背景
SpringMVC作为SSM组件之一,Java开发有必要了解SpringMVC是如何被集成到Spring框架以及整个项目的启动流程。本文以Tomcat作为Servlet容器进行介绍,默认认为读者使用过Tomcat且对Tomcat内部组件有足够的理解。
1.启动流程
当Tomcat被部署到服务器或者通过本地IDEA将项目war包通过local tomcat部署到Tomcat上后,可以通过startup.sh或者startup.bat触发Bootstrap的main方法,从而开启Tomcat容器组件的初始化和启动过程。从宏观上看,启动过程中对应着Listener-> Filter -> Servlet组件的触发流程。
本文涉及的组件包括Listener和Servlet:Tomcat在构造Context实例后会触发ServletContextEvent事件,通过ContextLoaderListener监听器触发Spring容器的创建和刷新过程;初始化Servlet时会进入DispatcherServlet的初始化方法,从而完成Spring MVC容器的创建和刷新过程。
2.使用方式
web.xml中常用的配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0">
<!-- 指定Spring容器的配置文件 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:application-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 指定Spring启动监听器 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- 配置DispatcherServlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 指定Spring MVC容器的配置文件 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
3.原理
3.1 Spring容器启动
当Tomcat启动时,通过ServletContextEvent事件进入ContextLoaderListener监听器中:
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
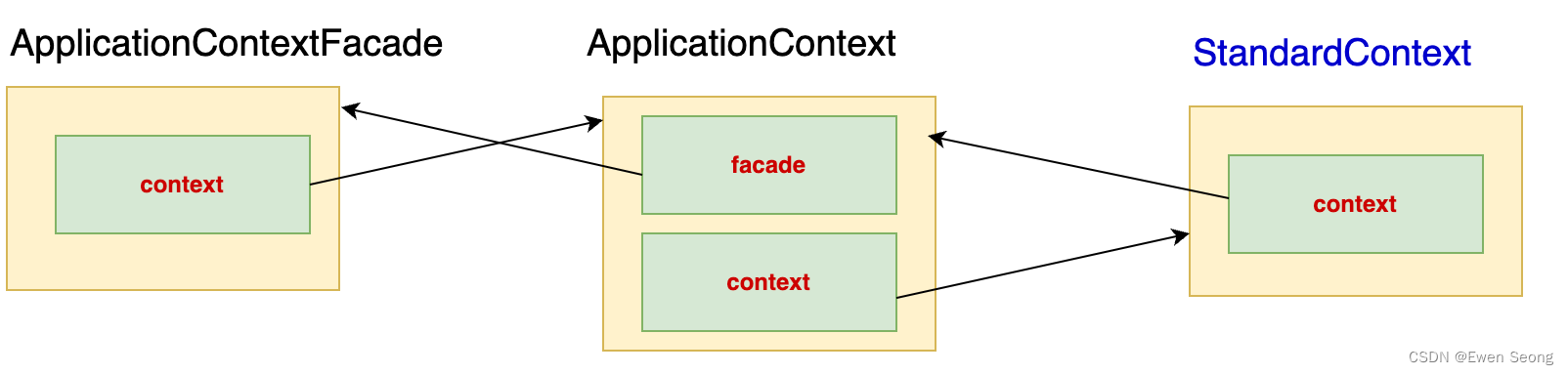
通过event.getServletContext()可以获取ServletContext对象,该对象实际为ApplicationContextFacade类,该对象将作为整个项目的上下文对象。本质上是StandardContext对象的代理类(Tomcat创建的Context对象),代理关系如下所示:
initWebApplicationContext方法的主线逻辑如下所示:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//⚠️1.创建ApplicationContext对象
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
//⚠️2.配置和刷新ApplicationContext
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
} else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
return this.context;
}
上述流程可以分为三部分:创建Spring容器、配置和刷新Spring容器、保存Spring容器信息至上下文。
3.1.1 创建Spring容器
跟进this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext)方法:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = this.determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
} else {
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
}
逻辑较为简单,根据ServletContext上下文对象获取Spring容器类型,然后调用BeanUtils.instantiateClass方法通过反射构造Spring容器对象。
这里可以关注一下Spring容器的类型:
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextClass");
if (contextClassName != null) {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
} else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
}
先从web.xml配置文件中的配置信息中获取,如果通过contextClass键指定了Spring容器类型则使用配置的类型,否则通过defaultStrategies.getProperty方法从ContextLoader.properties文件中读取,ContextLoader.properties文件内容如下:
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=\
org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
即Spring容器默认使用XmlWebApplicationContext类型。
3.1.2 配置和刷新Spring容器
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法完成了容器的刷新过程:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(sc, (ServletConfig)null);
}
this.customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
首先将上下文对象保存在Spring容器对象中;然后从web.xml配置信息中取出contextConfigLocation对应的文件来路径并将该路径设置给容器的configLocation属性,即为Spring容器指定了配置文件路径,此时可借助refreh()方法完成容器的刷新过程,该过程可参考Spring系列-1 启动流程。
在刷新容器之前,框架对环境变量的占位符做了替换处理(将环境变量中的占位符替换为真实的上下文对象)以及提供 customizeContext方法用于功能扩展。
在ContextLoaderListener监听器对象中,通过读取web.xml的contextInitializerClasses或者globalInitializerClasses属性信息收集ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>对象,并依次调用这些对象的initialize方。即,可以通过在web.xml中配置ApplicationContextInitializer实现类,实现容器刷新前的定制化操作(配置多个类时可以使用都好或者分号分割),如下所示:
public class SeongApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext) {
if (configurableApplicationContext instanceof XmlWebApplicationContext) {
((XmlWebApplicationContext)configurableApplicationContext).setAllowCircularReferences(true);
}
}
}
在配置文件中进行以下配置:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextInitializerClasses</param-name>
<param-value>SeongApplicationContextInitializer</param-value>
</context-param>
该案例实现了容器刷新前,强制设置容器支持循环依赖。
3.1.3 保存Spring容器信息至上下文
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
将Spring容器对象以org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT为key存放到上下文对象中。此时,上下文对象与Spring容器对象相互持有。
3.2 Spring MVC容器启动
Tomcat加载Servlet组件时,先实例化Servlet再调用Servlet的init方法。SpringMVC项目会在web.xml中配置的DispatcherServlet;而Spring MVC容器启动发生在DispatcherServlet的init方法中,跟随调用逻辑进入初始化方法(该方法定义在DispatcherServlet的父类HttpServletBean中):
public final void init() throws ServletException {
//1.获取配置信息
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException ex) {
throw ex;
}
}
initServletBean();
}
上述逻辑分为两个步骤:从web.xml中获取配置信息并将所需的属性信息通过反射设置到DispatcherServlet属性中,如contextConfigLocation属性;然后调用initServletBean()方法完成SpringMVC容器的创建和刷新过程:
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
initServletBean()方法的主体逻辑在initWebApplicationContext()方法中实现,而initFrameworkServlet()作为扩展方法,此时方法体为空。
initWebApplicationContext()方法的主体逻辑如下:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// ⚠️1.通过上下文获取Spring容器对象
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
// ⚠️2.创建和刷新SpringMVC容器
WebApplicationContext wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
// ⚠️3.保存SpringMVC容器至上下文对象
getServletContext().setAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT.", wac);
return wac;
}
3.2.1 通过上下文获取Spring容器对象
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext())静态方法通过org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT键从ServletContext上下文对象中出Spring容器对象。
3.2.2 创建和刷新SpringMVC容器
在步骤3.2.1中获取了Spring容器对象,并通过参数传递给了createWebApplicationContext方法:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
在DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet中通过contextClass属性的默认值设定了SpringMVC默认的容器对象为XmlWebApplicationContext:
private Class<?> contextClass = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;
通过getContextClass()方法得到XmlWebApplicationContext容器类型后,通过BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass)反射创建容器对象。
得到容器对象后,构造环境对象并赋值、通过wac.setParent(parent)将Spring容器设置为该对象的父容器对象、设置configLocation属性(配置文件地址),然后调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext初始化和刷新SpringMVC容器:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
首先对容器的servletContext、servletConfig、namespace的属性进行设置;然后进行环境变量占位符的替换以及ApplicationContextInitializer—initialize的调用(同上述Spring容器);
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac)方法为扩展方法,此时逻辑为空。
上述方法的核心逻辑在于wac.refresh(),完成SpringMVC容器的刷新,同Spring容器的刷新过程。
3.2.3 保存SpringMVC容器至上下文对象
getServletContext().setAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT.", wac);
getServletContext()可以获取ServletContext上下文对象,以"org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT."为键将SpringMVC容器对象储存到上下文对象的属性中。
至此,SpringMVC项目的整理启动流程已介绍完毕。