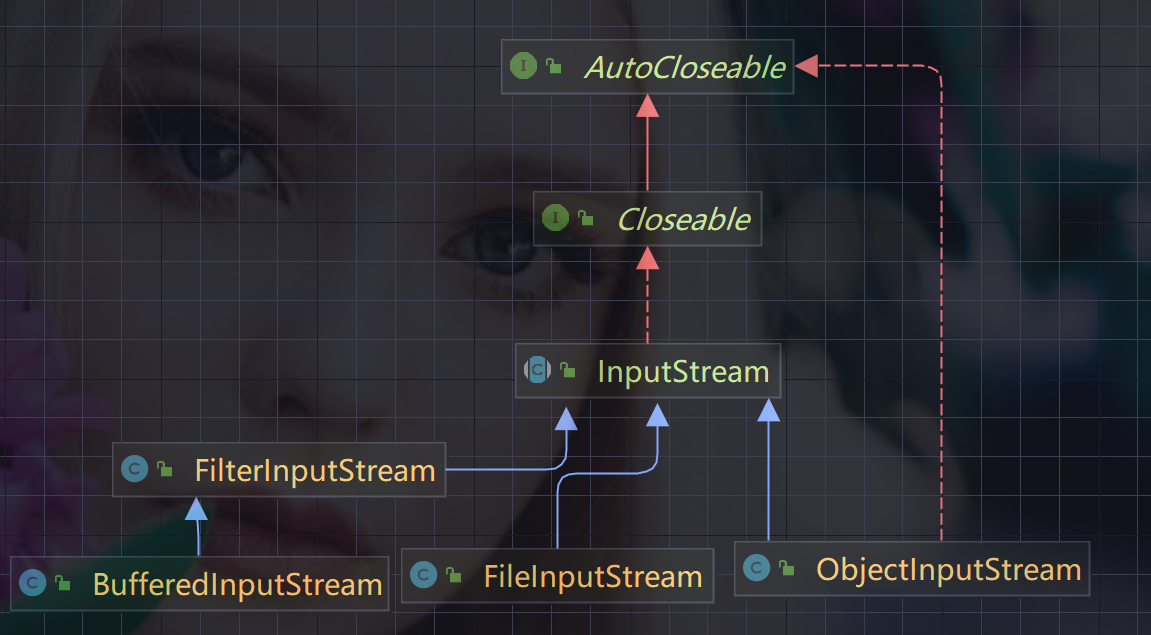
2.3.1、InputStream:字节输入流
- InputStream抽象类是所有类字节输入流的超类
- InputStream常用的子类
- FileInputStream:文件输入流
- BufferedInputStream:缓冲字节输入流
- ObjectInputStream:对象字节输入流
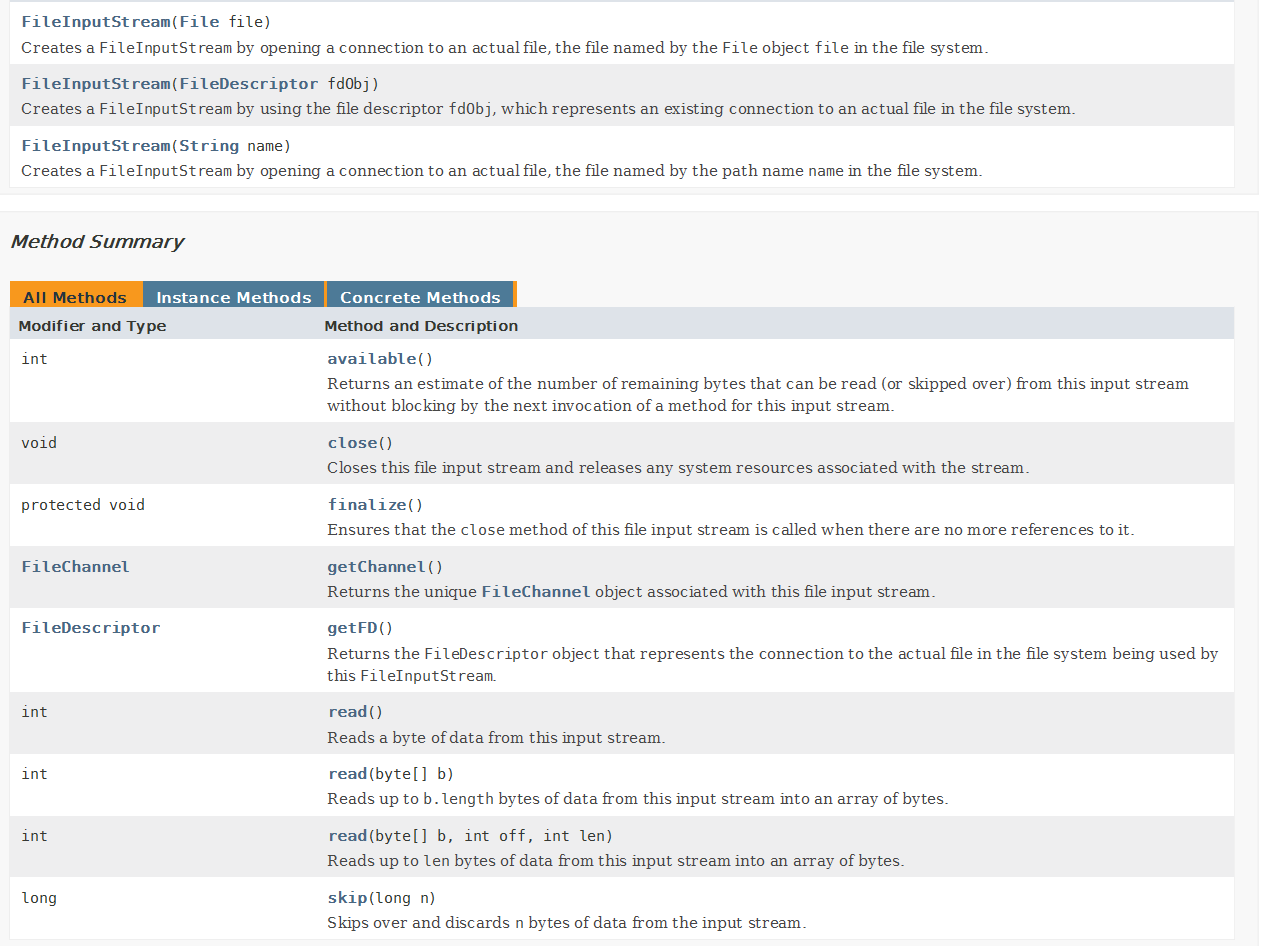
FileInputStream常用的方法
代码演示:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/13
* @description FileInputStream的使用
*/
public class FileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 演示读取文件
* read只能读取单个字节
* -> 使用read(byte[] b)读取
*/
@Test
public void readFile1() {
String filePath = "F:\\file\\hello.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
// 创建FileInputStream 对象,用于读取文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
int readData = 0;
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
// 转成char显示
System.out.print((char) readData);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭文件流,释放资源
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 使用read(byte[] b)读取文件,提高效率
*/
@Test
public void readFile2() {
String filePath = "F:\\file\\hello.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
// 创建FileInputStream 对象,用于读取文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
int readLen = 0;
// 定义字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
// 如果返回-1,表示读取完毕
// 如果读取正常,返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
// 转成char显示
System.out.print(new String(bytes, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭文件流,释放资源
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
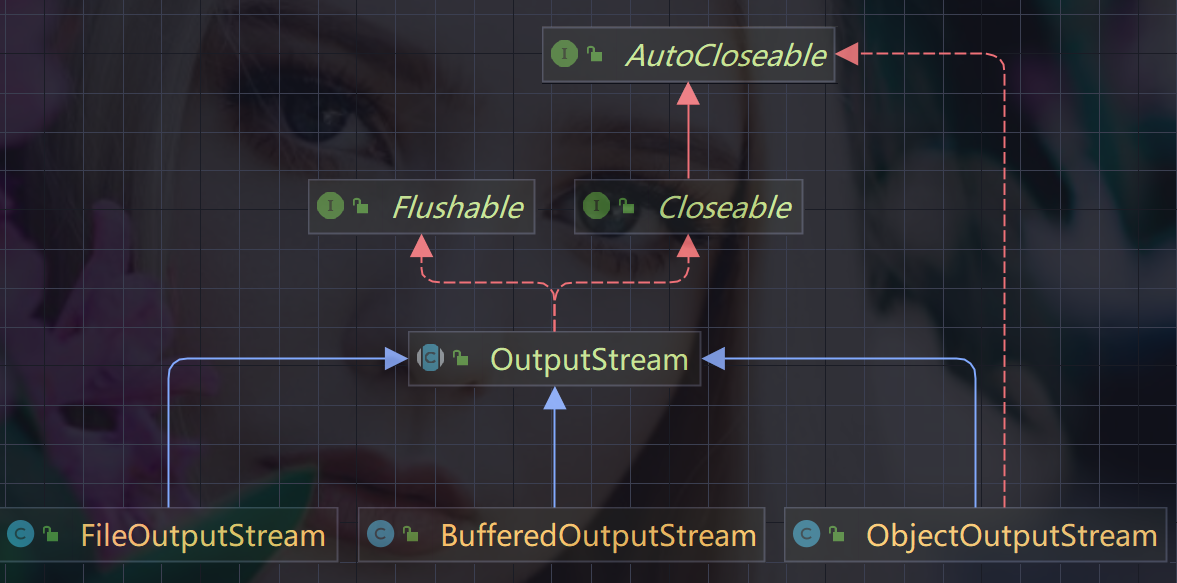
2.3.2、FileOutputStream常用的方法
- 创建FileOutputStream两种方式
- 1.如果 new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容时,会覆盖原来的内容
- 2.如果 new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容时,会追加到文件的末尾
- fileOutputStream.write(‘H’)写入一个字节
- fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes()); 写入字符串 str.getBytes() 可以把字符串 -> 字节数组
- write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流。
- fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, str.length());
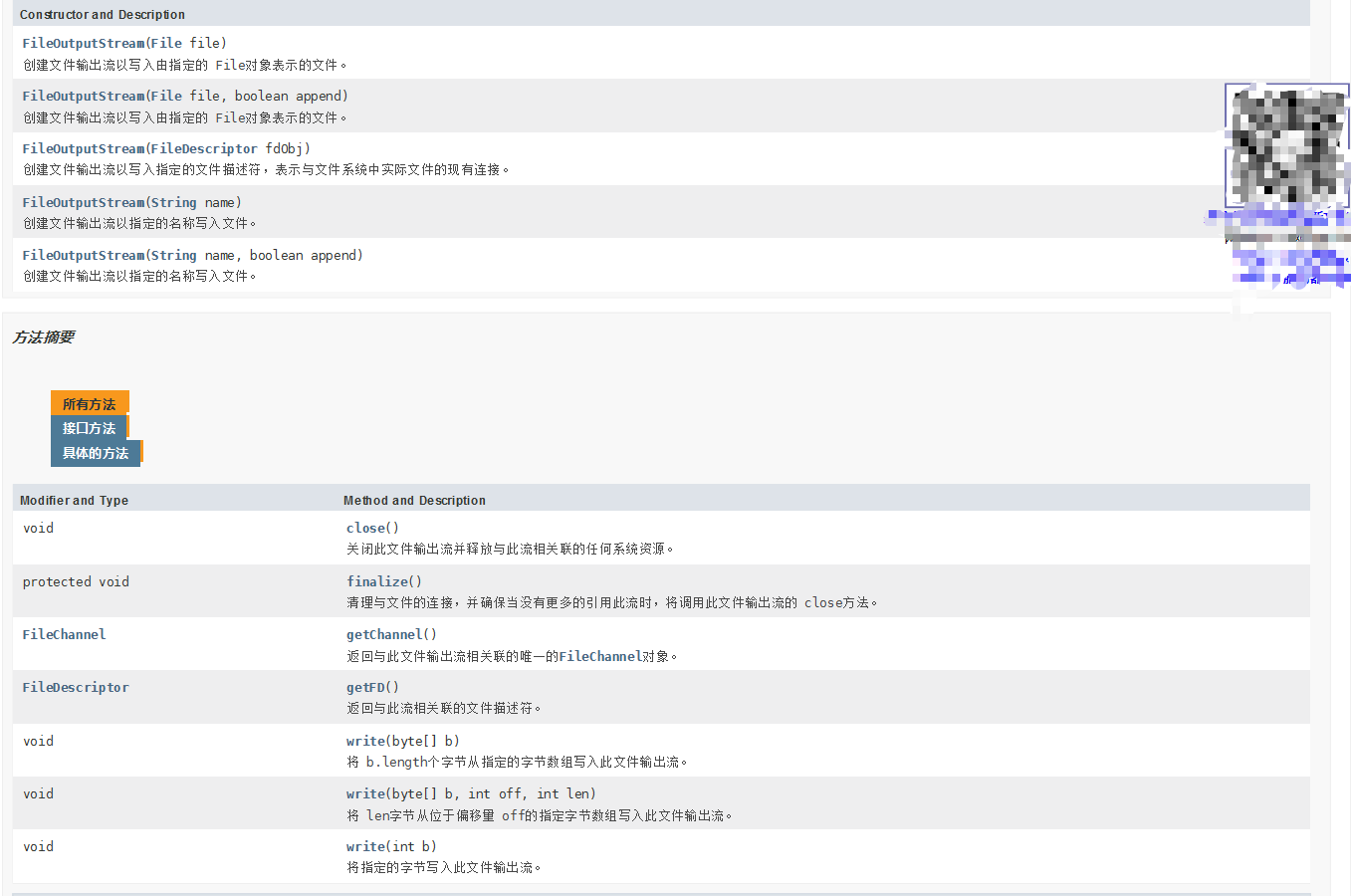
FileOutputStream的类图
演示代码:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/13
* @description OutputStream的演示
*/
public class FileOutputStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 演示使用FileOutputStream 将数据写到文件中,
* 如果该文件不存在,则创建该文件
*/
@Test
public void writeFile() {
// 创建 FileOutputStream对象
String filePath = "F:\\file\\a.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
// 得到FileOutputStream 对象
// 1.如果 new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容时,会覆盖原来的内容
// 2.如果 new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容时,会追加到文件的末尾
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
// 写入一个字节
// fileOutputStream.write('H');
// 写入字符串
String str = "Hello World!";
// str.getBytes() 可以把字符串 -> 字节数组
// fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
/*write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流。 */
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, str.length());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream综合演示
文件拷贝:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/14
* @description 文件拷贝
*/
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 完成文件拷贝
// 1.创建文件的输入流,将文件读入到程序
// 2.创建文件的输出流,将读取到的文件数据,写入到指定的文件
String srcFilePath = "源文件夹路径";
String destFilePath = "目标盘文件路径";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
// 定义一个字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
// 读取到后,就写入文件 通过 fileOutputStream
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, readLen);
}
System.out.println("拷贝成功!!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 关闭输入和输出流,关闭资源
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
2.3.3、FileReader和FileWriter
FileReader和FileWriter是字符流,即按照字符来操作io
1、FileReader
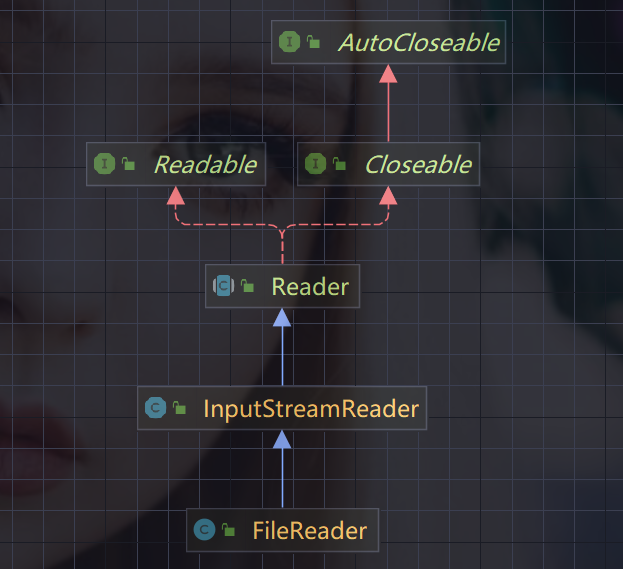
相关方法:
- new FileReader(String/File)
- read:每次读取单个字符,返回该字符,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- read(char[]):批量读取多个字符到数组,返回读取到的字符数组,如果到文件末尾返回-1
相关API:
- new String(char[]): 将char[]转换成String
- new String(char[], off, len): 将char[] 的指定部分转换成String
代码演示:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/14
* @description 字符输入流
*/
public class FileReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 单个字符读取文件
*/
@Test
public void readFile1() {
String filePath = "F:\\file\\story.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int dataLen = 0;
try {
// 1.创建FileReader对象
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
// 循环读取 单个字符读取
while ((dataLen = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) dataLen);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 字符数组读取文件
*/
@Test
public void readFile2() {
String filePath = "F:\\file\\story.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int readLen = 0;
char[] chars = new char[8];
try {
// 1.创建FileReader对象
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
// 循环读取 单个字符读取
while ((readLen = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(chars, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2、FileWriter
关系类图:
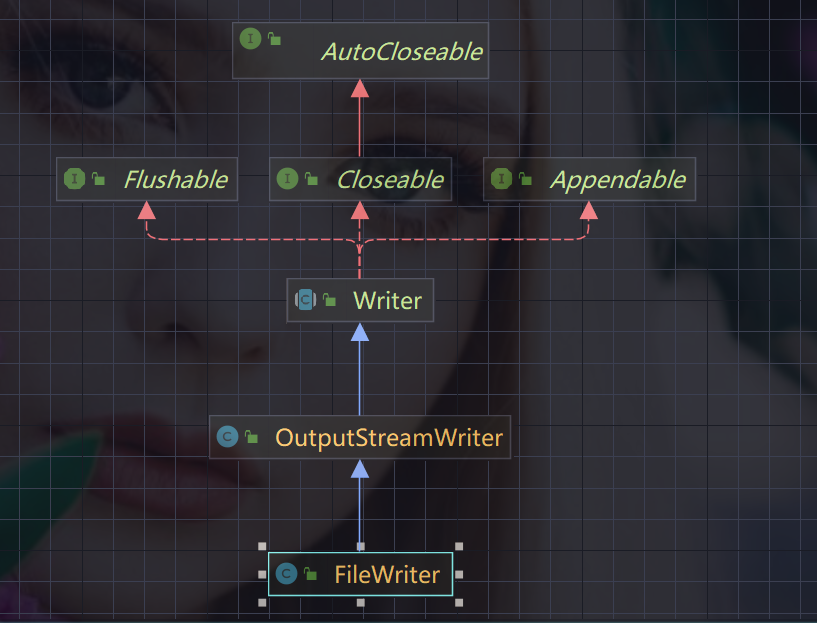
相关方法:
- new FileWriter(File/String):覆盖模式,相当于流的指针在首端
- new FileWriter(File/String, true):追加模式,相当于流的指针在尾端
- writer(int):写入单个字符
- writer(char[]):写入指定数组
- writer(char[], off, len):写入指定数组的指定部分
- writer(String):写入整个字符串
- writer(string, off, len):写入字符串的指定部分
注意:FileWriter使用后必须要关闭(close)或刷新(flush),否则写入不到指定的文件。
代码演示:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author java小豪
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2022/11/14
* @description 文件写入
*/
public class FileWwriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void fileWriter1() {
String filePath = "F:\\file\\note.txt";
// 创建FileWriter对象
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
char[] chars = {'a', 'b', 'c',};
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);
// 写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('H');
// 写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
// 写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write("天苍苍,野茫茫".toCharArray(), 0, 3);
// 写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write("你好信阳~");
// 写入字符串的指定部分
fileWriter.write("上海北京", 0, 2);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileWriter != null) {
fileWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}




![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django学生在线考试系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5b8ea42681eb4cb9ac41af4f29d7be7c.png)