作用:灵活的改变盒子在网页中的位置
实现:
1.定位模式:position
2.边偏移:设置盒子的位置
- left
- right
- top
- bottom
相对定位
position: relative
特点:
- 不脱标,占用自己原来位置
- 显示模式特点保持不变
- 设置边偏移则相对自己原来位置移动
div {
position: relative;
top: 100px;
left: 200px;
}绝对定位
position: absolute
使用场景:子级绝对定位,父级相对定位(子绝父相)
特点:
- 脱标,不占位
- 显示模式具备行内块特点
- 设置边偏移则相对最近的已经定位的祖先元素改变位置
- 如果祖先元素都未定位,则相对浏览器可视区改变位置
.father {
position: relative;
}
.father span {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
}定位居中
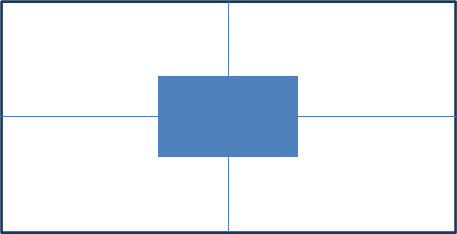
实现步骤:
- 绝对定位
- 水平、垂直边偏移为 50%
- 子级向左、上移动自身尺寸的一半
- 左、上的外边距为 –尺寸的一半
- transform: translate(-50%, -50%)
img {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
/* margin-left: -265px;
margin-top: -127px; */
/* 方便: 50% 就是自己宽高的一半 */
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}固定定位
position: fixed
场景:元素的位置在网页滚动时不会改变
特点:
- 脱标,不占位
- 显示模式具备行内块特点
- 设置边偏移相对浏览器窗口改变位置
div {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
right: 0;
width: 500px;
}堆叠层级z-index

默认效果:按照标签书写顺序,后来者居上
作用:设置定位元素的层级顺序,改变定位元素的显示顺序
属性名:z-index
属性值:整数数字(默认值为0,取值越大,层级越高)
.box1 {
background-color: pink;
/* 取值是整数,默认是0,取值越大显示顺序越靠上 */
z-index: 1;
}
.box2 {
background-color: skyblue;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
z-index: 2;
}