数据结构–顺序表的基本操作–插入
顺序表的插入操作
实现目标
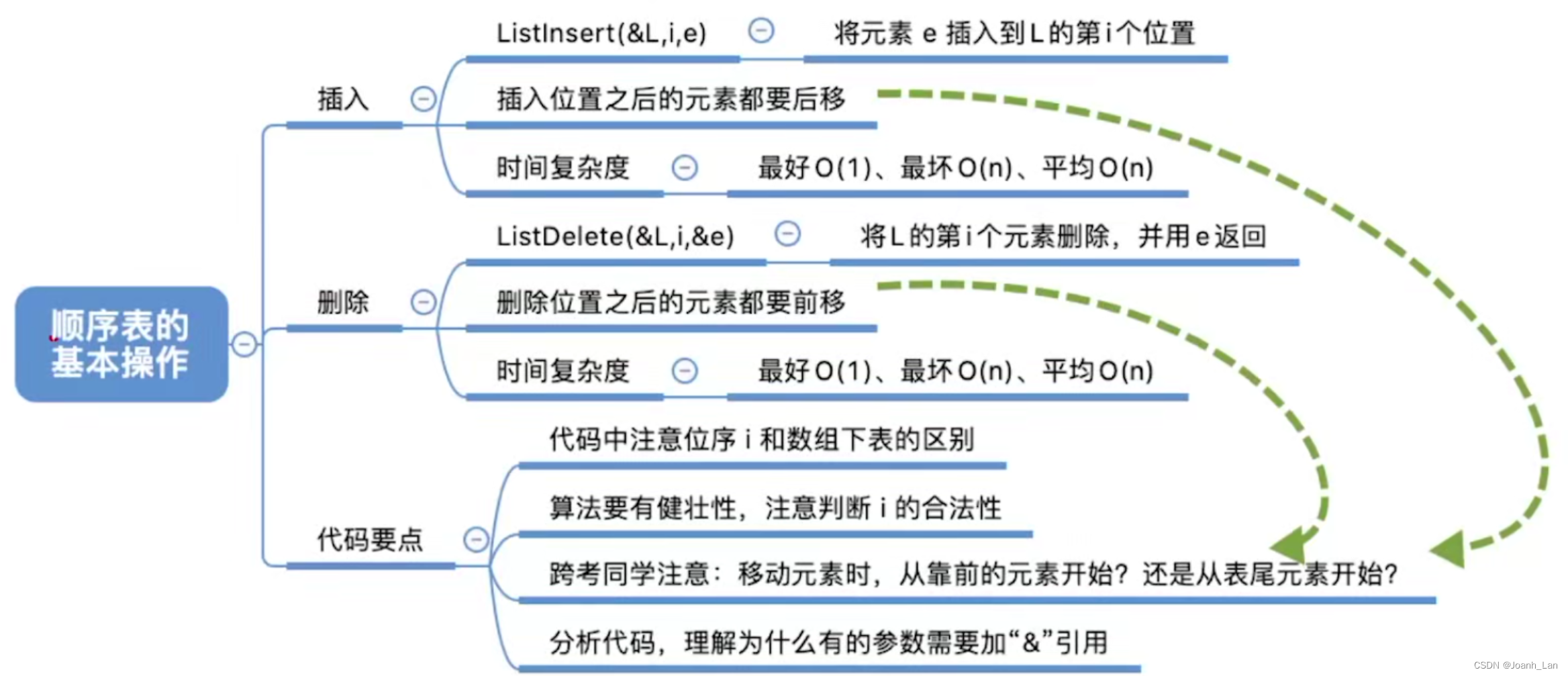
ListInsert(&L,i,e):插入操作。在表L中的第i个位置上插入指定元素e。
typedef struct
{
int data[MaxSize];
int len;
}Sqlist;

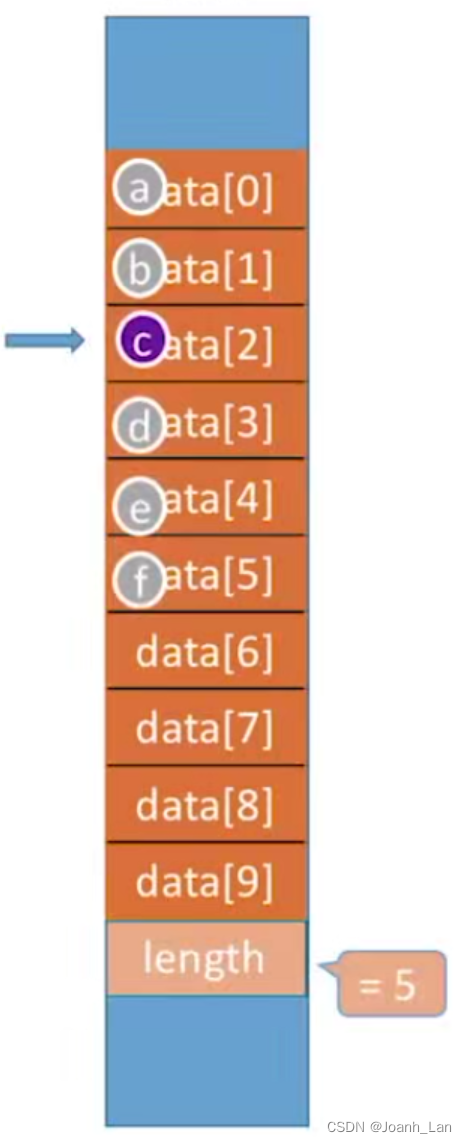
代码实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MaxSize 10 //定于的最大长度
typedef struct
{
int data[MaxSize];
int len;
}Sqlist;
void InitList(Sqlist &L)
{
L.len = 0;
}
bool ListInsert(Sqlist &L, int idx, int e)
{
if (idx > L.len + 1 || idx < 1) //判断是否合法
return false;
if (L.len >= MaxSize)
return false;
for (int j = L.len; j >= idx; j--) //将第idx个元素及之后的元素后移
L.data[j] = L.data[j - 1];
L.data[idx - 1] = e; //在位置i处放入e
L.len++; //长度加1
return true;
}
int main()
{
Sqlist L;
InitList(L);
if (ListInsert(L, 1, 1))
printf("Inserted successfully\n");
if (ListInsert(L, 2, 2))
printf("Inserted successfully\n");
// 测试结果
for (int i = 0; i < L.len; i++)
printf("%d ", L.data[i]);
}
ps:
好的算法,应该具有“健壮性”能处理异常情况,并给使用者反馈。
时间复杂度
最好情况:新元素插入到表尾,不需要移动元素 idx = n+1,循环0次;
最好时间复杂度
\color{red}最好时间复杂度
最好时间复杂度=O(1)
最坏情况:新元素插入到表头,需要将原有的n个元素全都向后移动 idx= 1,循环n次;
最坏时间复杂度
\color{red}最坏时间复杂度
最坏时间复杂度= O(n);
平均情况:假设新元素插入到任何一个位置的概率相同,即idx= 1,2,3, … len+1的概率都是
p
=
1
n
+
1
p=\frac{1}{n+1}
p=n+11 idx = 1,循环n次;idx=2时,循环n-1次; idx=3,循环n-2次…idx=n+1时,循环0次
平均循环次数 =
n
p
+
(
n
−
1
)
p
+
(
n
−
2
)
p
+
.
.
.
+
1
p
=
n
(
n
+
1
)
2
×
1
n
+
1
=
n
2
np + (n-1)p + (n-2)p + ... + 1p = \frac{n(n + 1)}{2} \times \frac{1}{n + 1} = \frac{n}{2}
np+(n−1)p+(n−2)p+...+1p=2n(n+1)×n+11=2n
平均时间复杂度
\color{red}{平均时间复杂度}
平均时间复杂度 = O(n)
顺序表的删除操作
实现目标
ListDelete(&L,i,&e):删除操作。删除表L中第i个位置的元素,并用e返回删除元素的值。
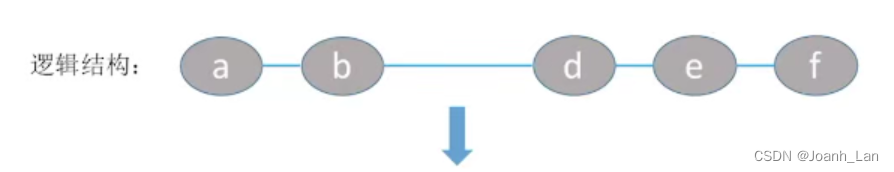

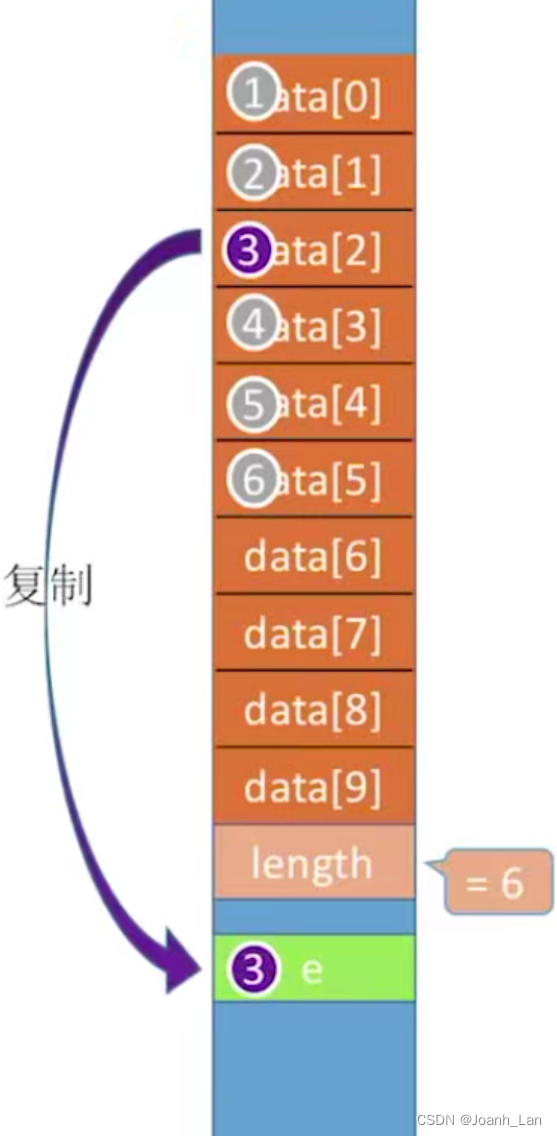
代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MaxSize 10 //定于的最大长度
typedef struct
{
int data[MaxSize];
int len;
}Sqlist;
void InitList(Sqlist &L)
{
L.len = 0;
}
bool ListInsert(Sqlist &L, int idx, int e)
{
if (idx > L.len + 1 || idx < 1) //判断是否合法
return false;
if (L.len >= MaxSize)
return false;
for (int j = L.len; j >= idx; j--) //将第idx个元素及之后的元素后移
L.data[j] = L.data[j - 1];
L.data[idx - 1] = e; //在位置i处放入e
L.len++; //长度加1
return true;
}
bool ListDelete(Sqlist &L, int idx, int &e)
{
if (idx > L.len && idx < 1) //判断i的范围是否有效
return false;
e = L.data[idx - 1]; //将被删除的元素赋值给e
for (int j = idx - 1; j < L.len; j++) //将第i个位置后的元素前移
L.data[j] = L.data[j + 1];
L.len--; //线性表长度减1
return true;
}
int main()
{
Sqlist L;
InitList(L);
if (ListInsert(L, 1, 1))
printf("Inserted successfully\n");
if (ListInsert(L, 2, 2))
printf("Inserted successfully\n");
int e = -1;
if (ListDelete(L,1,e))
printf("Deleted successfully\n");
// 测试结果
for (int i = 0; i < L.len; i++)
printf("%d ", L.data[i]);
}
时间复杂度
最好情况:删除表尾元素,不需要移动其他元素 idx= n 循环0次;
最好时间复杂度
\color{red}最好时间复杂度
最好时间复杂度=O(1)
最坏情况:删除表头元素,需要将后续的n-1个元素全都向前移动 idx= 1,循环 n-1 次;
最坏时间复杂度
\color{red}最坏时间复杂度
最坏时间复杂度= O(n);
平均情况:假设删除任何一个元素的概率相同,即 idx= 1,2,3. … , len的概率都是
p
=
1
n
p=\frac{1}{n}
p=n1
idx = 1,循环 n-1 次; idx=2 时,循环n-2次; idx=3,循环n-3 次… idx = n 时,循环 0 次
平均循环次数 =
(
n
−
1
)
p
+
(
n
−
2
)
p
+
.
.
.
.
.
.
+
1
p
=
n
(
n
−
1
)
2
×
1
n
=
n
−
1
2
(n-1)p+(n-2)p+......+1p = \frac{n(n-1)}{2} \times \frac{1}{n} = \frac{n-1}{2}
(n−1)p+(n−2)p+......+1p=2n(n−1)×n1=2n−1
平均时间复杂度
\color{red}平均时间复杂度
平均时间复杂度 = O(n)
知识点回顾与重要考点