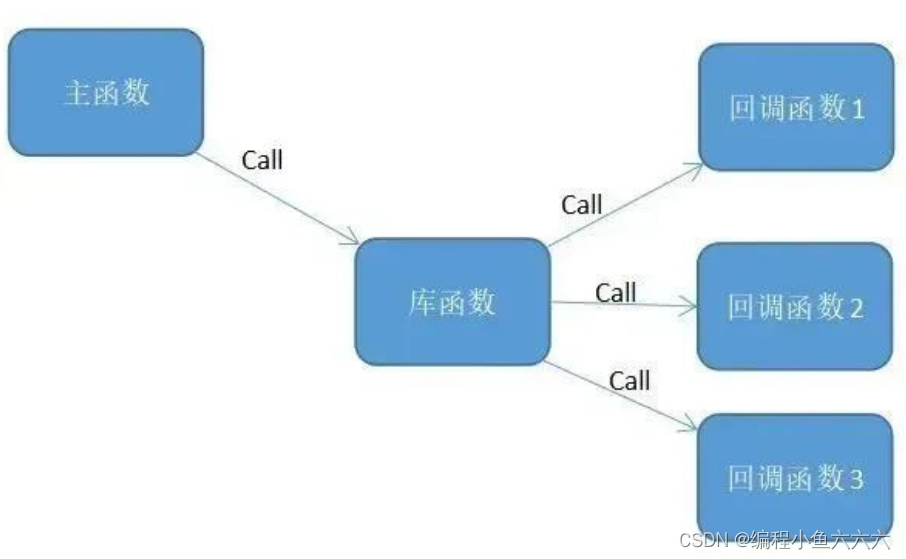
在过去的一段时间里,博主一直在给大家分享多线程并发编程里面的关键CompletableFfuture类的各种技术点,并发编程作为java开发里面关键点之一,也是大家向上提升重要的一点;对于CompletableFuture的学习一定要学到位,前面给大家分享了很多的知识点,这里分享一下CompletableFuture里面的关键方法的用法,码文不易,希望大家多多支持!
一、获取结果和主动触发计算的方法
1、T get() {}方法:
功能:它能获取异步线程里面执行完成的结果
/*1、get()方法的使用*/
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).get());2、T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit){}方法:
功能:get()方法需要等待线程执行完后才能获取到,这个是设置了一个等待时间,如果在设定的等待时间没获取到,就报错;
/*2、get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法的使用*/
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 2;
}).get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));3、T join(){}方法:
功能:和get()的功能一样,只是这个方法不需要抛异常
/*3、public T join()方法的使用*/
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 3;
}).join()); 4、T getNow(T valueIfAbsent){}方法
功能:也是获取结果的方法,在主程序走到方法执行的时候,异步程序如果运行完了就返回线程里面返回的结果,如果没运行完,程序不会报错,会返回一个托底数据valueIfAbsent
/*4、public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)方法的使用*/
CompletableFuture<Integer> async = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 4;
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
/*也是获取结果的方法,在主程序走到这一行的时候,异步程序如果运行完了就返回4,如果没运行完,不会报错,会返回一个托底数据2*/
System.out.println(async.getNow(2));5、public boolean complete(T value){}方法
功能:先判断get()是否是能获取到异步线程里面返回的值,如果有就返回true,如果没有就返回false并且将这个值设置为complete(2)里面设置的值
/*5、public boolean complete(T value)方法的使用*/
CompletableFuture<Integer> async = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 5;
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
/*先判断get()是否是能获取到异步线程里面返回的值,如果有就返回true,如果没有就返回false并且将这个值设置为complete(2)里面设置的值*/
System.out.println(async.complete(2)+" 结果是:"+async.get());二、对计算结果进行处理
1、thenApply方法
功能:对异步线程返回的结果进行进一步的计算,然后返回一个结果;
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("创建有返回值的线程");
return 1;
}).thenApply(a -> {
return a + 2;
}).thenApply(a -> {
return a + 3;
}).join());2、handle方法:
功能:因为thenApply方法是需要存在依赖关系,所以当前步骤错了,就不会继续往下一步执行,而handle可以,具体看代码;
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("执行第一步");
Integer i=1/0;
return 1;
}).handle((a,e)->{
System.out.println("执行第二步");
return a+2;
}).handle((a,e)->{
System.out.println("执行第三步");
return a+3;
}).whenComplete((c,e)->{
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("最后结果:"+c);
}
}).exceptionally(e->{
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});三、对计算结果进行消费
1、thenAccept方法
功能:接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("创建有返回值的线程");
return 1;
}).thenAccept(a->{
System.out.println("最终结果:"+a);
});四、对计算速度进行选用
1、applyToEither
功能:我们使用线程并不是为了做一道酸菜鱼,一步一步执行,有时候也需要多线程同时进行,比如游戏里面的打麻将,多人pk之类的,就是多个玩家同时进行,谁先结束就给谁标记完成,那么开启多个线程之间的pk怎么玩就看这个方法;
public class ThenApplyDemo {
private static int i=0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/*测试 applyToEither*/
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("1号进来了");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1号结束");
return 1;
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("2号进来了");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("2号结束");
i=5;
return 2;
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("线程3进来了");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 3;
}), a -> {
return a;
}), r -> {
return r;
}).join());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(i);
}
}五、对计算结果进行合并
1、thenCombine
功能:两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine来处理,举个例子,大家在调用2个或2个以上的接口时候,总有先后快慢之分,但是最终结果是需要整合2个接口里面的内容,那么这种如何进行呢?
/*测试thenCombine*/
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("步骤一执行");
return 1;
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("步骤二执行");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("步骤二结束");
return 2;
}), (r1, r2) -> {
System.out.println("执行相加");
return r1 + r2;
}).join();

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计抗疫医疗用品销售平台Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ec366047d3b44acb850d006652720e8f.png)




![Docker[2]-docker的组成与卸载](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/565beea160ab4bc2a421ba96b7ea7eb8.png)