您的Android密钥安全吗?一招教你安全加固
你是否担心你的Android应用中的敏感数据会被披露出去?如果是的话,别担心,你并不是唯一一个有这样担忧的人。在今天的世界里,保护你的应用的URL和密钥免受逆向工程的风险变得比以往任何时候都更加重要。
别担心,它并不像听起来那么无聊!
逆向工程是通过反编译应用程序的代码来提取源代码的过程。坏人可以利用这种方法窃取你应用程序的敏感数据,比如URL和密钥。
但别担心,我们至少有一些方法可以让逆向工程师难以提取出你应用程序的URL和密钥。
本文将向你展示两种方法,帮助你保护应用程序的敏感数据,即CMake和Android密钥库系统。
顺便提一下:我们都知道没有百分之百的方法可以完全防止逆向工程,但这篇文章可以帮助你增加这个过程的难度。
那你还等什么呢?咱们开始吧!
🔐 CMake的工作原理
CMake是一种构建自动化工具,用于为Android创建本地库。它使用一个简单的配置文件来描述构建过程,你可以在该文件中指定源文件、编译器标志以及需要链接到本地库的库文件。
当你完成CMake的配置文件后,可以使用CMake构建工具来生成本地库。该工具会编译源文件,将其与所需的库文件进行链接,从而生成一个本地库文件。
开始使用吧!
1 - 从Android SDK安装CMake
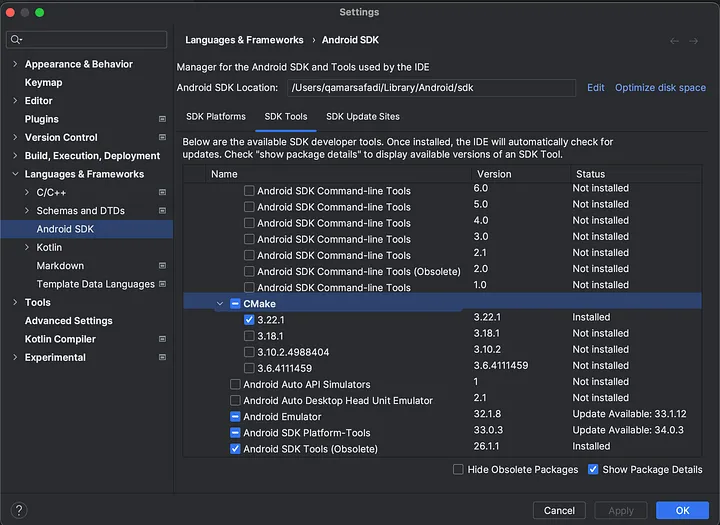
2 - 在 app/src/main 下。创建一个 C/C++ 文件来存储和访问你的密钥,命名为 native-lib.cpp。
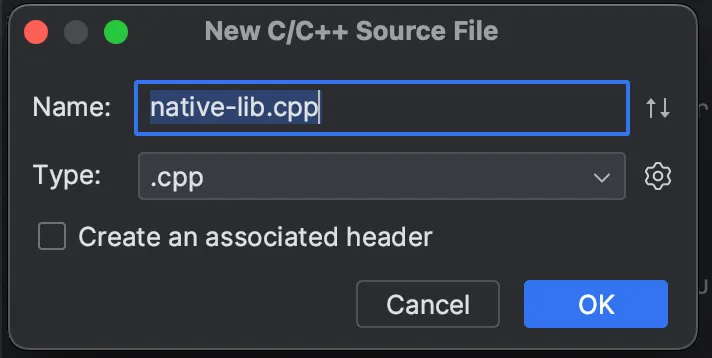
注意:为了使该函数在Java/Kotlin代码中可用,函数名称的格式为Java包名_活动名_函数名。
//
// Created by Qamar Safadi on 16/06/2023.
//
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
extern "C"
jstring
Java_com_qamar_myapplication_MainActivity_secureText(
JNIEnv* env,
jobject /* this */) {
std::string baseURL = "https://test/";
return env->NewStringUTF(baseURL.c_str());
}
3- 现在我们需要创建我们的CMakeLists,在应用程序上右键点击。
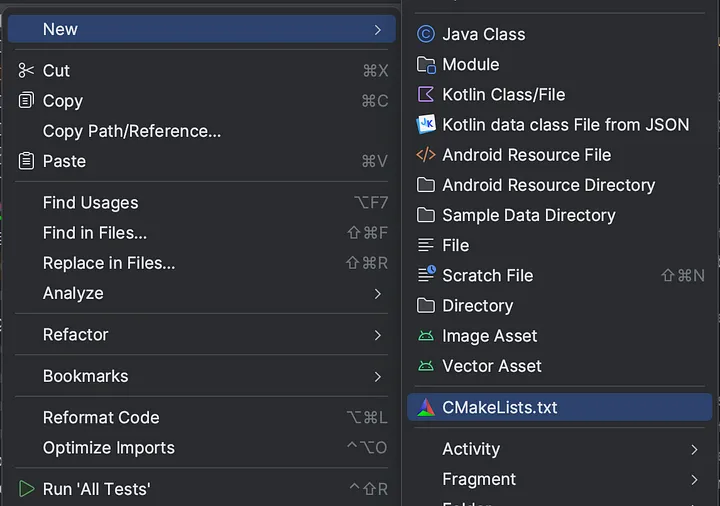
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native
# library. You should either keep the default value or only pass a
# value of 3.4.0 or lower.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds it for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
native-lib
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
# Associated headers in the same location as their source
# file are automatically included.
src/main/native-lib.cpp)
4 — 最后一步是通过 build.gradle 将这个本地库与我们的项目连接起来。
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path("CMakeLists.txt")
}
}
现在同步并刷新您的项目,将您的项目与本地程序库链接起来。
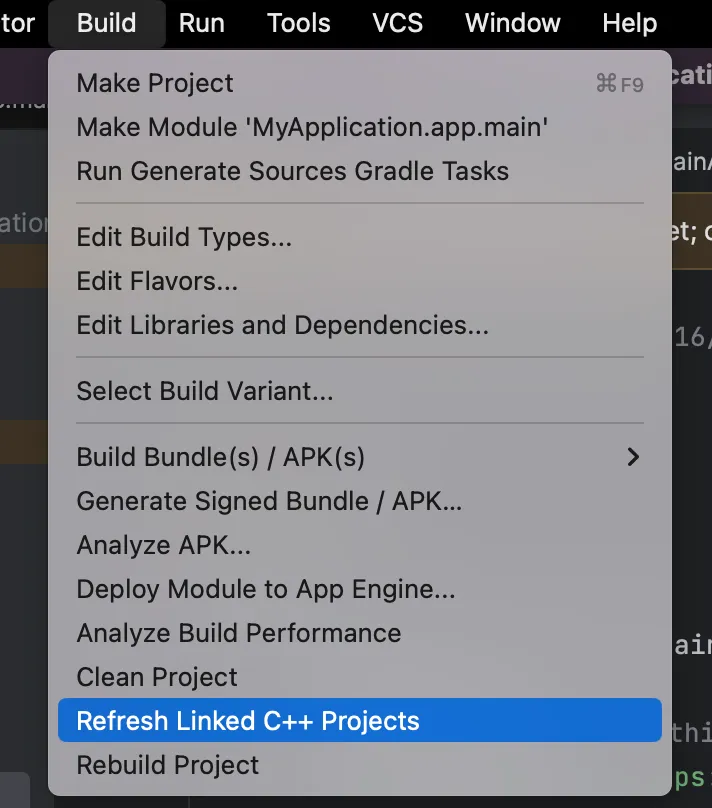
在你的 MainActiviy 中,你可以像下面这样访问你的密钥。
init {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib")
}
external fun secureText(): String
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
MyApplicationTheme {
// A surface container using the 'background' color from the theme
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.background
) {
Greeting(secureText())
}
}
}
}
🔐 Android Keystore System的工作原理
Android Keystore System是一个内置的安全系统,允许您将敏感数据存储在设备上的安全位置。
Keystore系统使用硬件支持的加密密钥来加密您的数据,这使得在没有正确凭据的情况下难以访问。
使用Keystore系统将防止任何攻击者提取这个密钥,因为它使用被称为TEE的特定硬件。
入门
首先,我们将创建Encryptor和Decryptor类,用于处理解密和加密过程。
class Encryptor {
lateinit var encryption: ByteArray
private set
lateinit var iv: ByteArray
private set
@Throws(
UnrecoverableEntryException::class,
NoSuchAlgorithmException::class,
KeyStoreException::class,
NoSuchProviderException::class,
NoSuchPaddingException::class,
InvalidKeyException::class,
IOException::class,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException::class,
SignatureException::class,
BadPaddingException::class,
IllegalBlockSizeException::class
)
fun encryptText(alias: String, textToEncrypt: String): ByteArray {
val cipher: Cipher = Cipher.getInstance(TRANSFORMATION)
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, getSecretKey(alias))
iv = cipher.getIV()
return cipher.doFinal(textToEncrypt.toByteArray(charset("UTF-8"))).also {
encryption = it
}
}
@Throws(
NoSuchAlgorithmException::class,
NoSuchProviderException::class,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException::class
)
private fun getSecretKey(alias: String): SecretKey {
val keyGenerator: KeyGenerator = KeyGenerator
.getInstance(KeyProperties.KEY_ALGORITHM_AES, ANDROID_KEY_STORE)
keyGenerator.init(
KeyGenParameterSpec.Builder(
alias,
KeyProperties.PURPOSE_ENCRYPT or KeyProperties.PURPOSE_DECRYPT
)
.setBlockModes(KeyProperties.BLOCK_MODE_GCM)
.setEncryptionPaddings(KeyProperties.ENCRYPTION_PADDING_NONE)
.build()
)
return keyGenerator.generateKey()
}
companion object {
private const val TRANSFORMATION = "AES/GCM/NoPadding"
private const val ANDROID_KEY_STORE = "AndroidKeyStore"
}
}
class Decryptor {
private var keyStore: KeyStore? = null
init {
initKeyStore()
}
@Throws(
KeyStoreException::class,
CertificateException::class,
NoSuchAlgorithmException::class,
IOException::class
)
private fun initKeyStore() {
keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance(ANDROID_KEY_STORE)
keyStore?.load(null)
}
@Throws(
UnrecoverableEntryException::class,
NoSuchAlgorithmException::class,
KeyStoreException::class,
NoSuchProviderException::class,
NoSuchPaddingException::class,
InvalidKeyException::class,
IOException::class,
BadPaddingException::class,
IllegalBlockSizeException::class,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException::class
)
fun decryptData(alias: String, encryptedData: ByteArray?, encryptionIv: ByteArray?): String {
val cipher: Cipher = Cipher.getInstance(TRANSFORMATION)
val spec = GCMParameterSpec(128, encryptionIv)
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, getSecretKey(alias), spec)
return String(cipher.doFinal(encryptedData))
}
@Throws(
NoSuchAlgorithmException::class,
UnrecoverableEntryException::class,
KeyStoreException::class
)
private fun getSecretKey(alias: String): SecretKey {
return (keyStore?.getEntry(alias, null) as KeyStore.SecretKeyEntry).getSecretKey()
}
companion object {
private const val TRANSFORMATION = "AES/GCM/NoPadding"
private const val ANDROID_KEY_STORE = "AndroidKeyStore"
}
}
现在在MainActivity中,我们开始使用这些类。
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var encryptor: Encryptor
private val SAMPLE_ALIAS = BuildConfig.MY_ALIAS // save your ALIAS key in local.properties for more security
init {
encryptText()
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
MyApplicationTheme {
// A surface container using the 'background' color from the theme
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.background
) {
Greeting(decryptText())
}
}
}
}
private fun encryptText() {
try {
encryptor = EnCryptor()
val encryptedText = encryptor.encryptText(SAMPLE_ALIAS, BuildConfig.SECRET_KEY) // your secret key form local.properties
Base64.encodeToString(encryptedText, Base64.DEFAULT)
} catch (e: Exception) {
Log.e("TAG", e.message, e)
}
}
private fun decryptText():String {
val deCryptor = Decryptor()
try {
val secretKey = deCryptor.decryptData(SAMPLE_ALIAS, encryptor.encryption, encryptor.iv)
return secretKey
} catch (e: Exception) {
Log.e("TAG", e.message, e)
return e.message.toString()
}
}
}
如何决定使用哪个?
正如您所见,Android密钥库系统比CMake更安全,但使用起来更复杂。CMake不太安全,但使用起来也更简单。
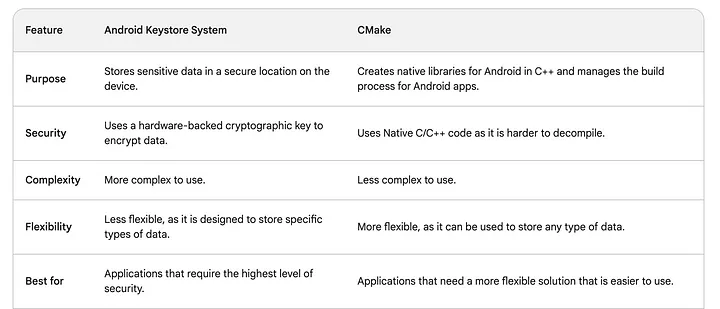
对于您来说,最佳选择将取决于您的具体需求。如果您需要最高级别的安全性,那么Android密钥库系统是最佳选择。如果您需要一个更灵活且更易于使用的解决方案,那么CMake是更好的选择。
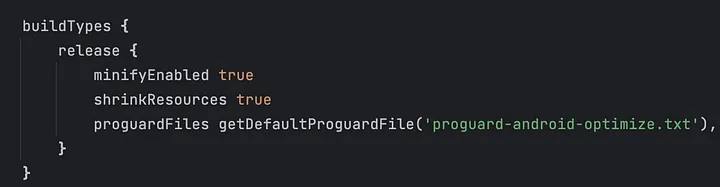
别忘了启用R8和资源收缩👇🏻
结论
最后,确保您应用程序的秘密密钥的安全性是非常有趣的一件事。想象一下您将面临的挑战!您需要想出强大的密钥名称和密码,找到安全的存储位置,并使用混淆技术使应用程序代码更难被理解。
这就像一场猫捉老鼠的游戏,您是猫,逆向工程师是老鼠。而且最棒的是,您能够获胜!通过遵循本文中的建议,您可以大大增加逆向工程师获取您的秘密密钥的难度,从而保护应用程序的敏感数据安全。



![[每周一更]-(第50期):Go的垃圾回收GC](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7460d825f5254b5b951e39f88ad755dc.jpeg#pic_center)