PDF 获取:微信公众号:灰海宽松,后台回复 “RFID” 获取。
文章目录
- RFID
- 1. Introduction
- Comparison of different automatic identification technologies
- The main features of RFID
- Constraints of RFID technology
- Core technologies of RFID
- The advantage of RFID in IoT, and the development trend
- 2. Identification
- Reader’s function
- Reader’s classification
- Influencing factors of R&W range
- Reader’s components and their functions
- Tag’s functions
- Tag classification: by package form, by power source, by work frequency, by R&W capability
- Two work modes of RFID middleware
- 3. Wireless Communication Principle of RFID
- Different work principles of different carrier frequency
- Signal voltage and energy: dB, dBm,重点:如何计算
- Modulation of reader signal: OOK and its problem, solution: PIE; Tag encoding: FM0
- Link budget (重点)
- Antenna gain and polarization, EIRP
- Effects of antenna gain,重点:分析 link budget,几个计算公式
- 4. Tag Identification Protocol
- Checksum procedure: parity checks, LRC, CRC
- ASK, FSK, PSK
- Difficulty of traditional anti-collision algorithms for solving collision detection between RFID tags
- TDMA, FDMA, CSMA
- ALOHA based protocols: pure ALOHA, S-ALOHA, FSA, DFSA, Q 算法。重点:性能分析、执行过程
- Binary tree based protocols: BT, QT, 重点:执行过程
- Binary search: Manchester code instead of NRZ code, 重点:执行过程
- Dynamic binary search, 重点:执行过程
- Advantages and disadvantages of ALOHA based anti-collision algorithm
- Advantages and disadvantages of binary tree based anti-collision algorithm
- 5. EPCglobal Standard & protocol
- Concept of EPC global network
- Five basic services of EPC global network, interaction of different components of EPCglobal network
- EPC code 组成
- Basic procedures of the EPC Network
- Binary tree based variant algorithm for EPCglobal Class 0
- EPCglobal C1 G1: PingID; C1G2: four commands (是什么,分别干什么用的), two types of performance trade-offs
RFID
1. Introduction
Comparison of different automatic identification technologies
首先明确一下比较对象。human identification(cost too high)是人力识别就不用说了。
fingerprint identification:
- stability 稳定,精确度高;
- high speed, 快速匹配;
- security issues: 容易被复制。
face recognition:
- easy to be influenced by surroundings, hair, age…
speech recognition:
- easy to use and accept by user;
- not involve privacy;
- due to international standards, is hard to promoting
1d barcode:
- limit storage capacity, 点线组合少;
- need to combine with database;
- barcode size is large;
- poor fault tolerance, 本来就需要摄像头可见,如果被污损遮挡很容易就无法识别;
2d barcode recognition:
- larger storage capacity;
- high information density;
- powerful fault tolerance;
- support for encryption 容量大了就支持更多编码解码等安全措施了。
rfid:
- low cost;
- low power consumption;
- high accuracy;
- non-contract, fast speed; 不用接触(哪怕是visual,薄纱条码)
- certain computing and storage capabilities;
主要考虑各个的缺点,人脸和声音特征点多速度慢,而且人脸容易被影响,声音由于国际标准技术难以提升;条码需要视觉可见;指纹容易被盗取。
The main features of RFID
-
Non-contact automatic and rapid identification 快速薄纱复杂的人脸和声音,无接触薄纱条码和指纹
-
Permanently store a certain amount of data 永久存储一定量数据
-
Simple logical processing 其包含的简单逻辑电路允许做一定的逻辑处理,比如安全协议、算法
-
Reflection signal strength is affected by the distance and other factors significantly 信号受到距离,读写器功率,其他信号,其他标签的干扰
-
Low cost, can be deployed at a large scale
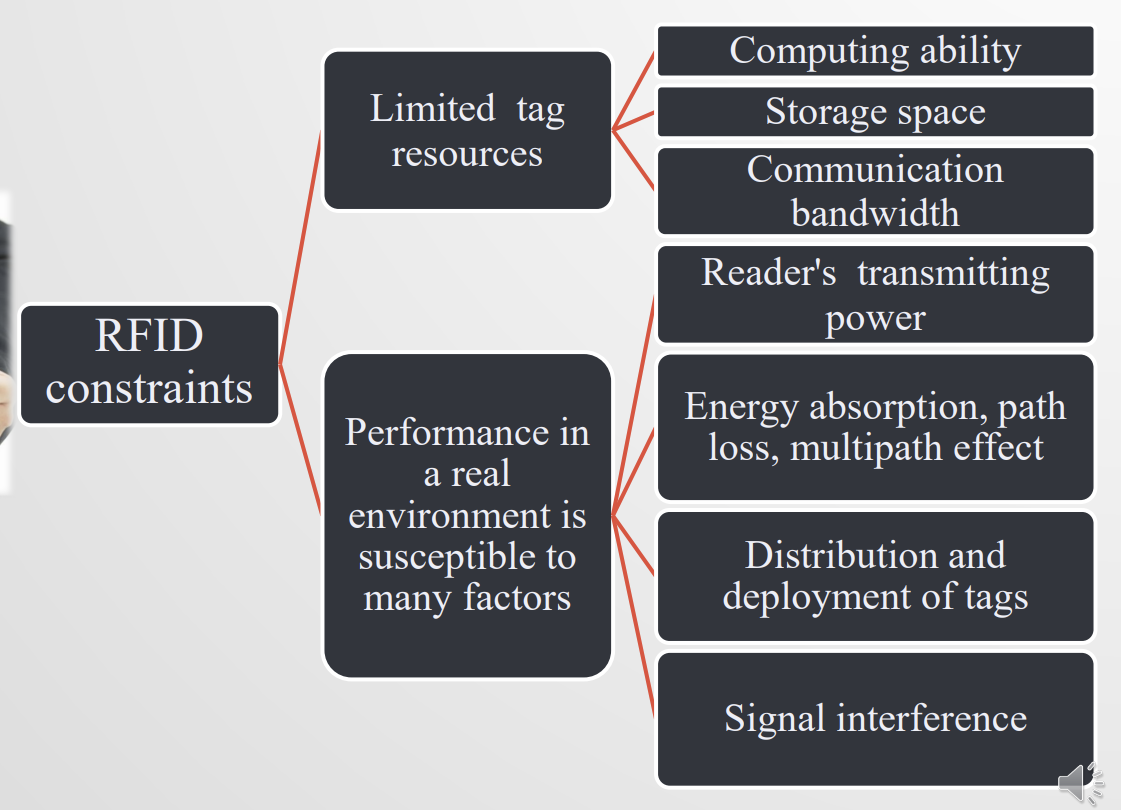
Constraints of RFID technology
Core technologies of RFID
Anti-collision mechanism:rfid并不支持传统的cmsa/ca无线通信协议,需要采取一些措施防碰撞(reader-reader, tag-reader, tag-tag)
Efficient information storage, retrieval and mining: 尽量节能的信息存储,检索,挖掘
Make full use of the attenuation laws of backscatter signal to assist in positioning and mobile behavior sensing: 我们知道rfid信号会随着距离衰减。反之我们也可以利用这一点来定位物体位置和移动行为感知。
Security certification and privacy protection: 如何利用逻辑门电路校验安全性。
The advantage of RFID in IoT, and the development trend
充电方式:Backscatter, small node and indefinitely time of endurance. but rely on reader, one to many centralized communication 利用无线电 ratio signal 充电的方式
ptp communication: 建立 channel awareness technologies 使得支持被动点对点通信来建立分布式系统
Combine with Sensors: 开发更多应用方式。
RFID and IoT:
- embed intelligence in the physical object, so that simple physical objects can also “say”.
- allows a physical object to be uniquely identified in a way similar to the “IP address” of a computing node in the Internet.
- provides a low-cost communication way to achieve effective communication between nodes.
- makes the physical objects in a passive environment achieve “passive intelligence“, providing fundamental guarantee for the “thing-thing connection”
2. Identification
简单说RFID就是物体上贴tag,用reader上的antenna去读取,这三个是主要组成。
Reader’s function
Energy supply: 比如有的标签自身不带能量需要reader提供信号中蕴含的能量
Communication: 最基本的功能,和tag识别,通信
Security Assurance: 比如加密解密
扩展功能:比如自组网 ad-hoc, 管理天线 antenna management 中间件接口 interface of middle components 连接外设 connecting peripherals
Reader’s classification
按频率:LF HF算低频,UHF和SHF算高频(ultra super),高频数据传输速度快,距离远,但是衰减快 signal attenuation,收到障碍物影响大 sensitive to obstacles。
按外观:
- Fixed 固定有线的,高度集成,快速启动 set up
- portable 可移动的像手持手机一样,small, charging battery, easy to move
- Industrial 为工厂目的而生,比如集成其他 sensor
Influencing factors of R&W range
许多东西都有说明书,规范,来提醒我们怎么不把东西玩坏比如手机提示不要放水里玩。
RFID的R&W range是其中一种。影响因素如下:
-
The way that antenna is coupled 天线耦合方式,比如把两个天线绑一起太近互相干扰。
-
The output power of the reader’s RF signal 功率,太低可能无法激发tags
-
The frequency of RF carrier signal 合适的频率
-
Antenna direction 天线,读取器天线和标签天线极性方向 polarization 相匹配时识别范围最大
-
Operation environment condition
-
Movement speed of tags
Reader’s components and their functions
Signal Processing and Control Module: 主要是控制功能,协调一些本地计算
- Communicate with upper computer, and execute command from it
- Control communication process with tags
- Encode and decode signal
- Perform anti-collision algorithm
- Encrypt and decrypt the data transferred between reader and tag
- Identity certification between reader and tag
Inductively Coupled RF Module: 主要是产生能量和调制发送信号功能
- Generate high frequency send energy, activate RF tags and provide energy (passive RF tags)
- Modulate signal to sent, transferring data to RF tags
- Receive and demodulate RF signal from RF tags.
Tag’s functions
- data storage
- energy harvesting 吸收能量,与reader的 energy supply 对应
- contactless with R&W 不用接触就能通信,与 reader 的 communication with tags 对应
- Security Encryption 与 reader 的 Security Assurance 对应
- Collision Concessions 碰撞让步
Tag classification: by package form, by power source, by work frequency, by R&W capability
Package form 也就是外观上的分类:
- card-like
- label-like
- Implantable, 比如动物植物体内
- Accessories-like 附件类标签,比如纽扣型的,这一类主要是方便携带
By Power Source 按能源供应方式分类:
- active 自己有电池供电
- passive 依靠 carrier signal 读取器发来的载波信号获取能量
- semi-passive 有电池作为后备隐藏能源,平时主要是passive 方式
By Work Frequency
LF HF UHF。UHF读写性能,距离最好,更多会使用 active 型。
By R&W Capability
read-only 和 R&W 两种,结构复杂度也有所不同
Two work modes of RFID middleware
interactive, independent。
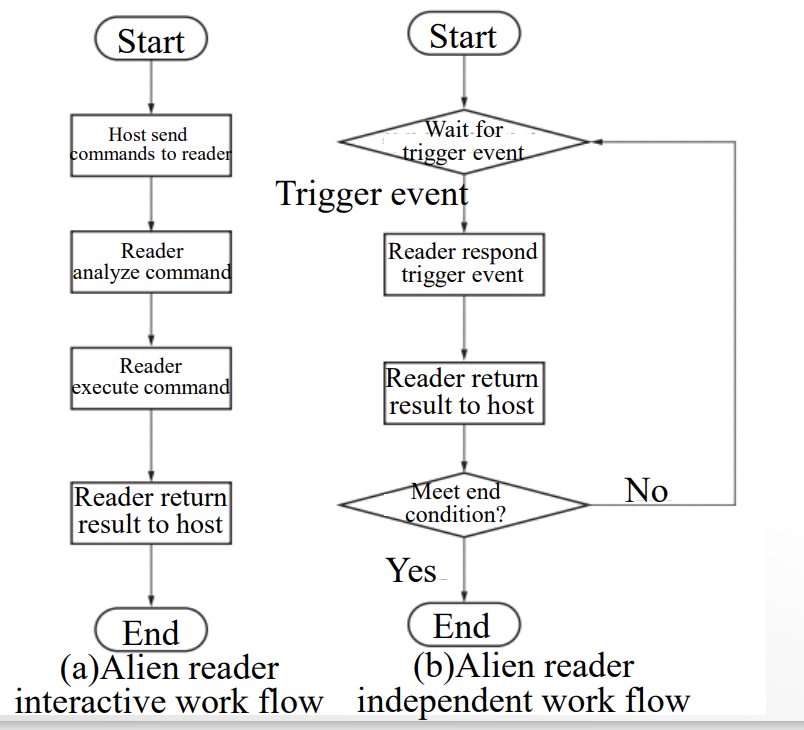
交互模式大概就是一直接收主机的命令,你让我读我就读,读完把结果还给你。
独立模式是可以不接收主机命令自行按预设的程序和读取到的结果信息循环执行指令,并将结果返回给主机。
3. Wireless Communication Principle of RFID
Different work principles of different carrier frequency
不同频率载波也适用不同的工作原则。
前面已经有所涉及,比如LF HF适用于近距离,UHF SHF适合远距离。
前者适用 Inductively Coupled RF Module 电感耦合,通过感应方式获取能量。
后者适用 Electromagnetic Backscatter Coupled RF Module 电磁反向散射耦合,持续不断发送射频信号来供给能量。backscatter 指的是接收机信号调制后通过发送机天线产生可被识别的信号。
两者的能量消耗都和距离平方成正比 squared distance
Signal voltage and energy: dB, dBm,重点:如何计算
变化的电压通常用 V ( t ) = v 0 c o s ( ω t ) V(t)=v_0cos(\omega t) V(t)=v0cos(ωt) 表示。
功率P=VI=V^2/R这不用多说。平均功率 = v 0 2 2 R =\frac{v_0^2}{2R} =2Rv02 很简单推因为正余弦平均就是/根2.
相对变化 The relative change,这是一个比较新鲜的而且信号变化中比较重要的指标。
G d B = 10 l o g 10 P 2 P 1 G_{dB}=10log_{10}\frac{P2}{P1} GdB=10log10P1P2
参考功率 referenced power d B m = 10 l o g 10 P 1 0 − 3 dBm=10log_{10}\frac{P}{10^{-3}} dBm=10log1010−3P
dBm单位是功率的W,GdB单位是dB,代表一个比值。
Modulation of reader signal: OOK and its problem, solution: PIE; Tag encoding: FM0
一些阅读器通过调制使得正弦电压信号携带信息的方法。
OOK:on off keying,高功率1低功率0.
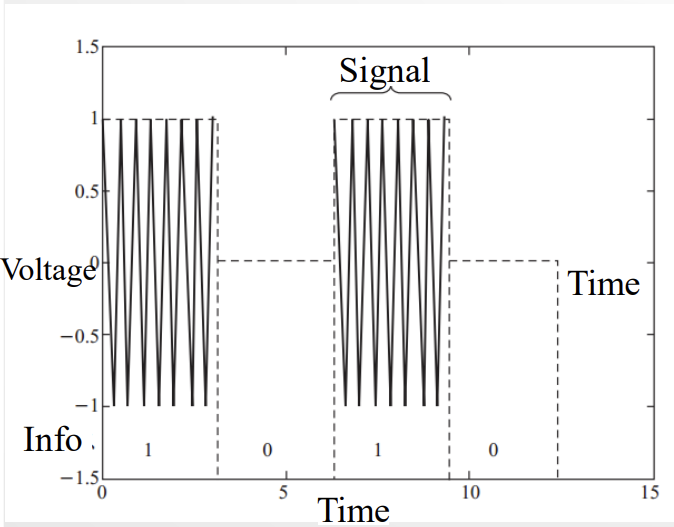
问题在于,低功率0的部分标签没法被激活,也无法正常工作。也就是说0信号标签压根启动不了,没法接收0信号。
PIE解决方法:长高功率是1,短高功率是0.
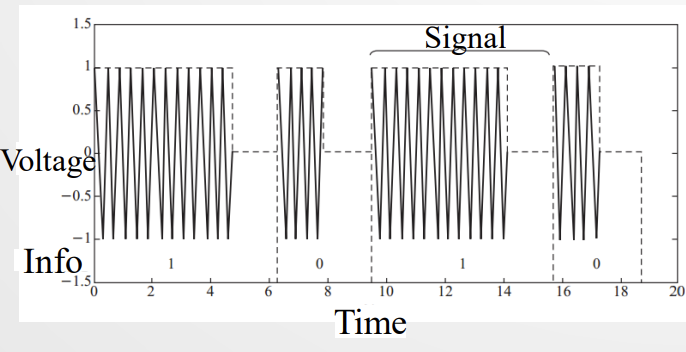
然后涉及到tags对reader发来的信号进行解码。空间中的信号发过来是有方向的矢量叠加,tags如何通过编码机制识别信号?
FM0编码方式:位窗起始处翻转信号表示1,中间翻转表示0.

FM0属于 FSK frequent shift key 通过信号变化频率来识别的机制。
Link budget (重点)
Link budget: forward link budget and backward link budget 发射过程中能量增减的总和
reader transmit energy(+) path loss(-) tag activate energy(-)
- pass loss: 读取器天线向360度的发送能量。其中只有一部分区域可以被tags antenna读取到,这一部分被称作 Effective Aperture (Ae) of the tag antenna。能量=有效面积*密度 P t = ρ A e P_t=\rho A_e Pt=ρAe 。总共发送的能量比收到的能量就等于总表面积比有效面积 P T X P R X = A e 4 π r 2 \frac{P_{TX}}{P_{RX}}=\frac{A_e}{4\pi r^2} PRXPTX=4πr2Ae
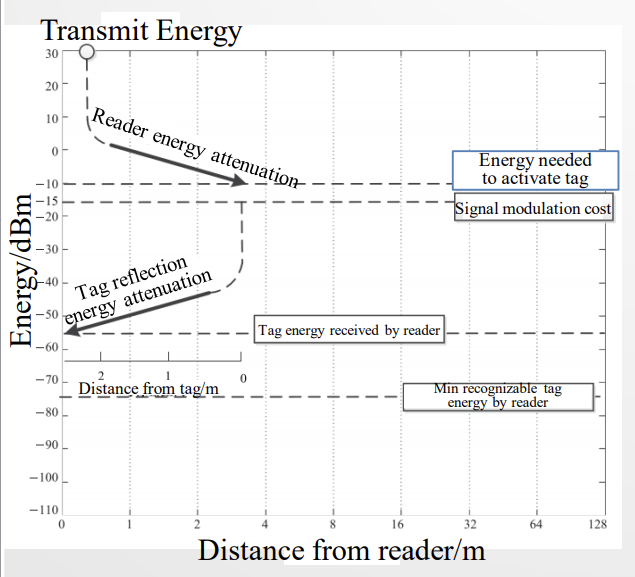
来看上例,发送方30dBm对应1W,tag接收到-10dBm对应10^-4W. 然后5dB的衰减到-15dBm。这个5dB衰减就是两个dBm做差得到的。
所以,dBm相当于对功率P的另一种衡量方式,为什么这么麻烦的要用log来表示?因为两个dBm的差值就是分贝(放大系数),所以由一个dBm能量转到另一个只需要加减两者间差的分贝即可,很方便。
从tags反射回来的信号 reflection link 和路径四次方成反比 inversely proportional. P R X , b a c k : 1 r 4 P_{RX,back}:\frac{1}{r^4} PRX,back:r41
Antenna gain and polarization, EIRP
antenna gain: 输入条件相同情况下,实际情况某一点能量密度/理想条件下的密度单元。反应了天线 concentrates the input power 的能力。就比如把阅读器放中间,标签围一圈,360度去读取周围标签对能量消耗就大,可能因此传输距离也近;但是如果把标签集中放在一块区域,周围放置的 reader 利用定向天线 Directional antenna,固定读取某一个角度范围内的tags能量利用效率就高。
Polarization:事物在一定条件下发生极化 polarization,使得其表现的和原有状态不一样 its properties deviate from the original state。
EIRP, Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power: 天线在所指方向上获得最大增益效果 maximum gain effect 所需要的能量。
For example, FCC regulations in the United States, a non-irradiated transmitter can transmit 1W of energy signals, and can use 6dBi antenna; antenna gain increased by 1dB, transmission energy needs to be reduced by 1dB. In fact, FCC is not more than 36dBm(30dBm+6dBi).
Effects of antenna gain,重点:分析 link budget,几个计算公式
directional gain: radiation density of one direction d / average value in all direction
power gain: radiation efficiency of that direction G
平面角:单位rad,比如圆周180度单位角=2pi rad
立体角:单位sr,比如球面立体角=4pi sr
能量增益G的计算方法是4pi/立体角大小。比如波束宽度72°也就是2pi/5大概是1.25rad, G = 4 π 1.2 5 2 G=\frac{4\pi}{1.25^2} G=1.2524π
dipole antenna: 垂直于轴沿各个方向发送信号,比全向天线 omnidirectional antenna 小2.2dB。
Effective aperture A = G λ 2 4 π A=G\frac{\lambda ^2}{4\pi} A=G4πλ2
P R X = P T X G R X G T X ( λ 4 π r ) 2 P_{RX}=P_{TX}G_{RX}G_{TX}(\frac{\lambda}{4\pi r})^2 PRX=PTXGRXGTX(4πrλ)2
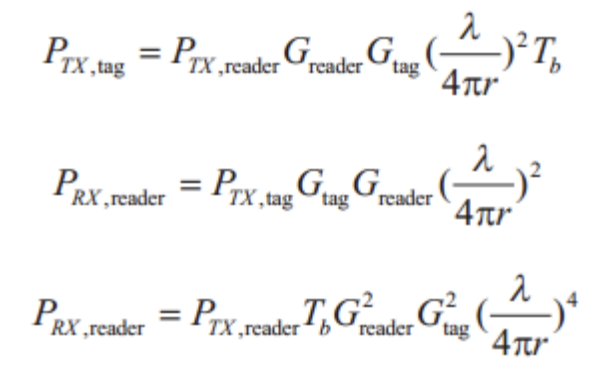
R f o r w a r d = λ 4 π P T X , r e a d e r T b G r e a d e r G t a g P m i n , t a g R_{forward}=\frac{\lambda}{4\pi}\sqrt{\frac{P_{TX,reader}T_bG_{reader}G_{tag}}{P_{min,tag}}} Rforward=4πλPmin,tagPTX,readerTbGreaderGtag
R r e v e r s e = λ 4 π P T X , r e a d e r T b G r e a d e r 2 G t a g 2 P m i n , r e a d e r 4 R_{reverse}=\frac{\lambda}{4\pi}\sqrt[4]{\frac{P_{TX,reader}T_bG_{reader}^2G_{tag}^2}{P_{min,reader}}} Rreverse=4πλ4Pmin,readerPTX,readerTbGreader2Gtag2
4. Tag Identification Protocol
Checksum procedure: parity checks, LRC, CRC
奇偶校验不多说,查1的个数,poor error recognition。电路通过所有位异或是偶校验,结果为1说明有错误;再取反是奇校验。
LRC longitudinal redundancy check (LRC) procedure 循环冗余检测,所有字节进行异或运算,得到的结果是LRC校验码。也就是说数据发送到终点后,所有字节(数据和LRC)进行字节异或运算结果应该为0. 也有一些错误无法纠正,主要用于小的数据块校验。
CRC (cyclic redundancy check) procedure
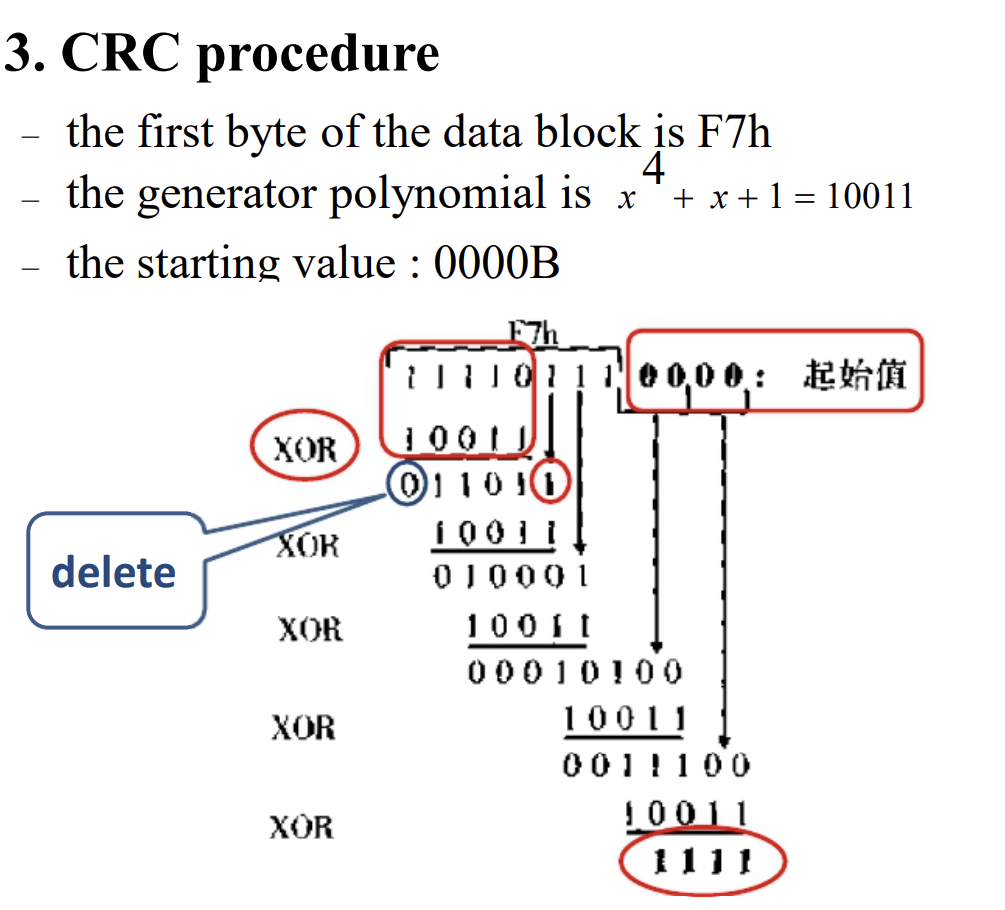
接收方计算原数据+CRC数据拼接起来的CRC数据值,应该为0. 不能纠错,不过检错效率很高。
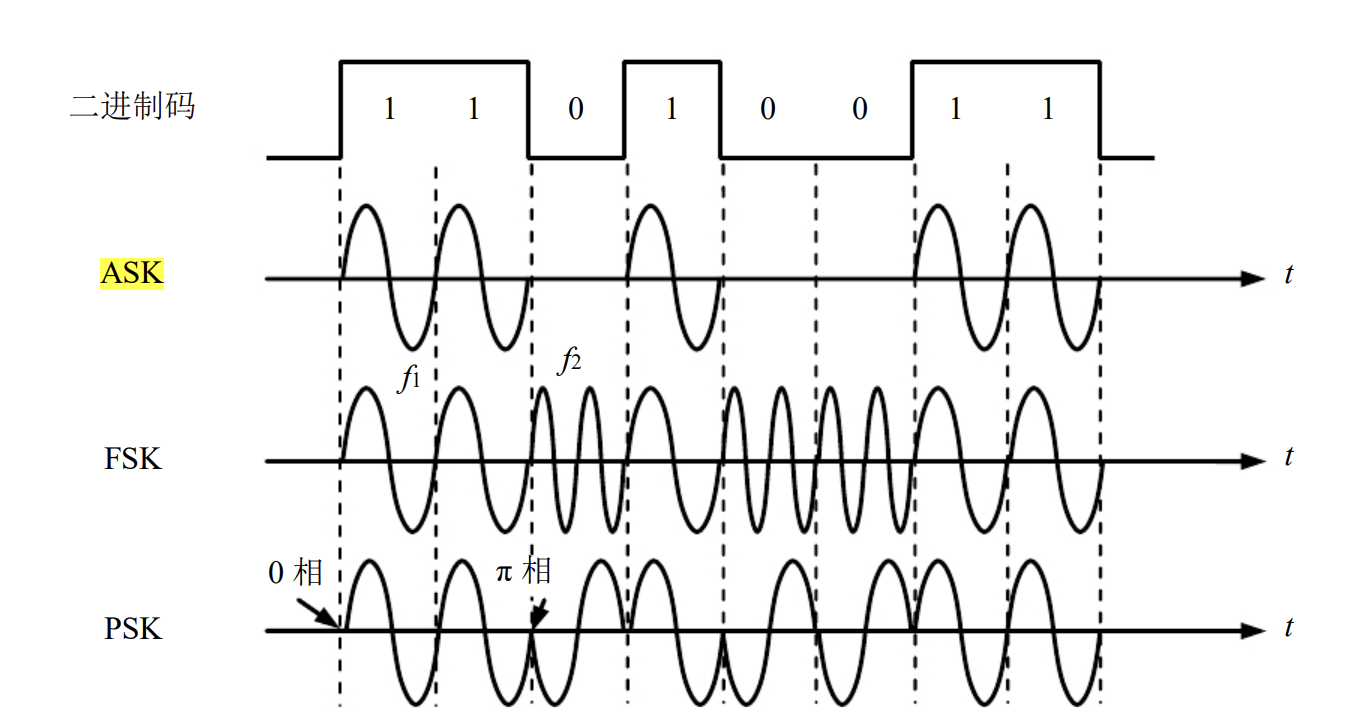
ASK, FSK, PSK
amplitude Shift Keying: 幅度调制,y轴上的调制。
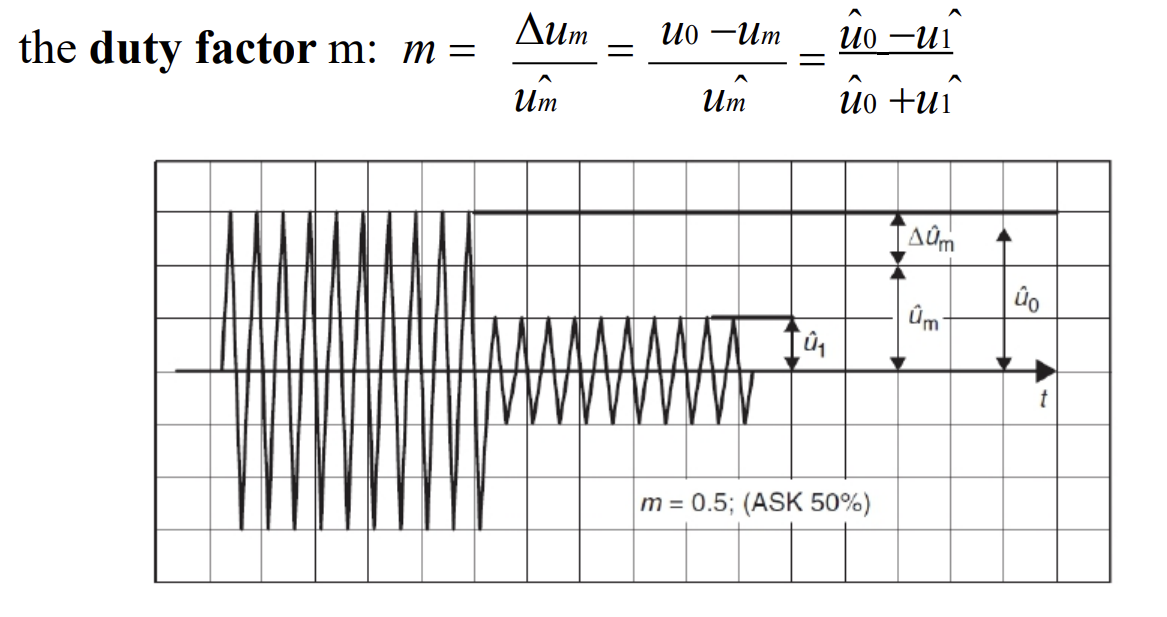
计算方法2:duty factor: m = 1 − u 1 u 0 m=1-\frac{u_1}{u_0} m=1−u0u1
U A S K ( t ) = ( m ⋅ u c o d e ( t ) + 1 − m ) ⋅ u H F ( t ) U_{ASK}(t) =(m·u_{code}(t)+1−m)·u_{HF}(t) UASK(t)=(m⋅ucode(t)+1−m)⋅uHF(t)
Frequency shift keying: 频率上的改变。
Phase shift keying: 频率相位翻转180.
Difficulty of traditional anti-collision algorithms for solving collision detection between RFID tags
Compared with the reader, limited by hardware resources, tags have very limited storage capacity and computing.
标签受制于硬件资源,存储容量和计算能力都不高。
TDMA, FDMA, CSMA
首先主要有两种方式,一个是reader broadcast 广播到诸多 tags,一个是多个 tags Multi-access 每个tags单独访问reader。
TDMA FDMA是multi-access, CSMA是broadcast
FDMA: 多个频率通道 several frequency channels 传输数据。
TDMA:
ALOHA based protocols: pure ALOHA, S-ALOHA, FSA, DFSA, Q 算法。重点:性能分析、执行过程
Pure ALOHA algorithm:收到成功确认 ack 后就不再发送。否则一直随机等待后继续发送。简单但是通道利用率 channel utilization 低,poor performance.
offered load G:单位时间 tau 里同时发送的应答器数量
s-aloha: 规定时间片 slot,一个时间片只能发一次,冲突就下一次时间片去发。channel utilization 几乎是 pure 的两倍。
S = G × e − G S = G × e^{-G} S=G×e−G G=1最大
frame S-ALOHA: 规定一个周期 frame,包含若干个 slots,会更加有组织有秩序。reader 广播一个 frame length,tags 自己选择组织时间片(0~f-1),每个时间片开始 reader 轮询一下tag里sn信号是不是0,是0就发送,不是0就-1.
conflict slot, single slot, idle slot(空)
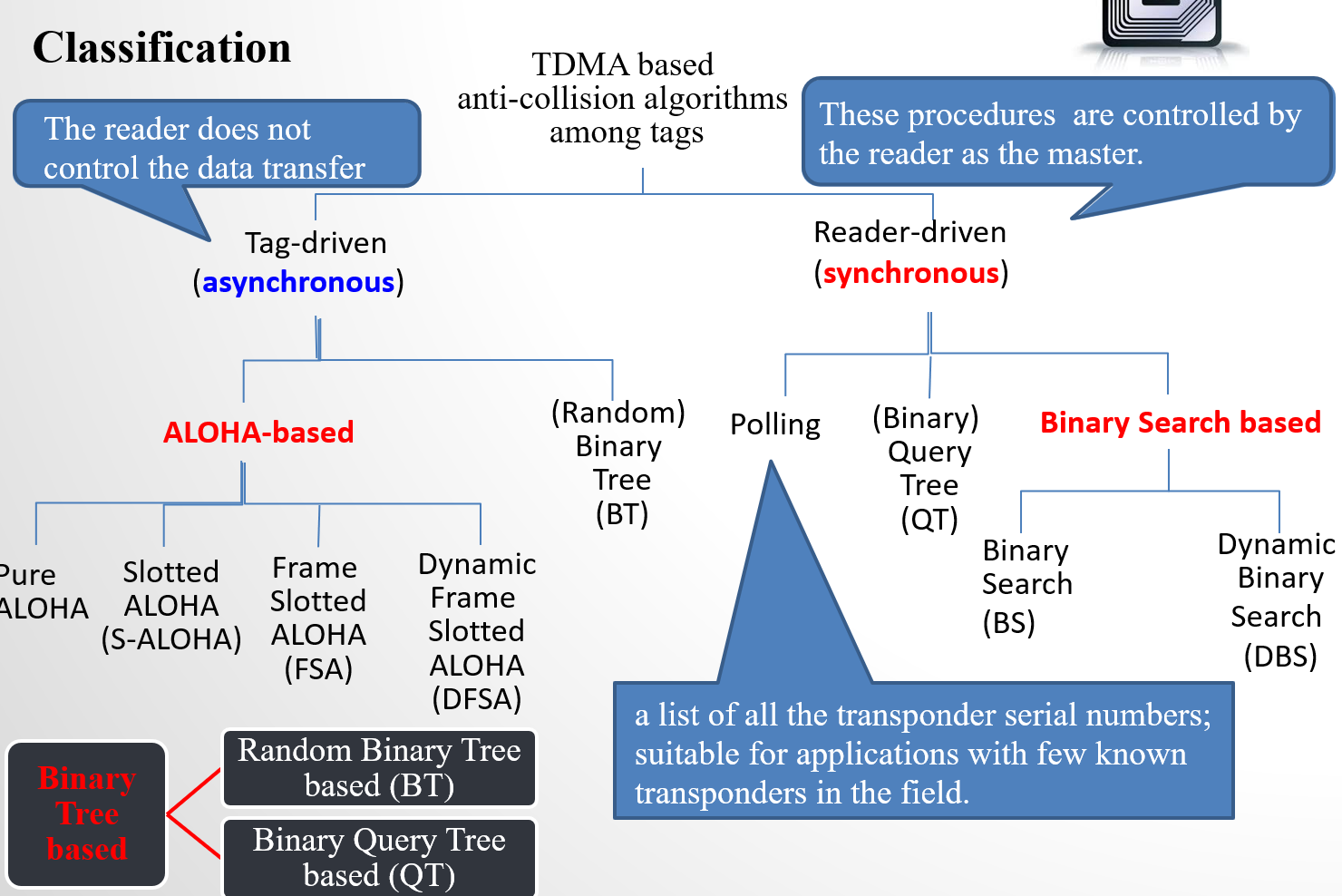
逻辑,电路设计,内存都比较简单,但是 frame length 长度不固定。tags 远远多于 frame length 冲突时间片就太多,tags 太少空时间片太多太浪费。负载 G=1 也就是 length=tags 利用率最好。
DFSA:利用以前的 frame 冲突反馈结果,和一些机器学习算法推测合适的 frame length。
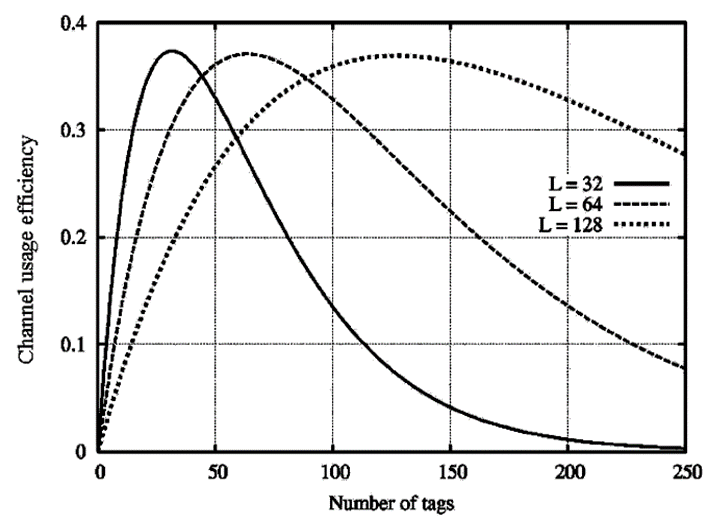
EPC Global(第五章介绍)规范里使用了一种Q算法。简单说就是如果冲突太多了,当前 frame 就别继续了,中断,新开一个大容量 frame. 同理 空闲太多了就新开一个小 frame。
Qfp是指定的初始值。每次先取整,然后发起 query。
没有回复:Qfp-C C是一个参数,比如0.1.
有冲突>1:+C。注意有上下限。
ALOHA 算法公平。但是可能发生饥饿 ,比如有一个 tag 每次都是有冲突的 slot,一直没有办法被处理。
Binary tree based protocols: BT, QT, 重点:执行过程
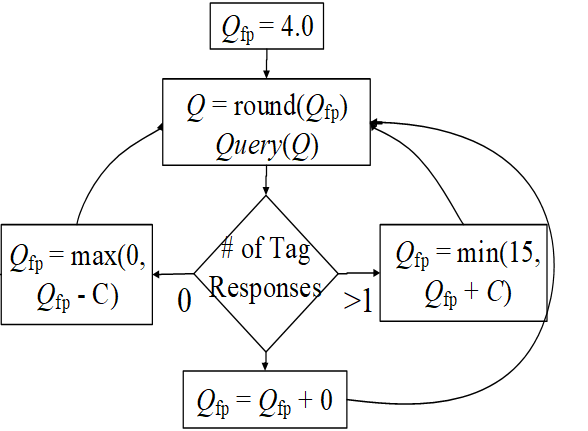
第二种算法,基于二进制数。就像二叉树不断拆分冲突的结点变为两个结点,直到节点里只有一个 tag。
random binary tree BT:随机。
binary query tree QT:排序,查询。
每一个 tag 需要有一个计数器来记录自己的状态。
每一个tag都会被识别,不会饥饿,但是需要存储每个tag的状态。
比如看下面的例子:

首先 tag1234 随机选一个数,比如选了0010,SN分别加自己选的数。
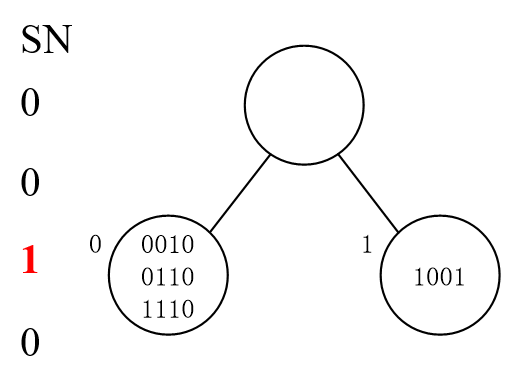
找SN=0的,发现有是有,但是他们几个都冲突了。那么继续分,比如1011,SN=1021
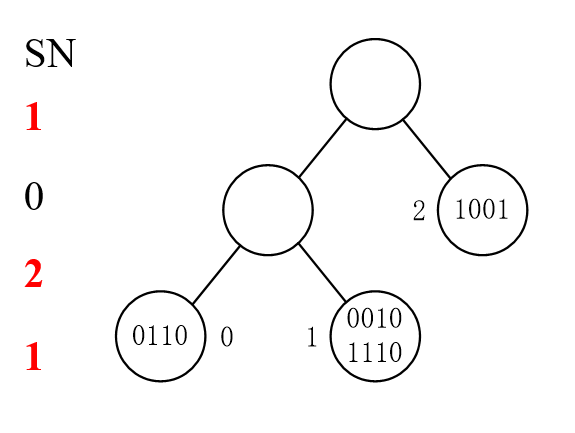
2的SN=0而且不冲突,把2读取了之后2不再继续参与。然后当有tag读取后,所有其他SN-=1
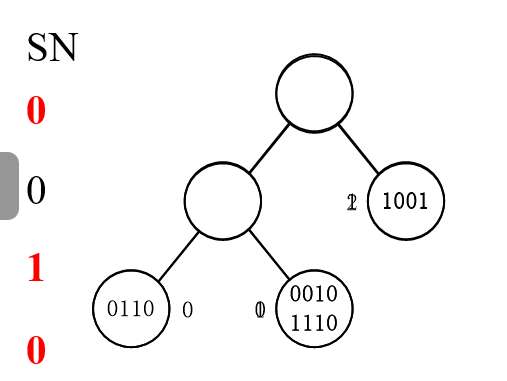
=0的是14,但是他俩冲突。然后再重新划分一下,比如011, SN=0021
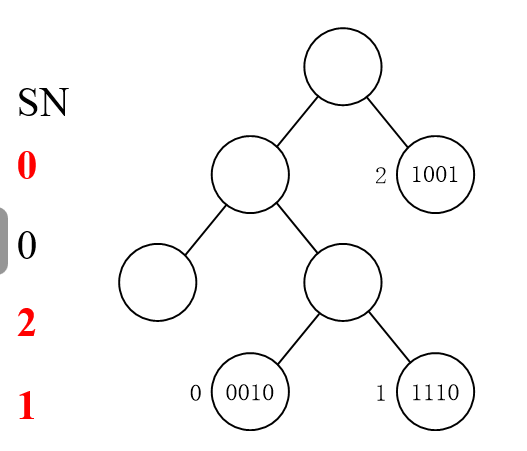
然后处理1,其他-=1,处理4,其他-=1,处理3.
QT 不需要存储状态,如何实现?读取tag的序列号比较。
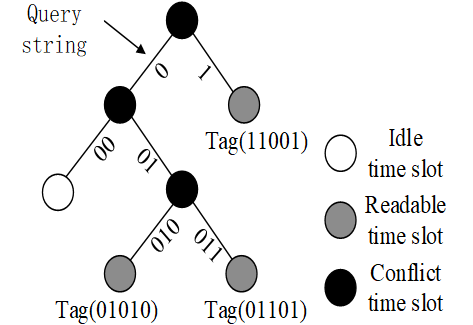
不会饿死,也不需要一个可以读写的cnt,识别的时间和 tag id 有关。
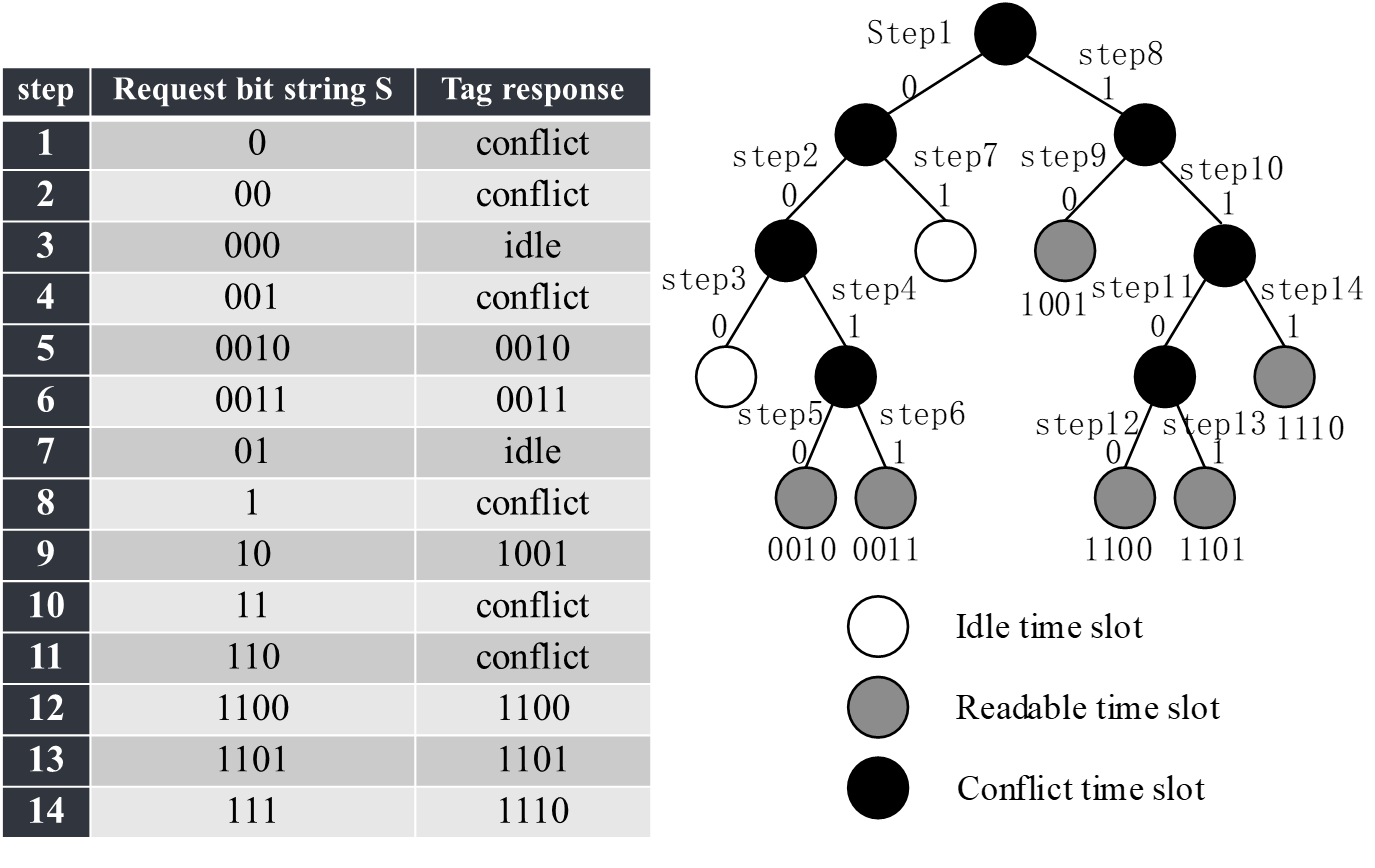
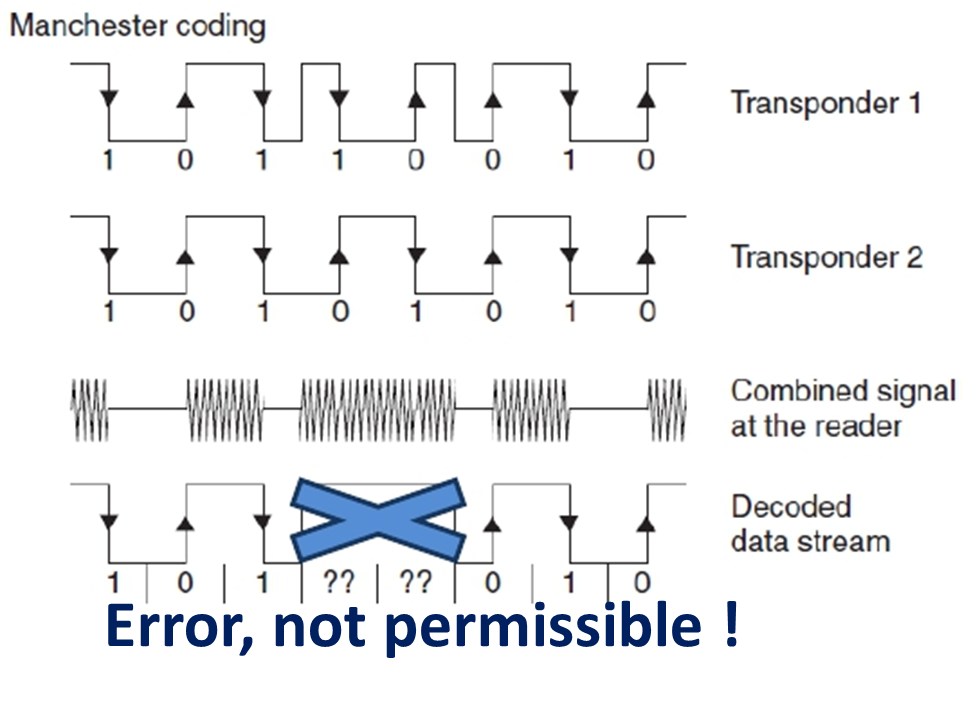
Binary search: Manchester code instead of NRZ code, 重点:执行过程
具体分辨哪一位有冲突。1代表冲突。
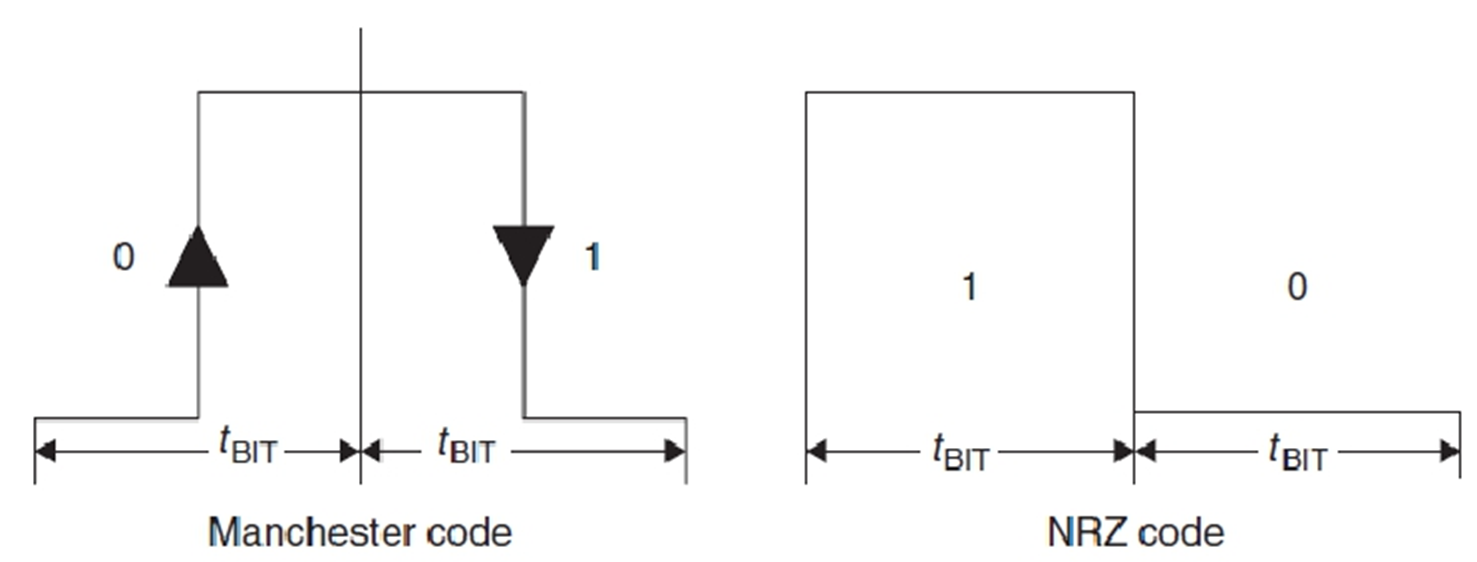
NRZ混合没法检测错误。
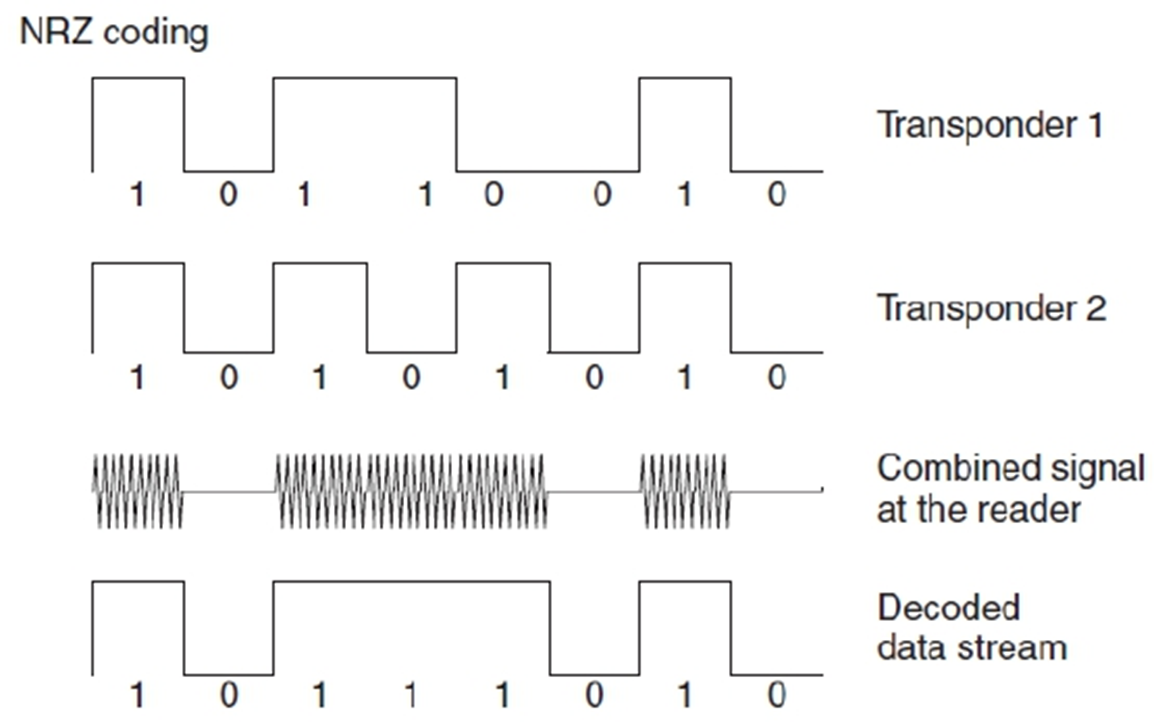
曼彻斯特可以,一个上升一个下降,合起来是0或者1.
查询的流程:
- request:发送一个序列号给tags的transponder,如果tags的序列号小于给定序列号返回。
- select:给定一个特定序列号,返回等序列号的tag。
- read_data:返回所选tag的信息。
- unselect:读取完data了,这个tag退出选择流程。
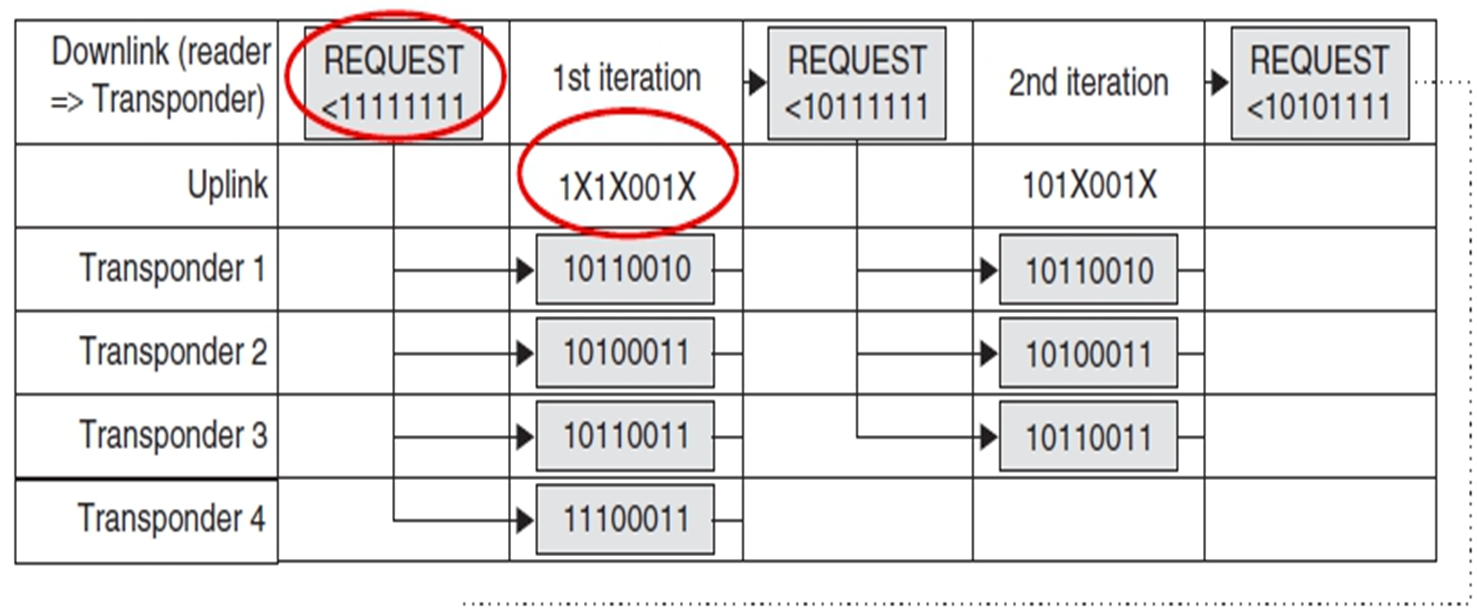
第一次迭代:返回uplink是所有transponder的id的共同信息(通过曼彻斯特编码找出没有冲突的位)。046位冲突了(从右往左),8个可能。
第二次迭代:限定 bit6 为0的request。发现有3个还是冲突04位(最高位冲突位=0,其他冲突位=1,如果range是大于等于,则正好相反)。
第三次迭代:限定bit4为0的request……
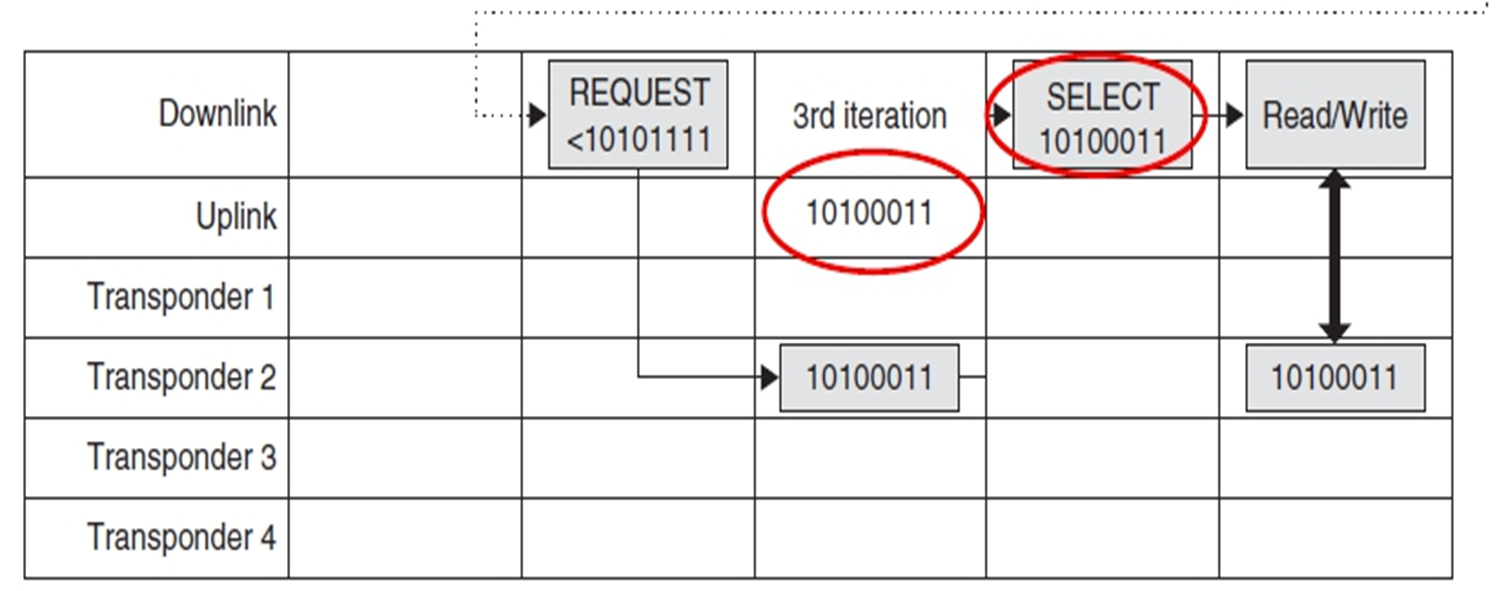
长度 L(N)=log2(N)+1
Dynamic binary search, 重点:执行过程
Binary Search 是每次都传输完整二进制字符串. 其实我们只需要动态改变的部分.
比如我们查询1010 1111 1111, 那返回值前面一定是1010呀, 就不用传输了. 前缀叫 NVB, Number of Valid Bits
每次请求发送的信息: Request+NVB=4+1010
Advantages and disadvantages of ALOHA based anti-collision algorithm
simple
good identification performance
results can be statistically analyzed 结果可以被统计化分析
缺点就是可能 starvation 饥饿,delay trend to ∞
Advantages and disadvantages of binary tree based anti-collision algorithm
simple
intermediate state variables 不需要存储中间状态变量(QT)
缺点:查询时间受到 tags id 和 长度限制,比如二叉树沿着一个方向一直偏。
5. EPCglobal Standard & protocol
Concept of EPC global network
EPCglobal Network: a technology that
- allows trading partners to document and determine the location of individual goods
- if possible in real time
- additional information: such as 生产使用日期,能否被贸易伙伴交换
Five basic services of EPC global network, interaction of different components of EPCglobal network
Electronic product code (EPC)
The identification system
EPCglobal Middleware
Discovery Service (DS)
EPC Information Services (EPCIS)
EPC码是唯一标识对象的代码。识别系统包括对象上的可被读取的包含EPC码的transponder和读取器reader可以识别EPC,然后通过EPCglobal Middleware传到网上,通过DS在 EPCglobal network 查找EPC码的相关信息(包括object naming service)。可以通过EPCIS和其他贸易伙伴交换EPC相关信息。
这其中的交互:
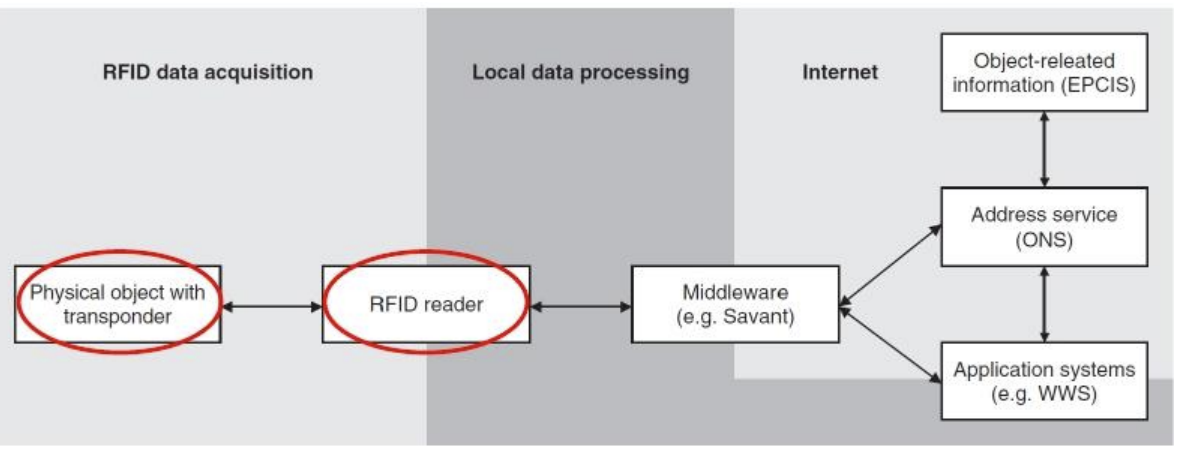
transponder and reader : data acquisition
Middleware
Discovery services
EPC Information Services : access to EPC-related data
EPC code 组成
Domain Manager Number + Object Class Number + Serial Number
Basic procedures of the EPC Network
EPC码用于标识对应对象
all information about the object 在EPCGlobal Network里注册 administer
each company in the EPCglobal Network: 各个公司管理数据集和数据对象
access rights to object data: 包含在EPCIS里,指明了trading partners 之间访问权限
-
the manufacturer:把transponder和product绑定
-
all data assigned to the product:在EPCIS里
-
EPCIS registers the entries with EPC Discovery Services:注册了DS之后方能找得到EPCIS
-
product:卖给零售商 retailer
-
At the retailer’s goods-in point 数据存储在零售商EPCIS中
-
registered by EPCIS with EPC Discovery Services
-
The company prefix send to root EPCIS
-
root -> local -> the EPCIS
Binary tree based variant algorithm for EPCglobal Class 0
这种tag是只读的,制造商赋值。
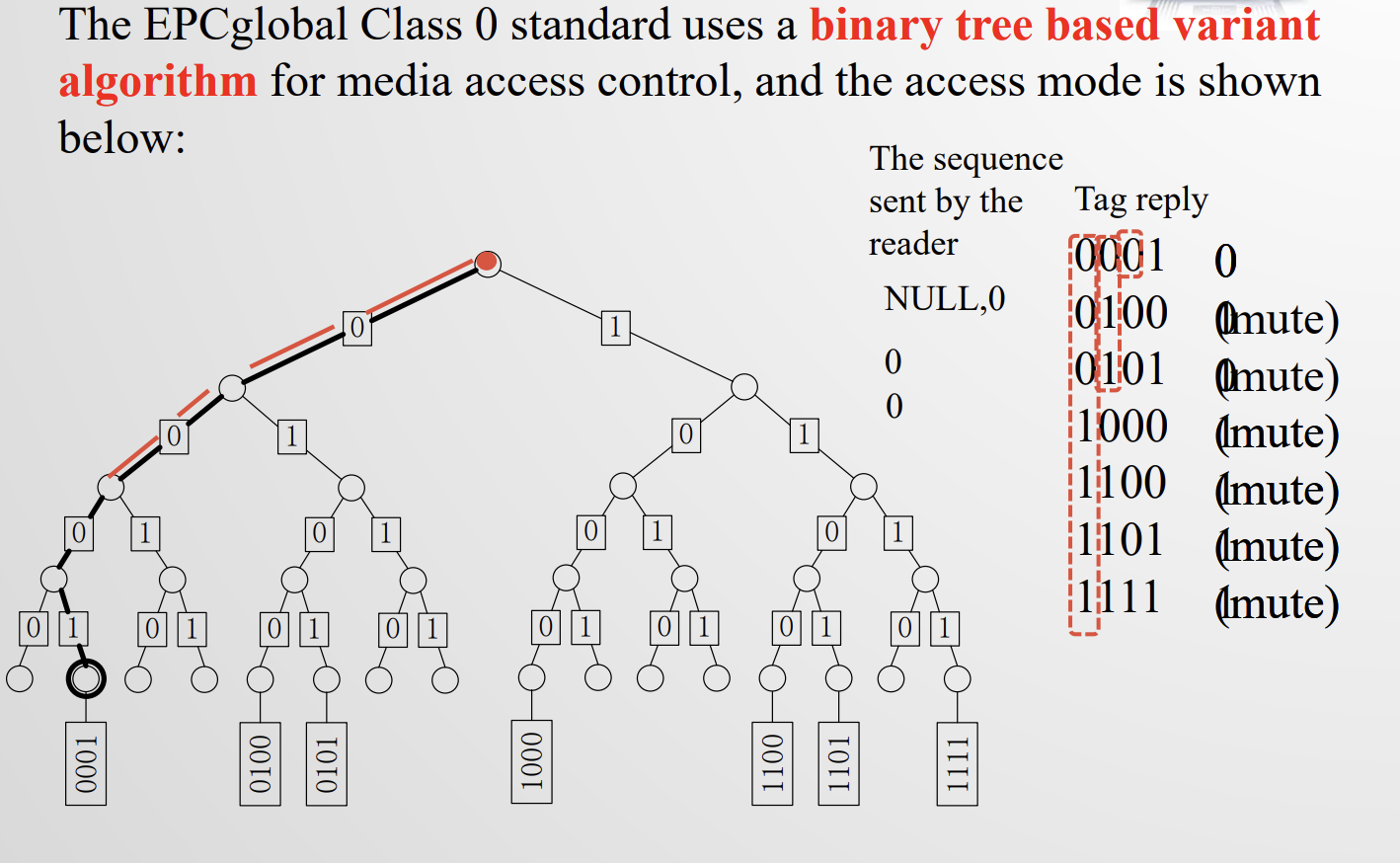
EPCglobal C1 G1: PingID; C1G2: four commands (是什么,分别干什么用的), two types of performance trade-offs
EPC C1G1:查询tags EPC的一种标准。
被动标签,支持kill和lock两种操作。
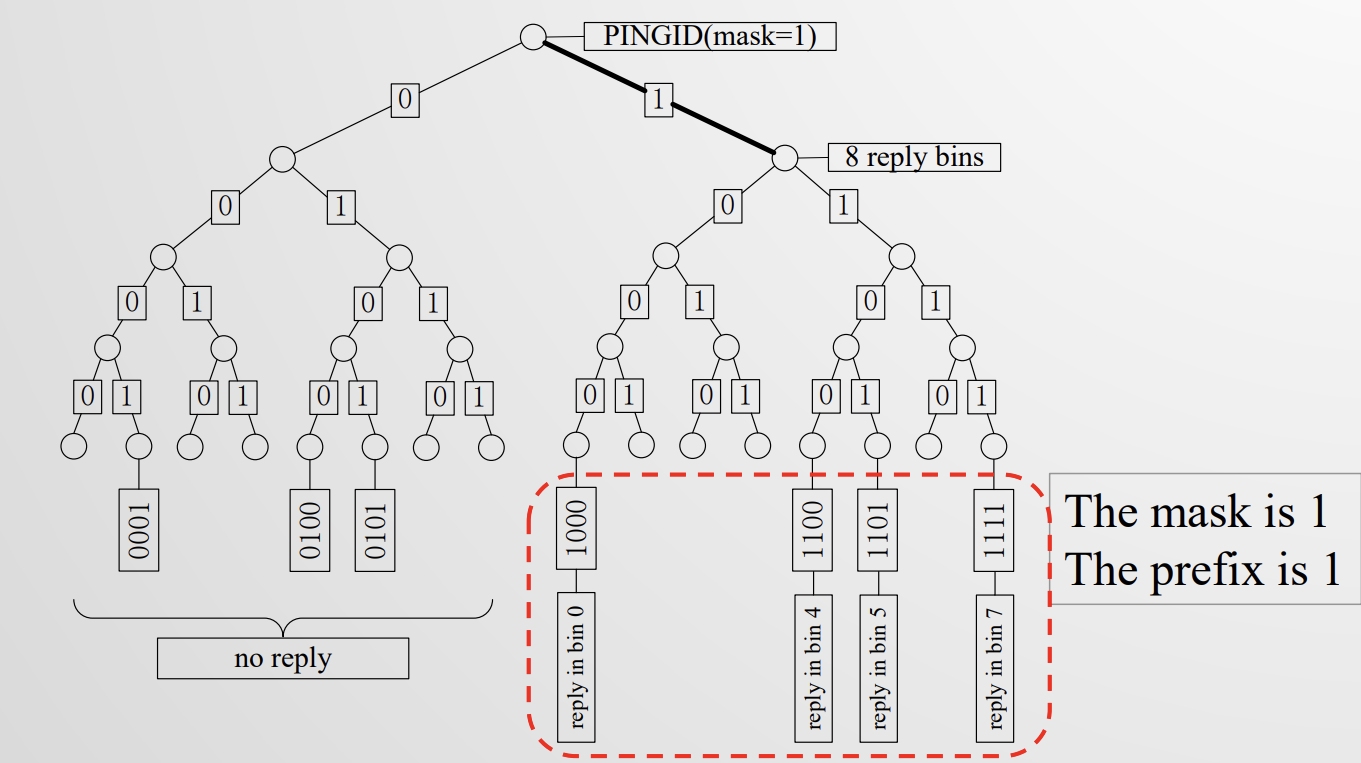
pingID:掩码,用于查询tag EPC
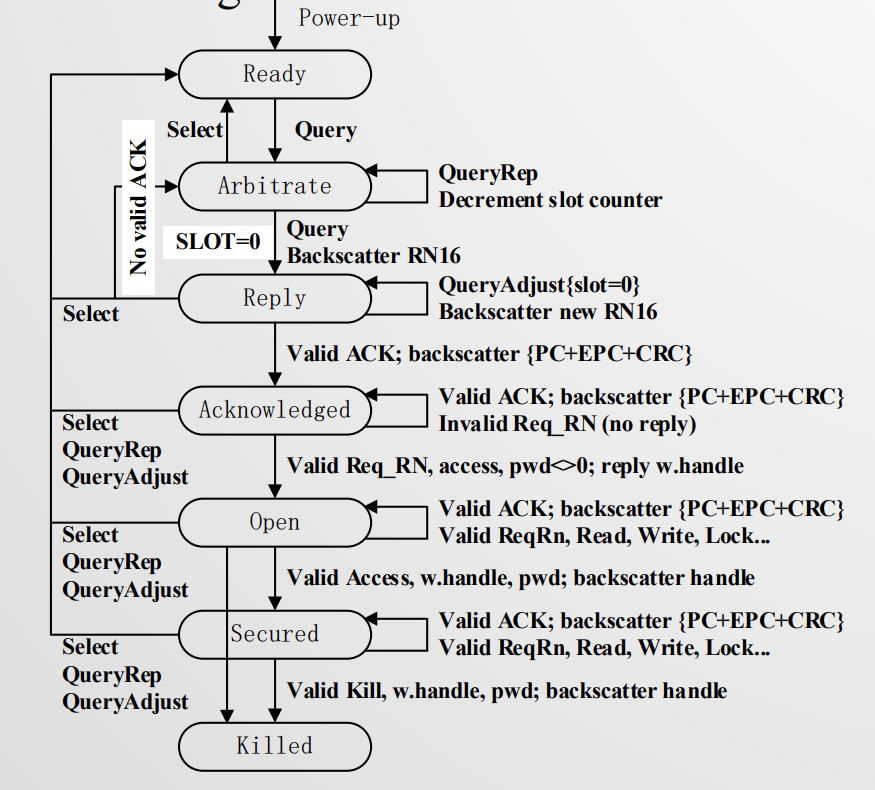
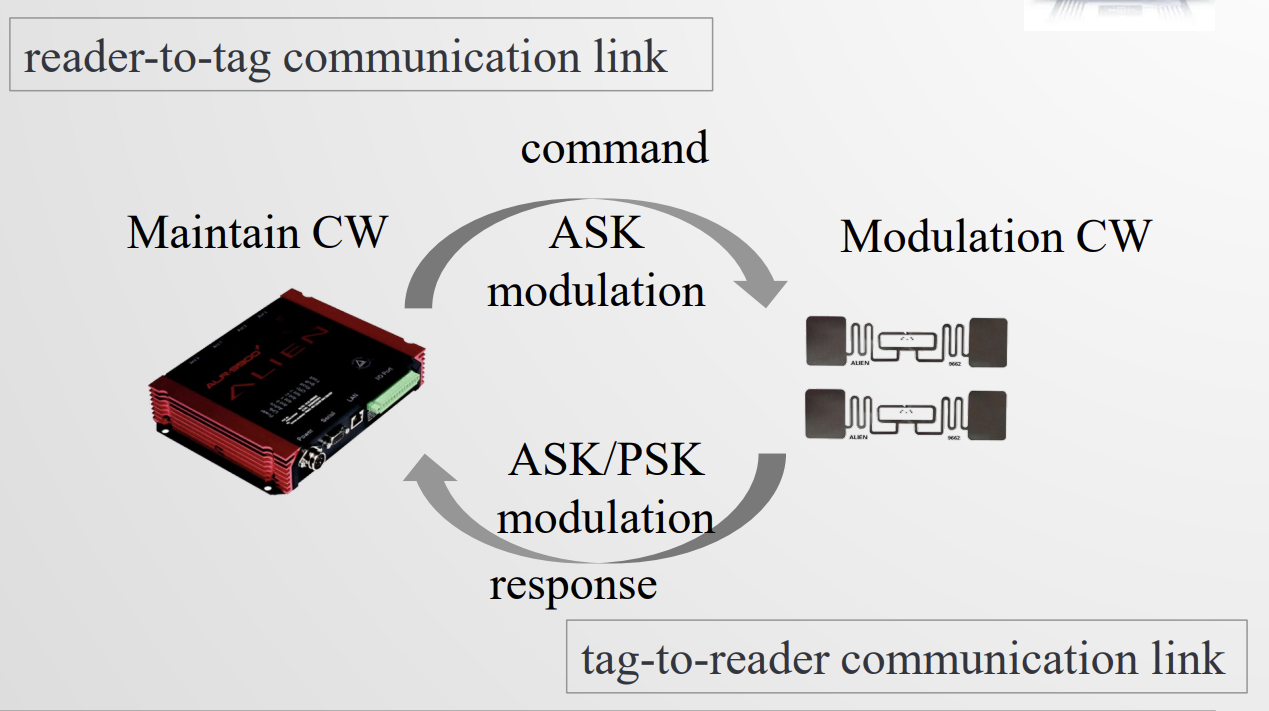
EPC C1G2 有 OSI 的七层模型,两条数据链路(R-T)
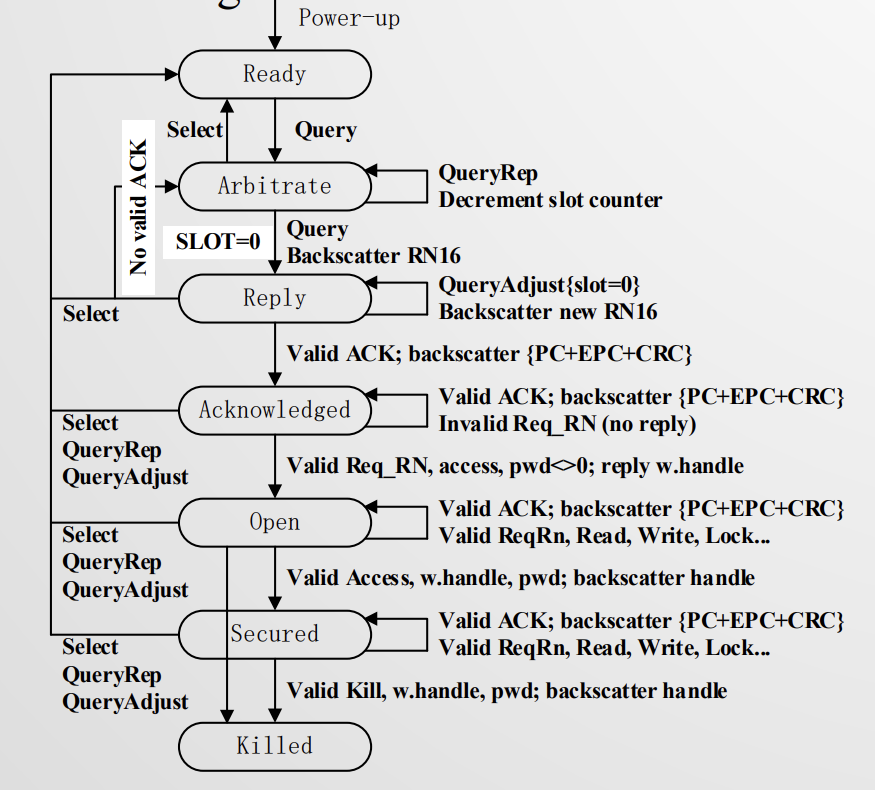
上电 ready
发 query 命令,aribtrate 仲裁。选择随机数生成时间片。
slot=0 的开始 reply
tag 发 ack 给 reader,acknowledged 状态。
tag 收到 reader 的命令后进入 open,校验后进入 secured,完成 killed。
4个识别 tags 的命令:Select command, Query command, QueryRep command, QueryAdjust command
select 指明要查哪些 tags 的集合。
query 启动新的识别过程。
Rep 开启下一轮 slot 查询,标签 SN–,到0时读取。
Adjust 调整时隙数,选择新的时隙计数器等。
两大性能问题:
- Build a set of tags involved in the recognition process,如何建立正确的tags集合来查询(select 和 query 负责)
- Select the way of data encoding, for the readerto-tag, the tag-to-reader, the reader itself and the tag itself 根据环境调整编码方式