android版本:android-11.0.0_r21
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/
android存储初始化分3个阶段:
1)清理环境。因android支持多用户,解锁后登录的可能是另一个用户,需把之前用户执行的一些信息清理干净。《android存储1--初始化.清理环境》已做分析,总结如下:
- start primary user
发送START消息、H_BOOT_COMPLETED消息给其他service处理。 - init用户目录的加密状态
初始化软件加解密的device的用户目录加密状态;对于硬件加密的device,什么事也不做。 - reset external storage service
umount外部存储、关闭mount service的所有connection。按电源键开机,外部存储还没有挂载,所以不需要卸载任何存储设备,也不需要关闭任何connection。 - reset vold service
销毁volume、重置disk对象、清空用户、添加用户。开机场景不需要销毁volume、重置disk对象、清空用户。 - 添加用户
在mAddedUsers中记录主用户。
2)启动存储服务(mount、vold、storaged这些service)。
3)挂载emulated存储(这系列文章只分析emulated存储)。
本文分析“启动存储服务”,涉及mount、vold、storaged service的启动流程。
一、存储相关的service
1,service介绍
存储有3个关键service:mount、vold、storaged,通过adb shell "service list"可以看到。
service代码:
| service | 代码路径 |
| mount service | frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/StorageManagerService.java |
| vold service | system/vold 目录 (注意,虽然vold是一个用户态程序,但它的log默认在内核里,需通过dmesg查看) |
| storaged service | system/core/storaged 目录 |
mount service负责mount和umount存储设备或存储卷,提供文件系统的访问接口。它的mount、umount请求下发给native层的vold处理。
vold (Volume Daemon)位于framework和kernel之间,管理存储卷的生命周期、处理mount service的mount和umount请求,以及提供存储卷的管理接口。
vold主要功能:
1)监听内核的存储设备uevent事件,并上报给mount service。
2)处理mount service下发的mount、umount请求。
storaged是一个deamon进程,提供存储相关的统计数据(磁盘使用信息、应用io信息、存储寿命信息等),并通过向应用程序和系统组件提供 API 接口,使它们能够监控和管理存储资源的使用情况。提供的命令如下:
| 命令 | 输出说明 |
| storaged或storaged -s | 注册storaged service和storaged_pri service。 我们在调试的过程中,不需要再执行storaged命令了。 |
| storaged -u storaged -t | 调试时,该命令用的比较多
<uid>/<foreground read bytes> <foreground write bytes> <foreground read chars> <foreground write chars> <background read bytes> <background write bytes> <background read chars> <background write chars>
storaged的help信息:
-u Dump uid I/O usage to stdout
-t Dump task I/O usage to stdout
但是,system/core/storaged/main.cpp的main函数中,-u,-t调用的都是storaged_service->dumpUids(&uid_io),所以功能是一样的。
|
| storaged -p | Dump I/O perf history to stdout |
2,service之间的关系
mount、vold、storaged之间的层次关系如下:
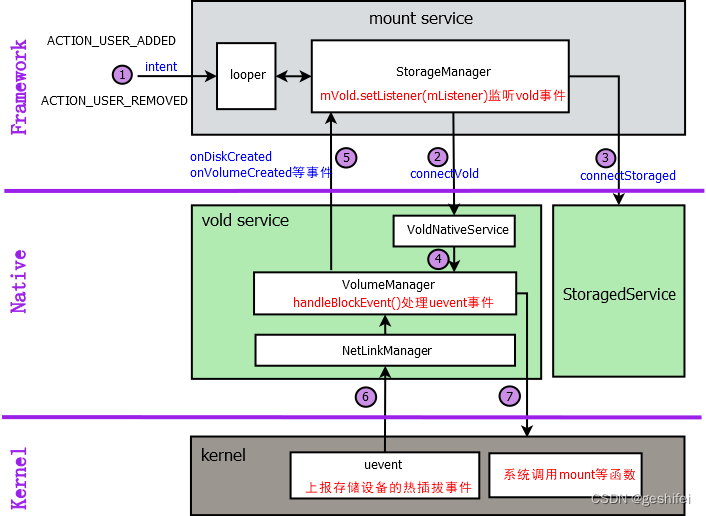
图中标号说明:
①:looper线程监听ACTION_USER_ADDED和ACTION_USER_REMOVED消息。
StorageManagerService::StorageManagerService --> mContext.registerReceiver(mUserReceiver, userFilter, null, mHandler)注册了BroadcastReceiver ,接收ACTION_USER_ADDED和ACTION_USER_REMOVED类型的 IntentFilter 广播消息, 参数mHandle所代表的线程上执行 BroadcastReceiver。
在StorageManagerService方法中,mHandler = new StorageManagerServiceHandler(hthread.getLooper()),所以Handler 代表的线程是looper线程。
mount service收到ACTION_USER_ADDED和ACTION_USER_REMOVED后,会做mount或者unmount操作。
②:mount service设置一个监听器,监听vold状态。
StorageManagerService::connectVold --> mVold = IVold.Stub.asInterface(binder)获取vold service的Binder对象,接着mount service通过mVold.setListener(mListener)设置监听器监听vold状态变化,监听器回调方法在StorageManagerService的匿名内部类中(见private final IVoldListener mListener = new IVoldListener.Stub()处的匿名类)。一旦vold状态变化,就会执行监听器回调方法,见⑤。
③:mount service获取storaged的binder对象,需要的时候执行storaged中的方法。
StorageManagerService::connectStoraged --> mStoraged = IStoraged.Stub.asInterface(binder)获取storaged service的Binder对象。mount service接收到相关事件后,比如unlock user,remove user等,执行storaged中的函数mStoraged.onUserStarted(userId),mStoraged.onUserStopped(userId)等。
④:VoldNativeService执行VolumeManager中的方法。
VoldNativeService通过类似于translate(VolumeManager::Instance()->XXX执行VolumeManager中的方法。比如VoldNativeService::onUserAdded --> translate(VolumeManager::Instance()->onUserAdded(userId, userSerial)),执行的是VolumeManager::onUserAdded。
⑤:VolumeManager上报存储设备事件给mount service。
用户add或删除,需要mount或者umount掉emulated storage;热插拔存储设备,kernel会上报uevent事件,这些都会引起vold状态变化,此时mount service在②中设置的监听器就监听到这些事件,执行对应的监听器回调方法。
⑥:NetlinkManager初始化socket,用于接收kernel的uevent事件。
system/vold/main.cpp中通过nm = NetlinkManager::Instance()实例化了一个NetlinkManager,用于接收kernel的uevent事件。
⑦:VolumeManager执行系统调用,执行mount等操作。
VolumeManager通过VolumeManager类执行kernel的系统调用,比如VolumeManager::mountAppFuse --> android::vold::MountAppFuse --> RunCommand --> mount等。
二、mount service的启动
SystemServer类定义了STORAGE_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS常量:
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java#SystemServer
private static final String JOB_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.server.job.JobSchedulerService";
private static final String LOCK_SETTINGS_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.server.locksettings.LockSettingsService$Lifecycle";
private static final String STORAGE_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS =http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java#SystemServer
Android启动时,SystemServer 进程启动其他系统服务(startOtherServices)。在这个过程中,SystemServer类定义的常量被用于加载各个服务。
以com.android.server.StorageManagerService$Lifecycle为例,看一下service的注册过程。
SystemServer::run
--> startOtherServices(t)
--> mSystemServiceManager.startService(STORAGE_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS)
--> SystemService startService(String className)
--> <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass)
--> startService(@NonNull final SystemService service)
--> service.onStart();以存储为例,即StorageManagerService$Lifecycle::onStart
--> publishBinderService("mount", mStorageManagerService) //注册到SystemServiceManager中 service.onStart对应的StorageManagerService$Lifecycle::onStart函数:
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/StorageManagerService.java#255
210 class StorageManagerService extends IStorageManager.Stub
211 implements Watchdog.Monitor, ScreenObserver {
……
246 public static class Lifecycle extends SystemService {
247 private StorageManagerService mStorageManagerService;
248
249 public Lifecycle(Context context) {
250 super(context);
251 }
252
253 @Override
254 public void onStart() {
255 mStorageManagerService = new StorageManagerService(getContext());
256 publishBinderService("mount", mStorageManagerService);
257 mStorageManagerService.start();
258 }255行,实例化一个StorageManagerService对象,在其构造函数:
1)通过HandlerThread hthread = new HandlerThread(TAG)创建一个消息处理线程,线程名为“StorageManagerService”(注意,内核记录的线程名最多16个字符,所以ps -AT看到的线程名是不完整的),处理ACTION_USER_ADDED和ACTION_USER_REMOVED事件。
2)通过mStorageSessionController = new StorageSessionController(mContext, mIsFuseEnabled)创建一个StorageSessionController,用来控制访问外部存储。
256行,publishBinderService将255行新创建的StorageManagerService以“mount”名字注册到serviceManager中(可通过adb shell "service list"命令查看service)。
257行, mStorageManagerService.start()启动service,代码如下:
1891 private void start() {
1892 connectStoraged();
1893 connectVold();
1894 }connectStoraged()和connectVold()都是在StorageManagerService类中定义的,简化后的代码:
private void connectStoraged() {
1897 IBinder binder = ServiceManager.getService("storaged");
……
1914 mStoraged = IStoraged.Stub.asInterface(binder);
1926 }
1927
1928 private void connectVold() {
1929 IBinder binder = ServiceManager.getService("vold"); // ⑧
……
1946 mVold = IVold.Stub.asInterface(binder); // ⑨
1948 mVold.setListener(mListener); // ⑩
1964 }connectStoraged() 设置 IStoraged mStoraged变量,connectVold() 设置 IVold mVold变量。以connectVold()为例说明代码:
⑧:获取名为 "vold" 的服务的 Binder 对象。
⑨:将获取到的 Binder 对象转换为 IVold 接口的实例,并将其赋值给变量mVold。
⑩:设置监听器,监听到mVold状态变化时,执行mListener的回调函数,比如onDiskCreated,onVolumeCreated等。
三、vold service的启动
init.rc脚本中定义了start vold语句,inti进程启动vold服务*(这里说的服务是linux中的service,不是android中的service)。
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/system/core/rootdir/init.rc#453
451 on early-fs
452 # Once metadata has been mounted, we'll need vold to deal with userdata checkpointing
453 start voldvold服务*(linux中的service)的描述:
vold.rc - OpenGrok cross reference for /system/vold/vold.rc
1 service vold /system/bin/vold \
2 --blkid_context=u:r:blkid:s0 --blkid_untrusted_context=u:r:blkid_untrusted:s0 \
3 --fsck_context=u:r:fsck:s0 --fsck_untrusted_context=u:r:fsck_untrusted:s0
4 class core
5 ioprio be 2
6 writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
7 shutdown critical
8 group root reserved_disknti进程加载/system/bin/vold二进制文件,启动vold进程。system/vold/main.cpp文件中main函数简化如下:
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
VolumeManager* vm;
NetlinkManager* nm;
//实例化一个VolumeManager,用于管理所有的volume,VolumeManager成员mDisks记录系统中所有的disk,Disk类描述disk,Disk成员mVolumes记录了本disk所有的分区。
if (!(vm = VolumeManager::Instance())) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to create VolumeManager";
exit(1);
}
//实例化一个NetlinkManager,用于接收kernel的uevent事件
if (!(nm = NetlinkManager::Instance())) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to create NetlinkManager";
exit(1);
}
//实例化一个VolumeBase,用来描述"/data/media"路径的emulated volume,并将该volume加入到mInternalEmulatedVolumes链表。注意,这个时候只是初始化了vloume(VolumeBase类型)的部分成员,并没有创建emulated volume,也即没有执行mount外部存储等一些列操作。
if (vm->start()) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to start VolumeManager";
exit(1);
}
//通过BinderService<VoldNativeService>::publish()发布"vold"服务。VoldNativeService::getServiceName返回的是"vold"字符串。
if (android::vold::VoldNativeService::start() != android::OK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to start VoldNativeService";
exit(1);
}
//nm->start初始化了socket,启动NetlinkManager监听kernel的uevent事件。
if (nm->start()) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to start NetlinkManager";
exit(1);
}
//当前线程加入到Binder线程池,一旦线程加入到Binder线程池中,它将持续监听并处理来自客户端的Binder调用请求。当有请求到达时,线程将调用相应的服务方法来处理请求,并将结果返回给客户端。
android::IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}main函数中的android::vold::VoldNativeService::start()发布vold service(android中的service概念,通过service list命令查看)。
四、storaged service的启动
storaged服务定义在system/core/storaged/storaged.rc中,编译刷机运行,脚本在/system/etc/init/storaged.rc。
system/core/init/main.cpp中main --> SecondStageMain --> LoadBootScripts --> parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init")代码如下:
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/system/core/init/parser.cpp#184
184 bool Parser::ParseConfig(const std::string& path) {
185 if (is_dir(path.c_str())) {
186 return ParseConfigDir(path);
187 }
188 return ParseConfigFile(path);
189 }/system/etc/init是一个目录,所以执行ParseConfigDir函数。
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/system/core/init/parser.cpp#ParseConfigDir
157 bool Parser::ParseConfigDir(const std::string& path) {
158 LOG(INFO) << "Parsing directory " << path << "...";
159 std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)> config_dir(opendir(path.c_str()), closedir);
160 if (!config_dir) {
161 PLOG(INFO) << "Could not import directory '" << path << "'";
162 return false;
163 }
164 dirent* current_file;
165 std::vector<std::string> files;
166 while ((current_file = readdir(config_dir.get()))) {
167 // Ignore directories and only process regular files.
168 if (current_file->d_type == DT_REG) {
169 std::string current_path =
170 android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", path.c_str(), current_file->d_name);
171 files.emplace_back(current_path);
172 }
173 }
174 // Sort first so we load files in a consistent order (bug 31996208)
175 std::sort(files.begin(), files.end());
176 for (const auto& file : files) {
177 if (!ParseConfigFile(file)) {
178 LOG(ERROR) << "could not import file '" << file << "'";
179 }
180 }
181 return true;
182 }ParseConfigDir遍历目录下的文件,然后调用ParseConfigFile启动/system/etc/init/storaged.rc定的storaged服务*(这里说的服务是linux中的service,不是android中的service)。
storaged服务描述:
http://aospxref.com/android-11.0.0_r21/xref/system/core/storaged/storaged.rc
1 service storaged /system/bin/storaged
2 class main
3 capabilities DAC_READ_SEARCH
4 priority 10
5 file /d/mmc0/mmc0:0001/ext_csd r
6 writepid /dev/cpuset/system-background/tasks
7 user root
8 group package_infointi进程加载/system/bin/storaged二进制文件,启动storaged进程。system/core/storaged/main.cpp中main函数简化如下:
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// storaged或者storaged -s命令,周期性统计
if (flag_main_service) { // start main thread
// Start the main thread of storaged
storaged_sp = new storaged_t();
storaged_sp->init();
storaged_sp->report_storage_info();
pthread_t storaged_main_thread;
errno = pthread_create(&storaged_main_thread, NULL, storaged_main, NULL);
if (errno != 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create main thread";
return -1;
}
if (StoragedService::start() != android::OK ||
StoragedPrivateService::start() != android::OK) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to start storaged service";
return -1;
}
android::ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
pthread_join(storaged_main_thread, NULL);
return 0;
}
sp<IStoragedPrivate> storaged_service = get_storaged_pri_service();
if (storaged_service == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find storaged service.\nMaybe run storaged --start first?\n");
return -1;
}
// 根据help信息:
// storaged -u按uid统计io使用信息,storaged -t按线程统计io使用信息
// flag_dump_uid代表storaged -u,flag_dump_task代码表stoaged -t
// 但我们从代码中可以看出,-u和-t是一样的,都是按uid统计io信息
if (flag_dump_uid || flag_dump_task) {
vector<UidInfo> uid_io;
binder::Status status = storaged_service->dumpUids(&uid_io);
if (!status.isOk() || uid_io.size() == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "UID I/O info is not available.\n");
return 0;
}
sort_running_uids_info(uid_io);
log_console_running_uids_info(uid_io, flag_dump_task);
}
//storaged -p统计io性能数据
if (flag_dump_perf) {
vector<int> perf_history;
binder::Status status = storaged_service->dumpPerfHistory(&perf_history);
if (!status.isOk() || perf_history.size() == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "I/O perf history is not available.\n");
return 0;
}
log_console_perf_history(perf_history);
}
return 0;
}
init进程执行的是/system/bin/storaged命令,所以 执行if (flag_main_service)为ture的分支,在这个分支中,StoragedService::start()发布storaged service(android中的service概念,通过service list命令查看),StoragedPrivateService::start()发布storaged_pri service(android中的service概念,通过service list命令查看)。
下一篇文章讲解锁时,存储相关的流程。