视觉SLAM十四讲——ch13学习过程及代码祥读
- 0. 可以下载文件的网址
- 1. 重读《视觉SLAM十四讲》ch13实践设计SLAM系统
- 2. 主函数的阅读
- 3. config配置文件
- 4. visual_odometry.cpp视觉里程计文件
- 5. frontend.cpp前端文件(重要文件1)
- 6. backend.cpp后端文件(重要文件2)
0. 可以下载文件的网址
本文主要是介绍比较主要的文件,已经对每个文件进行了详细阅读和注释,如果需要,可以参考:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_44164791/87935340
实践用到的数据可以参考的下载地址:
https://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
如果需要相对应的位姿文件,也就是如果想绘制出完整轨迹,可以参考:
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_44164791/87935348
1. 重读《视觉SLAM十四讲》ch13实践设计SLAM系统
这个过程参考了以下文章:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/372956625
2. 主函数的阅读
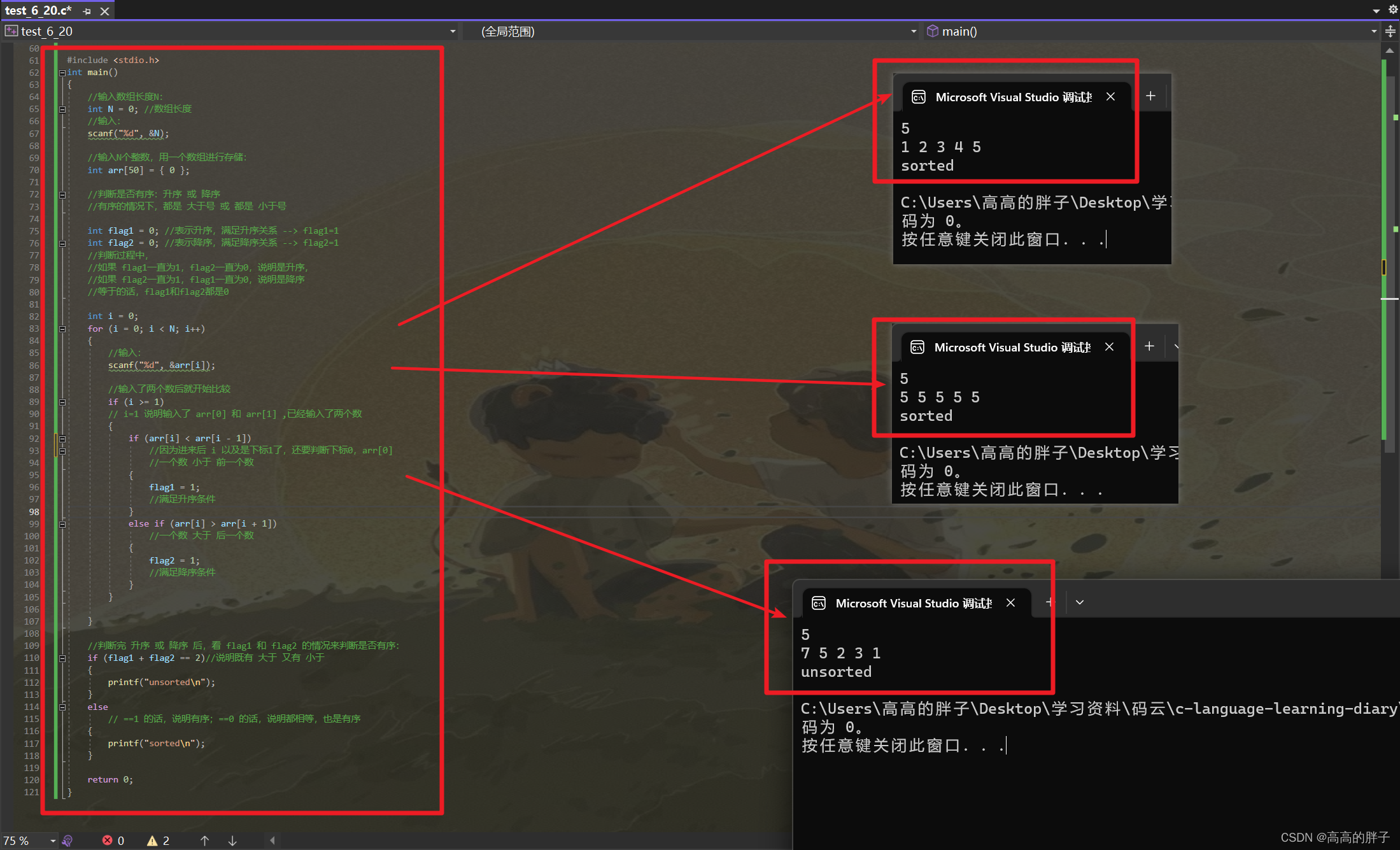
run_kitti_stereo.cpp文件
我们从开头开始阅读,可以看到第10行我们需要用的配置文件,可以参考3中的内容。
然后可以看到第18行,我们可以看到自己定义的一个类,可以在头文件myslam/visual_odometry.h中查看。
接着我们可以看到第22行的初始化,直接转到visual_odometry.cpp文件,也就是本文的目录4。
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-5-4.
//
//gflags是一个谷歌的库https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/369214077,官方文档库为https://gflags.github.io/gflags/
#include <gflags/gflags.h>
#include "myslam/visual_odometry.h"
//DEFINE_string参数1是一个变量;参数2是用户指定,给到参数1的;参数3,类似一个说明为这个变量的提示信息
//在程序中使用DEFINE_XXX函数定义的变量时,需要在每个变量前加上FLAGS_前缀。
DEFINE_string(config_file, "/home/fighter/project/slambook2/ch14/config/default.yaml", "config file path");
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
//怎么通过命令行设置?只需要在main函数后,添加::gflags::ParseCommandLineFlags函数(google::ParseCommandLineFlags),就能解析命令行,即解析argc、argv参数。
//为了能够解析命令行的参数
google::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, true);
//首先实例化了一个VisualOdometry类的类指针vo,传入config的地址
myslam::VisualOdometry::Ptr vo(
new myslam::VisualOdometry(FLAGS_config_file));
//VO初始化,assert 只在 debug 模式下存在,判断是否初始化成功
assert(vo->Init() == true);
//运行Run函数
vo->Run();
return 0;
}
3. config配置文件
default.yaml文件:
%YAML:1.0
# data
# the tum dataset directory, change it to yours!
# dataset_dir: /media/xiang/Data/Dataset/Kitti/dataset/sequences/00
dataset_dir: /home/fighter/slam/slambook2/ch13/00
# camera intrinsics
# 相机内参数,像素坐标系和成像平面之间,相差一个缩放和一个原点的平移,设在u轴上缩放了a倍,在v轴上缩放了b倍。同时原点平移了[cx,cy];
# 把af合并成fx,把bf合并成fy;f为焦距
# 所以,相机内参数为fx,fy,cx,cy
camera.fx: 517.3
camera.fy: 516.5
camera.cx: 325.1
camera.cy: 249.7
num_features: 150
num_features_init: 50
num_features_tracking: 50
4. visual_odometry.cpp视觉里程计文件
visual_odometry.cpp
从上向下阅读,第39行,可以跳转到frontend.cpp文件,参考本文目录5.
同样,第40行,可以跳至backend.cpp文件,参考本目录的6.
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-5-4.
//
#include "myslam/visual_odometry.h"
#include <chrono>
#include "myslam/config.h"
namespace myslam {
//VisualOdometry函数中的config_path继承自config_file_path_的config_path???继承不继承不清楚,但二者是相等的
//C++Primer的p237下
//VisualOdometry中的config_path为形参,使用string对象初始化config_file_path_
VisualOdometry::VisualOdometry(std::string &config_path)
: config_file_path_(config_path) {}
//视觉里程计初始化
bool VisualOdometry::Init() {
// read from config file(调用Config::SetParameterFile()函数读取配置文件,如果找不到对应文件(如果上一步没有成功建文件)就返回false。)
//config.cpp
if (Config::SetParameterFile(config_file_path_) == false) {
return false;
}
//yaml文件中dataset_dir: /home/xiaoduan/slambook2/ch14/00;此时,dataset_锁定到了数据文件夹
dataset_ =
Dataset::Ptr(new Dataset(Config::Get<std::string>("dataset_dir")));
//通过Dataset::Init()函数设置相机的内参数,以及双目相机的外参数;
//检测两个值是否相等,即建车是否初始化成功,如果不成立,输出信息后将退出;
CHECK_EQ(dataset_->Init(), true);
//初始化成功后,意味着能够正确获取数据,然后进行其他操作
// create components and links(创建组件和链接)
/*
实例化并初始化frontend_,backend_,map_,viewer_四个对象。
并且创建3个线程之间的联系,其实就是shared_ptr的初始化,这里和ORB-SLAM2的初始化创建线程的过程很像哈。
但是实际上在这个工程里面和SLAM相关的只有两个线程,前端一个线程,后端一个线程,还有一个线程是显示用的,
ORBSLAM里面总共有4个线程,前端线程、后端线程、回环线程+显示线程。我们看下初始化具体做了啥,我们看下每个类的构造函数。
*/
frontend_ = Frontend::Ptr(new Frontend);
backend_ = Backend::Ptr(new Backend);
map_ = Map::Ptr(new Map);
viewer_ = Viewer::Ptr(new Viewer);
frontend_->SetBackend(backend_);
frontend_->SetMap(map_);
frontend_->SetViewer(viewer_);
frontend_->SetCameras(dataset_->GetCamera(0), dataset_->GetCamera(1));
backend_->SetMap(map_);
backend_->SetCameras(dataset_->GetCamera(0), dataset_->GetCamera(1));
viewer_->SetMap(map_);
return true;
}
//视觉里程计运行
void VisualOdometry::Run() {
while (1) {
LOG(INFO) << "VO is running";
if (Step() == false) { //如果步骤错误,结束循环也就是结束运行
break;
}
}
//遍历完所有数据后,结束后端和可视化线程
backend_->Stop();
viewer_->Close();
LOG(INFO) << "VO exit";
}
bool VisualOdometry::Step() {
Frame::Ptr new_frame = dataset_->NextFrame(); //NextFrame() 就是从数据集里面读取一下帧图像,然后调用 Frame::CreateFrame() 函数为每一帧赋一个id号 。
if (new_frame == nullptr) return false; //如果没有读取到数据,则直接结束
auto t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); //记录当前时间点
bool success = frontend_->AddFrame(new_frame); //利用success记录是否成功插入帧
auto t2 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); //记录当前时间点,前后时间的记录来输出插入帧所花费的时间
auto time_used =
std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
LOG(INFO) << "VO cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds.";
return success;
}
} // namespace myslam
5. frontend.cpp前端文件(重要文件1)
frontend.cpp
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-5-2.
//
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc_c.h>
#include "myslam/algorithm.h"
#include "myslam/backend.h"
#include "myslam/config.h"
#include "myslam/feature.h"
#include "myslam/frontend.h"
#include "myslam/g2o_types.h"
#include "myslam/map.h"
#include "myslam/viewer.h"
namespace myslam {
/*
也就是前端的初始化主要就是根据配置文件(Config类) 的参数来创建GFTT的特征点提取器。
num_features_是每帧最多提取的特征点数量,
此外还保存一个参数num_features_init_,这个参数在后面的地图初始化中会用到。
GFTTDetector特征点提取器
*/
Frontend::Frontend() {
/*
在 ”光流跟踪“ 中,使用了 Harris 角点作为 LK 光流跟踪输入点。角点定义为在两个方向上均有较大梯度变化的小区域,使用自相关函数描述。
自相关函数为为图像平移前后某一个区域的相似度度量。图像可以看作二维平面上的连续函数,使用泰勒级数可以将自相关函数转换为自相关矩阵。
通过分析自相关矩阵的特征值,可以判断在该区域内各个方向上梯度变化情况,从而决定是否为角点。
GFTT是一个特征检测器,是Harris和GFTT检测算法检测特征值二合一的方法,具体使用哪一个由输入的参数决定
特点:只提取特征点,不提取描述子
static Ptr<GFTTDetector> create( int maxCorners=1000, double qualityLevel=0.01, double minDistance=1,
int blockSize=3, bool useHarrisDetector=false, double k=0.04 );
maxCorners 决定提取关键点最大个数;
qualityLevel 表示关键点强度阈值,只保留大于该阈值的关键点(阈值 = 最强关键点强度 * qualityLevel);
minDistance 决定关键点间的最小距离;
blockSize 决定自相关函数累加区域,也决定了 Sobel 梯度时窗口尺寸;
useHarrisDetector 决定使用 Harris 判定依据还是 Shi-Tomasi 判定依据;
k 仅在使用 Harris 判定依据时有效;
*/
gftt_ =
cv::GFTTDetector::create(Config::Get<int>("num_features"), 0.01, 20);//num_features是什么???
num_features_init_ = Config::Get<int>("num_features_init");
num_features_ = Config::Get<int>("num_features");
}
//增加帧
bool Frontend::AddFrame(myslam::Frame::Ptr frame) {
//给到当前帧的副本是为了线程间互斥???
current_frame_ = frame;
//判断前端状态
switch (status_) {
//如果前段状态是初始化则执行立体初始化
case FrontendStatus::INITING:
StereoInit();
break;
//如果好继续向下
case FrontendStatus::TRACKING_GOOD:
//如果不好
case FrontendStatus::TRACKING_BAD:
//追踪
Track(); //跟踪结束返回true
break;
case FrontendStatus::LOST:
Reset();
break;
}
last_frame_ = current_frame_;//对当前帧操作完毕,将当前帧置为上一帧
return true;
}
//正常状态下的跟踪
bool Frontend::Track() {
//用上一帧位姿获得当前位姿估计的初始值
if (last_frame_) {
current_frame_->SetPose(relative_motion_ * last_frame_->Pose()); //匀速模型
}
//LK光流匹配上一帧,返回的是匹配到的成对点的数量
int num_track_last = TrackLastFrame(); //根据上一帧的特征点,用光流匹配当前特征点位置
tracking_inliers_ = EstimateCurrentPose(); //G2O图优化估计当前帧位姿;G2O是图优化的库,图优化——————>非线性优化+图论
//根据追踪到的正常数值数量和设定的正常追踪数量50相比,根据比较判断确定当前状态的复本?
if (tracking_inliers_ > num_features_tracking_) { //跟踪点大于50个则状态较好
// tracking good
status_ = FrontendStatus::TRACKING_GOOD; // 修改标志位
} else if (tracking_inliers_ > num_features_tracking_bad_) {//跟踪点小于50个大于20个则状态较坏
// tracking bad
status_ = FrontendStatus::TRACKING_BAD; //修改标志位
} else {
// lost
status_ = FrontendStatus::LOST; //丢失
}
InsertKeyframe(); //将当前帧设置为关键帧并将其插入后端
relative_motion_ = current_frame_->Pose() * last_frame_->Pose().inverse();
if (viewer_) viewer_->AddCurrentFrame(current_frame_);//对可视化同样加入当前帧
return true;
}
//插入关键帧
bool Frontend::InsertKeyframe() {
// 关键点足够多,还不需要修改关键帧
if (tracking_inliers_ >= num_features_needed_for_keyframe_) {
// still have enough features, don't insert keyframe
return false;
}
//光流追踪到的特征点少于80个的时间插入关键帧
// current frame is a new keyframe
//当前帧设置为关键帧
current_frame_->SetKeyFrame();
//将当前帧插入到地图中
map_->InsertKeyFrame(current_frame_);
LOG(INFO) << "Set frame " << current_frame_->id_ << " as keyframe "
<< current_frame_->keyframe_id_;
//将新增的关键帧内的地图点
SetObservationsForKeyFrame();
//出现关键帧后需要重新匹配
//提取当前帧(左)关键点
DetectFeatures(); // detect new features
// track in right image
FindFeaturesInRight();
// triangulate map points // 三维重建
TriangulateNewPoints();
// update backend because we have a new keyframe
backend_->UpdateMap();
if (viewer_) viewer_->UpdateMap();
return true; //成功插入会返回true
}
//将关键帧的特征点添加到地图
void Frontend::SetObservationsForKeyFrame() {
for (auto &feat : current_frame_->features_left_) {
auto mp = feat->map_point_.lock();
if (mp) mp->AddObservation(feat);//加入观测到的特征点
}
}
//三角化新的关键点
int Frontend::TriangulateNewPoints() {
std::vector<SE3> poses{camera_left_->pose(), camera_right_->pose()}; //建立一个位姿容器,里面有左右相机观测到的位姿
SE3 current_pose_Twc = current_frame_->Pose().inverse(); //当前帧的位姿矩阵转换?
int cnt_triangulated_pts = 0;
//遍历整个地图所有的左侧图像地图点
for (size_t i = 0; i < current_frame_->features_left_.size(); ++i) {
if (current_frame_->features_left_[i]->map_point_.expired() &&
current_frame_->features_right_[i] != nullptr) {
// 左图的特征点未关联地图点且存在右图匹配点,尝试三角化————>图像构建初始化地图和估计的时候都使用到了三角化
std::vector<Vec3> points{
camera_left_->pixel2camera(
Vec2(current_frame_->features_left_[i]->position_.pt.x,
current_frame_->features_left_[i]->position_.pt.y)),
camera_right_->pixel2camera(
Vec2(current_frame_->features_right_[i]->position_.pt.x,
current_frame_->features_right_[i]->position_.pt.y))};
Vec3 pworld = Vec3::Zero();
if (triangulation(poses, points, pworld) && pworld[2] > 0) {
auto new_map_point = MapPoint::CreateNewMappoint();
pworld = current_pose_Twc * pworld;
new_map_point->SetPos(pworld);
new_map_point->AddObservation(
current_frame_->features_left_[i]);
new_map_point->AddObservation(
current_frame_->features_right_[i]);
current_frame_->features_left_[i]->map_point_ = new_map_point;
current_frame_->features_right_[i]->map_point_ = new_map_point;
map_->InsertMapPoint(new_map_point);
cnt_triangulated_pts++;
}
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "new landmarks: " << cnt_triangulated_pts;
return cnt_triangulated_pts;//返回所有三角化的点?
}
/*估计当前帧位姿;与backend.cpp中的Optimize中的g2o优化相似,第54行,区别在于此处无需优化,只是估计出来,新建一些信息
*返回计算成功匹配的数量
*https://blog.csdn.net/wujianing_110117/article/details/116253914
*/
int Frontend::EstimateCurrentPose() {
// setup g2o(g2o过程) 图优化:单节点+多条一元边
// 块求解器BlockSolver
typedef g2o::BlockSolver_6_3 BlockSolverType; //pose is 6 dof, landmark is 3 dof(位姿是6维度,地标是3维度)
// 第1步:创建一个线性求解器LinearSolver
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType>
LinearSolverType; //线性求解器
// 第3步:创建总求解器solver。并从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选一个,再用上述块求解器BlockSolver初始化
//此处类似与加锁互斥?确定一个求解器并加锁
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg( //求解器梯度下降方法采用LM
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(
g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
// 第4步:创建终极大boss 稀疏优化器(SparseOptimizer)构造Levenberg算法,该算法将使用给定的求解器来求解线性化系统。
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; //图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); //设置求解器,这里是三角化?
// 节点:一个节点(位姿)
// vertex定义图优化问题中的定点,顶点是当前帧到上一帧的位姿变化
// 第5步:定义图的顶点和边。并添加到SparseOptimizer中
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose(相机在图优化问题中的定点的位姿)
//设置图中节点的id,确保改变id后图保持一致
vertex_pose->setId(0);
//设置顶点的估计也调用updateCache()
vertex_pose->setEstimate(current_frame_->Pose());
/*
* adds a new vertex. The new vertex is then "taken".
* @return false if a vertex with the same id as v is already in the graph, true otherwise.
* 添加一个新顶点。新的顶点被“获取”。
* @返回false,如果与v具有相同id的顶点已经在图中,否则返回true。
*/
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
// K,相机内参数K
Mat33 K = camera_left_->K();
// edges 定义图优化问题的边,边是地图点(3D世界坐标)在当前帧的投影位置(像素坐标)
// 边:每对对应点都是
int index = 1;
std::vector<EdgeProjectionPoseOnly *> edges; //边的容器 EdgeProjectionPoseOnly仅估计位姿的一元边
std::vector<Feature::Ptr> features; //特征点的容器
// 往图中增加边
for (size_t i = 0; i < current_frame_->features_left_.size(); ++i) {//循环遍历当前帧的左侧图
auto mp = current_frame_->features_left_[i]->map_point_.lock();//判断地图点相关线程没有上锁
//没有上锁的时候,建立相关的边
if (mp) {
features.push_back(current_frame_->features_left_[i]);
EdgeProjectionPoseOnly *edge =
new EdgeProjectionPoseOnly(mp->pos_, K);//建立的是一元边
edge->setId(index); //设置边:每个路标点和其任意一个观测帧的位姿都要建立一条边
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose); //将超边缘上的第i个顶点设置为提供的指针;————>连接顶点
edge->setMeasurement(
toVec2(current_frame_->features_left_[i]->position_.pt)); //由边表示的测量的访问函数,对应的像素点
//设置边的信息矩阵:setInformation约束的信息矩阵,Identity返回单位矩阵的表达式(不一定是平方)
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity()); // 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵(之逆)
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber); //设置边鲁棒核函数
edges.push_back(edge); //将设置好的边推入容器边中
optimizer.addEdge(edge); //在optimizer(图模型)中加入该边,如果失败返回false
index++; //???
}
}
// estimate the Pose the determine the outliers(估计姿态,确定异常值)
const double chi2_th = 5.991; //卡方检验
int cnt_outlier = 0;
for (int iteration = 0; iteration < 4; ++iteration) {
vertex_pose->setEstimate(current_frame_->Pose());
optimizer.initializeOptimization(); //初始化结构以优化整个图,失败返回ifalse
optimizer.optimize(10);
cnt_outlier = 0;
// count the outliers // 计算异常
for (size_t i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) {
auto e = edges[i];
if (features[i]->is_outlier_) {
e->computeError();
}
//阈值:5.991(设置边缘的水平)
if (e->chi2() > chi2_th) {
features[i]->is_outlier_ = true;//标记
e->setLevel(1);
cnt_outlier++;
} else {
features[i]->is_outlier_ = false;
e->setLevel(0);
};
//???==2时,为什么?未相连任何的顶点?
if (iteration == 2) {
e->setRobustKernel(nullptr);
}
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "Outlier/Inlier in pose estimating: " << cnt_outlier << "/"
<< features.size() - cnt_outlier;
// Set pose and outlier // 记录位姿及异常的匹配结果
current_frame_->SetPose(vertex_pose->estimate());
LOG(INFO) << "Current Pose = \n" << current_frame_->Pose().matrix();
//遍历后,将所有异常值初始化
for (auto &feat : features) {
if (feat->is_outlier_) {
feat->map_point_.reset();
feat->is_outlier_ = false; // maybe we can still use it in future
}
}
return features.size() - cnt_outlier; //计算成功匹配的数量
}
//跟踪上一帧
int Frontend::TrackLastFrame() {
//和第398行中的LK光流追踪相似?看着好像相同
// use LK flow to estimate points in the right image(在右侧图中?)
std::vector<cv::Point2f> kps_last, kps_current;
for (auto &kp : last_frame_->features_left_) {
if (kp->map_point_.lock()) { //如果关键点上锁
// use project point(使用项目点)
auto mp = kp->map_point_.lock(); //复制给一个mp
// 将世界坐标系中的坐标投影到像素坐标系上
auto px =
camera_left_->world2pixel(mp->pos_, current_frame_->Pose());
//关键帧的上一个容器中推入匹配到的关键点
kps_last.push_back(kp->position_.pt);
//当前帧中推入对应的像素坐标系上的坐标
kps_current.push_back(cv::Point2f(px[0], px[1]));
} else { //没有上锁,直接推入对应的点
kps_last.push_back(kp->position_.pt);
kps_current.push_back(kp->position_.pt);
}
}
std::vector<uchar> status; // 设置一个状态的容器
Mat error; //设置一个error矩阵
//opencv自带的光流跟踪函数
/*
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42905141/article/details/93745116
void cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(cv::InputArray prevImg,
cv::InputArray nextImg,
cv::InputArray prevPts,
cv::InputOutputArray nextPts,
cv::OutputArray status,
cv::OutputArray err,
cv::Size winSize = cv::Size(21, 21),
int maxLevel = 3,
cv::TermCriteria criteria = cv::TermCriteria((TermCriteria::COUNT) + (TermCriteria::EPS),
30,
(0.01000000000000000021)),
int flags = 0,
double minEigThreshold = (0.0001000000000000000048))
Calculates an optical flow for a sparse feature set using the iterative Lucas-Kanade method with pyramids.
(利用金字塔迭代Lucas-Kanade方法计算稀疏特征集的光流。)金字塔迭代书P156页
参数:
prevImg – first 8-bit input image or pyramid constructed by buildOpticalFlowPyramid.
nextImg – second input image or pyramid of the same size and the same type as prevImg.
prevPts – vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found; point coordinates must be single-precision floating-point numbers.
nextPts – output vector of 2D points (with single-precision floating-point coordinates) containing the calculated new positions of input features in the second image; when OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW flag is passed, the vector must have the same size as in the input.
二维点(单精度浮点坐标)的输出向量,包含第二幅图像中计算出的输入特征的新位置;当传递OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW标志时,vector必须具有与输入中相同的大小。
status – output status vector (of unsigned chars); each element of the vector is set to 1 if the flow for the corresponding features has been found, otherwise, it is set to 0.
输出状态向量(无符号字符);如果找到对应特征的流,则将向量的每个元素设为1,否则设为0。
err – output vector of errors; each element of the vector is set to an error for the corresponding feature, type of the error measure can be set in flags parameter; if the flow wasn't found then the error is not defined (use the status parameter to find such cases).
winSize – size of the search window at each pyramid level.
maxLevel – 0-based maximal pyramid level number; if set to 0, pyramids are not used (single level), if set to 1, two levels are used, and so on; if pyramids are passed to input then algorithm will use as many levels as pyramids have but no more than maxLevel.
criteria – parameter, specifying the termination criteria of the iterative search algorithm (after the specified maximum number of iterations criteria.maxCount or when the search window moves by less than criteria.epsilon.
flags – operation flags: - **OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW** uses initial estimations, stored in nextPts; if the flag is not set, then prevPts is copied to nextPts and is considered the initial estimate. - **OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS** use minimum eigen values as an error measure (see minEigThreshold description); if the flag is not set, then L1 distance between patches around the original and a moved point, divided by number of pixels in a window, is used as a error measure.
minEigThreshold – the algorithm calculates the minimum eigen value of a 2x2 normal matrix of optical flow equations (this matrix is called a spatial gradient matrix in
备注:
- An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/lkdemo.cpp - (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_track.py - (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade tracker for homography matching can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_homography.py
*/
cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(
last_frame_->left_img_, current_frame_->left_img_, kps_last,
kps_current, status, error, cv::Size(11, 11), 3,
cv::TermCriteria(cv::TermCriteria::COUNT + cv::TermCriteria::EPS, 30,
0.01),
cv::OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW);
//统计匹配上的特征点个数,并存储
int num_good_pts = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < status.size(); ++i) {
//如果匹配到对应的流则个数加一;并指针继续向后指
if (status[i]) {
cv::KeyPoint kp(kps_current[i], 7);
Feature::Ptr feature(new Feature(current_frame_, kp));
feature->map_point_ = last_frame_->features_left_[i]->map_point_;
current_frame_->features_left_.push_back(feature);
num_good_pts++;
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "Find " << num_good_pts << " in the last image.";
//返回成功匹配的点对数量
return num_good_pts;
}
/*
*初始化(立体初始化??)
*成功@return true
*/
bool Frontend::StereoInit() {
//提取左目的GFTT特征点(数量)
int num_features_left = DetectFeatures();
//使用LK光流匹配左右目中的GFTT特征点(LK光流跟踪后结果)
int num_coor_features = FindFeaturesInRight();
//如果匹配到的特征点数量小于num_features_init_,默认100个,就返回false
if (num_coor_features < num_features_init_) {
return false;
}
//初始化地图
bool build_map_success = BuildInitMap();
//如果地图初始化成功就改前端状态为TRACKING_GOOD,并把当前帧和地图点传到viewer_线程里
if (build_map_success) {
status_ = FrontendStatus::TRACKING_GOOD;
//地图在可视化端的操作,添加当前帧并更新整个地图
if (viewer_) {
viewer_->AddCurrentFrame(current_frame_);
viewer_->UpdateMap();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
*提取关键点(左视角图像)
*return 关键点数量
**/
int Frontend::DetectFeatures() {
//为了GETT提取,给均匀化???
//opencv中mask的作用就是创建感兴趣区域,即待处理的区域。
/*
通常,mask大小创建分为两步,先创建与原图一致,类型为CV_8UC1或者CV_8UC3的全零图(即黑色图)。如mask = Mat::zeros(image.size(),CV_8UC1);
然后用rect类或者fillPoly()函数将原图中待处理的区域(感兴趣区域)置为1。
https://blog.csdn.net/yuandm819/article/details/78085550
*/
//Mat(const cv::dnn::dnn4_v20191202::MatShape &_sz, int _type, const cv::Scalar &_s)最后设置为255,则为全白??
cv::Mat mask(current_frame_->left_img_.size(), CV_8UC1, 255);
//循环遍历现在帧上的左侧图像特征,并 //绘制边框
for (auto &feat : current_frame_->features_left_) {
/*
void cv::rectangle(cv::InputOutputArray img, cv::Point pt1, cv::Point pt2,
const cv::Scalar &color, int thickness = 1, int lineType = 8, int shift = 0)
绘制一个简单的、厚的或向上填充的矩形。函数cv::rectangle绘制一个矩形轮廓或填充矩形,其两个相对的角分别为pt1和pt2。
position_.pt————————>关键点坐标
inline cv::Point2f::Point_(float _x, float _y)------>关键点上下左右10距离的矩形,color为0,就是黑色填充满
*/
cv::rectangle(mask, feat->position_.pt - cv::Point2f(10, 10),
feat->position_.pt + cv::Point2f(10, 10), 0, CV_FILLED);
}
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypoints;//建立一个关键点的vector
/*
virtual void cv::Feature2D::detect(cv::InputArray image, std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> &keypoints, cv::InputArray mask = noArray())
重载:
检测图像(第一种变体)或图像集(第二种变体)中的关键点。
参数:
image – 图像.
keypoints – The detected keypoints. In the second variant of the method keypoints[i] is a set of keypoints detected in images[i] .
检测到的关键点。在该方法的第二种变体中,keypoints[i]是在图像[i]中检测到的一组关键点。
mask – Mask specifying where to look for keypoints (optional). It must be a 8-bit integer matrix with non-zero values in the region of interest.
指定在何处查找关键点的掩码(可选)。它必须是一个8位整数矩阵,在感兴趣的区域中具有非零值。
GFTT角点
*/
gftt_->detect(current_frame_->left_img_, keypoints, mask);
//关联current_frame_和kp,同时统计这两次检测到的特征点数量
int cnt_detected = 0;
for (auto &kp : keypoints) {
//作为一个关键点Feature类型存储;push是推进、pop是跳出
current_frame_->features_left_.push_back(
Feature::Ptr(new Feature(current_frame_, kp)));//持有features的frame和关keypoint
cnt_detected++;//检测计数加一
}
LOG(INFO) << "Detect " << cnt_detected << " new features";
return cnt_detected;//返回的是检测出的数量
}
/**
*当前帧的右侧图像中查找相应的特征(右视角)
*return 关键点数量
**/
int Frontend::FindFeaturesInRight() {
//赋初值
// 用LK光流估计右侧图像中的点
std::vector<cv::Point2f> kps_left, kps_right;
//循环遍历当前帧的左侧图像关键点
for (auto &kp : current_frame_->features_left_) {
//存入这个关键点
kps_left.push_back(kp->position_.pt);
//检查是否上锁,返回的是null或者是不空,代表着未上锁还是已上锁
auto mp = kp->map_point_.lock();
//why???
if (mp) {//如果上锁
// use projected points as initial guess(使用投影点作为初始估计值)
auto px =
camera_right_->world2pixel(mp->pos_, current_frame_->Pose());
//存入右侧图像的关键点
kps_right.push_back(cv::Point2f(px[0], px[1]));
} else {//如果没上锁
// use same pixel in left iamge(使用统一坐标)
kps_right.push_back(kp->position_.pt);
}
}
// use LK flow to estimate points in the right image(使用LK流来估计右侧图像中的点)
std::vector<uchar> status;
Mat error;
//opencv自带的光流跟踪函数
/*
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42905141/article/details/93745116
void cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(cv::InputArray prevImg,
cv::InputArray nextImg,
cv::InputArray prevPts,
cv::InputOutputArray nextPts,
cv::OutputArray status,
cv::OutputArray err,
cv::Size winSize = cv::Size(21, 21),
int maxLevel = 3,
cv::TermCriteria criteria = cv::TermCriteria((TermCriteria::COUNT) + (TermCriteria::EPS),
30,
(0.01000000000000000021)),
int flags = 0,
double minEigThreshold = (0.0001000000000000000048))
Calculates an optical flow for a sparse feature set using the iterative Lucas-Kanade method with pyramids.
(利用金字塔迭代Lucas-Kanade方法计算稀疏特征集的光流。)金字塔迭代书P156页
参数:
prevImg – first 8-bit input image or pyramid constructed by buildOpticalFlowPyramid.
nextImg – second input image or pyramid of the same size and the same type as prevImg.
prevPts – vector of 2D points for which the flow needs to be found; point coordinates must be single-precision floating-point numbers.
nextPts – output vector of 2D points (with single-precision floating-point coordinates) containing the calculated new positions of input features in the second image; when OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW flag is passed, the vector must have the same size as in the input.
二维点(单精度浮点坐标)的输出向量,包含第二幅图像中计算出的输入特征的新位置;当传递OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW标志时,vector必须具有与输入中相同的大小。
status – output status vector (of unsigned chars); each element of the vector is set to 1 if the flow for the corresponding features has been found, otherwise, it is set to 0.
输出状态向量(无符号字符);如果找到对应特征的流,则将向量的每个元素设为1,否则设为0。
err – output vector of errors; each element of the vector is set to an error for the corresponding feature, type of the error measure can be set in flags parameter; if the flow wasn't found then the error is not defined (use the status parameter to find such cases).
winSize – size of the search window at each pyramid level.
maxLevel – 0-based maximal pyramid level number; if set to 0, pyramids are not used (single level), if set to 1, two levels are used, and so on; if pyramids are passed to input then algorithm will use as many levels as pyramids have but no more than maxLevel.
criteria – parameter, specifying the termination criteria of the iterative search algorithm (after the specified maximum number of iterations criteria.maxCount or when the search window moves by less than criteria.epsilon.
flags – operation flags: - **OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW** uses initial estimations, stored in nextPts; if the flag is not set, then prevPts is copied to nextPts and is considered the initial estimate. - **OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS** use minimum eigen values as an error measure (see minEigThreshold description); if the flag is not set, then L1 distance between patches around the original and a moved point, divided by number of pixels in a window, is used as a error measure.
minEigThreshold – the algorithm calculates the minimum eigen value of a 2x2 normal matrix of optical flow equations (this matrix is called a spatial gradient matrix in
备注:
- An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/lkdemo.cpp - (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithm can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_track.py - (Python) An example using the Lucas-Kanade tracker for homography matching can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python/lk_homography.py
*/
cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(
current_frame_->left_img_, current_frame_->right_img_, kps_left,
kps_right, status, error, cv::Size(11, 11), 3,
cv::TermCriteria(cv::TermCriteria::COUNT + cv::TermCriteria::EPS, 30,
0.01),
cv::OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW);//最后一个参数flag,使用初始估计,存储在nextPts中;如果未设置标志,则将prevPts复制到nextPts并将其视为初始估计。
//统计匹配上的特征点个数,并存储
int num_good_pts = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < status.size(); ++i) {
if (status[i]) {
//匹配
cv::KeyPoint kp(kps_right[i], 7);
Feature::Ptr feat(new Feature(current_frame_, kp));
feat->is_on_left_image_ = false;//?????
current_frame_->features_right_.push_back(feat);
num_good_pts++;
} else {
current_frame_->features_right_.push_back(nullptr);
}
}
//输出操作日志
LOG(INFO) << "Find " << num_good_pts << " in the right image.";
//返回成功匹配的点对数量
return num_good_pts;
}
/**
* 使用单个图像构建初始地图
* @return true if succeed
*/
bool Frontend::BuildInitMap() {
std::vector<SE3> poses{camera_left_->pose(), camera_right_->pose()}; //设置左右两个相机的位置
size_t cnt_init_landmarks = 0; //设置地图标志初始值
for (size_t i = 0; i < current_frame_->features_left_.size(); ++i) { //循环左侧图像特征点
if (current_frame_->features_right_[i] == nullptr) continue; //判断右侧图像是否有对应特征点,有则继续向下执行,没有就continue
// create map point from triangulation(尝试对每一对匹配点进行三角化)(利用三角测量创建路标点)
std::vector<Vec3> points{
camera_left_->pixel2camera(
Vec2(current_frame_->features_left_[i]->position_.pt.x,
current_frame_->features_left_[i]->position_.pt.y)),
camera_right_->pixel2camera(
Vec2(current_frame_->features_right_[i]->position_.pt.x,
current_frame_->features_right_[i]->position_.pt.y))};
Vec3 pworld = Vec3::Zero();//新建一个三维0矩阵
//三角化
/*
inline bool myslam::triangulation(const std::vector<SE3> &poses, std::vector<Vec3> points, Vec3 &pt_world)
linear triangulation with SVD 线性三角测量
参数:
poses – poses,
points – points in normalized plane
pt_world – triangulated point in the world
返回:
true if success
*/
if (triangulation(poses, points, pworld) && pworld[2] > 0) {
//创建地图存储数据
//创建一个新地图,用于信息更新
auto new_map_point = MapPoint::CreateNewMappoint();
new_map_point->SetPos(pworld);
//将观测到的特征点加入新地图
new_map_point->AddObservation(current_frame_->features_left_[i]);
new_map_point->AddObservation(current_frame_->features_right_[i]);
//当前帧的地图点指向新的地图点————————>更新当前帧上的地图点
current_frame_->features_left_[i]->map_point_ = new_map_point;
current_frame_->features_right_[i]->map_point_ = new_map_point;
//初始化地图点makr+1
cnt_init_landmarks++;
//在地图中插入当前新的更新点
map_->InsertMapPoint(new_map_point);
}
}
current_frame_->SetKeyFrame(); //把初始化的这一帧设置为关键帧
map_->InsertKeyFrame(current_frame_); //在地图中插入关键帧
backend_->UpdateMap(); //后端更新地图(在后端更新)
//输出操作日志
LOG(INFO) << "Initial map created with " << cnt_init_landmarks
<< " map points";
//单个图像构建初始地图成功
return true;
}
//跟踪失败:重置
bool Frontend::Reset() {
LOG(INFO) << "Reset is not implemented. ";
return true;
}
} // namespace myslam
6. backend.cpp后端文件(重要文件2)
backend.cpp
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-5-2.
//
#include "myslam/backend.h"
#include "myslam/algorithm.h"
#include "myslam/feature.h"
#include "myslam/g2o_types.h"
#include "myslam/map.h"
#include "myslam/mappoint.h"
namespace myslam {
Backend::Backend() {
/*
在后端初始化中,主要是新开一个线程backend_thread_,然后把这个线程中运行的函数设置为Backend::BackendLoopI()函数。线程运行状态 backend_running_ 设置为true。
Map类的构造函数是空的哈,没有在构造函数里面设置任何东西。
*/
backend_running_.store(true);//线程为运行状态,.store()用另一个非原子值替换当前原子化的值 对象类型必须和原子对象声明时一致
//个人理解为:此线程是将后端回环与this绑定,新开线程进行回环检测;定义新开的线程复制品
//使用std::bind可以将可调用对象和参数一起绑定,绑定后的结果使用std::function进行保存,并延迟调用到任何我们需要的时候。
backend_thread_ = std::thread(std::bind(&Backend::BackendLoop, this));
}
void Backend::UpdateMap() {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(data_mutex_);
map_update_.notify_one();
}
void Backend::Stop() {
backend_running_.store(false);
map_update_.notify_one();
backend_thread_.join();
}
//后端回环检测
void Backend::BackendLoop() {
while (backend_running_.load()) {
//lock必须在wait()前调用,可以用来守护访问stop_waiting()。wait(lock)返回后会重新获取该lock。
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(data_mutex_);
map_update_.wait(lock);
/// 后端仅优化激活的Frames和Landmarks;Keyframes的缩写
Map::KeyframesType active_kfs = map_->GetActiveKeyFrames();
Map::LandmarksType active_landmarks = map_->GetActiveMapPoints();
//优化关键帧和路标?
Optimize(active_kfs, active_landmarks);
}
}
//后端优化,使用g2o库;使用BA优化
//地图和地图的交互:前端调用InsertKeyframe和InsertMapPoint插入新帧和地图点,后端维护地图的结构,判定outlier/剔除等等
void Backend::Optimize(Map::KeyframesType &keyframes,
Map::LandmarksType &landmarks) {
// setup g2o;图优化、非线性;下面操作是构建图优化,先设定g2o
//块求解器BlockSolver
typedef g2o::BlockSolver_6_3 BlockSolverType; // 每个误差项优化变量维度为6,误差值维度为3
// 第1步:创建一个线性求解器LinearSolver
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType>
LinearSolverType;
// 第3步:创建总求解器solver。并从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选一个,再用上述块求解器BlockSolver初始化
//此处类似与加锁互斥
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(
g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
// 第4步:创建终极大boss 稀疏优化器(SparseOptimizer)构造Levenberg算法,该算法将使用给定的求解器来求解线性化系统。
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;//图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);//设置求解器
// pose 顶点,使用Keyframe id;vertex and edges used in g2o ba位姿顶点
std::map<unsigned long, VertexPose *> vertices;
unsigned long max_kf_id = 0;
// 共有7个关键帧------>map.h中最后设置激活关键帧的总数量
for (auto &keyframe : keyframes) {
auto kf = keyframe.second;//关键帧的复制的第二个值?keyframe第二个类型的副本
//往图中增加顶点
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose(顶点位姿???);
//设置图中节点的id,确保改变id后图保持一致;virtual void setId(int id) {_id = id;}
vertex_pose->setId(kf->keyframe_id_);
//设置顶点的估计也调用updateCache();void setEstimate(const EstimateType& et) { _estimate = et; updateCache();}
vertex_pose->setEstimate(kf->Pose());
//bool addVertex(OptimizableGraph::Vertex* v) { return addVertex(v, 0); };
/*
添加一个新顶点。新的顶点被“获取”。
* @返回false,如果与v具有相同id的顶点已经在图中,否则返回true。
*/
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
if (kf->keyframe_id_ > max_kf_id) {
max_kf_id = kf->keyframe_id_;
}
//插入关键帧id和顶点位姿
vertices.insert({kf->keyframe_id_, vertex_pose});
}
// 路标顶点,使用路标id索引
std::map<unsigned long, VertexXYZ *> vertices_landmarks;
// K 和左右外参
Mat33 K = cam_left_->K();
SE3 left_ext = cam_left_->pose();
SE3 right_ext = cam_right_->pose();
// edges
int index = 1;
double chi2_th = 5.991; // robust kernel ( 强大的内核?) 阈值
std::map<EdgeProjection *, Feature::Ptr> edges_and_features;
//遍历每一个路标点
for (auto &landmark : landmarks) {
//去除异常点,mappoint.h文件中设is_outlier_为false。故如果符合条件继续向下执行,也就是开始时默认没有离群值
if (landmark.second->is_outlier_) continue;
unsigned long landmark_id = landmark.second->id_;//复制的frame的id给到便利到的路标点??
auto observations = landmark.second->GetObs();//获取到的观测值
//遍历每个路标点的观测帧
for (auto &obs : observations) {
//先判断所要操作的观测帧是否在加锁状态
if (obs.lock() == nullptr) continue;
auto feat = obs.lock();//获取现在obs的状态,加锁or未加锁
//判断是都是离群值和加锁
if (feat->is_outlier_ || feat->frame_.lock() == nullptr) continue;
auto frame = feat->frame_.lock();
EdgeProjection *edge = nullptr;
//构造带有地图和位姿的二元边;构造边,判断标识是否在左图存在
if (feat->is_on_left_image_) {
edge = new EdgeProjection(K, left_ext);
} else {
edge = new EdgeProjection(K, right_ext);
}
// 如果landmark还没有被加入优化,则新加一个顶点;本文件77行类似
if (vertices_landmarks.find(landmark_id) ==
vertices_landmarks.end()) {
VertexXYZ *v = new VertexXYZ;
v->setEstimate(landmark.second->Pos());
v->setId(landmark_id + max_kf_id + 1);
v->setMarginalized(true);//!true,在优化过程中,这个节点应该被边缘化
vertices_landmarks.insert({landmark_id, v});
optimizer.addVertex(v);
}
//设置边:每个路标点和其任意一个观测帧的位姿都要建立一条边
edge->setId(index);
//.at返回的是.second的对应副本
//设置第一个顶点,注意该顶点类型与模板参数第一个顶点类型对应
edge->setVertex(0, vertices.at(frame->keyframe_id_)); // pose// 设置连接的顶点
//设置第二个顶点
edge->setVertex(1, vertices_landmarks.at(landmark_id)); // landmark
//设置观测值,类型与模板参数对应
edge->setMeasurement(toVec2(feat->position_.pt));// 观测数值
// 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵(之逆)
edge->setInformation(Mat22::Identity());
//设置鲁棒核函数(下数3行)
auto rk = new g2o::RobustKernelHuber();
rk->setDelta(chi2_th);
edge->setRobustKernel(rk);
//相当于是在图表信息中加入边和特征点?
edges_and_features.insert({edge, feat});
//优化边
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
}
// 第6步:设置优化参数,开始执行优化
// do optimization and eliminate the outliers(优化后去除异常数据)
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);//迭代10次
//标志数量,标志离群和非李群值的数量,用来判断阈值?
int cnt_outlier = 0, cnt_inlier = 0;
int iteration = 0;
while (iteration < 5) {
cnt_outlier = 0;
cnt_inlier = 0;
// determine if we want to adjust the outlier threshold
// 根据阈值判断异常值
for (auto &ef : edges_and_features) {
//chi2()函数返回的是return _error.dot(information()*_error)
if (ef.first->chi2() > chi2_th) {
cnt_outlier++;
} else {
cnt_inlier++;
}
}
//计算正常点的比例
double inlier_ratio = cnt_inlier / double(cnt_inlier + cnt_outlier);
//调整筛选阈值,直到合格
if (inlier_ratio > 0.5) {
break;
} else {
chi2_th *= 2;
iteration++;
}
}
//记录结果是否异常
for (auto &ef : edges_and_features) {
if (ef.first->chi2() > chi2_th) {//如果是超过阈值,那么将其设置为离群值
ef.second->is_outlier_ = true;
// remove the observation
ef.second->map_point_.lock()->RemoveObservation(ef.second);
} else {//如果是没有阈值,那么将离群值设置为false
ef.second->is_outlier_ = false;
}
}
//日志输出
LOG(INFO) << "Outlier/Inlier in optimization: " << cnt_outlier << "/"
<< cnt_inlier;
// Set pose and lanrmark position(存储相机位姿及路标点的位置)
//此处将first指向second的,也就是正常执行后,对整体进行了一个更新替换
for (auto &v : vertices) {
keyframes.at(v.first)->SetPose(v.second->estimate());
}
for (auto &v : vertices_landmarks) {
landmarks.at(v.first)->SetPos(v.second->estimate());
}
}
} // namespace myslam