深度学习(24)——YOLO系列(4)
文章目录
- 深度学习(24)——YOLO系列(4)
- 1. dataset准备
- (1)数据详解
- (2)dataset
- (3)敲黑板:YOLOv5第一个亮点——>mosaic!!
- 2. model详解
- (1)一个模型可视化的小工具——netron
- (2)YOLOs-v5
- (3)Focus
- (4)BottleneckCSP
- (5)SPP(spatial pyramid pooling)
- (6)PAN(path aggregation network)
- 3. 训练
核心目标:YOLO-v5 代码详解
代码源自GitHub
数据源于其中的 maskdata!(这里有40个可以用于CV的小型数据,当然没有ImageNet那么大型,但是真的有那么大数据集咱普通家庭的小孩也没能力消化,硬件完全支撑不起咱的算力。所以练手就这样的小数据试试水)
相比前面的版本,v5更具有工程型,代码写的很简洁,之所以分享一是自己学习大牛整理代码的过程,也是自己知识点详细的记录。
惯性路线:data,model,train,predict
1. dataset准备
今天这个数据集上面已经说过,是一些人待着口罩,主要是检测人有没有戴口罩的。有戴口罩就是0,没有带口罩就是1,看一下例图:
image:

label:

(1)数据详解
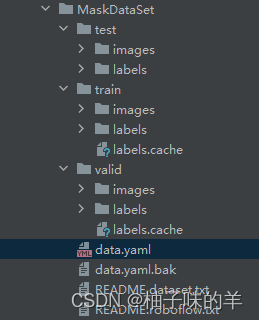
下载的数据整理以后是这样的结构
- train和valid中的labels.cache主要是为了加速数据读入速度直接将它存为cache格式。
- data.yaml 中主要记录train和validate的图像数据路径,以及检测区分的类别,(我们的任务主要区分有没有戴口罩,因此是2分类)
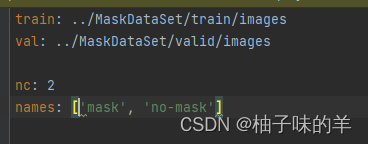
- 强调一下label中的数据格式是:[class,x,y,x,y](其中的xy是相对于整张图的相对位置,整张图现在是1*1,所以可以看到label的后四位都是小于1的数字)
(2)dataset
dataset.py
import glob
import math
import os
import random
import shutil
import time
from pathlib import Path
from threading import Thread
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from PIL import Image, ExifTags
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from tqdm import tqdm
from utils.general import xyxy2xywh, xywh2xyxy, torch_distributed_zero_first
help_url = 'https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Train-Custom-Data'
img_formats = ['.bmp', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tif', '.tiff', '.dng']
vid_formats = ['.mov', '.avi', '.mp4', '.mpg', '.mpeg', '.m4v', '.wmv', '.mkv']
# Get orientation exif tag
for orientation in ExifTags.TAGS.keys():
if ExifTags.TAGS[orientation] == 'Orientation':
break
def get_hash(files):
# Returns a single hash value of a list of files
return sum(os.path.getsize(f) for f in files if os.path.isfile(f))
def exif_size(img):
# Returns exif-corrected PIL size
s = img.size # (width, height)
try:
rotation = dict(img._getexif().items())[orientation]
if rotation == 6: # rotation 270
s = (s[1], s[0])
elif rotation == 8: # rotation 90
s = (s[1], s[0])
except:
pass
return s
def create_dataloader(path, imgsz, batch_size, stride, opt, hyp=None, augment=False, cache=False, pad=0.0, rect=False,
rank=-1, world_size=1, workers=8):
# Make sure only the first process in DDP process the dataset first, and the following others can use the cache.
with torch_distributed_zero_first(rank):
dataset = LoadImagesAndLabels(path, imgsz, batch_size,
augment=augment, # augment images
hyp=hyp, # augmentation hyperparameters
rect=rect, # rectangular training
cache_images=cache,
single_cls=opt.single_cls,
stride=int(stride),
pad=pad,
rank=rank)
batch_size = min(batch_size, len(dataset))
nw = min([os.cpu_count() // world_size, batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, workers]) # number of workers
sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(dataset) if rank != -1 else None
dataloader = InfiniteDataLoader(dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=nw,
sampler=sampler,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=LoadImagesAndLabels.collate_fn) # torch.utils.data.DataLoader()
return dataloader, dataset
class InfiniteDataLoader(torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader):
""" Dataloader that reuses workers.
Uses same syntax as vanilla DataLoader.
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
object.__setattr__(self, 'batch_sampler', _RepeatSampler(self.batch_sampler))
self.iterator = super().__iter__()
def __len__(self):
return len(self.batch_sampler.sampler)
def __iter__(self):
for i in range(len(self)):
yield next(self.iterator)
class _RepeatSampler(object):
""" Sampler that repeats forever.
Args:
sampler (Sampler)
"""
def __init__(self, sampler):
self.sampler = sampler
def __iter__(self):
while True:
yield from iter(self.sampler)
class LoadImages: # for inference
def __init__(self, path, img_size=640):
p = str(Path(path)) # os-agnostic
p = os.path.abspath(p) # absolute path
if '*' in p:
files = sorted(glob.glob(p, recursive=True)) # glob
elif os.path.isdir(p):
files = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(p, '*.*'))) # dir
elif os.path.isfile(p):
files = [p] # files
else:
raise Exception('ERROR: %s does not exist' % p)
images = [x for x in files if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in img_formats]
videos = [x for x in files if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in vid_formats]
ni, nv = len(images), len(videos)
self.img_size = img_size
self.files = images + videos
self.nf = ni + nv # number of files
self.video_flag = [False] * ni + [True] * nv
self.mode = 'images'
if any(videos):
self.new_video(videos[0]) # new video
else:
self.cap = None
assert self.nf > 0, 'No images or videos found in %s. Supported formats are:\nimages: %s\nvideos: %s' % \
(p, img_formats, vid_formats)
def __iter__(self):
self.count = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.count == self.nf:
raise StopIteration
path = self.files[self.count]
if self.video_flag[self.count]:
# Read video
self.mode = 'video'
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
if not ret_val:
self.count += 1
self.cap.release()
if self.count == self.nf: # last video
raise StopIteration
else:
path = self.files[self.count]
self.new_video(path)
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
self.frame += 1
print('video %g/%g (%g/%g) %s: ' % (self.count + 1, self.nf, self.frame, self.nframes, path), end='')
else:
# Read image
self.count += 1
img0 = cv2.imread(path) # BGR
assert img0 is not None, 'Image Not Found ' + path
print('image %g/%g %s: ' % (self.count, self.nf, path), end='')
# Padded resize
img = letterbox(img0, new_shape=self.img_size)[0]
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# cv2.imwrite(path + '.letterbox.jpg', 255 * img.transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]) # save letterbox image
return path, img, img0, self.cap
def new_video(self, path):
self.frame = 0
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
self.nframes = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
def __len__(self):
return self.nf # number of files
class LoadWebcam: # for inference
def __init__(self, pipe=0, img_size=640):
self.img_size = img_size
if pipe == '0':
pipe = 0 # local camera
# pipe = 'rtsp://192.168.1.64/1' # IP camera
# pipe = 'rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.64/1' # IP camera with login
# pipe = 'rtsp://170.93.143.139/rtplive/470011e600ef003a004ee33696235daa' # IP traffic camera
# pipe = 'http://wmccpinetop.axiscam.net/mjpg/video.mjpg' # IP golf camera
# https://answers.opencv.org/question/215996/changing-gstreamer-pipeline-to-opencv-in-pythonsolved/
# pipe = '"rtspsrc location="rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.64/1" latency=10 ! appsink' # GStreamer
# https://answers.opencv.org/question/200787/video-acceleration-gstremer-pipeline-in-videocapture/
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54095699/install-gstreamer-support-for-opencv-python-package # install help
# pipe = "rtspsrc location=rtsp://root:root@192.168.0.91:554/axis-media/media.amp?videocodec=h264&resolution=3840x2160 protocols=GST_RTSP_LOWER_TRANS_TCP ! rtph264depay ! queue ! vaapih264dec ! videoconvert ! appsink" # GStreamer
self.pipe = pipe
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(pipe) # video capture object
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 3) # set buffer size
def __iter__(self):
self.count = -1
return self
def __next__(self):
self.count += 1
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
self.cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
raise StopIteration
# Read frame
if self.pipe == 0: # local camera
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
img0 = cv2.flip(img0, 1) # flip left-right
else: # IP camera
n = 0
while True:
n += 1
self.cap.grab()
if n % 30 == 0: # skip frames
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.retrieve()
if ret_val:
break
# Print
assert ret_val, 'Camera Error %s' % self.pipe
img_path = 'webcam.jpg'
print('webcam %g: ' % self.count, end='')
# Padded resize
img = letterbox(img0, new_shape=self.img_size)[0]
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return img_path, img, img0, None
def __len__(self):
return 0
class LoadStreams: # multiple IP or RTSP cameras
def __init__(self, sources='streams.txt', img_size=640):
self.mode = 'images'
self.img_size = img_size
if os.path.isfile(sources):
with open(sources, 'r') as f:
sources = [x.strip() for x in f.read().splitlines() if len(x.strip())]
else:
sources = [sources]
n = len(sources)
self.imgs = [None] * n
self.sources = sources
for i, s in enumerate(sources):
# Start the thread to read frames from the video stream
print('%g/%g: %s... ' % (i + 1, n, s), end='')
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(eval(s) if s.isnumeric() else s)
assert cap.isOpened(), 'Failed to open %s' % s
w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) % 100
_, self.imgs[i] = cap.read() # guarantee first frame
thread = Thread(target=self.update, args=([i, cap]), daemon=True)
print(' success (%gx%g at %.2f FPS).' % (w, h, fps))
thread.start()
print('') # newline
# check for common shapes
s = np.stack([letterbox(x, new_shape=self.img_size)[0].shape for x in self.imgs], 0) # inference shapes
self.rect = np.unique(s, axis=0).shape[0] == 1 # rect inference if all shapes equal
if not self.rect:
print('WARNING: Different stream shapes detected. For optimal performance supply similarly-shaped streams.')
def update(self, index, cap):
# Read next stream frame in a daemon thread
n = 0
while cap.isOpened():
n += 1
# _, self.imgs[index] = cap.read()
cap.grab()
if n == 4: # read every 4th frame
_, self.imgs[index] = cap.retrieve()
n = 0
time.sleep(0.01) # wait time
def __iter__(self):
self.count = -1
return self
def __next__(self):
self.count += 1
img0 = self.imgs.copy()
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
raise StopIteration
# Letterbox
img = [letterbox(x, new_shape=self.img_size, auto=self.rect)[0] for x in img0]
# Stack
img = np.stack(img, 0)
# Convert
img = img[:, :, :, ::-1].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) # BGR to RGB, to bsx3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return self.sources, img, img0, None
def __len__(self):
return 0 # 1E12 frames = 32 streams at 30 FPS for 30 years
class LoadImagesAndLabels(Dataset): # for training/testing
def __init__(self, path, img_size=640, batch_size=16, augment=False, hyp=None, rect=False, image_weights=False,
cache_images=False, single_cls=False, stride=32, pad=0.0, rank=-1):
try:
f = [] # image files
for p in path if isinstance(path, list) else [path]: #win和linux有点区别 所以这里面代码稍微处理的内容多了点
p = str(Path(p)) # os-agnostic
parent = str(Path(p).parent) + os.sep
if os.path.isfile(p): # file
with open(p, 'r') as t:
t = t.read().splitlines()
f += [x.replace('./', parent) if x.startswith('./') else x for x in t] # local to global path
elif os.path.isdir(p): # folder
f += glob.iglob(p + os.sep + '*.*')
else:
raise Exception('%s does not exist' % p)
self.img_files = sorted(
[x.replace('/', os.sep) for x in f if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in img_formats])
except Exception as e:
raise Exception('Error loading data from %s: %s\nSee %s' % (path, e, help_url))
n = len(self.img_files)
assert n > 0, 'No images found in %s. See %s' % (path, help_url)
bi = np.floor(np.arange(n) / batch_size).astype(np.int) # batch index #batch索引
nb = bi[-1] + 1 # number of batches #一个epoch有多少个batch
self.n = n # number of images
self.batch = bi # batch index of image
self.img_size = img_size
self.augment = augment
self.hyp = hyp
self.image_weights = image_weights
self.rect = False if image_weights else rect
self.mosaic = self.augment and not self.rect # load 4 images at a time into a mosaic (only during training)
self.mosaic_border = [-img_size // 2, -img_size // 2] #限定范围
self.stride = stride#下采样总值
# Define labels
sa, sb = os.sep + 'images' + os.sep, os.sep + 'labels' + os.sep # /images/, /labels/ substrings
self.label_files = [x.replace(sa, sb, 1).replace(os.path.splitext(x)[-1], '.txt') for x in self.img_files]
# Check cache #可以设置缓存,再训练就不用一个个读了
cache_path = str(Path(self.label_files[0]).parent) + '.cache' # cached labels
if os.path.isfile(cache_path):
cache = torch.load(cache_path) # load
if cache['hash'] != get_hash(self.label_files + self.img_files): # dataset changed
cache = self.cache_labels(cache_path) # re-cache
else:
cache = self.cache_labels(cache_path) # cache
# Get labels
labels, shapes = zip(*[cache[x] for x in self.img_files])
self.shapes = np.array(shapes, dtype=np.float64)
self.labels = list(labels)
# Rectangular Training https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
if self.rect: #矩形
# Sort by aspect ratio
s = self.shapes # wh
ar = s[:, 1] / s[:, 0] # aspect ratio
irect = ar.argsort()
self.img_files = [self.img_files[i] for i in irect]
self.label_files = [self.label_files[i] for i in irect]
self.labels = [self.labels[i] for i in irect]
self.shapes = s[irect] # wh
ar = ar[irect]
# Set training image shapes
shapes = [[1, 1]] * nb
for i in range(nb):
ari = ar[bi == i]
mini, maxi = ari.min(), ari.max()
if maxi < 1:
shapes[i] = [maxi, 1]
elif mini > 1:
shapes[i] = [1, 1 / mini]
self.batch_shapes = np.ceil(np.array(shapes) * img_size / stride + pad).astype(np.int) * stride
# Cache labels,如果检测之后还有后续任务,可以更改以下参数,extract_bounding_box如果为true,可以将检测框中的内容提取出来
create_datasubset, extract_bounding_boxes, labels_loaded = False, False, False
nm, nf, ne, ns, nd = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 # number missing, found, empty, datasubset, duplicate
pbar = enumerate(self.label_files)
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar = tqdm(pbar)
for i, file in pbar:
l = self.labels[i] # label
if l is not None and l.shape[0]:
assert l.shape[1] == 5, '> 5 label columns: %s' % file #5列是否都有
assert (l >= 0).all(), 'negative labels: %s' % file #标签值是否大于0
assert (l[:, 1:] <= 1).all(), 'non-normalized or out of bounds coordinate labels: %s' % file #归一化
if np.unique(l, axis=0).shape[0] < l.shape[0]: # duplicate rows 计算重复的
nd += 1 # print('WARNING: duplicate rows in %s' % self.label_files[i]) # duplicate rows
if single_cls:
l[:, 0] = 0 # force dataset into single-class mode 单个类别,设置其类别为0
self.labels[i] = l
nf += 1 # file found
# Create subdataset (a smaller dataset)
if create_datasubset and ns < 1E4:
if ns == 0:
create_folder(path='./datasubset')
os.makedirs('./datasubset/images')
exclude_classes = 43
if exclude_classes not in l[:, 0]:
ns += 1
# shutil.copy(src=self.img_files[i], dst='./datasubset/images/') # copy image
with open('./datasubset/images.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(self.img_files[i] + '\n')
# Extract object detection boxes for a second stage classifier 把那个坐标框里面的数据截出来,看你任务需要
if extract_bounding_boxes:
p = Path(self.img_files[i])
img = cv2.imread(str(p))
h, w = img.shape[:2]
for j, x in enumerate(l):
f = '%s%sclassifier%s%g_%g_%s' % (p.parent.parent, os.sep, os.sep, x[0], j, p.name)
if not os.path.exists(Path(f).parent):
os.makedirs(Path(f).parent) # make new output folder
b = x[1:] * [w, h, w, h] # box
b[2:] = b[2:].max() # rectangle to square
b[2:] = b[2:] * 1.3 + 30 # pad
b = xywh2xyxy(b.reshape(-1, 4)).ravel().astype(np.int)
b[[0, 2]] = np.clip(b[[0, 2]], 0, w) # clip boxes outside of image
b[[1, 3]] = np.clip(b[[1, 3]], 0, h)
assert cv2.imwrite(f, img[b[1]:b[3], b[0]:b[2]]), 'Failure extracting classifier boxes'
else:
ne += 1 # print('empty labels for image %s' % self.img_files[i]) # file empty
# os.system("rm '%s' '%s'" % (self.img_files[i], self.label_files[i])) # remove
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar.desc = 'Scanning labels %s (%g found, %g missing, %g empty, %g duplicate, for %g images)' % (
cache_path, nf, nm, ne, nd, n)
if nf == 0:
s = 'WARNING: No labels found in %s. See %s' % (os.path.dirname(file) + os.sep, help_url)
print(s)
assert not augment, '%s. Can not train without labels.' % s
# Cache images into memory for faster training (WARNING: large datasets may exceed system RAM)
self.imgs = [None] * n
if cache_images:
gb = 0 # Gigabytes of cached images
pbar = tqdm(range(len(self.img_files)), desc='Caching images')
self.img_hw0, self.img_hw = [None] * n, [None] * n
for i in pbar: # max 10k images
self.imgs[i], self.img_hw0[i], self.img_hw[i] = load_image(self, i) # img, hw_original, hw_resized
gb += self.imgs[i].nbytes
pbar.desc = 'Caching images (%.1fGB)' % (gb / 1E9)
def cache_labels(self, path='labels.cache'):
# Cache dataset labels, check images and read shapes
x = {} # dict
pbar = tqdm(zip(self.img_files, self.label_files), desc='Scanning images', total=len(self.img_files))
for (img, label) in pbar:
try:
l = []
image = Image.open(img)
image.verify() # PIL verify
# _ = io.imread(img) # skimage verify (from skimage import io)
shape = exif_size(image) # image size
assert (shape[0] > 9) & (shape[1] > 9), 'image size <10 pixels'
if os.path.isfile(label):
with open(label, 'r') as f:
l = np.array([x.split() for x in f.read().splitlines()], dtype=np.float32) # labels
if len(l) == 0:
l = np.zeros((0, 5), dtype=np.float32)
x[img] = [l, shape]
except Exception as e:
x[img] = [None, None]
print('WARNING: %s: %s' % (img, e))
x['hash'] = get_hash(self.label_files + self.img_files)
torch.save(x, path) # save for next time
return x
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_files)
# def __iter__(self):
# self.count = -1
# print('ran dataset iter')
# #self.shuffled_vector = np.random.permutation(self.nF) if self.augment else np.arange(self.nF)
# return self
def __getitem__(self, index):
if self.image_weights:
index = self.indices[index]
hyp = self.hyp
mosaic = self.mosaic and random.random() < hyp['mosaic']
if mosaic:
# Load mosaic
img, labels = load_mosaic(self, index)
shapes = None
# MixUp https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf
if random.random() < hyp['mixup']:
img2, labels2 = load_mosaic(self, random.randint(0, len(self.labels) - 1))
r = np.random.beta(8.0, 8.0) # mixup ratio, alpha=beta=8.0
img = (img * r + img2 * (1 - r)).astype(np.uint8)
labels = np.concatenate((labels, labels2), 0)
else:
# Load image
img, (h0, w0), (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# Letterbox
shape = self.batch_shapes[self.batch[index]] if self.rect else self.img_size # final letterboxed shape
img, ratio, pad = letterbox(img, shape, auto=False, scaleup=self.augment)
shapes = (h0, w0), ((h / h0, w / w0), pad) # for COCO mAP rescaling
# Load labels
labels = []
x = self.labels[index]
if x.size > 0:
# Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels = x.copy()
labels[:, 1] = ratio[0] * w * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + pad[0] # pad width
labels[:, 2] = ratio[1] * h * (x[:, 2] - x[:, 4] / 2) + pad[1] # pad height
labels[:, 3] = ratio[0] * w * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + pad[0]
labels[:, 4] = ratio[1] * h * (x[:, 2] + x[:, 4] / 2) + pad[1]
if self.augment:
# Augment imagespace
if not mosaic: #这个之前在mosaic方法最后做过了
img, labels = random_perspective(img, labels,
degrees=hyp['degrees'],
translate=hyp['translate'],
scale=hyp['scale'],
shear=hyp['shear'],
perspective=hyp['perspective'])
# Augment colorspace h:色调 s:饱和度 V:亮度
augment_hsv(img, hgain=hyp['hsv_h'], sgain=hyp['hsv_s'], vgain=hyp['hsv_v'])
# Apply cutouts
# if random.random() < 0.9:
# labels = cutout(img, labels)
nL = len(labels) # number of labels
if nL: #1.调整标签格式 2.归一化标签取值范围
labels[:, 1:5] = xyxy2xywh(labels[:, 1:5]) # convert xyxy to xywh
labels[:, [2, 4]] /= img.shape[0] # normalized height 0-1
labels[:, [1, 3]] /= img.shape[1] # normalized width 0-1
if self.augment:#要不要做翻转操作
# flip up-down
if random.random() < hyp['flipud']:
img = np.flipud(img)
if nL:
labels[:, 2] = 1 - labels[:, 2]
# flip left-right
if random.random() < hyp['fliplr']:
img = np.fliplr(img)
if nL:
labels[:, 1] = 1 - labels[:, 1]
labels_out = torch.zeros((nL, 6))
if nL:
labels_out[:, 1:] = torch.from_numpy(labels)
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416 要满足pytorch的格式
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return torch.from_numpy(img), labels_out, self.img_files[index], shapes
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
img, label, path, shapes = zip(*batch) # transposed
for i, l in enumerate(label):
l[:, 0] = i # add target image index for build_targets()
return torch.stack(img, 0), torch.cat(label, 0), path, shapes
# Ancillary functions --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def load_image(self, index):
# loads 1 image from dataset, returns img, original hw, resized hw
img = self.imgs[index]
if img is None: # not cached
path = self.img_files[index]
img = cv2.imread(path) # BGR
assert img is not None, 'Image Not Found ' + path
h0, w0 = img.shape[:2] # orig hw
r = self.img_size / max(h0, w0) # resize image to img_size
if r != 1: # always resize down, only resize up if training with augmentation
interp = cv2.INTER_AREA if r < 1 and not self.augment else cv2.INTER_LINEAR
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w0 * r), int(h0 * r)), interpolation=interp)
return img, (h0, w0), img.shape[:2] # img, hw_original, hw_resized
else:
return self.imgs[index], self.img_hw0[index], self.img_hw[index] # img, hw_original, hw_resized
def augment_hsv(img, hgain=0.5, sgain=0.5, vgain=0.5):
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [hgain, sgain, vgain] + 1 # random gains
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV))
dtype = img.dtype # uint8
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=np.int16)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
img_hsv = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val))).astype(dtype)
cv2.cvtColor(img_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=img) # no return needed
# Histogram equalization
# if random.random() < 0.2:
# for i in range(3):
# img[:, :, i] = cv2.equalizeHist(img[:, :, i])
def load_mosaic(self, index):
# loads images in a mosaic
labels4 = []
s = self.img_size
yc, xc = [int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border] # mosaic center x, y
indices = [index] + [random.randint(0, len(self.labels) - 1) for _ in range(3)] # 3 additional image indices
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
img, _, (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left 1.初始化大图;2.计算当前图片放在大图中什么位置;3.计算在小图中取哪一部分放到大图中
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
#1.截图小图中的部分放到大图中 2.由于小图可能填充不满,所以还需要计算差异值,因为一会要更新坐标框标签
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels 标签值要重新计算,因为现在都放到大图中了
x = self.labels[index]
labels = x.copy()
if x.size > 0: # Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels[:, 1] = w * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + padw
labels[:, 2] = h * (x[:, 2] - x[:, 4] / 2) + padh
labels[:, 3] = w * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + padw
labels[:, 4] = h * (x[:, 2] + x[:, 4] / 2) + padh
labels4.append(labels)
# Concat/clip labels 坐标计算完之后可能越界,调整坐标值,让他们都在大图中
if len(labels4):
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
np.clip(labels4[:, 1:], 0, 2 * s, out=labels4[:, 1:]) # use with random_perspective
# img4, labels4 = replicate(img4, labels4) # replicate
# Augment 对整合的大图再进行随机旋转、平移、缩放、裁剪
img4, labels4 = random_perspective(img4, labels4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
def replicate(img, labels):
# Replicate labels
h, w = img.shape[:2]
boxes = labels[:, 1:].astype(int)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes.T
s = ((x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1)) / 2 # side length (pixels)
for i in s.argsort()[:round(s.size * 0.5)]: # smallest indices
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = boxes[i]
bh, bw = y2b - y1b, x2b - x1b
yc, xc = int(random.uniform(0, h - bh)), int(random.uniform(0, w - bw)) # offset x, y
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = [xc, yc, xc + bw, yc + bh]
img[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
labels = np.append(labels, [[labels[i, 0], x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a]], axis=0)
return img, labels
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
# Resize image to a 32-pixel-multiple rectangle https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 64), np.mod(dh, 64) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def random_perspective(img, targets=(), degrees=10, translate=.1, scale=.1, shear=10, perspective=0.0, border=(0, 0)):
# torchvision.transforms.RandomAffine(degrees=(-10, 10), translate=(.1, .1), scale=(.9, 1.1), shear=(-10, 10))
# targets = [cls, xyxy]
# 最后大图还要resize回正常的大小
height = img.shape[0] + border[0] * 2 # shape(h,w,c)
width = img.shape[1] + border[1] * 2
#旋转 平移 缩放等操作 都需要系数矩阵(参考opencv函数,这里全部随机)
# Center
C = np.eye(3)
C[0, 2] = -img.shape[1] / 2 # x translation (pixels)
C[1, 2] = -img.shape[0] / 2 # y translation (pixels)
# Perspective 平移
P = np.eye(3)
P[2, 0] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # x perspective (about y)
P[2, 1] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # y perspective (about x)
# Rotation and Scale 旋转与缩放
R = np.eye(3)
a = random.uniform(-degrees, degrees)
# a += random.choice([-180, -90, 0, 90]) # add 90deg rotations to small rotations
s = random.uniform(1 - scale, 1 + scale)
# s = 2 ** random.uniform(-scale, scale)
R[:2] = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=a, center=(0, 0), scale=s)
# Shear 裁剪
S = np.eye(3)
S[0, 1] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # x shear (deg)
S[1, 0] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # y shear (deg)
# Translation
T = np.eye(3)
T[0, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * width # x translation (pixels)
T[1, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * height # y translation (pixels)
# 一起执行这些随机变换
# Combined rotation matrix
M = T @ S @ R @ P @ C # order of operations (right to left) is IMPORTANT
if (border[0] != 0) or (border[1] != 0) or (M != np.eye(3)).any(): # image changed
if perspective:
img = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
else: # affine
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M[:2], dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
# Visualize
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))[1].ravel()
# ax[0].imshow(img[:, :, ::-1]) # base
# ax[1].imshow(img2[:, :, ::-1]) # warped
# Transform label coordinates 数据变化了,标签的坐标值也得跟着一起变
n = len(targets)
if n:
# warp points
xy = np.ones((n * 4, 3))
xy[:, :2] = targets[:, [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 4, 3, 2]].reshape(n * 4, 2) # x1y1, x2y2, x1y2, x2y1
xy = xy @ M.T # transform
if perspective:
xy = (xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3]).reshape(n, 8) # rescale
else: # affine
xy = xy[:, :2].reshape(n, 8)
# create new boxes
x = xy[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]]
y = xy[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]]
xy = np.concatenate((x.min(1), y.min(1), x.max(1), y.max(1))).reshape(4, n).T
# # apply angle-based reduction of bounding boxes
# radians = a * math.pi / 180
# reduction = max(abs(math.sin(radians)), abs(math.cos(radians))) ** 0.5
# x = (xy[:, 2] + xy[:, 0]) / 2
# y = (xy[:, 3] + xy[:, 1]) / 2
# w = (xy[:, 2] - xy[:, 0]) * reduction
# h = (xy[:, 3] - xy[:, 1]) * reduction
# xy = np.concatenate((x - w / 2, y - h / 2, x + w / 2, y + h / 2)).reshape(4, n).T
# clip boxes
xy[:, [0, 2]] = xy[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, width)
xy[:, [1, 3]] = xy[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, height)
# filter candidates
i = box_candidates(box1=targets[:, 1:5].T * s, box2=xy.T)
targets = targets[i]
targets[:, 1:5] = xy[i]
return img, targets
def box_candidates(box1, box2, wh_thr=2, ar_thr=20, area_thr=0.1): # box1(4,n), box2(4,n)
# Compute candidate boxes: box1 before augment, box2 after augment, wh_thr (pixels), aspect_ratio_thr, area_ratio
w1, h1 = box1[2] - box1[0], box1[3] - box1[1]
w2, h2 = box2[2] - box2[0], box2[3] - box2[1]
ar = np.maximum(w2 / (h2 + 1e-16), h2 / (w2 + 1e-16)) # aspect ratio
return (w2 > wh_thr) & (h2 > wh_thr) & (w2 * h2 / (w1 * h1 + 1e-16) > area_thr) & (ar < ar_thr) # candidates
def cutout(image, labels):
# Applies image cutout augmentation https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552
h, w = image.shape[:2]
def bbox_ioa(box1, box2):
# Returns the intersection over box2 area given box1, box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4. boxes are x1y1x2y2
box2 = box2.transpose()
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
# Intersection area
inter_area = (np.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2) - np.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clip(0) * \
(np.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2) - np.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clip(0)
# box2 area
box2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1) + 1e-16
# Intersection over box2 area
return inter_area / box2_area
# create random masks
scales = [0.5] * 1 + [0.25] * 2 + [0.125] * 4 + [0.0625] * 8 + [0.03125] * 16 # image size fraction
for s in scales:
mask_h = random.randint(1, int(h * s))
mask_w = random.randint(1, int(w * s))
# box
xmin = max(0, random.randint(0, w) - mask_w // 2)
ymin = max(0, random.randint(0, h) - mask_h // 2)
xmax = min(w, xmin + mask_w)
ymax = min(h, ymin + mask_h)
# apply random color mask
image[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax] = [random.randint(64, 191) for _ in range(3)]
# return unobscured labels
if len(labels) and s > 0.03:
box = np.array([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], dtype=np.float32)
ioa = bbox_ioa(box, labels[:, 1:5]) # intersection over area
labels = labels[ioa < 0.60] # remove >60% obscured labels
return labels
def reduce_img_size(path='path/images', img_size=1024): # from utils.datasets import *; reduce_img_size()
# creates a new ./images_reduced folder with reduced size images of maximum size img_size
path_new = path + '_reduced' # reduced images path
create_folder(path_new)
for f in tqdm(glob.glob('%s/*.*' % path)):
try:
img = cv2.imread(f)
h, w = img.shape[:2]
r = img_size / max(h, w) # size ratio
if r < 1.0:
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w * r), int(h * r)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # _LINEAR fastest
fnew = f.replace(path, path_new) # .replace(Path(f).suffix, '.jpg')
cv2.imwrite(fnew, img)
except:
print('WARNING: image failure %s' % f)
def recursive_dataset2bmp(dataset='path/dataset_bmp'): # from utils.datasets import *; recursive_dataset2bmp()
# Converts dataset to bmp (for faster training)
formats = [x.lower() for x in img_formats] + [x.upper() for x in img_formats]
for a, b, files in os.walk(dataset):
for file in tqdm(files, desc=a):
p = a + '/' + file
s = Path(file).suffix
if s == '.txt': # replace text
with open(p, 'r') as f:
lines = f.read()
for f in formats:
lines = lines.replace(f, '.bmp')
with open(p, 'w') as f:
f.write(lines)
elif s in formats: # replace image
cv2.imwrite(p.replace(s, '.bmp'), cv2.imread(p))
if s != '.bmp':
os.system("rm '%s'" % p)
def imagelist2folder(path='path/images.txt'): # from utils.datasets import *; imagelist2folder()
# Copies all the images in a text file (list of images) into a folder
create_folder(path[:-4])
with open(path, 'r') as f:
for line in f.read().splitlines():
os.system('cp "%s" %s' % (line, path[:-4]))
print(line)
def create_folder(path='./new'):
# Create folder
if os.path.exists(path):
shutil.rmtree(path) # delete output folder
os.makedirs(path) # make new output folder
- create_dataloader
- LoadImagesAndLabels
# Define labels
sa, sb = os.sep + 'images' + os.sep, os.sep + 'labels' + os.sep # /images/, /labels/ substrings
self.label_files = [x.replace(sa, sb, 1).replace(os.path.splitext(x)[-1], '.txt') for x in self.img_files]
这里作者的写法值得学习,在前面的data.yaml 文件中,作者只记录了image的路径,我第一次看到的时候疑惑怎么没有记录label的路径,后来看到这里发现很精妙的将image和label做了替换,前面的数据结构中,image和label在同一个文件夹下,这里替换也简单操作。
(3)敲黑板:YOLOv5第一个亮点——>mosaic!!
这是YOLOv5中的第一个让人眼前一亮的点,就是将四张图组合成一张大图后参与训练,这样就可以相当于在一个batch中,这种方法学习到更多图片的信息。怎么做的呢?看下面:
- 这四张图是怎么拼的呢?首先要选择一个中心点center,虽然说是中心点,但是这个其实不是真正最后组装图片的真正中心,而是一个随机的点,但是围绕这个点分布着四张图。
yc, xc = [int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border] - 既然是四张图片组合,另外的三张也是在所有图片中随机挑选的,她们的index组合而成一个list
indices = [index] + [random.randint(0, len(self.labels) - 1) for _ in range(3)] - list 中从0到3分别是左上,右上,左下和右下的四张图
- 当组合第一张图的时候要先初始化mosaic图片,在初始化的时候我们定义imgsize为640,所以这里图片的size变成[640* 2,640* 2]
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles - 因为组装大图后图片中的点相对于大图的位置变了,这样后面label的相对位置需要发生改变,因此要记录现在图片在大图中的坐标。此外,虽然我们设置了imgsize为640,但这是我们的期望值,或者说是进入网络的图片尺寸,所以我们组装大图的过程中是根据现在的组装情况来裁剪原图(如果原图太大),这一这就需要我们记录在原来的图片中裁剪的是哪一部分,需要记录在原图中的坐标。
这个部分看似有点绕,但是仔细推算一下就懂了,很明白,下面这个例子大家可以笔算一遍就懂了
如果中心点坐标为[x,y] = [808,862],
左上角的图片(简称t1)大小为[w,h] = [640,436],
那么t1在大图中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [168,426],[x,y](右下) = [808,862],在小图(原图)中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [0,0],[x,y](右下) = [640,436],
右上角的图片(简称t2)大小为[w,h] = [640,407],
那么t2在大图中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [808,455],[x,y](右下) = [1280,862],在小图(原图)中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [0,0],[x,y](右下) = [472,407],
左下角的图片(简称t3)大小为[w,h] = [640,444],
那么t3在大图中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [168,862],[x,y](右下) = [808,1280],在小图(原图)中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [0,0],[x,y](右下) = [640,418],
右下角的图片(简称t4)大小为[w,h] = [640,320],
那么t4在大图中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [808,862],[x,y](右下) = [1280,1182],在小图(原图)中的坐标为[x,y](左上) = [0,0],[x,y](右下) = [472,320]
def load_mosaic(self, index):
# loads images in a mosaic
labels4 = []
s = self.img_size
yc, xc = [int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border] # mosaic center x, y
indices = [index] + [random.randint(0, len(self.labels) - 1) for _ in range(3)] # 3 additional image indices
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
img, _, (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left 1.初始化大图;2.计算当前图片放在大图中什么位置;3.计算在小图中取哪一部分放到大图中
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
#1.截图小图中的部分放到大图中 2.由于小图可能填充不满,所以还需要计算差异值,因为一会要更新坐标框标签
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels 标签值要重新计算,因为现在都放到大图中了
x = self.labels[index]
labels = x.copy()
if x.size > 0: # Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels[:, 1] = w * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + padw
labels[:, 2] = h * (x[:, 2] - x[:, 4] / 2) + padh
labels[:, 3] = w * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + padw
labels[:, 4] = h * (x[:, 2] + x[:, 4] / 2) + padh
labels4.append(labels)
# Concat/clip labels 坐标计算完之后可能越界,调整坐标值,让他们都在大图中
if len(labels4):
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
np.clip(labels4[:, 1:], 0, 2 * s, out=labels4[:, 1:]) # use with random_perspective
# img4, labels4 = replicate(img4, labels4) # replicate
# Augment 对整合的大图再进行随机旋转、平移、缩放、裁剪
img4, labels4 = random_perspective(img4, labels4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
- 在原来的label中记录的是xyhw,在label改变的过程中要先将xywh转化为xyxy类型再计算
- 做完上面的这些处理之后就要进行数据增强,因为在检测过程中label和图片之间的位置具有强关联,因此,要注意使用相同的增强,尤其针对一些位置变换的增强过程。这里作者自己使用OpenCV做了增强,因为torchvision中我记得是没有同步的,所以也可以用albu这个package,这个可以将很多数据使用相同的随机数据增强。
数据就这些了,然后是model
2. model详解
(1)一个模型可视化的小工具——netron
安装onnx: pip install onnx
netron可以直接使用网页版,只需要将自己保存的模型.pth上传就可以可视化模型结构

如果觉得这个不够详细,可以使用下面代码将.pth文件转化为.onnx文件
"""Exports a YOLOv5 *.pt model to ONNX and TorchScript formats
Usage:
$ export PYTHONPATH="$PWD" && python models/export.py --weights ./weights/yolov5s.pt --img 640 --batch 1
"""
#首先pip install onnx
import argparse
import sys
import time
sys.path.append('./') # to run '$ python *.py' files in subdirectories
sys.path.append('../')
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import models
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.activations import Hardswish
from utils.general import set_logging, check_img_size
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./yolov5s.pt', help='weights path') # from yolov5/models/
parser.add_argument('--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640, 640], help='image size') # height, width
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=1, help='batch size')
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.img_size *= 2 if len(opt.img_size) == 1 else 1 # expand
print(opt)
set_logging()
t = time.time()
# Load PyTorch model
model = attempt_load(opt.weights, map_location=torch.device('cpu')) # load FP32 model
labels = model.names
# Checks
gs = int(max(model.stride)) # grid size (max stride)
opt.img_size = [check_img_size(x, gs) for x in opt.img_size] # verify img_size are gs-multiples
# Input
img = torch.zeros(opt.batch_size, 3, *opt.img_size) # image size(1,3,320,192) iDetection
# Update model
for k, m in model.named_modules():
m._non_persistent_buffers_set = set() # pytorch 1.6.0 compatibility
if isinstance(m, models.common.Conv) and isinstance(m.act, nn.Hardswish):
m.act = Hardswish() # assign activation
# if isinstance(m, models.yolo.Detect):
# m.forward = m.forward_export # assign forward (optional)
model.model[-1].export = True # set Detect() layer export=True
y = model(img) # dry run
# TorchScript export
try:
print('\nStarting TorchScript export with torch %s...' % torch.__version__)
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.torchscript.pt') # filename
ts = torch.jit.trace(model, img)
ts.save(f)
print('TorchScript export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('TorchScript export failure: %s' % e)
# ONNX export
try:
import onnx
print('\nStarting ONNX export with onnx %s...' % onnx.__version__)
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.onnx') # filename
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=12, input_names=['images'],
output_names=['classes', 'boxes'] if y is None else ['output'])
# Checks
onnx_model = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model) # check onnx model
# print(onnx.helper.printable_graph(onnx_model.graph)) # print a human readable model
print('ONNX export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('ONNX export failure: %s' % e)
# CoreML export
try:
import coremltools as ct
print('\nStarting CoreML export with coremltools %s...' % ct.__version__)
# convert model from torchscript and apply pixel scaling as per detect.py
model = ct.convert(ts, inputs=[ct.ImageType(name='image', shape=img.shape, scale=1 / 255.0, bias=[0, 0, 0])])
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.mlmodel') # filename
model.save(f)
print('CoreML export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('CoreML export failure: %s' % e)
# Finish
print('\nExport complete (%.2fs). Visualize with https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron.' % (time.time() - t))
之后使用onnx文件可视化(超详细!)
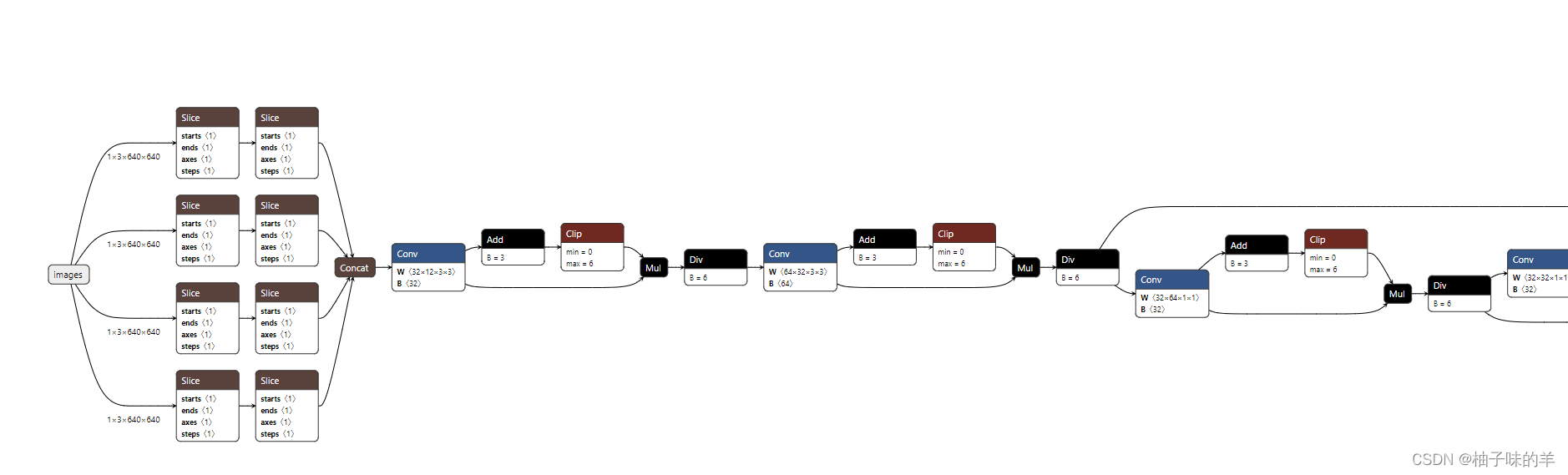
(2)YOLOs-v5
# parameters
nc: 2 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
# anchors
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [128]], #
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]],
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
然后就说一下里面的一些关键的block:Focus,BottleneckCSP,SPP,PAN (敲黑板,后面都是重点)
(3)Focus
- 先分块,后拼接,再卷积
- 间隔的完成分块任务
- 卷积的输入channel 变多
- 提高速度
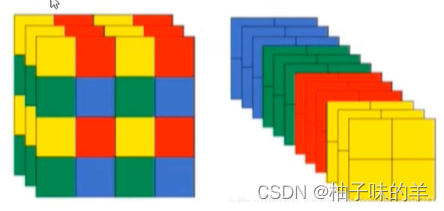
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
(4)BottleneckCSP
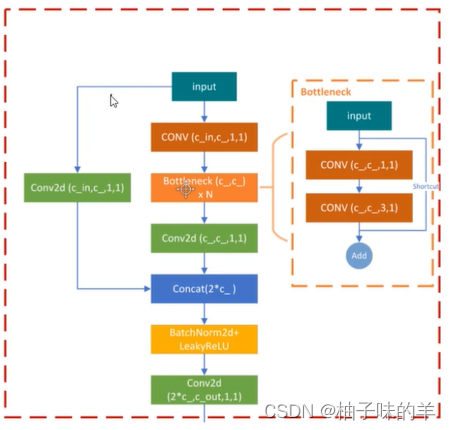
一个简单的卷积的残差连接
class BottleneckCSP(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(BottleneckCSP, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Conv2d(c1, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv3 = nn.Conv2d(c_, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv4 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * c_) # applied to cat(cv2, cv3)
self.act = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)])
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.cv3(self.m(self.cv1(x)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv4(self.act(self.bn(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))))
(5)SPP(spatial pyramid pooling)
- 为了更好满足不同输入大小,训练的时候要改变输入数据的大小
- SPP其实就是用最大池化来满足最终输入特征一致即可
- 这里将maxpooling的kernel设置为5,9,13,其对应的stride为1,1,1,padding为2,4,6。( output = (input-kernel+2padding)/stride +1)这样就可以根据不同的kernel和padding得到相同的output的特征,将他们cat后得到更丰富的特征
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial pyramid pooling layer used in YOLOv3-SPP
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPP, self).__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))
(6)PAN(path aggregation network)
- FPN是自顶向下的模式,将高层特征传下来,高层逐层向下兼容下层(单向)
- 缺少底层到高层,PAN登场
- 引入自底向上的路径,使得底层信息更容易传到顶部
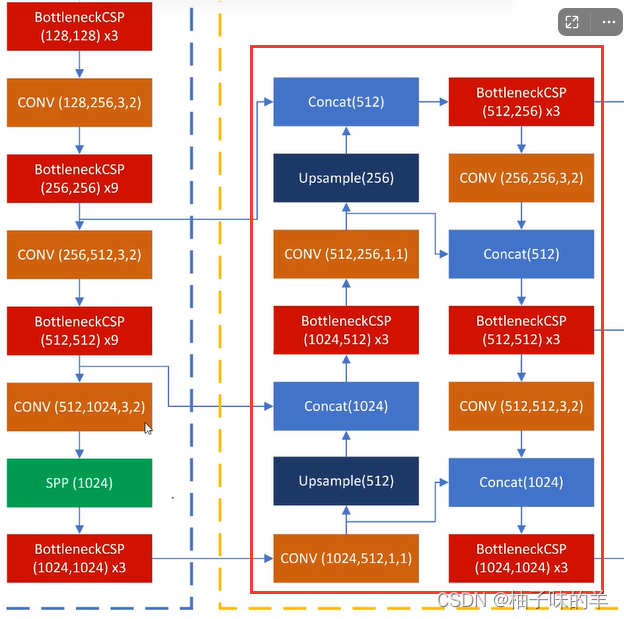
3. 训练
import argparse
import logging
import os
import random
import shutil
import time
from pathlib import Path
import math
import numpy as np
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.optim.lr_scheduler as lr_scheduler
import torch.utils.data
import yaml
from torch.cuda import amp
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from tqdm import tqdm
import test # import test.py to get mAP after each epoch
from models.yolo import Model
from utils.datasets import create_dataloader
from utils.general import (
torch_distributed_zero_first, labels_to_class_weights, plot_labels, check_anchors, labels_to_image_weights,
compute_loss, plot_images, fitness, strip_optimizer, plot_results, get_latest_run, check_dataset, check_file,
check_git_status, check_img_size, increment_dir, print_mutation, plot_evolution, set_logging, init_seeds)
from utils.google_utils import attempt_download
from utils.torch_utils import ModelEMA, select_device, intersect_dicts
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def train(hyp, opt, device, tb_writer=None):
logger.info(f'Hyperparameters {hyp}')#太够意思了,训练时候参数,各epoch情况,损失,测试集的结果全部保存
log_dir = Path(tb_writer.log_dir) if tb_writer else Path(opt.logdir) / 'evolve' # logging directory
wdir = log_dir / 'weights' # weights directory
os.makedirs(wdir, exist_ok=True)#保存路径
last = wdir / 'last.pt'
best = wdir / 'best.pt'
results_file = str(log_dir / 'results.txt')#训练过程中各种指标
epochs, batch_size, total_batch_size, weights, rank = \
opt.epochs, opt.batch_size, opt.total_batch_size, opt.weights, opt.global_rank
# Save run settings 保存当前参数
with open(log_dir / 'hyp.yaml', 'w') as f:
yaml.dump(hyp, f, sort_keys=False)
with open(log_dir / 'opt.yaml', 'w') as f:
yaml.dump(vars(opt), f, sort_keys=False)
# Configure
cuda = device.type != 'cpu'
init_seeds(2 + rank)#随机种子
with open(opt.data) as f:
data_dict = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader) # data dict
with torch_distributed_zero_first(rank):#所有进程都一起
check_dataset(data_dict) # check
train_path = data_dict['train']#数据路径与类别名字
test_path = data_dict['val']
nc, names = (1, ['item']) if opt.single_cls else (int(data_dict['nc']), data_dict['names']) # number classes, names
assert len(names) == nc, '%g names found for nc=%g dataset in %s' % (len(names), nc, opt.data) # check
# Model
pretrained = weights.endswith('.pt')
if pretrained:#有预训练模型的话,会自动下载,最好在github下载好 然后放到对应位置
with torch_distributed_zero_first(rank):
attempt_download(weights) # download if not found locally
ckpt = torch.load(weights, map_location=device) # load checkpoint
if hyp.get('anchors'):
ckpt['model'].yaml['anchors'] = round(hyp['anchors']) # force autoanchor
model = Model(opt.cfg or ckpt['model'].yaml, ch=3, nc=nc).to(device) # create
exclude = ['anchor'] if opt.cfg or hyp.get('anchors') else [] # exclude keys
state_dict = ckpt['model'].float().state_dict() # to FP32
state_dict = intersect_dicts(state_dict, model.state_dict(), exclude=exclude) # intersect
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False) # load
logger.info('Transferred %g/%g items from %s' % (len(state_dict), len(model.state_dict()), weights)) # report
else:
model = Model(opt.cfg, ch=3, nc=nc).to(device) # create 就是咱们之前讲的创建模型那块
# Freeze 要不要冻结一些层,做迁移学习.感觉没必要。。。
freeze = ['', ] # parameter names to freeze (full or partial)
if any(freeze):
for k, v in model.named_parameters():
if any(x in k for x in freeze):
print('freezing %s' % k)
v.requires_grad = False
# Optimizer
nbs = 64 # nominal batch size 累计多少次更新一次模型,咱们的话就是64/16=4次,相当于扩大batch
accumulate = max(round(nbs / total_batch_size), 1) # accumulate loss before optimizing
hyp['weight_decay'] *= total_batch_size * accumulate / nbs # scale weight_decay
pg0, pg1, pg2 = [], [], [] # optimizer parameter groups 设置了个优化组:权重,偏置,其他参数
for k, v in model.named_parameters():
v.requires_grad = True
if '.bias' in k:
pg2.append(v) # biases
elif '.weight' in k and '.bn' not in k:
pg1.append(v) # apply weight decay
else:
pg0.append(v) # all else
if opt.adam: #优化器与学习率衰减
optimizer = optim.Adam(pg0, lr=hyp['lr0'], betas=(hyp['momentum'], 0.999)) # adjust beta1 to momentum
else:
optimizer = optim.SGD(pg0, lr=hyp['lr0'], momentum=hyp['momentum'], nesterov=True)
optimizer.add_param_group({'params': pg1, 'weight_decay': hyp['weight_decay']}) # add pg1 with weight_decay
optimizer.add_param_group({'params': pg2}) # add pg2 (biases)
logger.info('Optimizer groups: %g .bias, %g conv.weight, %g other' % (len(pg2), len(pg1), len(pg0)))
del pg0, pg1, pg2
# Scheduler https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.01187.pdf
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.html#OneCycleLR
lf = lambda x: ((1 + math.cos(x * math.pi / epochs)) / 2) * (1 - hyp['lrf']) + hyp['lrf'] # cosine
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lf)
# plot_lr_scheduler(optimizer, scheduler, epochs)
# Resume 这个best_fitness是sum([0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.9]*[精确度, 召回率, mAP@0.5, mAP@0.5:0.95])
# 相当于一个综合指标来判断每一次的得分
start_epoch, best_fitness = 0, 0.0
if pretrained:
# Optimizer 优化器
if ckpt['optimizer'] is not None:
optimizer.load_state_dict(ckpt['optimizer'])
best_fitness = ckpt['best_fitness']
# Results结果
if ckpt.get('training_results') is not None:
with open(results_file, 'w') as file:
file.write(ckpt['training_results']) # write results.txt
# Epochs 训练了多少次了已经
start_epoch = ckpt['epoch'] + 1
if opt.resume:#又保存了一份?新训练的会覆盖之前旧的?
assert start_epoch > 0, '%s training to %g epochs is finished, nothing to resume.' % (weights, epochs)
shutil.copytree(wdir, wdir.parent / f'weights_backup_epoch{start_epoch - 1}') # save previous weights
if epochs < start_epoch:#就是你设置的epoch为100 但是现在模型已经训练了150 那就再训练100
logger.info('%s has been trained for %g epochs. Fine-tuning for %g additional epochs.' %
(weights, ckpt['epoch'], epochs))
epochs += ckpt['epoch'] # finetune additional epochs
del ckpt, state_dict
# Image sizes stride是总的下采样比例 目的是看下数据的大小能不能整除这个比例
gs = int(max(model.stride)) # grid size (max stride)
imgsz, imgsz_test = [check_img_size(x, gs) for x in opt.img_size] # verify imgsz are gs-multiples
# DP mode 如果你的机器里面有过个GPU,需要改一些参数。官网教程:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/475
if cuda and rank == -1 and torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
# SyncBatchNorm 多卡同步做BN
if opt.sync_bn and cuda and rank != -1:
model = torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm.convert_sync_batchnorm(model).to(device)
logger.info('Using SyncBatchNorm()')
# Exponential moving average 滑动平均能让参数更新的更平滑一点不至于波动太大
# 参考博客:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f99f982ad370
ema = ModelEMA(model) if rank in [-1, 0] else None
# DDP mode 多机多卡,有时候DP可能会出现负载不均衡,这个能直接解决该问题。DP用的时候 经常ID为0的GPU干满,其他的没咋用
if cuda and rank != -1:
model = DDP(model, device_ids=[opt.local_rank], output_device=opt.local_rank)
# Trainloader 创建dataloader就是我们一开始讲的部分
dataloader, dataset = create_dataloader(train_path, imgsz, batch_size, gs, opt,
hyp=hyp, augment=True, cache=opt.cache_images, rect=opt.rect,
rank=rank, world_size=opt.world_size, workers=opt.workers)
mlc = np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0].max() # max label class 判断类别数是否正常
nb = len(dataloader) # number of batches
assert mlc < nc, 'Label class %g exceeds nc=%g in %s. Possible class labels are 0-%g' % (mlc, nc, opt.data, nc - 1)
# Process 0
if rank in [-1, 0]:
ema.updates = start_epoch * nb // accumulate # set EMA updates
testloader = create_dataloader(test_path, imgsz_test, total_batch_size, gs, opt,
hyp=hyp, augment=False, cache=opt.cache_images and not opt.notest, rect=True,
rank=-1, world_size=opt.world_size, workers=opt.workers)[0] # testloader
if not opt.resume:
labels = np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)
c = torch.tensor(labels[:, 0]) # classes
# cf = torch.bincount(c.long(), minlength=nc) + 1. # frequency
# model._initialize_biases(cf.to(device))
plot_labels(labels, save_dir=log_dir)
if tb_writer:
# tb_writer.add_hparams(hyp, {}) # causes duplicate https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/384
tb_writer.add_histogram('classes', c, 0)
# Anchors
if not opt.noautoanchor:
check_anchors(dataset, model=model, thr=hyp['anchor_t'], imgsz=imgsz)
# Model parameters 类别个数,
hyp['cls'] *= nc / 80. # scale coco-tuned hyp['cls'] to current dataset
model.nc = nc # attach number of classes to model
model.hyp = hyp # attach hyperparameters to model
model.gr = 1.0 # iou loss ratio (obj_loss = 1.0 or iou)
#根据标签设置各类别数据初始权重
model.class_weights = labels_to_class_weights(dataset.labels, nc).to(device) # attach class weights
model.names = names
# Start training
t0 = time.time()
#热身持续多少个epoch
nw = max(round(hyp['warmup_epochs'] * nb), 1e3) # number of warmup iterations, max(3 epochs, 1k iterations)
# nw = min(nw, (epochs - start_epoch) / 2 * nb) # limit warmup to < 1/2 of training
# 日志要保存的结果,先初始化
maps = np.zeros(nc) # mAP per class
results = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) # P, R, mAP@.5, mAP@.5-.95, val_loss(box, obj, cls)
scheduler.last_epoch = start_epoch - 1 # do not move
#混合精度训练,参考官网说明:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html 1.6新功能 fp32与fp16混合 提速比较多
scaler = amp.GradScaler(enabled=cuda)
#打印信息
logger.info('Image sizes %g train, %g test\n'
'Using %g dataloader workers\nLogging results to %s\n'
'Starting training for %g epochs...' % (imgsz, imgsz_test, dataloader.num_workers, log_dir, epochs))
for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs): # epoch ------------------------------------------------------------------
model.train()
# Update image weights (optional)
if opt.image_weights:
# Generate indices
if rank in [-1, 0]:
cw = model.class_weights.cpu().numpy() * (1 - maps) ** 2 # class weights
iw = labels_to_image_weights(dataset.labels, nc=nc, class_weights=cw) # image weights
dataset.indices = random.choices(range(dataset.n), weights=iw, k=dataset.n) # rand weighted idx
# Broadcast if DDP
if rank != -1:
indices = (torch.tensor(dataset.indices) if rank == 0 else torch.zeros(dataset.n)).int()
dist.broadcast(indices, 0)
if rank != 0:
dataset.indices = indices.cpu().numpy()
# Update mosaic border
# b = int(random.uniform(0.25 * imgsz, 0.75 * imgsz + gs) // gs * gs)
# dataset.mosaic_border = [b - imgsz, -b] # height, width borders
mloss = torch.zeros(4, device=device) # mean losses
if rank != -1: #DDP模式每次取数据的随机种子都不同
dataloader.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
#创建进度条
pbar = enumerate(dataloader)
logger.info(('\n' + '%10s' * 8) % ('Epoch', 'gpu_mem', 'box', 'obj', 'cls', 'total', 'targets', 'img_size'))
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar = tqdm(pbar, total=nb) # progress bar
optimizer.zero_grad()
for i, (imgs, targets, paths, _) in pbar: # batch -------------------------------------------------------------
ni = i + nb * epoch # number integrated batches (since train start)
# 归一化
imgs = imgs.to(device, non_blocking=True).float() / 255.0 # uint8 to float32, 0-255 to 0.0-1.0
# Warmup 热身
if ni <= nw:
xi = [0, nw] # x interp
# model.gr = np.interp(ni, xi, [0.0, 1.0]) # iou loss ratio (obj_loss = 1.0 or iou)
accumulate = max(1, np.interp(ni, xi, [1, nbs / total_batch_size]).round())
for j, x in enumerate(optimizer.param_groups):
# bias lr falls from 0.1 to lr0, all other lrs rise from 0.0 to lr0 lf就是余弦衰退函数
x['lr'] = np.interp(ni, xi, [hyp['warmup_bias_lr'] if j == 2 else 0.0, x['initial_lr'] * lf(epoch)])
if 'momentum' in x:
x['momentum'] = np.interp(ni, xi, [hyp['warmup_momentum'], hyp['momentum']])
# Multi-scale 各种输入的大小,也是随机的范围[imgsz * 0.5, imgsz * 1.5 + gs] 其中gs=32
if opt.multi_scale:
sz = random.randrange(imgsz * 0.5, imgsz * 1.5 + gs) // gs * gs # size
sf = sz / max(imgs.shape[2:]) # scale factor
if sf != 1: #得到新的输入大小
ns = [math.ceil(x * sf / gs) * gs for x in imgs.shape[2:]] # new shape (stretched to gs-multiple)
imgs = F.interpolate(imgs, size=ns, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# Forward
with amp.autocast(enabled=cuda):# 用到了1.6新特性 混合精度
pred = model(imgs) # forward
#总损失,分类损失,回归损失,置信度损失
loss, loss_items = compute_loss(pred, targets.to(device), model) # loss scaled by batch_size
if rank != -1:
loss *= opt.world_size # gradient averaged between devices in DDP mode
# Backward
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
# Optimize 相当于Backward多次才更新一次参数
if ni % accumulate == 0:
scaler.step(optimizer) # optimizer.step
scaler.update()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if ema:
ema.update(model)
# Print 展示信息
if rank in [-1, 0]:
mloss = (mloss * i + loss_items) / (i + 1) # update mean losses
mem = '%.3gG' % (torch.cuda.memory_reserved() / 1E9 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0) # (GB)
s = ('%10s' * 2 + '%10.4g' * 6) % (
'%g/%g' % (epoch, epochs - 1), mem, *mloss, targets.shape[0], imgs.shape[-1])
pbar.set_description(s)
# Plot
if ni < 3:
f = str(log_dir / ('train_batch%g.jpg' % ni)) # filename
result = plot_images(images=imgs, targets=targets, paths=paths, fname=f)
if tb_writer and result is not None:
tb_writer.add_image(f, result, dataformats='HWC', global_step=epoch)
# tb_writer.add_graph(model, imgs) # add model to tensorboard
# end batch ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Scheduler 学习率衰减
lr = [x['lr'] for x in optimizer.param_groups] # for tensorboard
scheduler.step()
# DDP process 0 or single-GPU
if rank in [-1, 0]:
# mAP 更新EMA
if ema:
ema.update_attr(model, include=['yaml', 'nc', 'hyp', 'gr', 'names', 'stride'])
final_epoch = epoch + 1 == epochs
if not opt.notest or final_epoch: # Calculate mAP
results, maps, times = test.test(opt.data,
batch_size=total_batch_size,
imgsz=imgsz_test,
model=ema.ema,
single_cls=opt.single_cls,
dataloader=testloader,
save_dir=log_dir,
plots=epoch == 0 or final_epoch) # plot first and last
# Write
with open(results_file, 'a') as f:
f.write(s + '%10.4g' * 7 % results + '\n') # P, R, mAP@.5, mAP@.5-.95, val_loss(box, obj, cls)
if len(opt.name) and opt.bucket:#这个整不了,涉及上传
os.system('gsutil cp %s gs://%s/results/results%s.txt' % (results_file, opt.bucket, opt.name))
# Tensorboard
if tb_writer:
tags = ['train/box_loss', 'train/obj_loss', 'train/cls_loss', # train loss
'metrics/precision', 'metrics/recall', 'metrics/mAP_0.5', 'metrics/mAP_0.5:0.95',
'val/box_loss', 'val/obj_loss', 'val/cls_loss', # val loss
'x/lr0', 'x/lr1', 'x/lr2'] # params
for x, tag in zip(list(mloss[:-1]) + list(results) + lr, tags):
tb_writer.add_scalar(tag, x, epoch)
# Update best mAP
fi = fitness(np.array(results).reshape(1, -1)) # weighted combination of [P, R, mAP@.5, mAP@.5-.95]
if fi > best_fitness:
best_fitness = fi
# Save model
save = (not opt.nosave) or (final_epoch and not opt.evolve)
if save:
with open(results_file, 'r') as f: # create checkpoint
ckpt = {'epoch': epoch,
'best_fitness': best_fitness,
'training_results': f.read(),
'model': ema.ema,
'optimizer': None if final_epoch else optimizer.state_dict()}
# Save last, best and delete
torch.save(ckpt, last)
if best_fitness == fi:
torch.save(ckpt, best)
del ckpt
# end epoch ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# end training
if rank in [-1, 0]:
# Strip optimizers
n = opt.name if opt.name.isnumeric() else ''
fresults, flast, fbest = log_dir / f'results{n}.txt', wdir / f'last{n}.pt', wdir / f'best{n}.pt'
for f1, f2 in zip([wdir / 'last.pt', wdir / 'best.pt', results_file], [flast, fbest, fresults]):
if os.path.exists(f1):
os.rename(f1, f2) # rename
if str(f2).endswith('.pt'): # is *.pt
strip_optimizer(f2) # strip optimizer
os.system('gsutil cp %s gs://%s/weights' % (f2, opt.bucket)) if opt.bucket else None # upload
# Finish
if not opt.evolve:
plot_results(save_dir=log_dir) # save as results.png
logger.info('%g epochs completed in %.3f hours.\n' % (epoch - start_epoch + 1, (time.time() - t0) / 3600))
dist.destroy_process_group() if rank not in [-1, 0] else None
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
return results
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default=r'..\weights\yolov5s.pt', help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default=r'..\models\yolov5s.yaml', help='model.yaml path')#网络配置
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default=r'..\MaskDataSet\data.yaml', help='data.yaml path')#数据
parser.add_argument('--hyp', type=str, default='../data/hyp.scratch.yaml', help='hyperparameters path')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=300)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=2, help='total batch size for all GPUs')
parser.add_argument('--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640, 640], help='[train, test] image sizes')
parser.add_argument('--rect', action='store_true', help='rectangular training')#矩形训练
parser.add_argument('--resume', nargs='?', const=True, default=False, help='resume most recent training')#接着之前的训练
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='only save final checkpoint')#不保存
parser.add_argument('--notest', action='store_true', help='only test final epoch')#不测试
parser.add_argument('--noautoanchor', action='store_true', help='disable autoanchor check')#是否调整候选框
parser.add_argument('--evolve', action='store_true', help='evolve hyperparameters')#超参数更新
parser.add_argument('--bucket', type=str, default='', help='gsutil bucket')
parser.add_argument('--cache-images', action='store_true', help='cache images for faster training')#缓存图片
parser.add_argument('--image-weights', action='store_true', help='use weighted image selection for training')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='', help='renames experiment folder exp{N} to exp{N}_{name} if supplied')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--multi-scale', action='store_true', help='vary img-size +/- 50%%')#是否多尺度训练
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='train as single-class dataset')#是否一个类别
parser.add_argument('--adam', action='store_true', help='use torch.optim.Adam() optimizer')#优化器选择
parser.add_argument('--sync-bn', action='store_true', help='use SyncBatchNorm, only available in DDP mode')#跨GPU的BN
parser.add_argument('--local_rank', type=int, default=-1, help='DDP parameter, do not modify')#GPU ID
parser.add_argument('--logdir', type=str, default='runs/', help='logging directory')
parser.add_argument('--workers', type=int, default=0, help='maximum number of dataloader workers')#windows的同学别改
opt = parser.parse_args()
# Set DDP variables WORLD_SIZE:进程数 RANK:进程编号
opt.total_batch_size = opt.batch_size
opt.world_size = int(os.environ['WORLD_SIZE']) if 'WORLD_SIZE' in os.environ else 1
opt.global_rank = int(os.environ['RANK']) if 'RANK' in os.environ else -1
set_logging(opt.global_rank)
if opt.global_rank in [-1, 0]:
check_git_status()
# Resume
if opt.resume: # resume an interrupted run 是否继续训练
#传入模型的路径或者最后一次跑的模型(在runs中有last.pt)
ckpt = opt.resume if isinstance(opt.resume, str) else get_latest_run() # specified or most recent path
log_dir = Path(ckpt).parent.parent # runs/exp0
assert os.path.isfile(ckpt), 'ERROR: --resume checkpoint does not exist'
with open(log_dir / 'opt.yaml') as f:
opt = argparse.Namespace(**yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)) # replace
opt.cfg, opt.weights, opt.resume = '', ckpt, True
logger.info('Resuming training from %s' % ckpt)
else:#加载之前配置好的参数
# opt.hyp = opt.hyp or ('hyp.finetune.yaml' if opt.weights else 'hyp.scratch.yaml')
opt.data, opt.cfg, opt.hyp = check_file(opt.data), check_file(opt.cfg), check_file(opt.hyp) # check files
assert len(opt.cfg) or len(opt.weights), 'either --cfg or --weights must be specified'
opt.img_size.extend([opt.img_size[-1]] * (2 - len(opt.img_size))) # extend to 2 sizes (train, test)
log_dir = increment_dir(Path(opt.logdir) / 'exp', opt.name) # runs/exp1
device = select_device(opt.device, batch_size=opt.batch_size)
# DDP mode 分布式训练,没有多卡的同学略过
if opt.local_rank != -1:
assert torch.cuda.device_count() > opt.local_rank
torch.cuda.set_device(opt.local_rank)#选择GPU
device = torch.device('cuda', opt.local_rank)
dist.init_process_group(backend='nccl', init_method='env://') # distributed backend
assert opt.batch_size % opt.world_size == 0, '--batch-size must be multiple of CUDA device count'
opt.batch_size = opt.total_batch_size // opt.world_size
logger.info(opt)
with open(opt.hyp) as f:
hyp = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader) # load hyps
# Train
if not opt.evolve:
tb_writer = None
if opt.global_rank in [-1, 0]:
logger.info(f'Start Tensorboard with "tensorboard --logdir {opt.logdir}", view at http://localhost:6006/')
tb_writer = SummaryWriter(log_dir=log_dir) # runs/exp0
train(hyp, opt, device, tb_writer)
# 参数搜索与突变
# Evolve hyperparameters (optional) 参考github issue:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/392
else:
# Hyperparameter evolution metadata (mutation scale 0-1, lower_limit, upper_limit)
meta = {'lr0': (1, 1e-5, 1e-1), # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
'lrf': (1, 0.01, 1.0), # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
'momentum': (0.3, 0.6, 0.98), # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
'weight_decay': (1, 0.0, 0.001), # optimizer weight decay
'warmup_epochs': (1, 0.0, 5.0), # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
'warmup_momentum': (1, 0.0, 0.95), # warmup initial momentum
'warmup_bias_lr': (1, 0.0, 0.2), # warmup initial bias lr
'box': (1, 0.02, 0.2), # box loss gain
'cls': (1, 0.2, 4.0), # cls loss gain
'cls_pw': (1, 0.5, 2.0), # cls BCELoss positive_weight
'obj': (1, 0.2, 4.0), # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
'obj_pw': (1, 0.5, 2.0), # obj BCELoss positive_weight
'iou_t': (0, 0.1, 0.7), # IoU training threshold
'anchor_t': (1, 2.0, 8.0), # anchor-multiple threshold
'anchors': (2, 2.0, 10.0), # anchors per output grid (0 to ignore)
'fl_gamma': (0, 0.0, 2.0), # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
'hsv_h': (1, 0.0, 0.1), # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_s': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_v': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
'degrees': (1, 0.0, 45.0), # image rotation (+/- deg)
'translate': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image translation (+/- fraction)
'scale': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image scale (+/- gain)
'shear': (1, 0.0, 10.0), # image shear (+/- deg)
'perspective': (0, 0.0, 0.001), # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
'flipud': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image flip up-down (probability)
'fliplr': (0, 0.0, 1.0), # image flip left-right (probability)
'mosaic': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
'mixup': (1, 0.0, 1.0)} # image mixup (probability)
assert opt.local_rank == -1, 'DDP mode not implemented for --evolve'
opt.notest, opt.nosave = True, True # only test/save final epoch
# ei = [isinstance(x, (int, float)) for x in hyp.values()] # evolvable indices
yaml_file = Path(opt.logdir) / 'evolve' / 'hyp_evolved.yaml' # save best result here
if opt.bucket:
os.system('gsutil cp gs://%s/evolve.txt .' % opt.bucket) # download evolve.txt if exists
for _ in range(300): # generations to evolve
if os.path.exists('evolve.txt'): # if evolve.txt exists: select best hyps and mutate
# Select parent(s)
parent = 'single' # parent selection method: 'single' or 'weighted'
x = np.loadtxt('evolve.txt', ndmin=2)
n = min(5, len(x)) # number of previous results to consider
x = x[np.argsort(-fitness(x))][:n] # top n mutations
w = fitness(x) - fitness(x).min() # weights
if parent == 'single' or len(x) == 1:
# x = x[random.randint(0, n - 1)] # random selection
x = x[random.choices(range(n), weights=w)[0]] # weighted selection
elif parent == 'weighted':
x = (x * w.reshape(n, 1)).sum(0) / w.sum() # weighted combination
# Mutate
mp, s = 0.8, 0.2 # mutation probability, sigma
npr = np.random
npr.seed(int(time.time()))
g = np.array([x[0] for x in meta.values()]) # gains 0-1
ng = len(meta)
v = np.ones(ng)
while all(v == 1): # mutate until a change occurs (prevent duplicates)
v = (g * (npr.random(ng) < mp) * npr.randn(ng) * npr.random() * s + 1).clip(0.3, 3.0)
for i, k in enumerate(hyp.keys()): # plt.hist(v.ravel(), 300)
hyp[k] = float(x[i + 7] * v[i]) # mutate
# Constrain to limits
for k, v in meta.items():
hyp[k] = max(hyp[k], v[1]) # lower limit
hyp[k] = min(hyp[k], v[2]) # upper limit
hyp[k] = round(hyp[k], 5) # significant digits
# Train mutation
results = train(hyp.copy(), opt, device)
# Write mutation results
print_mutation(hyp.copy(), results, yaml_file, opt.bucket)
# Plot results
plot_evolution(yaml_file)
print(f'Hyperparameter evolution complete. Best results saved as: {yaml_file}\n'
f'Command to train a new model with these hyperparameters: $ python train.py --hyp {yaml_file}')
就这些了,欢迎大家留言讨论,累了,看书去了!